The Role of Blockchain in Decentralizing Healthcare Data Management – Blockchain: Decentralizing Healthcare Data Management. Sounds futuristic, right? But it’s not science fiction; it’s the potential key to unlocking a more secure, efficient, and patient-centric healthcare system. Imagine a world where your medical records are entirely under your control, instantly shareable with doctors of your choosing, and protected from breaches by unbreakable encryption. That’s the promise of blockchain technology applied to healthcare data, and we’re diving deep into how it works.
This isn’t just about fancy tech; it’s about tackling some serious issues plaguing current healthcare systems. Think data silos, privacy concerns, and the frustrating inefficiencies that slow down diagnosis and treatment. Blockchain offers a potential solution by creating a decentralized, transparent, and tamper-proof system for managing sensitive health information. We’ll explore how this revolutionary technology can revolutionize everything from data security and interoperability to patient empowerment and automated processes.
Introduction to Decentralized Healthcare Data Management: The Role Of Blockchain In Decentralizing Healthcare Data Management
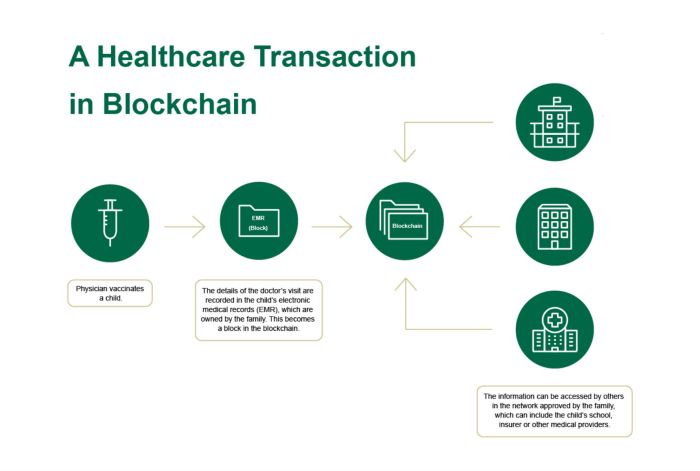
Source: usfhealthonline.com
The healthcare industry, while striving for progress, is bogged down by a surprisingly archaic system for managing patient data. Centralized databases, while seemingly efficient, create significant vulnerabilities and inefficiencies. The potential for data breaches, the difficulties in sharing information between providers, and the lack of patient control over their own medical records are just some of the challenges fueling the need for a revolutionary approach. Decentralized healthcare data management, leveraging the power of blockchain technology, offers a promising solution to these long-standing issues.
Centralized healthcare data management faces several key challenges. Data silos, where different healthcare organizations maintain separate and incompatible systems, hinder seamless information exchange. This fragmentation leads to duplicated efforts, potential for medical errors due to incomplete information, and significant administrative overhead. Furthermore, the centralized nature of these systems makes them prime targets for cyberattacks, with the potential for massive data breaches exposing sensitive patient information. The lack of patient control over their own data is another major concern, limiting their ability to manage and share their medical history effectively.
Decentralizing healthcare data offers numerous potential benefits. By distributing data across a network rather than concentrating it in a single location, the risk of large-scale data breaches is significantly reduced. Blockchain’s inherent security features enhance data integrity and prevent unauthorized alterations. Improved interoperability between different healthcare systems becomes possible, facilitating seamless information sharing and enhancing the quality of care. Moreover, patients gain greater control over their medical records, allowing them to selectively share their data with chosen healthcare providers and researchers while maintaining privacy. This empowers individuals and fosters trust in the healthcare system.
Blockchain technology, at its core, is a distributed, immutable ledger. This means that transactions (in this case, updates to patient records) are recorded across multiple computers in a network, making it incredibly difficult to alter or delete information without detection. Key principles relevant to healthcare include its transparency (all participants can view the transactions, provided they have the necessary access rights), its immutability (once recorded, data cannot be easily altered), and its security (cryptographic techniques ensure data integrity and prevent unauthorized access). These features make blockchain ideally suited for managing sensitive healthcare data, offering a level of security and transparency unmatched by traditional centralized systems.
