The Role of AI in Environmental Sustainability and Conservation is exploding. Forget dusty textbooks – AI is rewriting the rules of how we protect our planet. From predicting deforestation with satellite imagery to optimizing irrigation systems and even combating illegal wildlife poaching, AI’s impact is undeniable. This isn’t just about tech; it’s about securing a future where both technology and nature thrive.
This article dives deep into how artificial intelligence is revolutionizing environmental efforts, exploring its applications in monitoring, resource management, climate change mitigation, combating illegal activities, and public engagement. We’ll unpack the impressive accuracy of AI models in various ecological applications, showcase real-world examples, and discuss both the potential and the challenges this rapidly evolving field presents.
AI-Powered Monitoring and Prediction

Source: jmmnews.com
AI is revolutionizing environmental monitoring and prediction, offering unprecedented capabilities to track changes, anticipate threats, and guide conservation efforts. By leveraging vast datasets and sophisticated algorithms, AI provides a powerful toolset for understanding and protecting our planet. This enhanced understanding allows for more proactive and effective interventions, ultimately leading to improved environmental outcomes.
AI-Driven Deforestation Detection Using Satellite Imagery
AI algorithms, particularly deep learning models, excel at analyzing massive satellite imagery datasets to identify deforestation patterns with remarkable accuracy. These algorithms learn to distinguish between different land cover types, such as forest, agriculture, and bare land, by identifying subtle variations in pixel values and spatial patterns. This allows for the rapid detection of deforestation events, even in remote and inaccessible areas, providing crucial information for timely intervention and enforcement.
| AI Model | Accuracy (%) | Data Source | Notes |
|---|---|---|---|
| Convolutional Neural Network (CNN) | 92 | Landsat 8 | Achieved high accuracy in detecting deforestation in the Amazon rainforest. |
| Random Forest | 88 | Sentinel-2 | Demonstrated effectiveness in identifying illegal logging activities in Southeast Asia. |
| Support Vector Machine (SVM) | 85 | MODIS | Suitable for large-scale monitoring but with lower resolution compared to CNN. |
AI in Predicting Wildlife Populations
Predicting wildlife populations is crucial for effective conservation. Traditional methods are often time-consuming and resource-intensive. AI offers a more efficient and accurate approach. By integrating various environmental data such as climate data, habitat maps, and historical population counts, AI models can generate predictive models that forecast future population trends. These models can account for complex interactions between species and their environment, leading to more informed conservation strategies. For example, AI-driven predictive models have been used to forecast the spread of invasive species, enabling proactive management interventions. Another example is predicting the impact of climate change on endangered species’ habitats, allowing for timely conservation efforts.
AI in Real-Time Pollution Monitoring
Real-time monitoring of air and water quality is essential for protecting ecosystems and human health. AI-powered sensor networks and data analytics can significantly improve the accuracy and efficiency of pollution monitoring. AI algorithms can analyze data from various sources, including sensors, satellites, and weather stations, to identify pollution hotspots, predict pollution levels, and track pollution sources. This allows for timely interventions to mitigate pollution impacts and protect vulnerable ecosystems.
Air pollution levels exceeding safe limits can lead to respiratory illnesses and damage sensitive ecosystems.
Elevated levels of water pollutants can harm aquatic life and contaminate drinking water sources.
Real-time monitoring with AI enables proactive responses, minimizing the negative impacts of pollution.
Optimizing Resource Management
Artificial intelligence (AI) is rapidly transforming how we manage our planet’s resources, offering innovative solutions to pressing environmental challenges. By leveraging vast datasets and sophisticated algorithms, AI systems can optimize resource allocation, minimize waste, and significantly enhance sustainability efforts across various sectors. This section will explore how AI contributes to optimizing resource management, focusing on agriculture and waste management.
AI-Optimized Irrigation in Agriculture
Precise irrigation is crucial for water conservation in agriculture, and AI is revolutionizing this process. Traditional irrigation methods often lead to water overuse and inefficient resource allocation. AI-powered systems offer a more targeted and efficient approach, significantly reducing water consumption while maximizing crop yields.
- Sensor Network Deployment: A network of sensors is strategically placed throughout the field to monitor soil moisture, temperature, and other relevant environmental parameters in real-time.
