The Role of Blockchain in Securing Cryptocurrency Wallets: Forget flimsy passwords and dodgy security. We’re diving deep into how this revolutionary tech is changing the game for crypto safety. From hardware wallets to the magic of smart contracts, we’ll uncover the secrets behind keeping your digital dough safe from prying eyes and sneaky hackers. Get ready to level up your crypto security game.
This isn’t just about keeping your coins safe; it’s about understanding the core technology that underpins the entire cryptocurrency ecosystem. We’ll explore different wallet types, their strengths and weaknesses, and the crucial role of blockchain in protecting your private keys. We’ll also touch on the emerging threats and how innovative solutions are constantly evolving to stay ahead of the curve.
Blockchain Fundamentals and Cryptocurrency Wallets
Cryptocurrency wallets, the digital containers holding your precious digital assets, rely heavily on the security offered by blockchain technology. Understanding the fundamental principles of blockchain is crucial to grasping how these wallets keep your crypto safe. This section will delve into the core concepts of blockchain and explore the various types of cryptocurrency wallets available, comparing their security features and suitability for different users.
Blockchain Technology and Wallet Security
At its heart, blockchain is a distributed, immutable ledger. Think of it as a shared, constantly updated digital record book that’s replicated across numerous computers. Each transaction is recorded as a “block,” chained to the previous block using cryptographic techniques. This makes altering past transactions incredibly difficult, a cornerstone of blockchain’s security. This immutability extends to cryptocurrency transactions, providing a verifiable and tamper-proof history of ownership. When you use a cryptocurrency wallet, the blockchain acts as a public record, confirming that the cryptocurrency you own is actually yours. This transparency and verifiable history are crucial elements in ensuring the security of your wallet. The decentralized nature of blockchain also means there’s no single point of failure, making it more resilient to attacks compared to centralized systems.
Types of Cryptocurrency Wallets, The Role of Blockchain in Securing Cryptocurrency Wallets
Cryptocurrency wallets come in various forms, each with its own strengths and weaknesses regarding security and accessibility. Choosing the right wallet depends on your technical expertise, the amount of cryptocurrency you hold, and your risk tolerance.
Comparing Wallet Security Features
The security of different wallet types varies significantly. Let’s examine the key features of each:
| Wallet Type | Security Level | Accessibility | Cost |
|---|---|---|---|
| Hardware Wallet | Very High (offline storage, strong encryption) | Low (requires physical access) | Medium to High (purchase cost) |
| Software Wallet | Medium (vulnerable to malware if not properly secured) | High (accessible from any device with internet connection) | Low to Medium (some are free, others have subscription fees) |
| Paper Wallet | Medium to Low (vulnerable to physical theft and damage) | Low (requires manual access and transfer) | Very Low (only requires printing) |
The table highlights the trade-off between security and accessibility. Hardware wallets offer the highest security but are less convenient, while software wallets provide ease of access but require more vigilance against malware. Paper wallets, while simple and inexpensive, are highly susceptible to physical risks. The choice depends on individual needs and priorities. For instance, someone holding a large amount of cryptocurrency might prioritize the enhanced security of a hardware wallet, while someone occasionally using cryptocurrency might find a software wallet more convenient.
Blockchain’s Role in Securing Private Keys
Think of your cryptocurrency wallet’s private key as the ultimate password to your digital fortune. Losing it means losing access to your funds – a truly catastrophic event. Blockchain technology, while not directly storing private keys *on* the blockchain itself (for security reasons), plays a crucial role in securing them and facilitating their safe usage. This security isn’t magical; it relies on robust cryptographic techniques and clever design.
Blockchain’s primary contribution lies in providing a verifiable and tamper-proof record of transactions. This indirectly enhances private key security because every transaction involving your funds is immutably recorded. While the private key itself remains off-chain, the blockchain acts as a powerful audit trail, allowing you to track all activity related to your wallet address. This makes it incredibly difficult for malicious actors to tamper with transaction records or falsely claim ownership of your funds.