Challenges of Centralized Healthcare Data Management
Centralized systems are vulnerable to single points of failure. A cyberattack or system malfunction can compromise the entire database, leading to significant disruptions and potential data loss. The lack of standardization across different healthcare organizations creates significant interoperability challenges, hindering seamless data exchange and potentially impacting patient care. Furthermore, stringent regulations surrounding patient data privacy (like HIPAA in the US and GDPR in Europe) are difficult to consistently enforce across centralized systems, increasing the risk of non-compliance and penalties. The concentration of sensitive data in a single location also makes it a lucrative target for malicious actors seeking to exploit vulnerabilities for financial gain or other nefarious purposes. Examples of large-scale data breaches in healthcare have resulted in significant financial losses, reputational damage, and erosion of patient trust.
Benefits of Decentralized Healthcare Data Management using Blockchain
The enhanced security offered by blockchain significantly reduces the risk of data breaches and unauthorized access. The distributed nature of the system means that even if one part of the network is compromised, the remaining data remains secure. Improved interoperability facilitates seamless information sharing between healthcare providers, leading to better coordinated care and reduced medical errors. Patients gain greater control over their own data, allowing them to selectively share information with providers and researchers while maintaining privacy and ownership. This increased transparency and patient agency can foster greater trust and engagement within the healthcare ecosystem. The immutability of blockchain ensures the integrity of medical records, preventing tampering and ensuring accurate and reliable information is available when needed. This is particularly crucial in areas like clinical trials and research, where data integrity is paramount.
Blockchain’s Role in Data Security and Privacy
Blockchain technology offers a revolutionary approach to healthcare data management, significantly enhancing security and privacy compared to traditional methods. Its inherent features, such as cryptographic hashing and decentralized architecture, create a robust system resistant to unauthorized access and data breaches. This shift towards greater security and privacy is crucial in an era of increasing cyber threats and stringent data protection regulations.
The cryptographic foundation of blockchain is what truly sets it apart. Each block in the chain contains a cryptographic hash of the previous block, creating an immutable record. Altering even a single piece of data would change the hash, making the alteration immediately detectable. This ensures data integrity and prevents tampering. Furthermore, the use of public and private key cryptography allows for secure access control, ensuring only authorized individuals can view and modify patient data.
Blockchain’s Cryptographic Enhancements to Data Security
Blockchain employs several cryptographic techniques to bolster data security. These include cryptographic hashing, which creates a unique fingerprint for each data block, making any alteration immediately apparent. Digital signatures, using public and private key pairs, authenticate the origin and integrity of data, preventing forgery and ensuring non-repudiation. These cryptographic methods collectively create a highly secure and transparent system, minimizing the risk of unauthorized access or data manipulation. For instance, a hospital using a blockchain system could securely store patient records, knowing that any attempt to alter a diagnosis or medical history would be instantly flagged.
Blockchain and Patient Data Privacy Compliance
Blockchain’s decentralized nature contributes significantly to patient data privacy. Unlike centralized databases, which are vulnerable to single points of failure and potential breaches, blockchain distributes data across a network of computers. This makes it significantly more difficult for hackers to access all patient data at once. Furthermore, blockchain can facilitate granular access control, allowing patients to control which healthcare providers can access their data, enhancing patient autonomy and compliance with regulations like HIPAA (Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act) in the United States. For example, a patient could grant access to their medical records only to their primary care physician and oncologist, preventing other healthcare providers from viewing sensitive information without explicit permission.
Comparison of Blockchain-Based and Traditional Data Security
Traditional healthcare data security methods often rely on centralized databases protected by firewalls and access control lists. While these measures offer a degree of protection, they remain vulnerable to large-scale breaches and single points of failure. A successful attack on a centralized database could compromise the entire system, exposing sensitive patient information. In contrast, blockchain’s decentralized and cryptographic nature significantly reduces this risk. Data is distributed across multiple nodes, making it far more resilient to attacks. Moreover, the immutability of blockchain records provides an audit trail, facilitating investigations and accountability in case of security incidents. This increased security and transparency offer a significant advantage over traditional methods, especially given the growing concerns surrounding data breaches in the healthcare industry.