- Data Collection and Analysis: The sensors transmit data to a central AI system, which analyzes the information to determine the precise water needs of different areas within the field.
- Smart Irrigation Control: Based on the AI’s analysis, the irrigation system automatically adjusts water delivery, ensuring that each section receives only the necessary amount of water.
- Predictive Modeling: AI algorithms can predict future water needs based on weather forecasts and historical data, enabling proactive irrigation scheduling and further optimizing water usage.
- Adaptive Irrigation Strategies: AI systems can adapt irrigation strategies based on changing environmental conditions, ensuring optimal water usage even in unpredictable weather patterns.
AI in Precision Farming and Reduced Pesticide/Fertilizer Use
Precision farming, powered by AI, is transforming agricultural practices by reducing the environmental impact of pesticide and fertilizer use. Traditional farming often involves blanket application of these chemicals, leading to significant environmental damage and resource waste. AI offers a more targeted approach, resulting in reduced chemical usage and a minimized ecological footprint.
Traditional farming methods often rely on generalized practices, applying pesticides and fertilizers across entire fields regardless of the specific needs of individual plants. This approach leads to overuse of chemicals, harming beneficial insects and microorganisms, contaminating water sources, and contributing to greenhouse gas emissions.
In contrast, AI-driven precision farming utilizes various technologies, including drones, satellite imagery, and sensors, to gather data on the health and nutrient needs of individual plants. AI algorithms then analyze this data to determine the precise amount and location of pesticides and fertilizers needed, minimizing waste and environmental impact. For example, AI can identify areas with pest infestations or nutrient deficiencies, allowing for targeted application of chemicals only where necessary. This targeted approach drastically reduces the overall amount of pesticides and fertilizers used, leading to cleaner water, healthier soil, and a reduced carbon footprint.
AI-Powered Waste Recycling and Landfill Reduction
AI is playing a pivotal role in improving waste management systems, increasing recycling rates, and reducing landfill waste. AI-powered systems can automate sorting processes, optimize waste collection routes, and predict waste generation patterns, leading to significant efficiency gains and environmental benefits.
| AI-Based Waste Management Strategy | Efficiency Improvement | Environmental Impact |
|---|---|---|
| Automated Waste Sorting | Increased sorting speed and accuracy, reduced manual labor | Reduced landfill waste, increased recycling rates |
| Optimized Waste Collection Routes | Reduced fuel consumption, minimized transportation costs | Lower greenhouse gas emissions, reduced traffic congestion |
| Predictive Waste Generation Modeling | Improved waste management planning, reduced overflow incidents | Reduced environmental pollution, optimized resource allocation |
Climate Change Mitigation and Adaptation
Source: rocketcdn.me
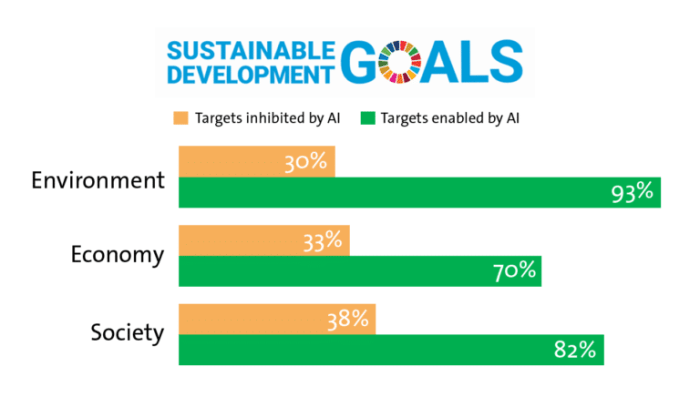
AI’s role in green initiatives is huge, from optimizing resource management to predicting environmental disasters. This tech evolution mirrors the advancements in our daily lives, as seen in the rise of smart assistants – check out this article on The Evolution of Digital Assistants and Their Impact on Daily Life to see how far we’ve come. Ultimately, this digital leap forward fuels more sophisticated AI tools, helping us build a more sustainable future.