Cryptographic Techniques in Securing Wallets
The security of cryptocurrency wallets heavily relies on sophisticated cryptographic techniques. These techniques ensure that only the rightful owner, possessing the corresponding private key, can access and spend the associated cryptocurrency. Public-key cryptography is central to this process. Each wallet generates a pair of keys: a public key (like your bank account number, visible to everyone) and a private key (your secret PIN, known only to you). The public key is used to receive funds, while the private key is used to authorize transactions. Any attempt to spend funds without the private key is computationally infeasible due to the strength of the underlying cryptographic algorithms. Common algorithms include Elliptic Curve Cryptography (ECC), which is highly efficient and widely used in securing Bitcoin and other cryptocurrencies.
Multi-Signature Wallets and Enhanced Security
Multi-signature wallets represent a significant advancement in security. Instead of requiring only one private key to authorize a transaction, they demand multiple signatures from different private keys. For example, a 2-of-3 multi-signature wallet requires two out of three authorized individuals to approve a transaction before it can be executed. This mechanism drastically reduces the risk of unauthorized access or theft, even if one private key is compromised. Imagine a company holding cryptocurrency; using a multi-sig wallet ensures that no single employee has complete control over the funds, thus mitigating the risk of fraud or insider threats.
Transaction Process Using a Blockchain-Secured Wallet
The following flowchart illustrates a typical transaction involving a blockchain-secured wallet.
[Illustrative Flowchart Description:]
Imagine a box representing the user’s wallet, containing their private key. The first step shows the user initiating a transaction, specifying the recipient’s public key and the amount to be sent. The next box depicts the wallet software using the private key and cryptographic algorithms to create a digitally signed transaction. This signed transaction is then broadcast to the network of nodes in the blockchain. The next box shows the network verifying the transaction’s validity using the public key, ensuring that the user possesses the corresponding private key. Once validated by a sufficient number of nodes, the transaction is added to a new block on the blockchain, becoming immutable and publicly verifiable. Finally, the box shows the transaction’s successful completion, with the funds transferred to the recipient’s wallet. The entire process is recorded on the blockchain, providing a transparent and auditable record of the transaction.
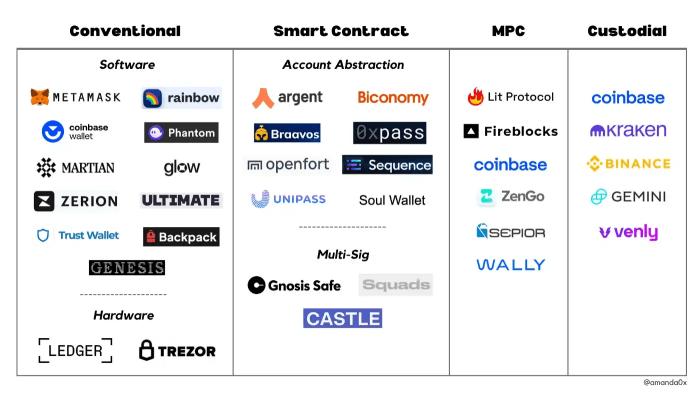
Smart Contracts and Wallet Security: The Role Of Blockchain In Securing Cryptocurrency Wallets
Source: thirdweb.com
Smart contracts, self-executing contracts with the terms of the agreement between buyer and seller being directly written into lines of code, are revolutionizing how we think about security in the cryptocurrency world. They offer a level of automation and transparency that traditional methods simply can’t match, significantly bolstering the security of cryptocurrency wallets. By automating crucial steps in transactions and enforcing pre-defined rules, smart contracts minimize the risk of human error and malicious attacks.
Smart contracts can enhance wallet security by acting as intermediaries, verifying transactions and ensuring funds are released only under specific conditions. This eliminates the need for trust in third-party intermediaries, a significant vulnerability in many traditional financial systems. Think of it as having a highly reliable, incorruptible digital notary constantly overseeing your transactions.
