The Role of Cloud Computing in Enabling Remote Work: Forget stuffy offices and hello flexible futures! This isn’t your grandpa’s remote work; we’re talking about a total digital transformation fueled by the cloud. From accessing files anywhere to collaborating seamlessly across continents, cloud computing has rewritten the rules of the workplace. We’ll dive into how it’s all possible, the challenges, and what the future holds for this increasingly vital work style.
We’ll explore the evolution of remote work, from its humble beginnings to its current explosion in popularity. Then, we’ll break down the core cloud services – IaaS, PaaS, and SaaS – and how they power remote teams. We’ll also tackle the not-so-glamorous parts: security concerns, potential pitfalls, and best practices to keep your data safe and your remote team humming. Finally, we’ll peek into the crystal ball and see what cutting-edge tech like AI and edge computing have in store for the future of work.
Introduction to Remote Work and Cloud Computing
The rise of remote work isn’t a recent phenomenon; it’s a story of gradual evolution, punctuated by technological leaps. From early telecommunications enabling geographically dispersed collaborations to the current ubiquity of internet-connected devices, the journey has been long and fascinating. Understanding this history is crucial to appreciating the transformative role cloud computing plays in modern remote work scenarios.
The Historical Context of Remote Work
Remote work, in its various forms, has existed for decades. Early examples include telecommuting via telephone and fax, primarily adopted by professionals in fields like journalism and sales. The advent of dial-up internet in the 1990s allowed for more sophisticated remote access to company networks, though bandwidth limitations and unreliable connections posed significant challenges. The turn of the millennium saw the rise of broadband internet, significantly improving speed and reliability, making remote work a more viable option for a wider range of professions. The COVID-19 pandemic acted as a massive catalyst, forcing a rapid and widespread adoption of remote work practices across numerous industries. This unexpected shift highlighted both the potential and the challenges of a largely remote workforce.
Key Technological Advancements Enabling Remote Work
Several key technological advancements have paved the way for widespread remote work. High-speed internet access, of course, is paramount, providing the necessary bandwidth for data-intensive tasks like video conferencing and file sharing. The development of robust and secure Virtual Private Networks (VPNs) allows employees to securely access company networks from anywhere with an internet connection. Furthermore, the proliferation of collaboration tools like Slack, Microsoft Teams, and Google Workspace has facilitated seamless communication and project management within distributed teams. Finally, the increasing sophistication of mobile devices has enabled employees to stay connected and productive regardless of their location.
Cloud Computing Defined and its Core Services
Cloud computing is the on-demand availability of computer system resources, especially data storage (cloud storage) and computing power, without direct active management by the user. Instead of relying on locally-installed software and hardware, users access these resources over the internet, typically paying only for what they use. This model offers significant advantages in terms of scalability, cost-effectiveness, and flexibility. The core services of cloud computing are generally categorized as:
* Infrastructure as a Service (IaaS): Provides fundamental computing resources like virtual machines, storage, and networking. Think of it as renting the raw materials for building your own applications. Examples include Amazon Web Services (AWS) EC2 and Microsoft Azure Virtual Machines.
* Platform as a Service (PaaS): Offers a platform for developing, running, and managing applications without the need to manage the underlying infrastructure. This includes tools for database management, application deployment, and scaling. Examples include AWS Elastic Beanstalk and Google App Engine.
* Software as a Service (SaaS): Delivers software applications over the internet, eliminating the need for local installation and maintenance. Familiar examples include Salesforce, Microsoft 365, and Google Workspace.
On-Premise vs. Cloud-Based Infrastructure for Remote Work
The following table compares on-premise infrastructure with cloud-based infrastructure for remote work, highlighting key differences:
| Location | Cost | Scalability | Security |
|---|---|---|---|
| On-site data center | High upfront investment; ongoing maintenance costs | Limited; requires significant planning and investment for expansion | Requires robust on-site security measures; potential for single point of failure |
| Cloud provider’s data centers | Pay-as-you-go model; typically lower upfront costs | Highly scalable; easily adjust resources based on demand | Security managed by the cloud provider; often incorporates multiple layers of security |
Essential Cloud Services for Remote Work: The Role Of Cloud Computing In Enabling Remote Work

Source: iswerk.ph
Cloud computing’s power fuels remote work, allowing seamless collaboration and data access. This same power is mirrored in other fields; for instance, the advancements in sports analytics are hugely dependent on cloud infrastructure, as seen in the detailed analysis discussed in The Role of Artificial Intelligence in Enhancing Sports Analytics. Ultimately, the scalability and accessibility offered by the cloud are key to both remote work efficiency and groundbreaking sports tech.
