The Role of Blockchain in Digital Copyright Protection sets the stage for a fascinating exploration of how this revolutionary technology is reshaping the landscape of intellectual property rights. Forget outdated systems riddled with loopholes; blockchain’s decentralized, immutable nature offers a fresh, powerful solution to the age-old problem of digital copyright infringement. We’ll dive into the core concepts, examine real-world applications, and uncover the potential—and the pitfalls—of this game-changing approach.
From understanding the fundamental principles of digital copyright and its inherent challenges in the digital age to exploring the intricacies of blockchain technology, we’ll navigate the complexities of this evolving field. We’ll unpack how blockchain’s features like decentralization, immutability, and transparency can be leveraged to create a more secure and efficient system for registering, verifying, and managing digital copyrights. We’ll also examine the role of smart contracts in automating licensing and royalty payments, transforming the way artists and creators interact with their work in the digital realm.
Introduction to Digital Copyright and its Challenges
Digital copyright, in its essence, grants creators exclusive rights over their original works in digital form. This includes the right to reproduce, distribute, display, perform, and create derivative works. Think of it as the same principles of traditional copyright, but applied to the ever-evolving landscape of the internet and digital media. However, the digital realm presents unique challenges that traditional copyright law struggles to address effectively.
Digital copyright’s core principle is to protect the intellectual property rights of creators in the digital space, ensuring they receive due credit and compensation for their work. This protection is crucial for fostering innovation and creativity. But the ease with which digital content can be copied, shared, and modified makes enforcement a significant hurdle.
Challenges in Enforcing Digital Copyright
The decentralized and borderless nature of the internet makes tracking and preventing copyright infringement incredibly difficult. The sheer volume of content uploaded and shared daily overwhelms traditional enforcement mechanisms. Moreover, the rapid evolution of technology, with new platforms and file-sharing methods constantly emerging, presents a moving target for copyright holders. Jurisdictional issues further complicate matters, as infringing activities may originate from different countries with varying legal frameworks. The anonymity offered by the internet also makes identifying and pursuing infringers a complex process. Consider the challenges faced by a musician whose song is illegally uploaded to a multitude of platforms across different countries – tracing and taking down each instance requires significant resources and expertise.
Examples of Copyright Infringement in the Digital Realm
Copyright infringement in the digital world manifests in various forms. Illegal downloading of music, movies, and software is a pervasive problem. The unauthorized sharing of copyrighted material through peer-to-peer networks remains common. Online platforms often struggle to effectively moderate content, leading to the proliferation of counterfeit goods, pirated software, and unauthorized copies of books and articles. Furthermore, the unauthorized use of copyrighted images or videos in social media posts, blogs, or websites is rampant. For instance, a photographer whose image is used without permission on a commercial website experiences a direct loss of potential income and a violation of their creative rights. Similarly, a writer whose work is plagiarized online suffers both financial and reputational damage.
Comparison of Traditional and Digital Copyright Protection Methods
| Method | Cost | Effectiveness | Ease of Implementation |
|---|---|---|---|
| Copyright Registration (Traditional) | Moderate (one-time fee) | Moderate (requires active enforcement) | Relatively Easy (filing with copyright office) |
| Digital Rights Management (DRM) | Variable (software licensing, implementation costs) | Variable (can be circumvented) | Moderate (requires technical expertise) |
| Watermarking | Low to Moderate (depending on sophistication) | Low to Moderate (easily removed in some cases) | Relatively Easy (software readily available) |
| Blockchain-based solutions | Variable (development and maintenance costs) | High (immutable record of ownership) | Moderate to High (requires technical expertise and infrastructure) |
Blockchain Technology Fundamentals
Blockchain technology, at its core, is a revolutionary approach to data management. Unlike traditional centralized databases controlled by a single entity, blockchain employs a decentralized, distributed ledger system. This means data isn’t stored in one place but is replicated across a network of computers, enhancing security and resilience.
This decentralized nature, coupled with the inherent immutability and transparency of blockchain, makes it a compelling solution for various applications, including digital copyright protection. Let’s delve deeper into these fundamental concepts.
