The Role of Robotics in Improving Medical Diagnostics: Forget clunky stethoscopes and blurry X-rays – the future of healthcare is here, and it’s robotic. We’re talking tiny, precise machines revolutionizing everything from biopsies to lab tests, offering a level of accuracy and efficiency that’s changing the game for doctors and patients alike. Prepare for a deep dive into the surprisingly cool world of medical robotics, where automation isn’t just about speed; it’s about saving lives.
This isn’t science fiction; it’s happening now. From robotic surgery systems that perform minimally invasive procedures with incredible precision to automated labs that handle samples with lightning-fast accuracy, robotics is transforming how we diagnose and treat illnesses. We’ll explore the various types of robots involved, their capabilities and limitations, and the ethical considerations that come with such groundbreaking technology. Get ready to see healthcare in a whole new light.
Introduction to Robotics in Medical Diagnostics
The landscape of medical diagnostics is undergoing a dramatic transformation, driven by technological advancements that promise faster, more accurate, and less invasive procedures. Robotics is playing an increasingly crucial role in this evolution, offering solutions to long-standing challenges and opening up new avenues for improved patient care. This shift is not merely about automation; it’s about enhancing the capabilities of medical professionals and ultimately leading to better health outcomes.
Medical diagnostics, traditionally reliant on human expertise and often limited by human dexterity and precision, are now benefiting significantly from the integration of robotic systems. These systems offer advantages in terms of precision, speed, minimally invasive procedures, and the ability to reach areas inaccessible to human hands. This translates to faster diagnosis, reduced patient discomfort, and improved overall efficiency within healthcare settings.
Types of Robots Used in Medical Diagnostics
Robotics in medical diagnostics encompasses a diverse range of applications and robotic systems. These robots are classified based on their specific function and the diagnostic procedure they assist.
| Robot Type | Diagnostic Application | Advantages | Limitations |
|---|---|---|---|
| Surgical Robots (e.g., da Vinci Surgical System) | Minimally invasive biopsies, targeted tissue sampling | Increased precision and dexterity, smaller incisions, reduced trauma, improved visualization | High cost, specialized training required, potential for technical malfunctions |
| Microrobots | Targeted drug delivery, minimally invasive imaging | Ability to navigate complex environments, precise targeting, reduced invasiveness | Technological challenges in control and navigation, limited payload capacity |
| Mobile Robots | Automated sample transport, disinfection of medical equipment | Increased efficiency, reduced risk of human error, improved hygiene | Limited autonomy in complex environments, potential for collisions |
| Robotic Arms with Imaging Capabilities | Automated ultrasound, MRI, CT scans | Improved image quality and consistency, reduced human intervention, increased speed | High initial investment, requires integration with existing imaging systems |
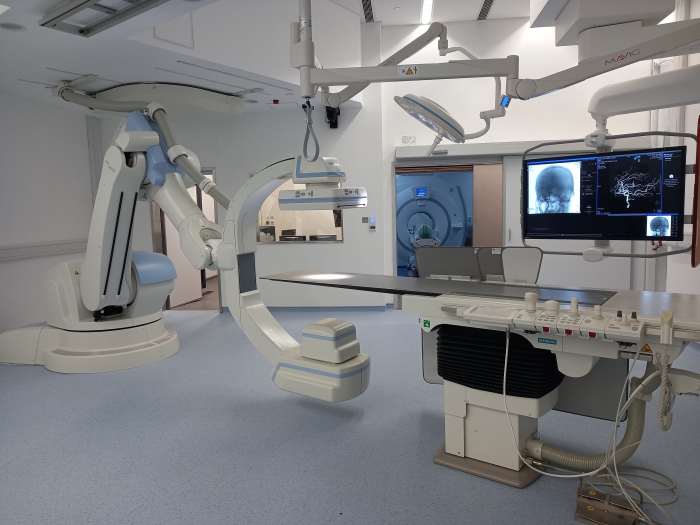
Robotics in Image-Guided Procedures

Source: awerobotics.com
The integration of robotics into image-guided procedures marks a significant leap forward in medical diagnostics and treatment. This technology enhances precision, minimizes invasiveness, and ultimately improves patient outcomes. By seamlessly blending robotic dexterity with advanced imaging techniques, surgeons and interventionalists can achieve levels of accuracy previously unimaginable.
