The Role of AI in Creating Smarter Cities and Safer Communities is no longer a futuristic fantasy; it’s the present, rapidly reshaping urban landscapes. From optimizing traffic flow with AI-powered systems to predicting crime patterns and improving emergency response times, artificial intelligence is fundamentally altering how we live, work, and interact within our cities. This isn’t just about technological advancement; it’s about building more efficient, sustainable, and ultimately, safer environments for everyone.
This exploration delves into the multifaceted ways AI is revolutionizing city life, examining its impact on infrastructure, public services, community safety, and environmental sustainability. We’ll uncover both the incredible potential and the crucial ethical considerations that come with harnessing the power of AI for the common good. Get ready to see how algorithms are changing the urban game.
AI-Powered Smart City Infrastructure: The Role Of AI In Creating Smarter Cities And Safer Communities
Smart cities leverage artificial intelligence (AI) to optimize various aspects of urban life, enhancing efficiency, sustainability, and safety for residents. AI’s ability to analyze vast datasets and make real-time decisions is transforming how cities function, paving the way for a more responsive and intelligent urban environment. This section delves into the specific applications of AI in building smarter and safer city infrastructure.
AI in Optimizing Traffic Flow
AI plays a crucial role in alleviating traffic congestion, a persistent challenge in many urban areas. By analyzing real-time data from various sources – traffic cameras, GPS devices, and social media – AI algorithms can predict traffic patterns, identify bottlenecks, and optimize traffic signal timings. This dynamic adjustment of traffic signals leads to smoother traffic flow, reduced congestion, and decreased commute times. For instance, the city of Pittsburgh uses AI-powered traffic management systems that adjust traffic signals based on real-time traffic conditions, resulting in a significant reduction in commute times and improved overall traffic flow. Another example is the use of AI in ride-sharing apps like Uber and Lyft, which optimize routes and dispatch vehicles based on real-time demand, reducing congestion caused by inefficient vehicle routing.
AI in Smart Grids for Efficient Energy Management
Smart grids utilize AI to enhance energy distribution and consumption efficiency. Traditional grids operate on a relatively static model, often leading to energy waste and inefficient resource allocation. In contrast, AI-powered smart grids use machine learning algorithms to analyze energy consumption patterns, predict demand fluctuations, and optimize energy distribution in real-time. This dynamic approach ensures that energy is delivered efficiently, reducing waste and improving grid stability. Furthermore, AI can facilitate the integration of renewable energy sources, like solar and wind power, into the grid more effectively.
| Feature | Traditional Grids | AI-Powered Smart Grids | Example |
|---|---|---|---|
| Energy Distribution | Static, based on historical data | Dynamic, real-time adjustment based on predicted demand and renewable energy availability | Predictive maintenance alerts for preventing outages |
| Demand Forecasting | Based on historical averages, often inaccurate | Accurate predictions using machine learning algorithms, considering various factors | Optimizing energy generation to meet real-time demand |
| Renewable Energy Integration | Limited integration, challenges in managing fluctuating supply | Seamless integration, optimizing energy mix and balancing supply and demand | Integrating solar and wind power efficiently into the grid |
| Fault Detection and Repair | Reactive, repairs only after outages occur | Proactive, AI algorithms detect anomalies and predict potential failures | Predictive maintenance reducing downtime and improving grid reliability |
AI-Powered Surveillance for Enhanced Public Safety
AI-powered sensors and cameras are transforming public safety in smart cities. These systems use computer vision and machine learning to analyze video feeds in real-time, identifying potential threats and alerting authorities. For instance, AI can detect suspicious activities like loitering, unauthorized access to restricted areas, or unusual gatherings. This proactive approach to crime prevention allows law enforcement to respond swiftly and effectively, potentially preventing crimes before they occur. Facial recognition technology, while controversial due to privacy concerns, can be used to identify suspects and track individuals involved in criminal activities. However, ethical considerations and data privacy must be carefully addressed when implementing such systems. In addition to crime prevention, AI-powered surveillance can also improve traffic safety by detecting reckless driving behaviors or accidents. For example, AI-powered systems can detect speeding vehicles, identify potential accidents, and automatically alert emergency services.
