The Role of Quantum Computing in Solving Global Healthcare Challenges – Quantum Computing: Solving Global Healthcare Challenges – it sounds like science fiction, right? But the reality is, this mind-bending technology is poised to revolutionize healthcare as we know it. Imagine a future where diseases are diagnosed faster, treatments are personalized with unprecedented accuracy, and drug discovery happens at warp speed. That future is closer than you think, thanks to the incredible power of quantum computing. This isn’t just about faster computers; it’s about unlocking solutions to some of humanity’s most pressing health problems.
From accelerating drug discovery and personalized medicine based on genomic data to enhancing medical imaging and predicting disease outbreaks, quantum computing offers a potent toolkit for tackling global healthcare challenges. We’ll explore how this revolutionary technology works, its potential applications, and the hurdles we need to overcome to harness its full potential for a healthier world.
Introduction to Quantum Computing and Healthcare
Quantum computing, a field leveraging the bizarre laws of quantum mechanics, holds immense promise for revolutionizing healthcare. Unlike classical computers that store information as bits representing 0 or 1, quantum computers utilize qubits. These qubits can exist in a superposition, representing 0, 1, or a combination of both simultaneously. This, along with other quantum phenomena like entanglement, allows quantum computers to perform calculations exponentially faster than classical computers for specific types of problems. This speed advantage is crucial in tackling complex healthcare challenges that are currently intractable for even the most powerful supercomputers.
The global healthcare landscape faces numerous daunting challenges. Drug discovery and development is a notoriously lengthy and expensive process, often failing to yield effective treatments. Diagnosing diseases accurately and efficiently, especially at early stages, remains a significant hurdle. Personalized medicine, tailoring treatments to individual genetic profiles, requires massive computational power to analyze complex genomic data. Finally, the sheer volume of medical data generated daily necessitates innovative solutions for storage, analysis, and interpretation.
Quantum computing offers a potential solution to these challenges. Its unparalleled computational power can significantly accelerate drug discovery by simulating molecular interactions with unprecedented accuracy, leading to faster identification of potential drug candidates and more effective treatments. In diagnostics, quantum algorithms could analyze medical images with greater sensitivity and speed, enabling earlier and more accurate disease detection. For personalized medicine, quantum computers can process and analyze vast genomic datasets, enabling the development of truly tailored therapies. Furthermore, quantum-resistant cryptography could enhance data security and privacy in the healthcare sector, protecting sensitive patient information. For example, researchers are exploring the use of quantum machine learning algorithms to identify patterns in patient data that could predict disease outbreaks or individual patient risk factors. The potential applications are vast and constantly expanding.
Drug Discovery and Development
The pharmaceutical industry faces a persistent challenge: developing effective drugs is a lengthy, expensive, and often inefficient process. Traditional methods rely heavily on trial and error, leading to high failure rates and substantial financial burdens. Quantum computing, with its potential to drastically accelerate simulations and data analysis, offers a promising pathway to revolutionize drug discovery and development.
Quantum simulations offer a powerful tool for modeling molecular interactions with unprecedented accuracy, enabling researchers to predict the behavior of drug candidates before they even enter the laboratory. This leap forward in predictive power could significantly reduce the time and cost associated with drug development.
Accelerating Drug Discovery with Quantum Simulations: A Hypothetical Workflow
Imagine a streamlined workflow where researchers design a potential drug molecule using quantum chemistry simulations. These simulations accurately predict the molecule’s interactions with the target protein, crucial for determining efficacy and potential side effects. This allows for early identification and elimination of ineffective candidates. Next, the quantum computer simulates the molecule’s behavior within a virtual cellular environment, predicting its absorption, distribution, metabolism, and excretion (ADME) properties. Finally, the results are refined using machine learning algorithms trained on vast datasets, optimizing the drug’s structure for maximum efficacy and minimal toxicity. This entire process, from initial design to pre-clinical testing, is significantly faster and more precise than traditional methods.