Robotic systems are transforming the landscape of image-guided biopsies and surgeries, ushering in an era of minimally invasive procedures with enhanced precision. This precision translates directly into better diagnostic accuracy and reduced risks for patients.
Robotic Systems in Image-Guided Biopsies
Robotic assistance significantly improves the accuracy and safety of biopsies. The dexterity and precision of robotic arms allow for the targeting of smaller and more difficult-to-reach lesions, reducing the risk of damage to surrounding healthy tissue. Real-time imaging, integrated with the robotic system, provides continuous feedback to the operator, ensuring accurate needle placement. This minimizes the number of passes required, resulting in less patient discomfort and a faster recovery time. For example, robotic systems are used to perform prostate biopsies, allowing for more precise sampling and a reduction in the number of biopsies needed.
Impact of Robotic Assistance on Diagnostic Accuracy
Robotic assistance directly contributes to improved diagnostic accuracy in image-guided procedures. The enhanced precision of robotic systems allows for more accurate sampling of lesions, leading to more reliable diagnoses. Furthermore, the ability to perform minimally invasive procedures reduces the risk of complications and artifacts that can interfere with image interpretation. Studies have shown that robotic-assisted biopsies lead to higher diagnostic yields compared to traditional techniques, especially in cases involving small or difficult-to-reach lesions.
Robotic Arms and Navigation Systems for Improved Visualization and Manipulation
Robotic arms equipped with advanced sensors and imaging capabilities provide surgeons with enhanced visualization and manipulation during procedures. These systems often incorporate 3D imaging and haptic feedback, giving the surgeon a more intuitive sense of the surgical field. Navigation systems integrate real-time image data with robotic movements, allowing for precise targeting and manipulation of instruments. This combination of advanced imaging and robotic control significantly improves the accuracy and safety of procedures. For instance, in neurosurgery, robotic arms can provide extremely precise movements, minimizing the risk of damage to delicate brain structures.
Examples of Robotic Systems Used in Image-Guided Procedures
Several robotic systems are currently used in image-guided procedures. The da Vinci Surgical System, while primarily known for its role in open surgery, also finds application in image-guided procedures, providing enhanced dexterity and precision. Other systems specifically designed for image-guided interventions are also available, often incorporating features like advanced imaging integration, haptic feedback, and sophisticated navigation software. These systems vary in their capabilities and functionalities depending on the specific application. For example, some systems are specifically designed for minimally invasive cardiac procedures, while others are tailored for neurosurgical applications. Each system’s unique features contribute to the overall improvement in precision and minimally invasive capabilities.
Robotics for Automated Sample Handling and Analysis
The clinical laboratory, a hidden powerhouse of modern medicine, is undergoing a quiet revolution. This revolution is driven by robotics, which are rapidly automating tasks once performed solely by human hands, significantly improving speed, accuracy, and efficiency in diagnostic testing. From the initial sample arrival to the final analysis report, robots are transforming how we handle and process the crucial biological specimens that underpin diagnoses.
Robotic systems are streamlining the entire process of sample preparation, handling, and analysis. These systems incorporate a range of technologies, including automated liquid handling, sophisticated imaging systems, and advanced analytical tools. This integration allows for high-throughput processing, minimizing human intervention and reducing the potential for human error.
Automated Sample Preparation and Handling
Automated sample preparation involves a series of steps, all meticulously performed by robotic arms and specialized instruments. These steps might include uncapping and recapping tubes, aliquoting samples into smaller containers, mixing reagents, and transferring samples between different analytical instruments. For instance, a robotic arm might precisely dispense a specific volume of blood serum into a microplate well, preparing it for analysis by an automated immunoassay analyzer. The precision and consistency offered by robotic systems ensure accurate and reproducible results, far surpassing the capabilities of manual methods. The benefits extend beyond accuracy; automation significantly reduces the risk of contamination and biohazard exposure for laboratory personnel.
Benefits of Automation in Diagnostic Testing
The benefits of automating sample handling and analysis in clinical laboratories are substantial and far-reaching. Automation drastically increases the speed of processing, allowing for a higher throughput of samples. This is particularly crucial during peak periods or when dealing with large-scale testing, such as during a public health crisis. Furthermore, the inherent precision of robotic systems translates to significantly higher accuracy in test results. Manual processes are inherently prone to human error, whether it’s a miscalculation in reagent volumes or a simple pipetting mistake. Automation minimizes these errors, leading to more reliable diagnostic information. Finally, the increased efficiency achieved through automation allows laboratory staff to focus on more complex tasks requiring human expertise, such as result interpretation and quality control. For example, a large hospital lab might process thousands of blood samples daily. Automation reduces the time spent on basic tasks, freeing technicians to focus on complex analyses and patient care.