Data Integrity and Immutability
Source: medium.com
Imagine a world where medical records are tamper-proof, ensuring patient data remains accurate and reliable throughout a person’s life. This is the promise of blockchain technology in healthcare. Immutability, a core characteristic of blockchain, plays a crucial role in achieving this. It’s not just about security; it’s about trust – trust in the accuracy and integrity of the information upon which life-altering medical decisions are made.
Blockchain prevents unauthorized alteration of patient data by creating a permanent, auditable record of every transaction or update. Each new piece of information is added as a “block” linked cryptographically to the previous block, creating an unbroken chain. Any attempt to alter a previous block would require altering all subsequent blocks, a computationally infeasible task given the cryptographic strength of the blockchain. This inherent resistance to tampering is what makes blockchain so powerful in maintaining data integrity.
Blockchain’s Mechanism for Maintaining Data Integrity
The process of ensuring data integrity using blockchain involves several key steps. First, new data, such as a doctor’s note or test result, is encrypted and packaged into a block. This block includes a timestamp and a cryptographic hash of the previous block. The cryptographic hash acts as a unique fingerprint of the data; even a tiny change in the data will result in a completely different hash. This new block is then broadcast to the network of participating nodes. These nodes verify the block’s validity and add it to the chain through a consensus mechanism, like Proof-of-Work or Proof-of-Stake. Once added, the block becomes part of the permanent, immutable record. This decentralized and transparent process makes it virtually impossible for a single entity to manipulate the data without detection.
Illustrative Scenario: Tracking a Patient’s Allergy History
Let’s consider a patient, Sarah, with a known penicillin allergy. This information is recorded on a blockchain-based healthcare system. Initially, Sarah’s allergy is recorded as a block, with a timestamp and cryptographic hash. Later, during a routine checkup, a new block is added containing details of the appointment and reaffirming the penicillin allergy. If, hypothetically, a malicious actor attempts to remove or alter the allergy information from an earlier block, it would be immediately detectable. The new hash wouldn’t match the previous block’s hash, invalidating the attempted alteration. The system would alert relevant parties to the attempted tampering, maintaining the integrity of Sarah’s medical record and preventing potentially life-threatening errors. This transparent and auditable history provides a high degree of confidence in the accuracy of Sarah’s allergy information, improving the safety and efficacy of her healthcare.
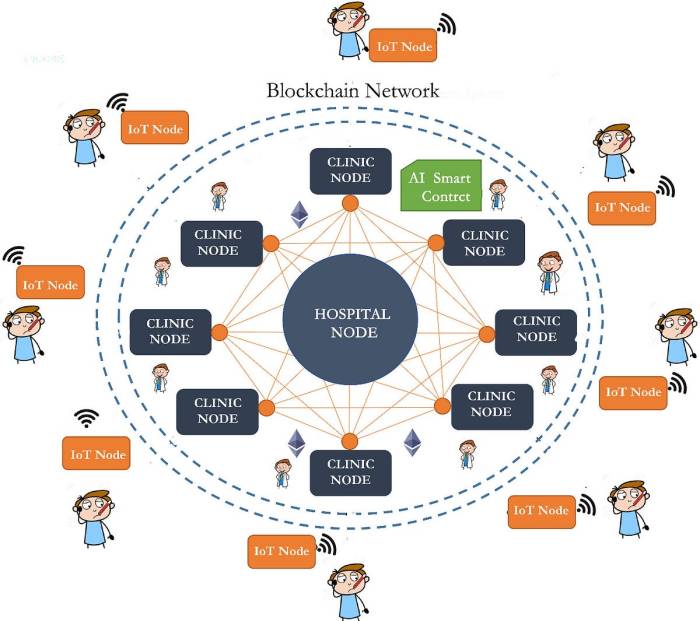
Interoperability and Data Sharing

Source: statezerolabs.com
Blockchain’s secure, decentralized nature is revolutionizing healthcare data management, offering patients greater control over their information. This echoes the potential of AI in personalized education, as seen in the transformative impact described in The Role of AI in Personalized Learning for Students with Special Needs , where tailored learning pathways improve outcomes. Similarly, blockchain’s potential to improve healthcare accessibility and data privacy is undeniable, creating a future where individuals are empowered.