Enhancing Public Services with AI
Smart cities aren’t just about shiny new infrastructure; they’re about using technology to improve the everyday lives of their citizens. AI is proving to be a powerful tool in this endeavor, revolutionizing how public services are delivered and experienced. By analyzing vast amounts of data and identifying patterns, AI can optimize resource allocation, predict future needs, and ultimately, make cities more efficient and responsive to their residents.
AI’s impact on public services is multifaceted, impacting everything from transportation to waste management and citizen engagement. This section will delve into specific examples of how AI is transforming these crucial aspects of city life.
AI-Optimized Public Transportation
Optimizing public transportation routes and schedules is a complex challenge, involving numerous variables like traffic patterns, passenger demand, and infrastructure limitations. AI offers a powerful solution by analyzing real-time data from various sources – GPS tracking of vehicles, passenger usage statistics, and even social media feeds – to dynamically adjust routes and schedules. This leads to improved efficiency, reduced travel times, and a more reliable public transport system.
The benefits and challenges of AI-driven public transport optimization are summarized below:
- Benefits: Reduced congestion, improved on-time performance, optimized resource allocation (fewer buses/trains needed for the same level of service), increased passenger satisfaction, better accessibility for underserved areas through dynamic route adjustments.
- Challenges: High initial investment in data infrastructure and AI systems, the need for robust data security and privacy measures, potential job displacement for some transportation personnel, reliance on accurate and real-time data, the need for ongoing system maintenance and updates.
AI-Powered Waste Management
Waste management is a critical aspect of city operations, and AI is transforming this sector by improving efficiency and reducing environmental impact. AI-powered systems can optimize waste collection routes, predict waste generation levels, and even identify recyclable materials more accurately. This leads to cost savings, reduced landfill usage, and a cleaner environment.
A step-by-step procedure for an AI-powered waste management system could look like this:
- Smart Bins: Install smart bins equipped with sensors to monitor fill levels and identify the type of waste (e.g., using image recognition).
- Data Collection & Analysis: Collect data from smart bins and other sources (e.g., weather patterns, population density) and use AI algorithms to analyze this data, predicting waste generation and optimizing collection routes.
- Route Optimization: AI dynamically adjusts waste collection routes based on real-time data, ensuring efficient and timely pickup.
- Material Sorting: AI-powered sorting facilities use computer vision and robotics to automatically sort recyclable materials, improving recycling rates and reducing contamination.
- Predictive Maintenance: AI predicts potential equipment failures, allowing for proactive maintenance and minimizing service disruptions.
AI-Enhanced Personalized Citizen Services
AI is revolutionizing citizen engagement by providing personalized access to government information and services. AI-powered chatbots, for instance, can answer frequently asked questions, guide citizens through complex processes, and provide 24/7 support. This improves accessibility, reduces wait times, and enhances overall citizen satisfaction. For example, a chatbot could help a citizen find the nearest vaccination center, file a complaint, or access their tax information. This personalized, readily-available assistance fosters greater trust and engagement between citizens and their local government. Furthermore, AI can analyze citizen feedback to identify areas for improvement in public services and tailor services to meet specific community needs. The city of Amsterdam, for instance, uses AI to analyze citizen data to improve its public services and tailor them to meet the needs of specific neighborhoods.
AI for Safer Communities

Source: ielts.net
AI’s impact on urban planning is huge, optimizing traffic flow and predicting crime hotspots for safer communities. This data-driven approach mirrors how businesses leverage AI; check out this insightful piece on The Role of Artificial Intelligence in Business Decision Making to see the parallels. Ultimately, smarter decision-making, whether in city management or corporate strategy, hinges on harnessing AI’s predictive power for better outcomes.
The integration of artificial intelligence (AI) into public safety is transforming how we approach crime prevention, emergency response, and resource allocation. Moving beyond traditional reactive policing models, AI offers proactive strategies that aim to predict and prevent crime before it occurs, ultimately creating safer communities for everyone. This shift requires careful consideration of ethical implications and potential biases, but the potential benefits are undeniable.