Smart Contract Applications for Secure Cryptocurrency Transactions
Smart contracts find numerous applications in securing cryptocurrency transactions. For example, multi-signature wallets utilize smart contracts to require multiple approvals before funds can be released. This prevents unauthorized access even if one private key is compromised. Another example is escrow services, where a smart contract holds funds until both parties fulfill their obligations. This protects both the buyer and seller from fraud. Furthermore, decentralized exchanges (DEXs) often rely on smart contracts to automate the trading process, eliminating the need for a centralized entity and reducing the risk of manipulation. Imagine a scenario where a smart contract automatically releases funds to a seller only after the buyer confirms receipt of goods, ensuring a secure and transparent transaction for both parties.
Best Practices for Using Smart Contracts to Improve Wallet Security
Employing smart contracts effectively requires careful consideration. Thorough auditing of the smart contract code is paramount. Independent security audits by reputable firms can help identify vulnerabilities before deployment. Using established, well-vetted smart contract templates can reduce the risk of errors. Furthermore, limiting the scope of the smart contract to its essential functions reduces the attack surface. Keeping the smart contract code as concise and straightforward as possible minimizes the chances of unforeseen bugs or vulnerabilities. Finally, regularly updating the smart contract to address any discovered vulnerabilities is crucial for maintaining optimal security.
Potential Vulnerabilities in Smart Contracts Related to Wallet Security
Despite their advantages, smart contracts are not without vulnerabilities. Reentrancy attacks, where a malicious contract calls back into the original contract before the first transaction is completed, can drain funds. Arithmetic overflow and underflow errors, caused by limitations in how integers are handled in code, can lead to unexpected behavior and loss of funds. Logic errors in the contract’s code can also create exploitable vulnerabilities. Finally, vulnerabilities in the underlying blockchain platform itself can indirectly impact the security of smart contracts and, consequently, the wallets they protect. These vulnerabilities highlight the importance of rigorous testing, auditing, and ongoing monitoring of smart contracts used for wallet security.
Decentralized Exchanges (DEXs) and Wallet Security

Source: solulab.com
Blockchain’s immutable ledger secures crypto wallets by recording every transaction, creating a transparent and tamper-proof system. This same technology, ensuring trust and provenance, is revolutionizing other sectors too; for example, check out how it’s boosting IP protection in this article: How Blockchain Technology is Enhancing Intellectual Property Protection. Ultimately, this core principle – verifiable records – is what underpins both secure crypto wallets and a new era of intellectual property rights management.
Decentralized exchanges (DEXs) are shaking up the crypto world, offering a compelling alternative to their centralized counterparts. But with this exciting innovation comes a new set of security considerations for your precious digital assets. Let’s dive into how DEXs impact the security of your cryptocurrency wallets.
DEXs, unlike centralized exchanges (CEXs), don’t hold your funds. Instead, you retain complete control of your private keys, interacting directly with smart contracts on the blockchain. This sounds amazing for security, right? Well, it’s a bit more nuanced than that.
Security Comparison: DEXs vs. CEXs
Centralized exchanges, while convenient, are single points of failure. A hack on a CEX can wipe out all your holdings. DEXs, by contrast, distribute trust across the network, making them theoretically more resilient to large-scale attacks targeting a single entity. However, this doesn’t mean DEXs are impervious to vulnerabilities. The security landscape shifts from protecting a single entity to safeguarding individual user interactions with smart contracts and the blockchain itself. The responsibility for security is, to a larger extent, placed on the user.
Potential Vulnerabilities of DEXs
While DEXs offer enhanced security in some aspects, they are not without their vulnerabilities. Smart contract vulnerabilities are a major concern. Bugs in the code can be exploited by malicious actors to drain user funds. For instance, a poorly written smart contract might allow someone to manipulate the exchange rate or drain liquidity pools. Another potential risk lies in the user’s own actions – phishing scams, compromised hardware wallets, or simply making mistakes when interacting with the DEX interface can lead to significant losses. Furthermore, the lack of robust KYC/AML procedures in many DEXs presents a challenge for regulators and can attract illicit activities, indirectly affecting the security of the overall ecosystem. Consider the infamous DAO hack of 2016, where a vulnerability in a smart contract allowed for the theft of millions of dollars worth of ETH. This illustrates the critical need for thorough audits and rigorous testing of smart contracts before deployment on a DEX.