Comparison of Automated and Manual Methods
A direct comparison between automated robotic systems and manual methods reveals a clear advantage for automation. In terms of throughput, automated systems can process many times more samples per hour than manual methods. A single robotic system can easily handle hundreds or even thousands of samples in a day, compared to the much lower capacity of manual processing. Similarly, the error rates are drastically reduced. While manual methods are susceptible to a range of human errors, robotic systems, with their inherent precision and repeatability, minimize errors to a negligible level. The consistency of automated systems ensures that the results are reliable and reproducible, regardless of the operator or the time of day. Studies have shown that error rates in automated systems are orders of magnitude lower than in manual processing, translating to improved diagnostic accuracy and patient care.
Workflow Diagram of Automated Sample Processing, The Role of Robotics in Improving Medical Diagnostics
Imagine a conveyor belt system feeding samples into a robotic workstation. The workflow begins with sample arrival, where barcodes are scanned for identification and tracking. Next, the robot uncaps the sample tubes, and precisely measured aliquots are transferred to designated locations on microplates. Automated liquid handling robots then add necessary reagents. After incubation (often in automated incubators), the samples are analyzed using various automated instruments, such as spectrophotometers or mass spectrometers. Finally, the results are electronically recorded and integrated into the laboratory information system (LIS). The entire process is tracked and monitored in real-time, ensuring quality control and providing an auditable trail of sample handling. This automated workflow minimizes manual intervention, reduces the potential for errors, and ensures rapid turnaround times for diagnostic results.
Robotics in Telemedicine and Remote Diagnostics: The Role Of Robotics In Improving Medical Diagnostics
Source: gov.hk
The integration of robotics into telemedicine is revolutionizing healthcare access and delivery, particularly in remote or underserved areas. Robotic systems are bridging geographical gaps, allowing specialists to perform examinations and even administer certain procedures remotely, thereby improving the quality and timeliness of medical care for patients who might otherwise lack access. This technology is not just about convenience; it’s about expanding the reach of specialized medical expertise and potentially saving lives.
Robotic systems facilitate remote diagnostic consultations and procedures by providing a physical interface between the specialist and the patient. A surgeon located hundreds of miles away, for example, might control a robotic arm equipped with a high-definition camera and surgical instruments to perform a minimally invasive procedure. Similarly, a dermatologist could examine a patient’s skin lesion remotely using a robotic arm with high-resolution imaging capabilities, allowing for a more accurate diagnosis than might be possible through traditional telemedicine methods alone. This extension of the physician’s presence allows for a level of precision and dexterity not achievable through simple video conferencing.
Improved Access to Specialized Care in Underserved Areas
Robotic telemedicine significantly enhances access to specialized medical expertise in areas with limited resources or a shortage of healthcare professionals. Imagine a rural community lacking access to a cardiologist. Through a robotic telemedicine system, a cardiologist in a major city can remotely perform an echocardiogram, analyze the results, and provide a diagnosis and treatment plan. This eliminates the need for patients to travel long distances, potentially incurring significant costs and delays, and ensures they receive timely, expert care. The successful implementation of such systems in remote areas of developing countries is already demonstrating the transformative potential of this technology in improving global health equity.
Technological Challenges and Ethical Considerations
While the benefits of robotic telemedicine are considerable, several technological and ethical challenges must be addressed. Reliable high-speed internet connectivity is crucial for seamless operation, a challenge in many underserved areas. Ensuring the security and privacy of patient data transmitted during remote procedures is paramount. Furthermore, the need for robust system reliability and redundancy is critical, as any technical failure during a procedure could have serious consequences. From an ethical standpoint, questions surrounding liability in case of complications, informed consent for remote procedures, and the potential displacement of local healthcare workers require careful consideration and robust regulatory frameworks.