Decentralization, Immutability, and Transparency
Decentralization refers to the distribution of the ledger across multiple participants, eliminating single points of failure and reducing the risk of manipulation. Immutability ensures that once data is recorded on the blockchain, it cannot be altered or deleted, providing a permanent and verifiable record. Transparency, while not necessarily revealing the identities of all participants, allows anyone to view the transaction history on the blockchain, promoting accountability and trust. This combination of characteristics makes blockchain a powerful tool for establishing provenance and ownership.
Cryptographic Hashing, The Role of Blockchain in Digital Copyright Protection
Blockchain security relies heavily on cryptographic hashing. Each block in the chain contains a cryptographic hash – a unique digital fingerprint – of the previous block’s data. This creates a chain of linked blocks, making it computationally infeasible to alter any block without affecting subsequent blocks and invalidating the entire chain. Even a small change to the data within a block will result in a completely different hash value, instantly revealing any tampering attempts. The algorithm used for hashing is typically designed to be one-way, meaning it’s easy to compute the hash from the data, but computationally impossible to reverse the process and derive the original data from the hash.
Blockchain Consensus Mechanisms
Different blockchains employ various consensus mechanisms to validate and add new blocks to the chain. Two prominent examples are Proof-of-Work (PoW) and Proof-of-Stake (PoS).
Proof-of-Work, famously used by Bitcoin, requires miners to solve complex computational puzzles to add new blocks. The first miner to solve the puzzle gets to add the block and receives a reward, incentivizing participation and security. However, PoW is energy-intensive.
Proof-of-Stake, on the other hand, is a more energy-efficient alternative. In PoS, validators are chosen based on the amount of cryptocurrency they stake, meaning those with more stake have a higher chance of validating transactions and adding blocks. This reduces the energy consumption compared to PoW, while still maintaining a high level of security. Other consensus mechanisms exist, such as Delegated Proof-of-Stake (DPoS) and Practical Byzantine Fault Tolerance (PBFT), each with its own strengths and weaknesses.
Advantages and Disadvantages of Blockchain for Copyright Protection
The use of blockchain for copyright protection offers several potential benefits, but it also presents certain challenges.
- Advantages:
- Enhanced security and immutability of copyright records.
- Improved transparency and traceability of ownership.
- Reduced reliance on centralized authorities.
- Automated royalty payments and licensing management.
- Faster and more efficient dispute resolution.
- Disadvantages:
- Scalability issues with handling large volumes of data.
- Complexity of implementation and integration with existing systems.
- Potential for high transaction fees depending on the blockchain used.
- Regulatory uncertainty and lack of legal frameworks in some jurisdictions.
- Dependence on the security of the underlying blockchain network.
Blockchain’s Application in Copyright Protection
The decentralized and immutable nature of blockchain technology offers a compelling solution to the persistent challenges of digital copyright protection. By creating a transparent and tamper-proof record of ownership, blockchain can revolutionize how we manage and enforce intellectual property rights in the digital realm. This goes beyond simply registering copyrights; it promises to streamline licensing, automate royalty payments, and offer more efficient dispute resolution mechanisms.
Blockchain for Copyright Registration and Verification
Blockchain’s inherent security and transparency make it ideal for registering and verifying digital copyrights. Instead of relying on centralized registries that are susceptible to manipulation or data loss, a blockchain-based system allows creators to record their work’s metadata—including creation date, authorship, and unique identifiers—on a distributed ledger. This creates a permanent and verifiable record, making it difficult to dispute ownership claims. Each transaction is cryptographically secured and added to the blockchain, forming an auditable trail that tracks the work’s entire lifecycle. This provides a much stronger legal foundation for copyright claims compared to traditional methods. For instance, a musician could record the metadata of their newly composed song on a blockchain, creating a verifiable timestamp and proof of ownership, even before official registration with a copyright office.
Smart Contracts for Automated Licensing and Royalty Payments
Smart contracts, self-executing contracts with the terms of the agreement directly written into code, are another powerful application of blockchain in copyright protection. These contracts can automatically manage licensing agreements, ensuring that creators receive the correct royalties whenever their work is used. For example, a smart contract could be programmed to release a specific amount of payment to the copyright holder every time their digital artwork is downloaded or used in a project, based on pre-defined terms. This eliminates the need for intermediaries, reducing administrative overhead and ensuring timely and accurate payments. This automated system promotes trust and transparency between creators and users, facilitating a more efficient and fair marketplace for digital content.