Identifying Drug Targets and Predicting Drug Efficacy Using Quantum Algorithms
Quantum algorithms excel at tackling complex optimization problems inherent in drug discovery. Variational Quantum Eigensolver (VQE) and Quantum Approximate Optimization Algorithm (QAOA) are examples of algorithms that can identify optimal drug targets by analyzing massive datasets of genomic and proteomic information. They can sift through millions of potential drug targets far more efficiently than classical algorithms. Furthermore, quantum machine learning algorithms can analyze complex interactions between drug candidates and their targets, accurately predicting drug efficacy and potential off-target effects. For example, quantum algorithms could analyze the binding affinity of a drug molecule to its target protein with much greater precision than classical molecular dynamics simulations, leading to more accurate predictions of drug efficacy.
Comparing Quantum and Classical Approaches to Drug Discovery
Quantum-based drug discovery offers significant advantages over traditional methods. While classical approaches often rely on approximations and simplified models, quantum simulations provide a far more accurate representation of molecular interactions. This leads to faster identification of promising drug candidates and reduces the need for extensive and costly experimental validation. The speed and accuracy improvements translate to significant cost savings and faster time to market for new drugs. However, it is important to note that quantum computing is still in its early stages of development, and widespread adoption in drug discovery is yet to come.
| Method | Time to Discovery | Accuracy | Cost |
|---|---|---|---|
| Classical Drug Discovery | 10-15 years | Moderate (high failure rate) | Billions of dollars |
| Quantum-Assisted Drug Discovery | Potentially 5-7 years | High (reduced failure rate) | Potentially significantly lower |
Genomics and Personalized Medicine: The Role Of Quantum Computing In Solving Global Healthcare Challenges
The sheer volume of data generated by genomic sequencing presents a monumental challenge for traditional computing. Human genomes contain billions of base pairs, and analyzing this information to understand individual genetic predispositions to disease, predict treatment responses, and ultimately personalize healthcare requires processing power far beyond the capabilities of current classical computers. Quantum computing, with its potential to exponentially accelerate computations, offers a promising solution to unlock the full potential of genomics for personalized medicine.
Quantum computing’s ability to handle massive datasets efficiently opens doors to previously unimaginable breakthroughs in genomic analysis. Imagine analyzing the entire genome of a patient in minutes, not months – this is the kind of speedup quantum computing promises. This speed and efficiency allows for deeper insights into complex genetic interactions, leading to more accurate diagnoses and tailored treatment plans.
Quantum Algorithms for Genomic Sequence Analysis and Variant Detection
Several quantum algorithms show promise for revolutionizing genomic analysis. Quantum machine learning algorithms, for instance, can be trained on massive genomic datasets to identify patterns and predict disease risks with greater accuracy than classical methods. Quantum annealing, a specific type of quantum computation, can efficiently solve optimization problems crucial for aligning and comparing genomic sequences. Furthermore, quantum algorithms designed for searching and pattern recognition can accelerate the detection of disease-causing genetic variants, enabling earlier and more effective interventions. Grover’s algorithm, a quantum search algorithm, could significantly speed up the search for specific genetic sequences within a vast genome. This faster search could be crucial in identifying disease-related mutations or variations.
Ethical Implications of Quantum Computing in Personalized Medicine
The application of quantum computing in personalized medicine raises important ethical considerations. The potential for highly accurate genomic analysis raises concerns about data privacy and security. Protecting sensitive genetic information from unauthorized access and misuse is paramount. Moreover, the potential for genetic discrimination based on predictive genomic analysis needs careful consideration and robust legal frameworks. Ensuring equitable access to quantum-based genomic technologies is crucial to avoid exacerbating existing healthcare disparities. The interpretation and application of quantum-generated genomic insights must be transparent and understandable, avoiding undue influence or misinterpretation of results. Finally, careful consideration needs to be given to the psychological impact of receiving highly personalized genetic risk assessments.