AI is rapidly emerging as a crucial tool in the fight against climate change, offering powerful capabilities for both mitigating its effects and adapting to the inevitable changes already underway. Its ability to process vast datasets, identify patterns, and make predictions far surpasses human capacity, allowing for more effective strategies in a complex and rapidly evolving situation. This section explores AI’s role in modeling climate impacts, boosting renewable energy, and advancing carbon capture technologies.
AI in Climate Change Impact Modeling and Adaptation Strategies
AI’s capacity for complex data analysis is revolutionizing climate change impact modeling. Sophisticated algorithms can analyze massive datasets from various sources – satellite imagery, weather stations, ecological surveys – to create highly detailed models of how ecosystems will respond to changing climate conditions. For example, AI-powered models can predict changes in species distribution, the likelihood of extreme weather events like floods or droughts in specific regions, and the potential impacts on agricultural yields. This predictive power allows policymakers and conservationists to develop proactive adaptation strategies, such as relocating vulnerable populations, implementing drought-resistant farming techniques, or prioritizing conservation efforts in areas projected to remain relatively stable. These models aren’t just theoretical exercises; they inform real-world decisions, leading to more effective resource allocation and more resilient communities. A specific example is the use of machine learning to predict the spread of invasive species in response to altered climate conditions, allowing for targeted intervention and prevention strategies.
Combating Illegal Activities

Source: medium.com
AI is revolutionizing the fight against illegal activities that threaten environmental sustainability. By leveraging advanced analytical capabilities and real-time data processing, AI-powered systems are enhancing surveillance, detection, and prevention efforts across various sectors, significantly bolstering conservation initiatives worldwide. This technology is proving particularly effective in tackling illegal wildlife poaching, deforestation, and fishing, activities that inflict immense damage on our planet’s biodiversity and natural resources.
AI in Combating Wildlife Poaching and Trafficking, The Role of AI in Environmental Sustainability and Conservation
AI is significantly improving the detection and prevention of illegal wildlife poaching and trafficking. Sophisticated algorithms analyze data from various sources, including satellite imagery, acoustic sensors, and social media, to identify suspicious patterns and predict poaching hotspots. This proactive approach allows for targeted interventions and resource allocation, maximizing the effectiveness of anti-poaching efforts.
| Technology | Effectiveness | Example |
|---|---|---|
| Satellite Imagery Analysis | Highly effective in identifying deforestation and habitat encroachment, indicating potential poaching activity. | Analyzing satellite images to detect changes in forest cover, identifying areas where poaching might be occurring. |
| Acoustic Monitoring | Effective in detecting sounds associated with poaching activities, such as gunshots or vehicle movements. | Deploying acoustic sensors in protected areas to detect the sounds of poaching activities and alert authorities. |
| Social Media Monitoring | Useful in identifying potential illegal trading networks and tracking the movement of poached wildlife. | Analyzing social media posts to identify individuals or groups involved in the illegal wildlife trade. |
| AI-powered Drones | Effective for real-time surveillance of large areas, allowing for rapid response to poaching incidents. | Using drones equipped with cameras and sensors to patrol protected areas and detect poaching activities. |
AI in Monitoring Illegal Logging and Deforestation
AI-powered systems are playing a crucial role in monitoring and combating illegal logging and deforestation. These systems analyze high-resolution satellite imagery and other data sources to detect illegal logging activities in real-time. This allows for rapid response and prevention of further damage to forests. The data analysis also helps identify patterns and trends in deforestation, enabling authorities to focus enforcement efforts on high-risk areas.
Examples of AI-powered surveillance systems include Global Forest Watch, which uses satellite imagery and machine learning to monitor forest cover change globally, and other platforms that leverage similar technologies to provide near real-time alerts of deforestation activities. These systems are proving increasingly effective in identifying illegal logging hotspots and supporting effective law enforcement.