Healthcare data is notoriously siloed. Imagine trying to assemble a jigsaw puzzle where crucial pieces are scattered across different hospitals, clinics, and labs, each using incompatible systems. That’s the reality of interoperability challenges in healthcare. The lack of standardized data formats and communication protocols creates significant hurdles in sharing patient information effectively, leading to delays in treatment, duplicated tests, and increased healthcare costs.
Blockchain technology offers a potential solution to this fragmented landscape. By providing a secure and transparent platform for data exchange, blockchain can facilitate seamless data sharing among different healthcare providers. This is achieved through the creation of a shared, immutable ledger that allows authorized parties to access and update patient records without compromising data integrity or privacy.
Blockchain-Facilitated Seamless Data Sharing
Blockchain’s decentralized nature eliminates the need for a central authority to control data access. Instead, data is distributed across a network of nodes, each holding a copy of the ledger. This decentralized architecture enhances security and reduces the risk of data breaches or single points of failure. Furthermore, smart contracts, self-executing contracts with the terms of the agreement between buyer and seller being directly written into lines of code, can automate data sharing processes, ensuring that only authorized parties can access specific information based on predefined rules. For instance, a smart contract could be programmed to automatically share a patient’s lab results with their physician upon completion of the test. This automated process streamlines workflows and reduces the administrative burden on healthcare professionals. Consider a scenario where a patient visits multiple specialists. With a blockchain-based system, each specialist can access the relevant portions of the patient’s medical history without needing to request permission from other providers or rely on potentially unreliable data exchange methods. This improves the quality of care by providing a complete and accurate picture of the patient’s health.
Hypothetical System Architecture for Improved Interoperability
A blockchain-based healthcare data management system could be structured as follows:
| Component | Description | Interaction | Benefits |
|---|---|---|---|
| Patient | The individual whose health data is stored on the blockchain. | Grants access to their data via cryptographic keys; verifies data accuracy. | Enhanced control and privacy over personal health information. |
| Healthcare Provider (Hospital, Clinic, Lab) | Organizations that collect, store, and share patient data. | Uploads and updates patient data; accesses authorized data using smart contracts. | Improved data access and collaboration; reduced administrative overhead. |
| Blockchain Network | A distributed ledger storing encrypted patient data. | Facilitates secure and transparent data sharing; maintains data integrity and immutability. | Enhanced security, transparency, and trust in data exchange. |
| Smart Contracts | Automated agreements governing data access and sharing rules. | Automates data exchange processes; ensures compliance with data privacy regulations. | Streamlined workflows; reduced errors and delays. |
Smart Contracts and Automated Processes
Imagine a healthcare system where paperwork is minimized, transactions are transparent, and processes run smoothly like clockwork. That’s the promise of smart contracts integrated with blockchain technology in healthcare data management. Smart contracts are self-executing contracts with the terms of the agreement between buyer and seller being directly written into lines of code. This automation drastically reduces the need for intermediaries and streamlines various healthcare processes.
Smart contracts leverage the inherent security and transparency of blockchain to automate tasks, ensuring accuracy and efficiency. They operate based on pre-defined conditions, eliminating delays and human error commonly associated with traditional methods. This automated execution not only speeds up processes but also enhances trust and accountability throughout the system.
Claims Processing Automation
Smart contracts can revolutionize claims processing by automating the verification of patient eligibility, procedure codes, and billing information. Once a claim is submitted, the smart contract automatically verifies the data against the patient’s insurance policy and the provider’s credentials stored on the blockchain. If everything matches, the payment is automatically released to the provider. This eliminates the lengthy delays and administrative burden associated with manual claims processing, leading to faster reimbursements for providers and improved cash flow for healthcare organizations. For example, a system could be programmed to automatically reject a claim if the procedure code doesn’t match the patient’s diagnosis, flagging it for manual review and preventing fraudulent claims. This automated verification not only speeds up processing but also reduces the risk of errors and fraud.