Potential Benefits and Risks of Quantum-Based Genomic Analysis
The potential benefits of using quantum computing for genomic analysis are substantial. Improved diagnostic accuracy, earlier disease detection, and personalized treatment plans can lead to significantly better health outcomes. The development of novel drugs and therapies targeted at specific genetic variations is another major potential benefit. However, several risks must be considered. The high cost of developing and implementing quantum computing technologies could limit accessibility. The complexity of interpreting quantum-generated genomic data requires specialized expertise, potentially creating a knowledge gap and widening existing inequalities in healthcare access. Finally, the potential for misuse of sensitive genetic information necessitates robust security measures and ethical guidelines.
- Benefits: Improved diagnostic accuracy, earlier disease detection, personalized treatment plans, development of novel drugs and therapies.
- Risks: High cost, limited accessibility, complexity of data interpretation, potential for misuse of sensitive information, ethical concerns regarding data privacy and equitable access.
Medical Imaging and Diagnostics
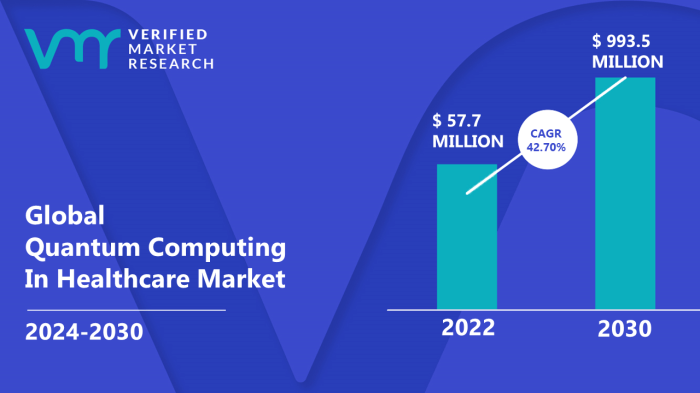
Source: verifiedmarketresearch.com
Quantum computing’s potential to revolutionize healthcare is massive, from drug discovery to personalized medicine. But training the next generation of experts requires innovative methods, which is where advancements like virtual reality come in; check out this article on How Virtual Reality is Advancing Medical Training and Education to see how. Ultimately, these tech leaps are crucial for quantum computing to truly unlock its potential in global healthcare solutions.
Quantum computing has the potential to revolutionize medical imaging and diagnostics, offering improvements in speed, accuracy, and overall efficiency that could lead to earlier and more accurate diagnoses, ultimately improving patient outcomes. Current imaging techniques, while powerful, often struggle with processing large datasets and dealing with noise, leading to limitations in resolution and clarity. Quantum algorithms offer a pathway to overcome these limitations.
Quantum computing’s speed advantage stems from its ability to perform calculations exponentially faster than classical computers for specific types of problems. This speed boost translates directly to faster image reconstruction, allowing for quicker processing of medical scans and reduced wait times for patients. Furthermore, quantum algorithms can significantly improve image quality by reducing noise and artifacts, leading to clearer and more detailed images.
Quantum Algorithms for Image Enhancement
The enhanced speed and accuracy of quantum computing in medical imaging is driven by several promising quantum algorithms. Quantum Annealing, for instance, can be used to optimize the reconstruction process, finding the best possible image from incomplete or noisy data. Quantum Machine Learning algorithms can be trained on vast datasets of medical images to identify subtle patterns and anomalies that might be missed by human eyes or classical image analysis techniques. These algorithms can learn to differentiate between healthy and diseased tissues with greater accuracy, improving the reliability of diagnostic assessments. For example, quantum algorithms could be applied to MRI data to more effectively detect subtle tumors, or to CT scan data to better distinguish between different tissue types. Another promising area is the use of quantum tomography for improved image reconstruction, offering higher resolution and clearer images with reduced artifacts.
