The Role of Robotics in Assisting the Elderly and Disabled – Robotics: Helping Elderly and Disabled Thrive. Forget clunky, cold machines – we’re talking about a revolution in care, using cutting-edge technology to boost independence and improve quality of life for our aging population and those with disabilities. From robotic arms assisting with daily tasks to AI-powered companions combating loneliness, the future of care is surprisingly human, thanks to the incredible advancements in robotics.
This isn’t just about gadgets; it’s about empowering individuals to live fuller, more meaningful lives. We’ll explore the different types of robotic assistance available, examine the impact on daily living, and delve into the ethical considerations that come with this exciting technological leap. Get ready to see how robots are changing the game, one helpful hand (or wheel) at a time.
Types of Robotic Assistance for the Elderly and Disabled: The Role Of Robotics In Assisting The Elderly And Disabled
Robotics is rapidly transforming eldercare and disability support, offering innovative solutions to improve quality of life and independence. From mobility aids to social companions, robots are stepping up to address the challenges faced by an aging population and individuals with disabilities. This section explores the diverse range of robotic assistance available, highlighting their capabilities and limitations.
Robotic Mobility Assistance
Several types of robots are designed to enhance mobility for the elderly and disabled. These range from sophisticated exoskeletons providing strength and stability to smart wheelchairs offering advanced navigation and control. The following table compares three prominent examples:
| Feature | Exoskeleton (e.g., Ekso Bionics) | Smart Wheelchair (e.g., Permobil M7) | Robotic Walker (e.g., WalkAide by Bioness) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Cost | Tens of thousands of dollars | Several thousand to tens of thousands of dollars depending on features | Tens of thousands of dollars |
| Mobility Assistance | Provides powered assistance for walking, standing, and stair climbing | Offers advanced navigation, obstacle avoidance, and personalized settings | Provides assistance with walking, balance, and reducing the risk of falls. |
| Limitations | Requires significant training, may be bulky and heavy, limited range of motion in some models | Can be expensive, battery life can be limited, may struggle with uneven terrain | Requires user to still have some leg function, may not be suitable for all types of gait impairments. |
| Target Users | Individuals with paraplegia, stroke survivors, individuals with other mobility impairments | Individuals with reduced mobility, limited dexterity, or fatigue | Individuals with partial paralysis or weakness in their legs. |
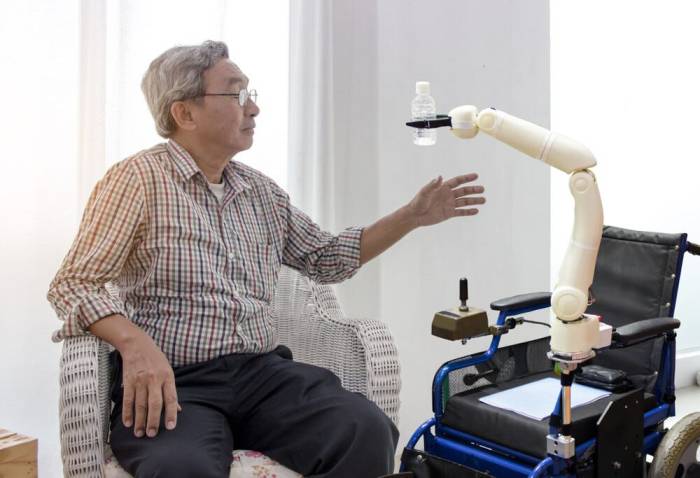
Robotic Arm Design for Daily Tasks
A robotic arm designed for assisting with daily tasks like eating and dressing would need a sophisticated combination of sensors, actuators, and control systems. The arm itself would ideally be lightweight and adaptable, with multiple degrees of freedom allowing for precise movements. Force sensors would be crucial to prevent accidental injury during interaction with the user. The end effector, or “hand,” would be designed to grip a variety of objects, from utensils to clothing, with varying degrees of force. Advanced computer vision and machine learning algorithms would be integrated to allow the robot to recognize objects, understand the user’s intentions (e.g., picking up a spoon), and plan movements accordingly. Safety features, such as emergency stop buttons and force limits, would be essential to ensure the user’s well-being. Imagine a robotic arm that can seamlessly assist someone with limited dexterity to button a shirt or lift a fork to their mouth, improving their independence and dignity.
Robotic Companions for Social Interaction
Loneliness and social isolation are significant concerns for many elderly individuals and those with disabilities. Robotic companions offer a potential solution, providing engaging social interaction and reducing feelings of isolation. These robots can engage in simple conversations, play games, remind users about medication, and even provide companionship through storytelling or music. For example, Paro, a therapeutic robot seal, has been shown to reduce stress and anxiety in elderly care facilities. These robots are not meant to replace human interaction but rather to supplement it, providing a consistent source of engagement and emotional support. The design of these companions often focuses on creating a friendly and approachable appearance, with features like soft textures and expressive eyes, fostering a sense of connection and trust. The development of more sophisticated AI allows these robots to learn user preferences and adapt their interactions accordingly, enhancing the personalized experience and maximizing their therapeutic benefits.