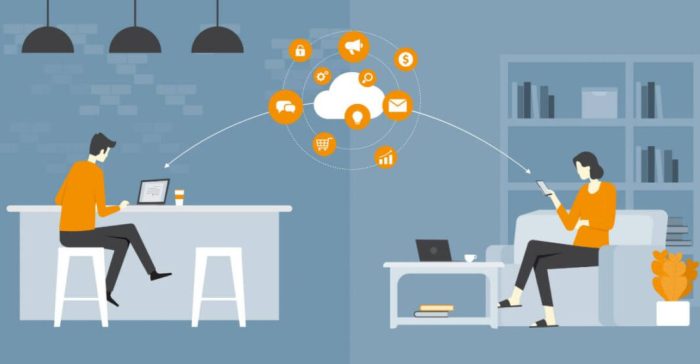
Remote work wouldn’t be the seamless experience it is for many without the backbone of cloud computing. It’s the invisible infrastructure powering everything from sharing documents to holding virtual meetings, transforming how we work and collaborate. Let’s dive into the key cloud services making this possible.
Cloud Storage and File Sharing
Cloud storage is the digital filing cabinet of the modern workplace, allowing remote teams to access, share, and collaborate on files from anywhere with an internet connection. Services like Dropbox, Google Drive, and Microsoft OneDrive offer robust storage solutions with version control, allowing teams to track changes, revert to previous versions, and ensure everyone is working with the most up-to-date information. This eliminates the chaos of emailing large files back and forth or relying on outdated versions stored locally. The collaborative features often built into these platforms allow multiple users to edit documents simultaneously, fostering real-time teamwork and boosting productivity. For instance, Google Docs’ real-time co-editing feature enables simultaneous editing, allowing multiple team members to work on a single document concurrently, significantly improving efficiency.
Cloud-Based Communication Tools
Effective communication is the lifeblood of any remote team. Cloud-based communication tools are essential for keeping everyone connected and informed. Video conferencing platforms like Zoom, Google Meet, and Microsoft Teams facilitate face-to-face interactions, replicating the experience of in-person meetings. Instant messaging platforms such as Slack and Microsoft Teams provide quick, asynchronous communication for day-to-day updates and quick questions. These tools significantly reduce communication barriers, fostering a sense of community and ensuring everyone stays in the loop, even across geographical boundaries. Consider the impact of a quick video call to resolve a complex issue, saving hours of back-and-forth emails.
Cloud-Based Productivity Suites
Cloud-based productivity suites integrate various applications to streamline workflows. Microsoft 365, Google Workspace, and other similar platforms offer a comprehensive suite of tools including word processing, spreadsheets, presentations, email, and calendar applications. These tools are often seamlessly integrated, allowing for smooth data transfer between applications and enhanced collaboration. For example, the ability to embed a Google Sheet directly into a Google Doc allows for dynamic data visualization and updates within a single document. This level of integration drastically simplifies workflows, ensuring everyone is working from a centralized and unified system.
Cloud Security Measures for Remote Work Data, The Role of Cloud Computing in Enabling Remote Work
Protecting sensitive data is paramount for any organization, especially those relying on remote workforces. Reputable cloud providers invest heavily in security measures to protect user data. These measures typically include data encryption both in transit and at rest, robust access controls, multi-factor authentication, and regular security audits. Furthermore, many providers offer features like intrusion detection and prevention systems, and comprehensive data loss prevention (DLP) tools. For instance, Google Workspace employs various security protocols, including encryption, access controls, and regular security updates, to ensure the security of user data. This robust security infrastructure mitigates the risks associated with remote work and provides peace of mind for both employees and employers.
Challenges and Considerations of Cloud-Based Remote Work
The seemingly utopian world of remote work, powered by cloud computing, isn’t without its hurdles. While offering incredible flexibility and scalability, cloud-based remote work presents significant challenges in data security, network reliability, and compliance. Navigating these complexities requires a proactive and well-informed approach, blending robust security measures with a clear understanding of different cloud deployment models.
Data Security and Network Connectivity Issues in Remote Work Environments
Data breaches and unreliable network connections are major concerns for organizations embracing cloud-based remote work. A single security lapse can expose sensitive company information, leading to financial losses, reputational damage, and legal repercussions. Similarly, inconsistent internet access can disrupt workflows, reduce productivity, and impact employee morale. For instance, a sudden internet outage in a remote worker’s location can halt an ongoing project, potentially delaying deadlines and impacting client relationships. The reliance on robust and redundant internet connections becomes paramount, along with robust security protocols implemented at both the individual and organizational levels.