Improved Image Clarity: A Visual Comparison
Imagine two images side-by-side. The image on the left, representing a classical MRI scan, shows a blurry representation of a brain, with some indistinct areas and noticeable noise obscuring details. The grayscale image is speckled with noise, making it difficult to discern the precise boundaries of brain structures. In contrast, the image on the right, depicting a quantum-enhanced MRI scan, reveals a significantly sharper and clearer picture. The grayscale is smoother, with significantly reduced noise. Fine details, such as the subtle differences in tissue density, are now clearly visible. The boundaries of different brain regions are sharply defined, allowing for more accurate identification of potential abnormalities. The overall contrast is greatly improved, highlighting key features and facilitating more precise diagnosis. This visual difference illustrates the potential of quantum computing to drastically enhance the diagnostic capabilities of medical imaging.
Disease Modeling and Prediction
Quantum computing’s potential to revolutionize healthcare extends beyond drug discovery and diagnostics; it offers a powerful new lens for understanding and predicting diseases. By leveraging the principles of quantum mechanics, we can create significantly more accurate and detailed models of complex biological systems, paving the way for more effective disease management and prevention strategies. This leap forward promises a paradigm shift in our approach to tackling global health challenges.
Quantum simulations offer a powerful tool for modeling the intricate interactions within biological systems, far exceeding the capabilities of classical computers. These simulations can capture the behavior of molecules, proteins, and cells with unprecedented accuracy, allowing researchers to study disease progression at a level of detail never before possible. This granular understanding can lead to the identification of novel drug targets, the development of personalized therapies, and the prediction of disease outbreaks with improved accuracy.
Quantum Simulations of Biological Systems
Traditional computational methods often struggle to model the complex interactions within biological systems due to the sheer number of variables involved. Quantum computers, however, can tackle these challenges more effectively by exploiting the principles of superposition and entanglement. This allows them to simulate the behavior of molecules and proteins with greater precision, revealing subtle interactions that are crucial for understanding disease mechanisms. For instance, quantum simulations can model the folding of proteins, a process crucial for their function and implicated in many diseases. Incorrect protein folding is a hallmark of conditions like Alzheimer’s and Parkinson’s disease, and quantum simulations could offer crucial insights into these processes. Further, simulations can explore the interactions between drugs and target proteins, leading to the design of more effective medications with fewer side effects.
Predicting Disease Outbreaks and Personalizing Treatment, The Role of Quantum Computing in Solving Global Healthcare Challenges
The ability to accurately predict disease outbreaks is crucial for effective public health interventions. Quantum computing’s superior computational power allows for the development of more sophisticated epidemiological models that can incorporate a vast amount of data, including genetic factors, environmental influences, and social networks. This improved predictive capability could lead to more timely and targeted interventions, potentially mitigating the impact of future pandemics or outbreaks of infectious diseases. For example, by analyzing large datasets of patient information and environmental factors, a quantum-enhanced model could predict the likelihood of a flu outbreak in a specific region, allowing for the proactive allocation of resources and the implementation of preventative measures. Similarly, in personalized medicine, quantum computing could analyze an individual’s genetic profile and medical history to predict their risk of developing specific diseases, leading to the development of tailored preventative strategies or early intervention treatments.
Comparing Quantum and Traditional Epidemiological Models
Traditional epidemiological models often rely on simplified assumptions and approximations, limiting their accuracy in capturing the complexities of disease spread. Quantum models, on the other hand, can handle far more intricate datasets and interactions, leading to more precise predictions. Consider, for example, the spread of an infectious disease. A traditional model might rely on average contact rates and population densities. A quantum model could incorporate individual-level data, such as mobility patterns, social networks, and genetic susceptibility, providing a far more nuanced and accurate prediction of the disease’s trajectory. This increased accuracy is crucial for effective resource allocation and intervention strategies. The difference could be the difference between a regional outbreak and a national pandemic.