Future Applications of Telemedicine Robotics in Medical Diagnostics
Advancements in communication technologies, artificial intelligence (AI), and robotics hold immense potential for expanding the capabilities of telemedicine robotics in medical diagnostics. For example, the integration of AI-powered diagnostic tools into robotic systems could allow for faster and more accurate interpretation of medical images. The development of more dexterous and versatile robotic systems could enable a wider range of remote procedures, including complex surgeries. Furthermore, improved bandwidth and network infrastructure will facilitate higher-resolution image transmission and more sophisticated remote control capabilities. We can envision a future where robotic telemedicine systems are commonplace, providing accessible, high-quality medical care to individuals worldwide, regardless of their location or socioeconomic status. The integration of haptic feedback systems, allowing surgeons to feel the tissue during remote procedures, will also improve the precision and safety of robotic surgery. This technology will undoubtedly transform healthcare delivery, especially in regions currently lacking access to specialized medical expertise.
Impact on Diagnostic Accuracy and Patient Outcomes

Source: mymedicalpanel.com
Robotics is revolutionizing medical diagnostics, offering faster and more accurate results. This precision is mirrored in other fields leveraging AI, like customer service, where the application of machine learning is rapidly evolving, as detailed in this insightful piece on The Future of Machine Learning in Automated Customer Support. Ultimately, both advancements highlight the power of intelligent automation to improve efficiency and accuracy across diverse sectors, impacting healthcare and beyond.
The integration of robotics into medical diagnostics has ushered in a new era of precision and efficiency, profoundly impacting both diagnostic accuracy and patient outcomes. Robotic systems, with their enhanced dexterity, precision, and repeatability, are transforming various diagnostic procedures, leading to improvements across the board. This section explores the multifaceted ways in which robotics is reshaping medical diagnostics, focusing on accuracy improvements, patient benefits, and cost-effectiveness.
Robotic systems offer several advantages that contribute to improved diagnostic accuracy. For instance, in minimally invasive surgery, robotic arms provide surgeons with a magnified, three-dimensional view of the surgical field, enabling them to perform procedures with greater precision than traditional methods. This enhanced precision translates directly to more accurate biopsies, leading to earlier and more accurate diagnoses of cancerous and other lesions. Furthermore, robotic systems can perform repetitive tasks with unwavering consistency, minimizing human error and enhancing the reliability of diagnostic tests. This is particularly crucial in high-throughput laboratories, where consistent performance is paramount for accurate results. Automated sample handling and analysis, facilitated by robotics, reduces the risk of human error in sample preparation, processing, and analysis, all contributing to increased diagnostic accuracy.
Improved Diagnostic Accuracy through Robotic Precision
The enhanced precision offered by robotic systems directly translates to improved diagnostic accuracy. For example, in image-guided biopsies, robotic arms can accurately position needles to target specific areas within the body, reducing the margin of error and improving the quality of tissue samples obtained. This leads to more reliable diagnoses, particularly in cases of early-stage cancers or other subtle lesions where accurate tissue sampling is critical. Moreover, robotic systems can perform tasks with greater dexterity and precision than human hands, enabling the collection of samples from difficult-to-reach areas, improving the completeness and quality of diagnostic information. This is particularly beneficial in procedures such as minimally invasive biopsies of organs like the liver or prostate. Studies have shown a significant reduction in the number of repeat biopsies needed when robotic systems are used, highlighting the improved accuracy achieved.
Positive Impact on Patient Outcomes
The benefits of robotic-assisted diagnostics extend beyond improved accuracy to a significant positive impact on patient outcomes. Minimally invasive procedures, facilitated by robotics, lead to smaller incisions, reduced trauma to surrounding tissues, less pain, and shorter hospital stays. This translates to faster recovery times and improved quality of life for patients. For example, robotic-assisted surgery for prostate cancer often results in less blood loss, fewer complications, and improved urinary and sexual function compared to traditional open surgery. Similarly, robotic-assisted biopsies can lead to fewer complications such as bleeding or infection, further enhancing patient safety and improving their overall experience.
Cost-Effectiveness of Robotic-Assisted Diagnostics
While the initial investment in robotic systems can be substantial, the long-term cost-effectiveness needs to be carefully evaluated. Although the upfront costs are higher compared to traditional methods, the advantages in terms of improved accuracy, reduced complications, shorter hospital stays, and fewer repeat procedures can lead to significant cost savings over time. The reduced need for repeat procedures, alone, can offset the initial investment. Moreover, the increased efficiency offered by robotic systems can enhance the throughput of diagnostic laboratories, allowing for faster processing of samples and reduced waiting times for patients. A comprehensive cost-benefit analysis considering both the initial investment and the long-term operational costs is crucial to determine the overall economic viability of robotic-assisted diagnostics in specific healthcare settings.