Impact on Daily Living Activities
Robotic systems are quietly revolutionizing the lives of elderly individuals and those with disabilities, offering a helping hand (or rather, a robotic arm) in navigating the challenges of daily life. These advancements aren’t about replacing human interaction; instead, they’re about enhancing independence and dignity, allowing individuals to maintain a higher quality of life for longer. By providing assistance with activities of daily living (ADLs), robotic aids are empowering individuals to remain in their homes and communities, fostering a sense of self-reliance and reducing the burden on caregivers.
Robotic systems significantly improve the independence of elderly individuals in performing ADLs. From simple tasks like retrieving objects to more complex activities like dressing and bathing, robots are designed to adapt to individual needs and preferences. This assistance extends beyond mere physical help; the emotional benefits of maintaining autonomy and reducing reliance on others are equally, if not more, significant. The feeling of control over one’s own life, even in the face of age-related limitations, is invaluable.
Robotic Assistance with Personal Hygiene and Toileting
The use of robotic aids for personal hygiene and toileting presents both significant benefits and challenges. On the positive side, robotic toilets and bathing systems can provide assistance to individuals with limited mobility, allowing them to maintain their personal hygiene with greater ease and dignity. For example, robotic arms can assist with washing and drying, while smart toilets can offer automated cleaning and assistance with transferring. However, challenges exist regarding cost, user acceptance (some may find the technology intrusive), and the need for careful integration with existing bathroom infrastructure. Moreover, ensuring the privacy and security of personal data collected by these systems is crucial.
Robotic Solutions for Medication Management and Reminders, The Role of Robotics in Assisting the Elderly and Disabled
Medication management is a critical aspect of healthcare, particularly for the elderly who often manage multiple prescriptions. Robotic systems can play a vital role in ensuring adherence to medication schedules and reducing medication errors. Smart pill dispensers, for instance, can automatically dispense medications at pre-programmed times, sending reminders to the user via visual or auditory cues. Some systems even track medication intake and provide reports to caregivers or healthcare providers. This reduces the risk of missed doses or accidental overdoses, improving overall health outcomes. Furthermore, some robots can even identify and alert users about potential drug interactions, adding an extra layer of safety.
Enhancing Safety and Reducing Fall Risks in the Home
Falls are a major concern for the elderly, often leading to serious injuries and reduced mobility. Robotic systems can contribute significantly to a safer home environment by minimizing fall risks.
- Fall detection systems: These systems use sensors to detect falls and automatically alert caregivers or emergency services.
- Smart home monitoring: Sensors and cameras can monitor activity levels and identify potential hazards, such as obstacles or slippery surfaces.
- Assistive robots: Robots can provide physical assistance with balance and mobility, reducing the likelihood of falls.
- Lighting and obstacle avoidance systems: Automated lighting and obstacle detection systems can enhance visibility and prevent trips and falls.
- Robotic exoskeletons: These wearable robots provide support and enhance strength, enabling safer movement and reducing the risk of falls.
Implementing these safety measures can create a more secure and independent living environment for elderly individuals, allowing them to maintain their active lifestyle with reduced fear of falls and subsequent injuries. The peace of mind offered to both the individual and their caregivers is a significant benefit of these technological advancements.
Technological Advancements and Future Trends
The field of robotics for elderly and disabled care is rapidly evolving, driven by advancements in artificial intelligence, sensor technology, and materials science. The next decade promises significant breakthroughs that will transform how we support and care for vulnerable populations. We’re moving beyond basic assistance towards truly intuitive and personalized robotic companions.
This evolution is fueled by several key technological advancements. Imagine robots that not only help with daily tasks but also proactively anticipate needs, learn individual preferences, and provide engaging social interaction. This isn’t science fiction; it’s the rapidly approaching reality.
Robotics are revolutionizing elderly and disabled care, offering personalized assistance and improved quality of life. This tech-driven revolution mirrors the positive impact seen in other sectors, like the fashion industry, where innovation is key; check out how tech is boosting sustainability in fashion The Growing Influence of Technology on Sustainable Fashion for a fascinating parallel. Ultimately, both fields show how smart tech can build a brighter, more inclusive future.