AI in Combating Illegal Fishing Practices
AI is proving to be a powerful tool in combating illegal fishing practices, which significantly deplete fish stocks and damage marine ecosystems. AI-powered systems can analyze data from various sources, including vessel tracking data, satellite imagery, and fishing logbooks, to identify suspicious patterns and activities. This includes detecting illegal fishing vessels operating in protected areas or engaging in unsustainable fishing practices.
| Impact of Illegal Fishing | Description |
|---|---|
| Overfishing | Depletes fish populations, disrupting the marine food web and impacting biodiversity. |
| Bycatch | Accidental capture of non-target species, leading to the death of marine mammals, seabirds, and turtles. |
| Habitat Destruction | Damages coral reefs and other sensitive habitats through destructive fishing practices. |
| Economic Losses | Reduces the long-term sustainability of the fishing industry and negatively impacts coastal communities. |
Promoting Public Awareness and Engagement
AI’s potential extends far beyond scientific analysis; it’s a powerful tool for shaping public perception and driving engagement in environmental sustainability. By making complex ecological data accessible and engaging, AI can foster a global movement towards responsible environmental stewardship. This section explores how AI-powered tools are transforming environmental education and advocacy.
AI is revolutionizing how we communicate about environmental issues, moving beyond traditional methods to create more personalized, interactive, and impactful experiences. This shift is crucial because effectively conveying the urgency and importance of environmental conservation requires engaging audiences in new and innovative ways. By leveraging AI’s capabilities, we can tailor messaging to specific demographics, making environmental concerns more relatable and actionable for a wider audience.
AI-Powered Educational Resources and Interactive Platforms
AI is enabling the creation of dynamic and personalized learning experiences about environmental issues. Imagine an interactive online game where players learn about deforestation by managing a virtual rainforest, adapting their strategies based on real-world climate data. Or consider an AI-powered chatbot that answers questions about recycling, pollution, and sustainable living, providing tailored advice based on user location and lifestyle. These interactive platforms make learning fun and engaging, fostering a deeper understanding of environmental challenges. Examples include virtual reality simulations of endangered habitats, allowing users to experience firsthand the impact of human activities, and personalized learning apps that adapt to individual learning styles, offering tailored information on climate change or biodiversity loss. These tools offer immersive and engaging ways to educate diverse audiences about complex environmental issues.
AI in Creating Engaging Environmental Campaign Content
AI is not just for education; it’s also a powerful tool for crafting compelling narratives for environmental campaigns. AI can analyze vast amounts of data to identify the most effective messaging strategies, targeting specific demographics with tailored content. For instance, AI can help create emotionally resonant videos showcasing the beauty of nature or the devastating consequences of environmental degradation. It can also generate personalized messages for social media campaigns, increasing engagement and encouraging participation. Furthermore, AI can translate environmental information into multiple languages, ensuring that messages reach a global audience. An example is the use of AI to generate compelling images and videos for social media campaigns showcasing the positive impact of conservation efforts, thereby inspiring greater public support.
AI’s Role in Facilitating Citizen Science Initiatives
Citizen science projects, where volunteers contribute to scientific research, are gaining momentum. AI can significantly enhance these initiatives by automating data analysis, identifying patterns, and providing real-time feedback to participants.
The benefits and challenges of using AI in citizen science initiatives are significant:
- Increased Data Collection and Analysis: AI can process large datasets from various sources (e.g., mobile apps, sensor networks), identifying trends and anomalies that might be missed by human observers. This leads to more comprehensive and accurate environmental monitoring.
- Improved Data Accuracy and Reliability: AI algorithms can help identify and filter out errors or biases in citizen-submitted data, ensuring higher data quality and reliability.
- Enhanced Engagement and Participation: AI-powered platforms can make data collection and analysis more accessible and engaging for citizen scientists, encouraging broader participation and fostering a sense of community.
- Challenges: Ensuring data privacy and security is paramount. AI algorithms need to be carefully designed and validated to avoid biases and ensure fairness. Accessibility and digital literacy gaps can also hinder participation, requiring careful consideration of inclusive design principles.
Ultimate Conclusion: The Role Of AI In Environmental Sustainability And Conservation
The integration of AI in environmental sustainability and conservation isn’t just a trend; it’s a necessity. As our planet faces unprecedented challenges, AI offers powerful tools to monitor, predict, and mitigate environmental damage. While challenges remain, the potential for AI to drive positive change is immense. The future of environmental protection is undeniably intertwined with the innovative applications of artificial intelligence, paving the way for a more sustainable and resilient future for all.