Potential Risks and Limitations
It is important to acknowledge the potential risks and limitations associated with the use of robotics in medical diagnostics.
- High initial investment costs for robotic systems and the need for specialized training for healthcare professionals.
- Potential for technical malfunctions or software errors that could compromise the accuracy or safety of diagnostic procedures.
- The reliance on sophisticated technology may increase the risk of system failures or disruptions, potentially delaying or impacting the quality of care.
- The need for specialized infrastructure and maintenance to support the operation of robotic systems.
- Ethical considerations related to the use of artificial intelligence and autonomous systems in medical decision-making.
Future Trends and Challenges in Robotic Diagnostics
The integration of robotics into medical diagnostics is rapidly evolving, driven by advancements in artificial intelligence, miniaturization, and our ever-increasing demand for faster, more accurate, and less invasive procedures. However, realizing the full potential of robotic diagnostics requires addressing significant challenges related to workflow integration, standardization, and training.
Emerging Trends in Robotic Diagnostic Technology
Several key technological advancements are poised to revolutionize medical diagnostics in the coming years. Artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning (ML) algorithms are being integrated into robotic systems, enabling them to analyze medical images with greater speed and accuracy than human experts in certain areas. This leads to faster diagnosis and personalized treatment plans. Miniaturization is another significant trend, with the development of smaller, more flexible robots allowing for minimally invasive procedures and access to previously unreachable areas within the body. For instance, imagine tiny robotic probes navigating blood vessels to collect tissue samples for analysis, reducing the need for larger, more invasive surgical procedures. This trend is also driving the development of microfluidic devices integrated with robots, automating complex laboratory processes on a smaller scale.
Challenges in Integrating Robotics into Healthcare
Integrating robotic diagnostic systems into existing healthcare workflows and infrastructure presents substantial challenges. High initial costs of robotic systems and their maintenance can be a significant barrier for many healthcare facilities, particularly in resource-constrained settings. The need for specialized training for healthcare professionals to operate and maintain these sophisticated systems also represents a hurdle. Moreover, ensuring seamless data integration between robotic systems and existing electronic health record (EHR) systems is crucial for efficient data management and clinical decision-making, but it’s a complex technical challenge. Finally, regulatory approvals and safety protocols need to be robustly established to guarantee patient safety and ethical considerations.
Standardization and Training in Robotic Diagnostics
The lack of standardized protocols and training programs for healthcare professionals working with robotic diagnostic systems is a major impediment to widespread adoption. To ensure consistent quality of care and patient safety, the development of universally accepted training curricula and certification programs is essential. These programs should cover both technical aspects of operating the robotic systems and clinical aspects of interpreting the diagnostic data generated by these systems. Standardization of data formats and communication protocols between different robotic systems and healthcare information systems is also crucial for interoperability and seamless data exchange.
A Hypothetical Future Scenario in Robotic Diagnostics
Imagine a future where a patient experiencing unexplained fatigue undergoes a minimally invasive diagnostic procedure using a swarm of microscopic robots. These robots, guided by AI-powered image analysis, navigate the patient’s bloodstream, collecting cellular samples and performing real-time analysis. The data is instantaneously transmitted to a central diagnostic hub, where advanced machine learning algorithms analyze the information and identify the underlying cause of the fatigue – a previously undetectable genetic predisposition to a specific metabolic disorder. This rapid and precise diagnosis enables early intervention, preventing the progression of the disease and improving the patient’s quality of life. This scenario illustrates the transformative potential of advanced robotics in medical diagnostics, leading to earlier and more accurate diagnoses, personalized treatment plans, and improved patient outcomes. The societal impact would be profound, with reduced healthcare costs, increased life expectancy, and improved overall public health.
Conclusive Thoughts
The integration of robotics into medical diagnostics isn’t just about technological advancement; it’s a fundamental shift in how we approach healthcare. By improving accuracy, efficiency, and access to specialized care, robotic systems are paving the way for better patient outcomes and a more equitable healthcare system. While challenges remain in terms of cost, training, and ethical considerations, the potential benefits are undeniable. The future of diagnostics is undeniably robotic, and it’s a future worth embracing.