Cloud Deployment Models and Their Suitability for Remote Work
Choosing the right cloud deployment model – public, private, or hybrid – is crucial for successful remote work. Public clouds, like AWS or Azure, offer cost-effectiveness and scalability but might raise concerns about data security and compliance for organizations handling sensitive information. Private clouds, hosted on-premises or by a third-party provider, provide greater control and security but can be more expensive and less scalable. Hybrid clouds combine elements of both, offering a balance between cost, security, and flexibility. For example, a company might use a public cloud for less sensitive data and applications while keeping highly confidential information on a private cloud. The optimal choice depends on the organization’s specific needs, budget, and risk tolerance.
Strategies for Ensuring Data Privacy and Compliance in Cloud-Based Remote Work
Protecting data privacy and ensuring compliance with regulations like GDPR or CCPA are paramount. Implementing strong access controls, data encryption both in transit and at rest, and regular security audits are essential. Furthermore, employee training on data security best practices is crucial. Companies should also carefully select cloud providers that adhere to relevant security standards and compliance certifications. For example, a healthcare provider would need to choose a cloud provider that complies with HIPAA regulations to protect patient data. A multi-layered approach, combining technological safeguards with robust policies and procedures, is the key to maintaining data privacy and compliance.
Best Practices for Securing Remote Access to Cloud-Based Resources
Implementing robust security measures is vital for protecting cloud-based resources accessed remotely. Here are some best practices:
- Implement multi-factor authentication (MFA) for all user accounts.
- Use strong, unique passwords and encourage password managers.
- Regularly update software and operating systems on all devices.
- Employ a Virtual Private Network (VPN) to encrypt all internet traffic.
- Enforce regular security awareness training for employees.
- Implement intrusion detection and prevention systems.
- Conduct regular security audits and penetration testing.
These measures collectively minimize the risks associated with remote access, creating a more secure environment for both the organization and its employees.
Impact of Cloud Computing on Remote Work Productivity and Collaboration
The rise of cloud computing has fundamentally reshaped the landscape of remote work, transforming it from a niche practice to a widely adopted and increasingly efficient way of working. Cloud-based tools and platforms have become the backbone of remote team productivity and collaboration, offering seamless communication, efficient project management, and enhanced accessibility to resources, regardless of geographical location. This shift has unlocked unprecedented levels of flexibility and efficiency for both businesses and individual workers.
Cloud computing’s impact on remote work productivity is multifaceted. It streamlines processes, reduces reliance on physical infrastructure, and fosters a more dynamic and collaborative work environment. The accessibility of shared documents, instant communication channels, and centralized project management tools drastically reduces the friction often associated with remote teamwork. This results in a significant boost in overall efficiency and allows for better utilization of time and resources.
Enhanced Remote Team Collaboration and Communication
Cloud-based communication tools like Slack, Microsoft Teams, and Google Chat facilitate instant messaging, video conferencing, and file sharing, creating a virtual office environment that mirrors the spontaneity and ease of in-person collaboration. These platforms foster a sense of community and connectedness among geographically dispersed teams, enabling quick responses to queries, efficient brainstorming sessions, and real-time problem-solving. The ease of sharing documents and collaborating on projects in real-time eliminates the delays and misunderstandings that can arise from relying on email or traditional file-sharing methods. For example, a marketing team using Google Docs can simultaneously edit a campaign proposal, ensuring everyone is on the same page and reducing the time spent on version control and revisions.
Improved Efficiency and Productivity of Remote Workers
Cloud computing directly contributes to increased efficiency and productivity for individual remote workers. Access to company resources and applications from anywhere with an internet connection eliminates the need to be physically present in the office. This flexibility allows workers to manage their time more effectively, working when they are most productive and integrating work seamlessly into their personal lives. Cloud-based project management tools like Asana, Trello, and Monday.com provide centralized task management, progress tracking, and deadline reminders, helping remote workers stay organized and on track. This eliminates the need for manual tracking and reduces the risk of missed deadlines or forgotten tasks. The automation capabilities within these tools further streamline workflows, freeing up valuable time for more strategic work.
Real-time Project Management and Task Tracking for Remote Teams
Cloud-based project management tools are indispensable for remote teams. These platforms provide a centralized hub for all project-related information, allowing team members to access updates, track progress, and collaborate on tasks in real-time. Features like task assignment, progress visualization (e.g., Kanban boards), and automated notifications ensure everyone is informed and accountable. For instance, a software development team using Jira can track bugs, manage sprints, and collaborate on code changes, ensuring seamless progress and transparency throughout the development lifecycle. The ability to track progress in real-time allows for proactive problem-solving and prevents minor issues from escalating into major delays.