AI-Driven Crime Prediction and Prevention Compared to Traditional Policing
Traditional policing methods often rely on reactive responses to reported crimes, leading to potential delays and limited preventative measures. AI-driven strategies, conversely, leverage data analysis to identify crime hotspots, predict potential incidents, and allocate resources more effectively. The following table illustrates this comparison:
| Feature | Traditional Policing | AI-Driven Policing |
|---|---|---|
| Approach | Reactive; responds to reported crimes | Proactive; predicts and prevents crime |
| Data Analysis | Limited; relies on reported incidents | Comprehensive; analyzes various data sources (crime reports, social media, sensor data) |
| Resource Allocation | Often uneven; based on historical crime patterns | Optimized; allocates resources based on predicted crime hotspots and risk levels |
| Predictive Capabilities | Limited; relies on human intuition and experience | Advanced; uses machine learning to identify patterns and predict future crime |
AI’s Role in Improving Emergency Response Times and Resource Allocation, The Role of AI in Creating Smarter Cities and Safer Communities
AI significantly enhances emergency response by optimizing resource allocation and accelerating response times. For example, AI-powered systems can analyze real-time data from various sources – such as traffic cameras, social media feeds, and emergency calls – to identify the location and severity of incidents. This information allows emergency services to dispatch the appropriate resources to the scene quickly and efficiently.
Here’s a flowchart illustrating an AI-driven emergency response process:
Start → Incident Detection (sensors, calls, social media) → Data Analysis (AI algorithms) → Incident Prioritization (severity, location) → Resource Allocation (ambulances, police, fire) → Dispatch & Response → Situation Monitoring (real-time updates) → Post-Incident Analysis (improvements) → End
Ethical Considerations and Potential Biases in AI-Driven Public Safety
While AI offers significant advantages in enhancing public safety, it’s crucial to address ethical considerations and potential biases. AI algorithms are trained on data, and if this data reflects existing societal biases (e.g., racial or socioeconomic biases in arrest records), the AI system may perpetuate and even amplify these biases. For instance, an AI system trained on data showing disproportionate arrests in certain neighborhoods might incorrectly predict higher crime rates in those areas, leading to increased police surveillance and potentially unfair targeting of innocent individuals.
To mitigate these biases, several strategies are essential. This includes carefully curating and auditing the data used to train AI algorithms, ensuring diverse representation in the datasets. Regularly evaluating the AI system’s performance for biases and implementing mechanisms for human oversight and accountability are also crucial. Transparency in the development and deployment of AI systems is vital, allowing for public scrutiny and fostering trust. Furthermore, ongoing research and development of bias-mitigation techniques are necessary to ensure fairness and equity in the application of AI in public safety.
AI and Environmental Sustainability in Smart Cities
Smart cities are increasingly leveraging artificial intelligence (AI) to address pressing environmental challenges. By analyzing vast amounts of data and automating processes, AI offers innovative solutions for reducing carbon emissions, optimizing resource management, and improving overall urban sustainability. This move towards a greener future is not just an environmental imperative, but also an economic and social one, fostering a more resilient and livable urban environment.
AI’s contribution to environmental sustainability in urban areas is multifaceted. It allows for the precise monitoring and prediction of environmental conditions, enabling proactive interventions to mitigate risks and optimize resource allocation. This proactive approach, driven by AI-powered insights, offers a significant advantage over traditional reactive methods. The integration of AI into various city systems allows for a more holistic and efficient approach to environmental management, leading to measurable improvements in air and water quality, waste management, and energy consumption.
AI Applications in Renewable Energy Management and Environmental Monitoring
AI plays a crucial role in optimizing renewable energy sources like solar and wind power. Machine learning algorithms can predict energy output based on weather patterns, allowing for better grid management and reduced reliance on fossil fuels. For example, AI-powered systems can predict fluctuations in solar energy production and adjust energy distribution accordingly, minimizing energy waste and maximizing the utilization of renewable resources. Similarly, in environmental monitoring, AI algorithms analyze data from sensors deployed across the city to identify pollution hotspots, track deforestation, and monitor water quality. This real-time data allows for quicker responses to environmental threats and enables the implementation of targeted mitigation strategies. One example is the use of drones equipped with AI-powered image recognition to monitor illegal dumping sites or deforestation activities.