Hypothetical Blockchain-Based Copyright Management System
Imagine a system where creators upload their work’s metadata to a blockchain network. This metadata includes a unique identifier, timestamp of creation, and other relevant information. Access control is managed through smart contracts, which define the terms of use and distribution. These contracts could grant different levels of access—allowing free viewing, limited downloads, or commercial use—all automatically enforced. Data storage could be decentralized, using technologies like IPFS (InterPlanetary File System) to store the actual files, while the blockchain stores only the metadata and pointers to the file location. Dispute resolution could be facilitated through an on-chain arbitration system, where parties agree to a neutral third party to review evidence stored on the blockchain and issue a binding decision. This entire process, from registration to dispute resolution, is transparent, secure, and auditable.
Comparison of Blockchain-Based Copyright Platforms
Several platforms are emerging that leverage blockchain technology for copyright management, each with its own strengths and weaknesses. Some platforms focus on specific types of digital content, like music or artwork, while others aim for broader applicability. Features vary, including the type of blockchain used (public vs. private), the level of access control offered, and the integration with existing copyright registries. A detailed comparison would require analyzing each platform’s security features, scalability, and user-friendliness. However, the underlying principle remains consistent: using blockchain to create a more secure, transparent, and efficient system for managing and protecting digital copyrights. For example, one platform might prioritize speed and low transaction fees by using a fast blockchain, while another might prioritize data security and immutability by using a more robust, though potentially slower, blockchain.
Case Studies and Real-World Examples
Blockchain’s potential in digital copyright protection isn’t just theoretical; several real-world applications demonstrate its effectiveness and limitations. These examples highlight how blockchain technology can tackle the persistent challenges of proving ownership, tracking usage, and enforcing copyright in the digital realm. Let’s dive into some compelling case studies.
Examples of Blockchain in Copyright Protection
Several projects are actively employing blockchain technology to address digital copyright issues. These initiatives showcase diverse approaches and highlight the technology’s adaptability to various creative industries. Understanding their successes and shortcomings provides a clearer picture of blockchain’s role in the future of copyright management.
CopyrightNow
CopyrightNow is a platform leveraging blockchain to register and manage copyrights. Artists upload their work, generating a unique cryptographic hash that’s recorded on the blockchain. This creates a verifiable record of ownership and creation date, providing irrefutable proof in case of infringement. The system offers a transparent and secure method for managing copyright, eliminating the need for centralized authorities. However, CopyrightNow’s success hinges on widespread adoption within the creative community. Limited user base and the challenge of educating artists about the platform’s functionality are current limitations. The platform primarily addresses the challenge of proving ownership and establishing a verifiable timeline for creation.
Audile
Audile is a music platform using blockchain to facilitate royalty payments to artists. Each song uploaded to the platform generates a unique token representing ownership and usage rights. When a song is streamed or downloaded, the corresponding tokens are automatically distributed to the rights holders, ensuring transparent and accurate royalty payouts. This addresses the long-standing problem of fair compensation for artists in the digital music industry. However, the platform’s success depends on its ability to attract both artists and listeners, and scalability remains a challenge as the number of users and transactions increases. The primary challenge addressed here is the efficient and transparent distribution of royalties.
Binded
Binded is a platform focusing on protecting the copyright of visual assets like images and videos. It uses blockchain to record the metadata of digital assets, including creation date, ownership details, and usage licenses. This immutable record provides strong evidence of ownership and usage rights, making it easier to track and prevent infringement. The platform’s decentralized nature enhances security and transparency. However, integration with existing content management systems and the need for user education are ongoing challenges. The focus here is on creating a verifiable and secure record of ownership for visual assets, combating unauthorized use.