Emerging Technologies in Robotics
Several emerging technologies are poised to revolutionize elderly and disabled care. Soft robotics, for instance, uses flexible materials to create robots that are safer and more adaptable to human interaction. These robots can gently assist with tasks like transferring patients or providing physical therapy without the risk of injury. Furthermore, advancements in AI are enabling robots to learn and adapt to individual needs, providing personalized care that’s more effective and efficient. Miniaturization of components allows for smaller, more discreet robots that can seamlessly integrate into the home environment. Finally, advancements in haptic feedback technology will allow for more natural and intuitive interaction between humans and robots. For example, a robot assisting with eating could adjust its grip based on the user’s subtle hand movements.
Sensor Technology Comparison
Different sensors play crucial roles in enabling robots to perceive their environment and interact with users effectively. The choice of sensor depends on the specific application and the required level of detail.
| Sensor Type | Functionality | Advantages | Disadvantages |
|---|---|---|---|
| Infrared Sensors | Detect proximity and presence; measure temperature | Low cost, robust, widely available | Limited range, susceptible to interference |
| Ultrasonic Sensors | Measure distance and detect obstacles | Relatively inexpensive, good for long-range detection | Less accurate than other methods, affected by environmental factors |
| Cameras (Computer Vision) | Image processing for object recognition, navigation, and gesture recognition | High level of detail, versatile | Computationally intensive, privacy concerns |
| Tactile Sensors | Detect pressure, force, and texture | Enables delicate manipulation and interaction | Can be expensive, complex to implement |
Hypothetical Robotic System: “CareBot”
The “CareBot” system integrates multiple functionalities to provide comprehensive assistance. It utilizes a mobile base equipped with advanced navigation and obstacle avoidance capabilities, allowing it to move freely around the home. Its arm has multiple degrees of freedom and incorporates tactile sensors for precise manipulation, enabling it to assist with activities of daily living (ADLs) such as dressing, eating, and personal hygiene. A secure medication dispenser module, controlled via a user-friendly interface, ensures timely and accurate medication administration. Furthermore, CareBot incorporates advanced AI capabilities for natural language processing and social interaction, allowing it to engage in conversation, play games, and provide companionship. Facial recognition allows CareBot to identify family members and adjust its behavior accordingly.
Impact of Artificial Intelligence
AI is fundamental to creating more intuitive and adaptable robotic assistants. Machine learning algorithms allow robots to learn user preferences, anticipate needs, and adapt their behavior over time. For example, a robot might learn that a user prefers their coffee at a specific temperature or that they tend to be more active in the mornings. Natural language processing enables more natural and fluid communication between the robot and the user, fostering a stronger sense of connection and trust. AI-powered predictive maintenance can anticipate potential problems and schedule repairs before they occur, ensuring the robot remains operational and reliable. Consider companies like Boston Dynamics, constantly refining their robots’ AI capabilities to enhance their adaptability and responsiveness. Their robots already demonstrate remarkable progress in navigating complex environments and performing intricate tasks, offering a glimpse into the future of AI-powered robotic assistance.
Ethical and Societal Considerations
Source: medium.com
The integration of robots into elder care and disability assistance raises a complex web of ethical and societal questions. While the potential benefits are undeniable, we must carefully consider the implications for individual autonomy, privacy, and the very nature of human connection in caregiving. Ignoring these aspects risks creating a future where technological advancement overshadows the fundamental human needs of our aging population and those with disabilities.
The use of robotic assistants in care settings presents several ethical dilemmas, particularly concerning privacy and autonomy.
Privacy Concerns in Robotic Elder Care
Robotic assistants, equipped with sensors and cameras to monitor vital signs and activities, inevitably collect vast amounts of personal data. This data, if improperly secured or misused, could lead to privacy violations. For example, sensitive information about an elderly person’s health, routines, and even conversations could be accessed without their knowledge or consent. Robust data protection measures, including strong encryption and clear data governance policies, are crucial to mitigate these risks and ensure ethical data handling. Furthermore, transparent communication with users about data collection practices is essential to build trust and respect individual autonomy. The potential for data breaches and the misuse of this sensitive information are significant considerations that need careful ethical frameworks to address.
Impact on the Healthcare Workforce and the Human Element of Care
The widespread adoption of robotic assistants in elder care could significantly alter the healthcare workforce. While robots can automate certain tasks, freeing up human caregivers to focus on more complex aspects of care, there’s a concern that it might lead to job displacement for some caregivers. Furthermore, the over-reliance on robots could diminish the human element of care, potentially leading to feelings of isolation and loneliness among elderly individuals. The emotional and social connection provided by human caregivers is invaluable and should not be underestimated. A balanced approach that integrates robots to augment, not replace, human care is essential. The transition needs to be carefully managed, perhaps with retraining programs for caregivers to focus on tasks requiring human interaction and emotional intelligence. The focus should remain on enhancing the quality of care, not simply reducing costs.