Blockchain’s Role in Mitigating DEX Risks
Despite the potential vulnerabilities, blockchain technology itself plays a crucial role in mitigating some of the risks associated with DEX usage. The immutable nature of the blockchain provides a transparent record of all transactions. This transparency allows for easier identification of fraudulent activities and helps in tracking stolen funds. Furthermore, the decentralized nature of the blockchain makes it incredibly difficult for a single entity to manipulate the system. While smart contract vulnerabilities remain a concern, the open-source nature of many DEXs allows for community scrutiny and rapid patching of identified flaws. The use of multi-signature wallets can also enhance security by requiring multiple approvals for significant transactions, reducing the risk of unauthorized access.
Security Threats and Mitigation Strategies
Cryptocurrency wallets, while offering the promise of decentralized financial freedom, aren’t immune to the ever-evolving landscape of cyber threats. Understanding these threats and implementing robust mitigation strategies is crucial for safeguarding your digital assets. This section dives into the common dangers and the best practices for keeping your crypto secure.
Protecting your cryptocurrency requires a multi-layered approach, combining technical safeguards with responsible user behavior. Failing to address any single point of vulnerability can leave your hard-earned crypto exposed to theft or loss. Think of it like a castle – a single weak wall can bring down the entire fortress.
Phishing Attacks
Phishing attempts to trick users into revealing their private keys or seed phrases through deceptive emails, websites, or messages. These often mimic legitimate services, using convincing branding and urgent requests for action. A successful phishing attack grants the attacker complete control over the victim’s wallet. For example, a seemingly legitimate email from a cryptocurrency exchange might ask you to update your account details, leading to a fake website where your credentials are stolen. Successful mitigation involves verifying the authenticity of communication channels, avoiding suspicious links, and enabling two-factor authentication (2FA) wherever possible.
Malware Infections
Malware, including viruses, trojans, and keyloggers, can silently infiltrate your system and steal your cryptocurrency. Keyloggers record keystrokes, capturing your private keys as you type them. Trojans can execute malicious code, granting unauthorized access to your wallet. A recent example involved a sophisticated piece of malware disguised as a cryptocurrency trading application; once installed, it silently drained user funds. Strong antivirus software, regular system updates, and caution when downloading applications are essential defenses. Running regular security scans and avoiding untrusted sources are key to preventing malware infections.
Hardware Failures
While less of a security breach and more of a data loss issue, hardware failures can render your cryptocurrency inaccessible if your private keys are stored solely on a compromised device. A sudden hard drive crash or phone malfunction could mean the loss of your entire portfolio. Mitigation involves employing robust backup strategies, storing your seed phrase securely offline, and using hardware wallets for increased protection. A simple example: If your computer crashes and you haven’t backed up your wallet, your crypto is lost. Regular backups and multiple storage locations for your seed phrase are crucial.
Best Practices for Securing Cryptocurrency Wallets
Understanding the threats is only half the battle. Proactive measures are equally important. The following practices represent a comprehensive approach to protecting your digital assets.
- Use strong, unique passwords for each cryptocurrency exchange and wallet.
- Enable two-factor authentication (2FA) on all accounts.
- Regularly update your antivirus software and operating system.
- Be wary of suspicious emails, links, and attachments.
- Only download software from official sources.
- Store your seed phrase offline in a secure location.
- Consider using a hardware wallet for enhanced security.
- Diversify your holdings across multiple wallets and exchanges.
- Regularly back up your wallets and seed phrases.
- Stay informed about the latest security threats and best practices.
Examples of Successful Mitigation Strategies
Many cryptocurrency wallet providers employ robust security measures, including multi-signature transactions, which require multiple approvals before a transaction is executed. Others utilize advanced encryption techniques to protect user data, even in the event of a data breach. Cold storage solutions, where private keys are stored offline, represent another successful mitigation strategy employed by many exchanges and custodians. These measures significantly reduce the risk of unauthorized access and theft.