Summary of Case Studies
| Platform | Key Features | Benefits | Drawbacks |
|---|---|---|---|
| CopyrightNow | Blockchain-based copyright registration, cryptographic hashing | Immutable proof of ownership, transparent record | Limited user base, need for wider adoption |
| Audile | Tokenized music ownership, automated royalty distribution | Transparent royalty payments, fair compensation for artists | Scalability challenges, user acquisition |
| Binded | Blockchain-based metadata recording for visual assets | Secure and verifiable ownership records, simplified infringement tracking | Integration challenges, user education |
Security and Scalability Considerations: The Role Of Blockchain In Digital Copyright Protection
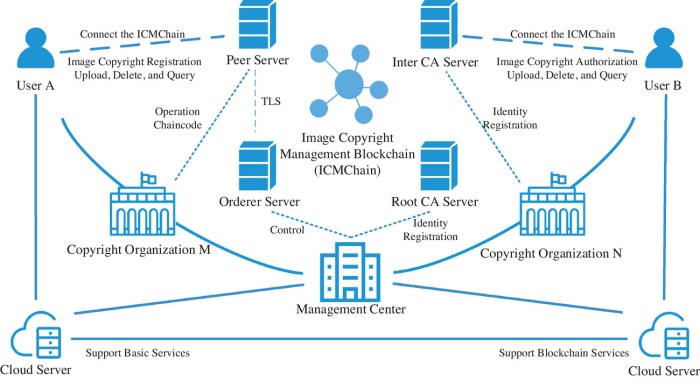
Source: wiley.com
Blockchain’s secure ledger is revolutionizing digital copyright, offering artists verifiable proof of ownership. This contrasts sharply with the ease of digital piracy, but innovative tech like AR is changing the game. Check out how augmented reality is improving customer engagement in retail here , a model that could inspire new ways to showcase and protect digital art, potentially leading to more robust blockchain-based copyright solutions.
Blockchain’s promise in digital copyright protection is undeniably exciting, but its practical implementation faces significant hurdles. While offering a decentralized and tamper-proof system, the technology isn’t without its vulnerabilities and limitations, particularly concerning security and scalability. Understanding these challenges is crucial for realizing the full potential of blockchain in this domain.
The inherent security of blockchain, relying on cryptographic hashing and distributed consensus mechanisms, makes it incredibly resistant to unauthorized alterations. However, this doesn’t render it completely invulnerable. Smart contract vulnerabilities, for example, could be exploited to manipulate copyright registrations or transfer rights illegally. Furthermore, the security of the nodes themselves – the computers maintaining the blockchain – is paramount. A compromised node could potentially introduce malicious data or disrupt the network’s operation. The reliance on public keys for authentication also introduces risks associated with key management and potential phishing attacks.
Security Implications of Blockchain in Copyright Protection
Blockchain’s decentralized nature, while a strength, also presents challenges. The very distributed nature that makes it resistant to single points of failure can also complicate security audits and vulnerability assessments. Unlike centralized systems, there’s no single entity responsible for overall security. Moreover, the complexity of smart contracts, often written in specialized programming languages, introduces the risk of coding errors that malicious actors could exploit. Finally, the sheer volume of data involved in managing global copyright information necessitates robust security protocols to prevent data breaches and ensure the integrity of the entire system. Effective security measures, such as multi-signature transactions, regular security audits of smart contracts, and robust key management practices, are crucial to mitigate these risks.
Scalability Challenges of Blockchain in Copyright Protection
The current limitations in blockchain scalability pose a significant challenge to its widespread adoption in copyright management. Many existing blockchains, particularly those using Proof-of-Work consensus mechanisms, struggle to handle the high transaction throughput required for a global copyright registration system. Each transaction, representing a copyright registration or transfer, adds to the blockchain’s size, increasing storage requirements and slowing down processing times. This can lead to high transaction fees and long processing delays, rendering the system impractical for large-scale applications. For instance, registering millions of copyright claims daily would severely strain the capacity of many current blockchain platforms.
Potential Solutions to Improve Security and Scalability
Addressing the security and scalability concerns requires a multi-pronged approach. Improved smart contract security practices, including formal verification methods and rigorous testing, are crucial. Employing more secure key management systems, such as hardware security modules (HSMs), can reduce the risk of key compromises. On the scalability front, layer-2 scaling solutions, such as state channels and sidechains, offer promising avenues for increasing transaction throughput without sacrificing security. Sharding, a technique that divides the blockchain into smaller, more manageable parts, can also enhance scalability. Furthermore, exploring alternative consensus mechanisms, such as Proof-of-Stake, which generally offer higher transaction speeds and lower energy consumption than Proof-of-Work, could significantly improve performance. The adoption of more efficient data structures and optimized database technologies also play a crucial role in managing the vast amounts of copyright data.