Workflow of a Typical Remote Work Scenario Enabled by Cloud Computing
[Imagine a flowchart here. The flowchart would begin with a “Project Initiation” box, branching to “Task Assignment (Cloud-based PM tool)” and “Resource Allocation (Cloud storage)”. These would then lead to “Individual Work (Cloud-based applications)”, followed by “Collaboration & Communication (Cloud-based communication tools)”. The next step would be “Progress Tracking & Reporting (Cloud-based PM tool)”, leading to “Project Review & Iteration” and finally “Project Completion”. Each box would represent a stage, and the arrows would indicate the flow of the process.] This flowchart visually depicts how cloud-based tools seamlessly integrate into each stage of a typical remote work project, from initiation to completion, fostering efficient collaboration and real-time progress tracking. The centralized nature of the cloud allows all team members to access and contribute to the project at any time, from any location.
Future Trends in Cloud Computing and Remote Work
Source: enterpriseig.com
The future of work is inextricably linked to the continued evolution of cloud computing. As technology advances, we’re seeing a convergence of powerful trends that will redefine how and where we work, creating opportunities for unprecedented flexibility and efficiency. This section explores some of the key technological advancements shaping this future and their impact on the remote work landscape.
Emerging Technologies and Their Impact on Remote Work
Edge computing, serverless computing, and other emerging technologies are poised to significantly enhance the remote work experience. Edge computing, by processing data closer to its source, reduces latency and improves responsiveness for applications like video conferencing and real-time collaboration tools. This is particularly beneficial for remote workers in areas with limited bandwidth. Serverless computing, on the other hand, allows developers to build and deploy applications without managing servers, reducing operational overhead and enabling faster iteration cycles. This translates to more agile and responsive remote work tools and applications. Imagine a future where real-time data analysis for remote engineers is instantly available, regardless of their location, thanks to the combined power of edge and serverless architectures. This speed and efficiency directly impacts productivity and reduces the reliance on centralized data centers.
The Role of AI and Machine Learning in Enhancing Remote Work Experiences
Artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning (ML) are revolutionizing the way we work remotely. AI-powered tools can automate repetitive tasks, freeing up remote workers to focus on more strategic initiatives. For example, intelligent assistants can schedule meetings, manage emails, and even generate reports, significantly reducing administrative burden. ML algorithms can analyze vast datasets to identify trends and patterns, improving decision-making and enabling more effective remote collaboration. Think of personalized learning platforms that adapt to individual employee needs, offering targeted training and support based on their performance and learning style. This leads to a more engaged and productive remote workforce.
Predictions About the Future of Work and the Role of Cloud Computing
The future of work will be increasingly decentralized, fluid, and globally connected. Cloud computing will play a pivotal role in enabling this shift, providing the infrastructure and tools necessary for seamless collaboration across geographical boundaries. We predict a significant rise in the adoption of hybrid work models, where employees blend remote and on-site work. Companies like Spotify have already successfully adopted this model, demonstrating its viability and effectiveness. Cloud-based solutions will be crucial in facilitating this transition, providing the necessary security, scalability, and flexibility to support a distributed workforce. Furthermore, the lines between personal and professional lives will continue to blur, with cloud-based tools enabling a more integrated and seamless experience.
A Hypothetical Future Scenario: Seamless Integration of Cloud Computing and Remote Work
Imagine a world in 2035 where a software engineer in rural Japan seamlessly collaborates with a designer in London and a marketing specialist in New York on a cutting-edge augmented reality project. All three individuals work remotely, utilizing cloud-based collaborative platforms that integrate AI-powered tools for real-time translation, design feedback, and marketing analysis. The project’s data is stored securely in a decentralized cloud environment, accessible to all team members with appropriate permissions. AI-powered assistants manage project schedules, track progress, and provide proactive support. High-bandwidth, low-latency edge computing ensures smooth communication and rapid data processing, regardless of location. This scenario showcases the transformative potential of cloud computing in creating a truly global and interconnected workplace, fostering innovation and collaboration on an unprecedented scale.
Conclusion

Source: wfhbee.com
So, there you have it: cloud computing isn’t just a tech buzzword; it’s the backbone of the modern remote workplace. From boosting productivity and collaboration to enabling global teams, its impact is undeniable. While challenges exist, the solutions are constantly evolving, making the future of remote work brighter and more connected than ever. Embrace the cloud, embrace the future of work – it’s more flexible, more efficient, and more exciting than you ever imagined.