Examples of Diseases Where Quantum Modeling Could Offer Advancements
Quantum modeling holds immense promise for a wide range of diseases. For example, in cancer research, quantum simulations can help understand the complex interactions between cancer cells and the immune system, potentially leading to the development of more effective immunotherapies. In neurodegenerative diseases like Alzheimer’s and Parkinson’s, quantum simulations can provide insights into the misfolding of proteins and the development of neurofibrillary tangles and plaques, crucial for developing disease-modifying therapies. Finally, in infectious diseases, quantum computing can help design more effective vaccines and antiviral drugs by simulating the interactions between pathogens and the host immune system. The ability to model these complex systems with greater accuracy will undoubtedly lead to significant advancements in the treatment and prevention of these diseases.
Challenges and Future Directions
Quantum computing’s potential in healthcare is undeniable, but realizing this potential requires navigating significant hurdles. The technology is still in its nascent stages, and widespread adoption faces technological, infrastructural, and collaborative challenges that need careful consideration and strategic planning. Overcoming these obstacles will unlock a new era of medical breakthroughs.
The path to integrating quantum computing into healthcare isn’t paved with gold; it’s strewn with obstacles. Significant technological advancements are needed before quantum computers become robust, reliable, and accessible enough for routine clinical use. The sheer cost of developing and maintaining these machines is currently prohibitive for most healthcare institutions. Furthermore, the development of quantum algorithms specifically tailored for healthcare applications is still in its early phases, requiring substantial research and development investment. Data security and privacy are also major concerns, as quantum computers could potentially break current encryption methods, demanding the development of new, quantum-resistant security protocols.
Technological and Infrastructural Hurdles
Developing stable, scalable, and fault-tolerant quantum computers is paramount. Current quantum computers are prone to errors, and their computational power is limited. The need for cryogenic cooling systems adds to the complexity and cost, hindering widespread accessibility. Moreover, the lack of standardized interfaces and protocols makes it challenging to integrate quantum computers into existing healthcare IT infrastructure. Consider the immense amount of data generated in healthcare; efficiently managing and processing this data within a quantum computing framework is a substantial technical challenge. For example, the sheer volume of genomic data generated through next-generation sequencing far exceeds the capacity of classical computers, highlighting the need for quantum computing solutions capable of handling such large datasets.
Collaboration in Quantum Healthcare
Successful implementation hinges on robust collaboration between researchers, clinicians, and technology developers. Researchers need to focus on developing quantum algorithms relevant to specific healthcare problems, while clinicians must provide the medical expertise to define those problems and validate the results. Technology developers are crucial in building user-friendly interfaces and integrating quantum computing solutions into existing healthcare systems. A prime example of successful collaboration would be a joint project between a quantum computing company, a leading genomics research institute, and a network of hospitals to develop and deploy a quantum-based diagnostic tool for early cancer detection. This cross-disciplinary approach ensures that the technology developed is both scientifically sound and clinically relevant.
Future Applications of Quantum Computing in Healthcare
Beyond the applications already discussed, quantum computing holds the promise of revolutionizing several other areas of healthcare. Quantum machine learning could lead to the development of more accurate and personalized diagnostic tools, capable of predicting disease progression and tailoring treatment plans to individual patients’ needs. Quantum simulations could allow researchers to study complex biological systems with unprecedented accuracy, leading to a deeper understanding of disease mechanisms and the development of novel therapies. For example, quantum simulations could be used to design new drugs that are more effective and have fewer side effects. Furthermore, quantum cryptography could enhance the security of patient data, ensuring confidentiality and protecting sensitive medical information. This will be especially crucial as the amount of healthcare data generated and stored increases exponentially.
Epilogue
The potential of quantum computing to reshape global healthcare is undeniable. While challenges remain in terms of infrastructure and development, the breakthroughs already achieved and the potential for future advancements are incredibly exciting. As quantum computers become more powerful and accessible, we can expect a cascade of innovations that will dramatically improve diagnosis, treatment, and prevention of diseases worldwide. This isn’t just about technological advancement; it’s about building a healthier, more equitable future for everyone.