Drug Supply Chain Management Optimization, The Role of Blockchain in Decentralizing Healthcare Data Management
The pharmaceutical supply chain is complex and vulnerable to counterfeiting. Smart contracts can enhance traceability and security by recording every step of a drug’s journey, from manufacturing to dispensing. Each transaction, including manufacturing date, batch number, and location, is recorded on the blockchain, creating an immutable audit trail. This allows healthcare providers and patients to verify the authenticity of drugs, reducing the risk of counterfeit medications entering the market. For instance, a smart contract could be triggered to automatically alert relevant authorities if a drug’s temperature exceeds a certain threshold during transportation, indicating potential spoilage or compromise. This level of transparency and control significantly improves patient safety and public health.
Benefits and Risks of Smart Contracts in Healthcare
The benefits of using smart contracts in healthcare are substantial, including increased efficiency, reduced costs, enhanced security, and improved transparency. However, there are also potential risks to consider. Legal and regulatory frameworks are still evolving, and the lack of clear legal precedents regarding smart contract disputes could pose challenges. Furthermore, the technical complexity of implementing and maintaining smart contracts requires specialized expertise and robust infrastructure. Security vulnerabilities, while mitigated by blockchain’s inherent security, still need to be carefully addressed to prevent malicious attacks. Finally, ensuring data privacy and compliance with regulations like HIPAA remains crucial. Careful planning and robust security measures are vital to mitigate these risks and harness the full potential of smart contracts in the healthcare sector.
Data Access and Patient Control
Imagine a world where you, the patient, are the ultimate custodian of your health information. No more worrying about data breaches or unauthorized access – you’re in complete control. Blockchain technology makes this vision a reality, empowering individuals to manage their medical data with unprecedented autonomy and security.
Blockchain empowers patients with greater control over their own health data by placing them at the center of the data ecosystem. Instead of their information being scattered across various healthcare providers, often with limited access or oversight, a blockchain-based system allows patients to securely store their data and selectively share it with authorized individuals or institutions. This granular control enhances privacy and fosters trust in the healthcare system.
Patient Data Access Mechanisms
The ability to grant or revoke access is facilitated through cryptographic keys and smart contracts. Patients hold the private key to their data, akin to a digital password. They can use this key to generate a unique access token for each healthcare provider or application they wish to share their data with. This token grants temporary or permanent access, depending on the patient’s configuration. If access needs to be revoked, the patient simply invalidates the token, effectively cutting off access without affecting the integrity of the data itself. This fine-grained control provides a level of security and privacy that traditional systems struggle to match. For instance, a patient might grant a specialist access to their allergy information for a specific consultation but revoke that access afterward.
A Patient’s Journey Managing Data on a Blockchain-Based System
Let’s follow a hypothetical patient, Sarah, as she navigates her health data on a blockchain platform.
- Data Onboarding: Sarah creates a secure digital wallet, akin to a personal health record vault, using a unique private key. She then uploads her medical records, securely encrypted, onto the blockchain.
- Access Control: Sarah needs to share her latest blood test results with her general practitioner, Dr. Lee. She uses her private key to generate a temporary access token granting Dr. Lee read-only access to the specified data. This token is securely transmitted to Dr. Lee.
- Data Sharing: Dr. Lee uses the token to access Sarah’s blood test results on the blockchain. The system verifies the token’s validity and grants access. Dr. Lee cannot download or modify the data; he can only view it.
- Access Revocation: After the consultation, Sarah decides to revoke Dr. Lee’s access. She simply invalidates the token, rendering it useless. Dr. Lee can no longer access Sarah’s data.
- Data Updates: Sarah receives new test results from a specialist. She updates her record in her digital wallet, automatically updating the blockchain with the new information. This ensures all her records are consistently up-to-date.
This step-by-step illustration showcases the ease and security with which patients can manage their health data on a blockchain platform, highlighting the shift from passive data subjects to active data controllers. Sarah retains complete control and transparency over her medical information throughout the entire process.