The Future of Blockchain in Wallet Security
The security of cryptocurrency wallets, intrinsically linked to the security of the underlying blockchain, is constantly evolving. As blockchain technology matures and new threats emerge, innovative solutions are developed to bolster its defenses. The next decade promises significant advancements, driven by both technological progress and the ever-increasing value of digital assets. This section explores the emerging trends shaping the future of blockchain-based wallet security.
Emerging Technologies Enhancing Wallet Security
Several emerging technologies are poised to significantly enhance the security of cryptocurrency wallets. These advancements go beyond traditional cryptographic methods, incorporating biometrics, hardware security modules (HSMs), and multi-factor authentication (MFA) systems to create more robust and resilient security architectures. For instance, the integration of advanced biometric authentication, such as fingerprint or iris scanning, adds an extra layer of protection beyond passwords and PINs. Furthermore, the use of HSMs, specialized hardware devices designed to protect cryptographic keys, offers a highly secure environment for managing private keys, reducing the risk of theft or compromise. The widespread adoption of MFA protocols further strengthens security by requiring multiple forms of verification before granting access to a wallet.
Quantum Computing’s Impact on Blockchain Security
The advent of quantum computing presents both a challenge and an opportunity for blockchain-based wallet security. Quantum computers, with their immense processing power, possess the theoretical ability to break widely used cryptographic algorithms like RSA and ECC, currently forming the backbone of many blockchain networks. This potential threat necessitates the development of quantum-resistant cryptographic techniques, also known as post-quantum cryptography (PQC). Research into PQC algorithms, such as lattice-based cryptography, code-based cryptography, and multivariate cryptography, is actively underway. The transition to PQC will be a gradual process, requiring careful planning and coordination across the blockchain ecosystem to ensure a smooth and secure migration. The timeline for widespread adoption of PQC is uncertain, but leading experts suggest it could take a decade or more. The implementation of PQC will be a critical step in future-proofing blockchain wallet security against the potential threat of quantum computers.
Innovative Solutions for Improved Wallet Security
The quest for enhanced wallet security is driving the development of numerous innovative solutions. One example is the use of threshold cryptography, where a private key is split into multiple shares, distributed among different devices or individuals. This approach ensures that no single point of failure can compromise the entire key. Another promising area is the development of self-custody wallets with advanced security features, such as hardware-based security elements and tamper-evident designs. These wallets minimize the reliance on third-party custodians, giving users greater control and security over their funds. Furthermore, the integration of blockchain analytics and machine learning algorithms is showing promise in detecting and preventing fraudulent transactions and suspicious activities. These solutions leverage the vast amounts of data available on the blockchain to identify patterns and anomalies that might indicate malicious behavior.
Anticipated Evolution of Wallet Security Measures
Over the next 5-10 years, we can anticipate a significant evolution in wallet security measures. The adoption of quantum-resistant cryptography will be a pivotal development, ensuring the long-term security of blockchain networks against future quantum computing threats. We can also expect to see increased integration of biometric authentication, HSMs, and advanced MFA systems, creating more robust and user-friendly security protocols. Furthermore, the development and deployment of more sophisticated security auditing tools will enhance the detection and prevention of vulnerabilities. The growing use of decentralized identity systems, which leverage blockchain technology to manage digital identities securely, will also play a significant role in improving wallet security by enabling more secure and verifiable authentication processes. Ultimately, the future of blockchain wallet security will be characterized by a layered approach, combining multiple security mechanisms to create a highly resilient and secure ecosystem for managing digital assets.
Last Recap
Source: 101blockchains.com
So, there you have it – a peek into the fascinating world of blockchain and crypto wallet security. While the tech is constantly evolving, understanding the fundamentals empowers you to make informed decisions about protecting your digital assets. Remember, staying informed is your best defense against the ever-present threats in the crypto landscape. Stay safe, stay savvy, and keep those crypto coins secure!