Challenges Related to Affordability and Accessibility
The cost of developing, manufacturing, and maintaining robotic assistants is currently high, making them inaccessible to many elderly individuals and those with disabilities, particularly those with limited financial resources. This creates a significant equity issue, potentially exacerbating existing healthcare disparities.
- High initial purchase price of the robots.
- Ongoing maintenance and repair costs.
- Need for specialized training for users and caregivers.
- Limited availability of affordable, reliable repair services.
- Lack of insurance coverage for robotic assistance technologies.
Addressing these challenges requires a multi-pronged approach, including government subsidies, innovative financing models, and the development of more cost-effective robotic technologies. Ensuring equitable access is crucial to avoid creating a two-tiered system of care.
Societal Attitudes Towards Technology and Aging
Societal attitudes towards technology and aging play a significant role in the acceptance and integration of robotic assistants. Some individuals may embrace robotic assistance as a way to maintain independence and improve their quality of life. However, others may view robots with suspicion or fear, perceiving them as a threat to human connection and dignity. These differing perspectives need to be addressed through public education campaigns that highlight the potential benefits of robotic assistance while also acknowledging and addressing concerns about privacy, autonomy, and the human element of care. Successful integration will depend on building public trust and fostering a positive perception of robots as supportive tools rather than replacements for human interaction. For example, successful integration in Japan, known for its aging population and technological advancements, demonstrates the impact of a generally positive cultural perception of robots. Conversely, societies with strong cultural emphasis on family-based care may experience more resistance.
Case Studies and Examples of Successful Implementations
Robotics is rapidly transforming the lives of elderly and disabled individuals, offering innovative solutions to enhance independence and improve quality of life. While still a developing field, several successful implementations showcase the transformative potential of robotic assistance. These case studies highlight the tangible benefits and pave the way for wider adoption of this technology.
Elderly Care: The GiraffPlus System
The GiraffPlus system is a telepresence robot designed to support elderly individuals living independently at home. This system combines video conferencing capabilities with sensors that monitor the environment and the user’s well-being. For example, if a fall is detected, the system automatically alerts caregivers or family members. Furthermore, the robot’s mobility allows caregivers to remotely check on the individual, interact in real-time, and even assist with tasks like medication reminders. One successful implementation involved a 78-year-old woman with mild cognitive impairment who was able to maintain her independence for longer thanks to the GiraffPlus system’s constant monitoring and communication capabilities. The system fostered a sense of security and reduced feelings of isolation, allowing her to remain actively connected with her support network. This improved her overall well-being and reduced the burden on her family.
Disability Assistance: Robotic Exoskeletons for Paralysis
Robotic exoskeletons represent a significant advancement in assistive technology for individuals with paralysis. These devices use sophisticated sensors and actuators to provide support and enable movement. One notable example is the Ekso Bionics exoskeleton, which has helped paraplegic individuals regain the ability to walk. This has profound implications for physical therapy, rehabilitation, and overall quality of life. For instance, a study showed that regular use of an exoskeleton improved cardiovascular health, reduced muscle atrophy, and significantly enhanced patients’ mental well-being. The ability to stand and walk, even with assistance, can dramatically improve mobility, reduce pain, and boost self-esteem, leading to greater independence and participation in social activities.
Criteria for Evaluating the Effectiveness and Safety of Robotic Assistive Devices
The successful integration of robotic assistive devices hinges on careful evaluation of their effectiveness and safety. Several key criteria must be considered.
It’s crucial to establish a framework for assessing both the functional and psychosocial impact of these devices. This involves considering aspects beyond mere functionality.
- Functionality: Does the device effectively address the user’s specific needs and limitations? Does it improve mobility, independence, and the performance of daily living activities?
- Usability: Is the device intuitive and easy to use? Does it require extensive training or specialized knowledge?
- Safety: Does the device incorporate sufficient safety features to prevent accidents or injuries? Has it undergone rigorous testing and safety certification?
- Reliability: Is the device durable and reliable? What is the frequency of malfunctions or required maintenance?
- Cost-Effectiveness: What is the overall cost of the device, including purchase price, maintenance, and training? Does the benefit justify the cost?
- Social Integration: Does the device facilitate social interaction and reduce feelings of isolation? Does it enhance the user’s participation in social activities?
- Ethical Considerations: Does the device respect the user’s autonomy and privacy? Are there potential risks of dependence or social exclusion?
Conclusion
The integration of robotics into elder and disability care isn’t just a technological advancement; it’s a societal shift. By embracing innovative solutions, we’re not only improving the lives of individuals but also reshaping our understanding of aging and accessibility. The future holds even more promise, with AI and further technological breakthroughs poised to create even more intuitive and personalized care. It’s a future where technology empowers us all to age with grace and live with dignity, regardless of physical limitations. The journey is just beginning, and the possibilities are endless.