Challenges and Limitations of Blockchain in Healthcare
While blockchain technology holds immense promise for revolutionizing healthcare data management, its implementation isn’t without significant hurdles. Several challenges related to scalability, cost, regulatory compliance, and technical vulnerabilities need careful consideration before widespread adoption can be achieved. Overcoming these obstacles is crucial for realizing the full potential of blockchain in the healthcare sector.
Scalability, Cost, and Regulatory Compliance Issues represent a significant hurdle for widespread blockchain adoption in healthcare. The inherent complexity of blockchain technology, coupled with the massive volume of healthcare data, necessitates robust and efficient solutions to ensure smooth operation.
Scalability Issues in Blockchain Healthcare Systems
Blockchain’s scalability remains a key concern. Processing large volumes of healthcare data, especially in a decentralized network, can lead to slow transaction speeds and high latency. Current blockchain architectures, like the widely used Proof-of-Work consensus mechanism, struggle to handle the sheer amount of data generated by a global healthcare system. Solutions like sharding (partitioning the blockchain into smaller, more manageable parts) and improved consensus mechanisms are being explored to address this challenge, but they require significant technological advancements and may introduce new complexities. For example, a large hospital system attempting to record every patient interaction on a single blockchain would quickly encounter significant performance bottlenecks.
Cost Considerations of Implementing Blockchain in Healthcare
The cost of implementing and maintaining blockchain-based healthcare systems can be substantial. This includes the expenses associated with developing and deploying blockchain infrastructure, integrating with existing healthcare systems, and ensuring ongoing security and maintenance. The initial investment can be a significant barrier to entry, particularly for smaller healthcare providers or organizations with limited budgets. For instance, the cost of specialized hardware and software, coupled with the need for skilled blockchain developers, can be prohibitive for many. Furthermore, the ongoing costs of network maintenance and upgrades can be substantial, adding to the financial burden.
Regulatory Compliance and Blockchain Technology
Navigating the complex regulatory landscape surrounding healthcare data is another significant challenge. Blockchain systems must comply with various regulations, including HIPAA in the United States, GDPR in Europe, and other country-specific data privacy laws. Ensuring compliance requires careful design and implementation of blockchain solutions to meet stringent data protection and security requirements. The lack of clear regulatory frameworks for blockchain technology in healthcare adds to the complexity and uncertainty. For example, the process of obtaining necessary approvals and certifications can be lengthy and expensive, potentially delaying or hindering the deployment of blockchain solutions.
Standardization and Interoperability in Blockchain Healthcare Systems
Lack of standardization and interoperability is a major obstacle to seamless data exchange between different healthcare systems using blockchain technology. Different blockchain platforms may employ varying data formats and communication protocols, making it difficult for them to interact effectively. Establishing common standards and protocols is crucial for ensuring interoperability and enabling data sharing across diverse healthcare ecosystems. Without such standards, different hospitals or clinics may find their blockchain systems incompatible, hindering efficient data exchange and collaboration. This necessitates collaborative efforts from industry stakeholders, standardization bodies, and regulatory agencies to establish universally accepted protocols.
Technical Vulnerabilities and Security Risks in Blockchain Systems
While blockchain technology is inherently secure, it’s not immune to vulnerabilities. Smart contracts, which are essential components of many blockchain-based healthcare applications, can contain bugs or flaws that can be exploited by malicious actors. Furthermore, the decentralized nature of blockchain can make it challenging to address security breaches or vulnerabilities effectively. The potential for attacks, such as 51% attacks, which involve gaining control of a majority of the network’s computing power, also needs to be considered. Robust security measures, including regular audits and penetration testing, are crucial to mitigate these risks and protect sensitive patient data. Moreover, educating healthcare professionals about potential security threats and best practices is essential to enhance the overall security posture of blockchain-based healthcare systems.
Future Trends and Applications
Blockchain’s potential in healthcare extends far beyond current applications. Its inherent security and transparency are poised to revolutionize various aspects of the medical landscape, creating a more efficient, equitable, and patient-centric system. The future holds exciting possibilities for how this technology can reshape healthcare as we know it.