Potential Future Improvements and Innovations
Several avenues for future development hold the potential to transform blockchain-based copyright systems:
- Development of more robust and secure smart contracts: Utilizing formal verification techniques and incorporating advanced security features to prevent vulnerabilities.
- Wider adoption of layer-2 scaling solutions: State channels and sidechains can significantly increase transaction throughput and reduce latency.
- Integration with other technologies: Combining blockchain with AI and machine learning for automated copyright claim verification and infringement detection.
- Improved interoperability between different blockchain platforms: Enabling seamless data exchange and cross-chain transactions.
- Development of decentralized identity systems: Providing secure and verifiable digital identities for copyright holders and users.
- Enhanced data privacy features: Implementing privacy-preserving technologies to protect sensitive copyright information.
Legal and Ethical Implications
The integration of blockchain into copyright protection presents a fascinating legal and ethical landscape, riddled with both exciting possibilities and significant hurdles. While offering a potentially revolutionary solution to long-standing copyright infringement issues, its implementation necessitates careful consideration of existing legal frameworks and the ethical implications for creators, consumers, and the broader digital ecosystem. The path forward requires navigating a complex web of legal interpretations and societal values.
The legal frameworks surrounding blockchain-based copyright protection are still evolving. Many jurisdictions lack specific legislation addressing the unique aspects of blockchain’s application in this context. Existing copyright laws, designed for a pre-digital era, may struggle to fully encompass the decentralized and immutable nature of blockchain technology. This creates uncertainty for both rights holders and users, potentially hindering wider adoption. The legal validity of blockchain-recorded copyrights, their admissibility as evidence in court, and the enforcement mechanisms needed to protect them remain key areas of ongoing debate and development.
Legal Frameworks and Regulations
Current copyright laws primarily focus on centralized systems for registration and enforcement. Blockchain, however, introduces a decentralized approach, challenging established legal norms. Questions arise concerning the recognition of blockchain-based copyright registrations by courts, the enforceability of smart contracts governing copyright usage, and the jurisdictional issues related to cross-border copyright disputes involving blockchain-based systems. Harmonization of international legal frameworks will be crucial to facilitate global adoption and prevent legal loopholes. For example, the EU’s Copyright Directive has attempted to address certain aspects of online copyright, but the specific application to blockchain technologies remains largely uncharted territory. The US Copyright Office, while showing some interest in blockchain technology, has yet to fully integrate it into its registration processes. This lack of clear legal guidelines creates uncertainty for creators who wish to leverage blockchain for copyright protection.
Data Privacy and Access Control
Blockchain’s inherent transparency, while beneficial for verifying ownership, raises significant data privacy concerns. Public blockchains record all transactions, potentially exposing sensitive information about copyrighted works and their creators. This conflicts with existing data protection regulations like GDPR (General Data Protection Regulation) and CCPA (California Consumer Privacy Act), which emphasize individual control over personal data. Solutions like private or permissioned blockchains, or the use of zero-knowledge proofs, could mitigate these concerns, but they also introduce complexities in terms of implementation and scalability. Balancing transparency with privacy is a critical ethical challenge. For instance, a blockchain system could record ownership and usage rights without publicly disclosing the creator’s identity or the specific content of the copyrighted work.
Legal Challenges and Obstacles
One major challenge is the potential for misuse of blockchain technology for copyright infringement. The immutability of blockchain doesn’t inherently prevent illegal copying or distribution; it simply provides a more transparent record of ownership. Furthermore, the technical complexity of blockchain technology may create a barrier to entry for smaller creators, potentially exacerbating existing inequalities in the creative industry. The cost of implementing and maintaining blockchain-based copyright systems could also be prohibitive for many artists. Addressing these issues requires not only technological solutions but also educational initiatives to empower creators with the knowledge and resources to utilize blockchain effectively.