The decentralized nature of blockchain offers a unique opportunity to address long-standing challenges in healthcare, particularly in data management and access. This technology is not merely an incremental improvement; it’s a paradigm shift that promises to democratize healthcare data and empower both patients and providers.
Clinical Trials and Research
Blockchain can streamline clinical trials by securely storing and managing patient data, ensuring data integrity and transparency throughout the research process. Imagine a scenario where patient consent is recorded on the blockchain, instantly verifiable and auditable by all relevant parties. This eliminates the need for cumbersome paperwork and significantly reduces the risk of data breaches or manipulation. Furthermore, blockchain can facilitate the efficient sharing of research data among researchers, accelerating the pace of medical discovery and potentially leading to faster development of new treatments and cures. For instance, a pharmaceutical company could use a blockchain-based system to track the progress of a drug trial, ensuring data integrity and allowing researchers across different institutions to access and analyze the data securely.
Telehealth and Remote Patient Monitoring
The rise of telehealth has highlighted the need for secure and reliable data transfer. Blockchain can provide the necessary infrastructure for secure remote patient monitoring, enabling seamless data exchange between patients, doctors, and other healthcare providers. Imagine a scenario where a patient’s wearable device transmits vital health data directly to a secure blockchain network, accessible only to authorized healthcare professionals. This allows for real-time monitoring and proactive intervention, potentially preventing serious health complications. For example, a patient with a chronic condition could have their blood pressure and heart rate monitored remotely, with alerts automatically sent to their doctor if any abnormalities are detected.
Precision Medicine and Personalized Healthcare
Precision medicine relies on the analysis of vast amounts of patient data to tailor treatments to individual needs. Blockchain can facilitate the secure and efficient sharing of genomic data and other relevant information, enabling researchers and clinicians to develop more effective personalized treatments. Consider a future where a patient’s complete medical history, including genomic data, is stored securely on a blockchain, accessible only with their consent. This allows healthcare providers to make more informed decisions, leading to better patient outcomes. This also addresses concerns about data privacy and ownership, empowering individuals to control their own health information.
Building a More Equitable and Accessible Healthcare System
Blockchain has the potential to address healthcare disparities by creating a more equitable and accessible system. By facilitating secure data sharing and interoperability, blockchain can improve access to healthcare services for underserved populations. For example, patients in remote areas could access their medical records and telehealth services through a blockchain-based system, overcoming geographical barriers. Furthermore, blockchain can help to create a more transparent and accountable healthcare system, reducing the risk of fraud and ensuring that resources are allocated efficiently. A hypothetical example could involve a government agency using blockchain to track the distribution of healthcare funding, ensuring transparency and preventing misuse of resources.
A Futuristic Healthcare Scenario
Imagine a world where every individual possesses a secure digital health record stored on a blockchain network. This record, accessible only with the individual’s permission, contains their complete medical history, genomic data, and wearable sensor readings. Healthcare providers can access this information securely and efficiently, providing personalized care based on the individual’s unique needs. Smart contracts automate insurance claims and billing processes, eliminating delays and reducing administrative burdens. Researchers can access anonymized data for research purposes, accelerating the development of new treatments and cures. This decentralized, secure, and transparent system fosters trust and empowers individuals to take control of their own health journey, creating a truly patient-centric healthcare system. The visual representation would be a vibrant, interconnected network of nodes, representing patients, providers, and researchers, all securely connected through a blockchain backbone, with data flowing seamlessly and securely within the network. Each node would glow with a soft, personalized light, representing the individual’s unique health data, while the overall network pulses with a gentle rhythm, symbolizing the continuous flow of information and the dynamic nature of the system.
Conclusion
The potential of blockchain in revolutionizing healthcare data management is undeniable. While challenges remain in terms of scalability, standardization, and regulatory hurdles, the benefits—enhanced security, improved data integrity, increased patient control, and streamlined processes—are too significant to ignore. As the technology matures and adoption increases, we can expect to see a more efficient, secure, and patient-centered healthcare landscape emerge. The future of healthcare is decentralized, and it’s powered by blockchain.