Impact on Artists and Creators
Blockchain offers artists the potential for greater control over their work and its distribution. It could facilitate direct-to-consumer sales, eliminating intermediaries and enabling artists to retain a larger share of the revenue. The transparent record of ownership could simplify licensing agreements and prevent unauthorized use. However, the transition to a blockchain-based system may also present challenges. Artists need to understand the technical aspects of blockchain and its implications for their work. The initial investment in setting up blockchain-based systems could be significant. Furthermore, the legal uncertainties surrounding blockchain-based copyright protection may create hesitation among artists. Successfully integrating blockchain requires not only technological development but also comprehensive support and education for the creative community.
Future Trends and Developments
The intersection of blockchain and digital copyright is still in its nascent stages, but the potential for disruption is immense. We’re moving beyond simple proof-of-ownership models towards a more sophisticated and integrated system that fundamentally reshapes how creative works are managed and monetized. Expect rapid advancements fueled by both technological innovations and evolving legal frameworks.
The future of blockchain in digital copyright protection hinges on addressing current limitations and capitalizing on emerging technologies. This will lead to more robust, efficient, and user-friendly systems for creators and consumers alike. The creative industries themselves will be transformed, fostering new business models and empowering artists in unprecedented ways.
Interoperability and Standardization
The current landscape of blockchain platforms is fragmented, hindering seamless data exchange between different systems. Future development will likely focus on achieving greater interoperability through the development of standardized protocols and APIs. This will allow different blockchain networks to communicate and share information effectively, creating a more unified and efficient ecosystem for copyright management. Imagine a future where a creator registers their work on one blockchain and it’s instantly recognized and validated across multiple platforms, simplifying licensing and royalty distribution.
Artificial Intelligence and Machine Learning Integration
AI and machine learning (ML) can significantly enhance the efficiency and accuracy of blockchain-based copyright systems. AI algorithms can automate tasks like copyright registration, infringement detection, and royalty calculations, reducing the need for manual intervention and minimizing human error. ML models can learn to identify patterns of infringement and predict potential risks, enabling proactive measures to protect intellectual property. For example, an AI-powered system could analyze large datasets of digital content to identify instances of copyright infringement with greater speed and accuracy than human review.
Decentralized Autonomous Organizations (DAOs) for Copyright Management
DAOs offer a promising approach to managing copyright collaboratively and transparently. These self-governing organizations, powered by smart contracts, can automate processes like royalty distribution, dispute resolution, and community governance. This empowers creators to establish their own terms and conditions, fostering a more equitable and democratic environment for copyright management. A DAO could, for example, manage the collective rights of a group of artists, ensuring fair compensation and transparent accounting for their works.
Enhanced Security Measures
As blockchain technology matures, so will its security measures. We can anticipate the development of more robust cryptographic techniques and consensus mechanisms to protect against attacks and ensure the integrity of copyright records. Quantum-resistant cryptography, for example, is being developed to safeguard against the potential threat of quantum computing to existing cryptographic systems.
Impact on Creative Industries
The widespread adoption of blockchain in copyright protection will profoundly impact creative industries. It will empower creators by giving them greater control over their works, simplifying licensing and distribution, and enabling more efficient royalty collection. New business models will emerge, facilitating direct-to-consumer sales and fostering more transparent and equitable relationships between creators and consumers. The music industry, for instance, could see a significant shift towards decentralized platforms that empower artists to directly monetize their work and bypass traditional intermediaries.
Future Landscape Visualization
Imagine a vibrant, interconnected network. This network represents the future of digital copyright, a landscape where diverse blockchain platforms seamlessly interact, sharing verified copyright information. Creators are empowered with user-friendly interfaces, effortlessly registering their works and managing their rights. AI-powered systems act as vigilant guardians, automatically detecting infringements and facilitating swift resolution. DAOs empower communities of creators to collectively manage their rights, fostering collaboration and fair compensation. The entire ecosystem thrives on transparency, security, and efficiency, transforming the way creative works are valued and protected. This visualization represents a future where technology empowers creativity and ensures fair compensation for artists.
Closing Notes
Ultimately, the role of blockchain in digital copyright protection is poised to revolutionize how we safeguard creative works in the digital age. While challenges remain in terms of scalability and legal frameworks, the potential benefits – increased security, transparency, and efficiency – are undeniable. As blockchain technology matures and legal landscapes adapt, we can expect to see even more innovative solutions emerge, empowering creators and fostering a fairer, more sustainable digital ecosystem for intellectual property.