AI in Optimizing Water Resource Management and Reducing Water Waste
Efficient water management is paramount in urban areas. AI-driven solutions can significantly improve water resource management by optimizing water distribution networks, detecting leaks, and predicting water demand. Smart water meters equipped with AI can monitor water consumption in real-time, identifying unusual patterns that might indicate leaks or inefficiencies. This data enables utility companies to quickly address leaks and minimize water loss. Predictive modeling based on AI can forecast future water demand based on various factors like weather patterns and population growth, allowing for proactive adjustments in water allocation and infrastructure planning. For instance, AI can optimize irrigation systems in parks and green spaces, reducing water consumption while maintaining healthy vegetation.
The benefits and challenges of AI-driven water management are summarized below:
- Benefits: Reduced water waste, improved water quality, optimized water distribution, proactive leak detection, efficient irrigation, better water resource planning.
- Challenges: High initial investment costs, data security and privacy concerns, integration with existing infrastructure, need for skilled personnel to manage and maintain AI systems, potential bias in algorithms leading to inaccurate predictions.
AI in Improving Air Quality Monitoring and Pollution Control
AI significantly enhances air quality monitoring and pollution control. AI-powered sensors can provide real-time data on various pollutants, enabling authorities to identify sources of pollution and implement targeted interventions. For instance, AI algorithms can analyze traffic patterns and identify areas with high levels of vehicle emissions, informing decisions on traffic management and emission reduction strategies. Furthermore, AI can predict air quality levels based on weather patterns and pollution sources, allowing for timely public health advisories and proactive measures to protect vulnerable populations. Predictive modeling also enables the optimization of pollution control measures, ensuring maximum effectiveness.
Infographic: AI’s Impact on Air Quality Improvement
The infographic would be visually compelling, using a combination of charts and icons. A large central image would depict a cityscape gradually transitioning from hazy and polluted to clear and vibrant, symbolizing the improvement in air quality. One section would show a bar chart comparing air pollution levels before and after the implementation of AI-powered monitoring and control systems, demonstrating a significant reduction in key pollutants like particulate matter (PM2.5) and nitrogen dioxide (NO2). Another section would illustrate the workflow of AI in air quality management, starting with sensor data collection, followed by AI-powered analysis, prediction, and finally, targeted interventions like traffic management adjustments or industrial emission controls. The infographic would conclude with key success metrics, such as percentage reduction in pollution levels, improved public health outcomes, and cost savings achieved through optimized resource allocation. The overall design would be clean, modern, and easily understandable, conveying the positive impact of AI on air quality in a clear and concise manner.
Challenges and Future Directions of AI in Smart Cities
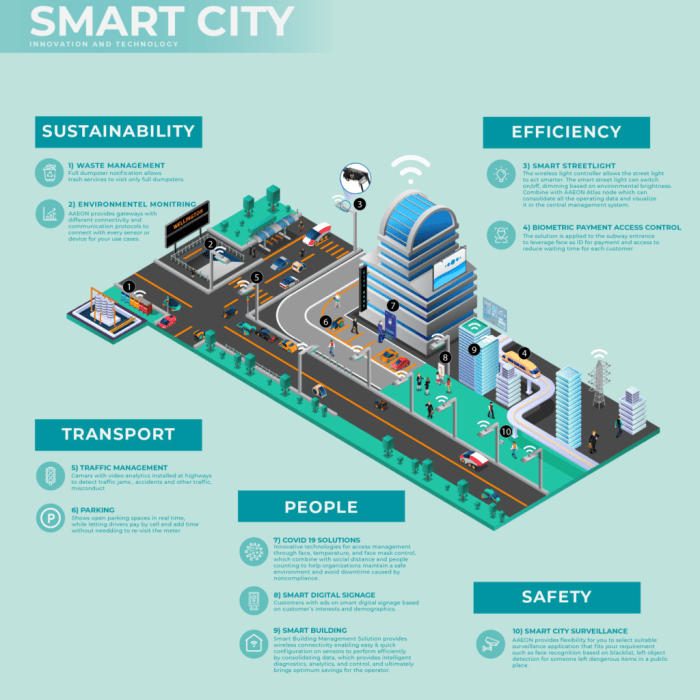
Source: aaeon.com
The integration of artificial intelligence into smart city infrastructure, while promising immense benefits, faces significant hurdles. Successfully navigating these challenges is crucial for realizing the full potential of AI in creating truly intelligent and resilient urban environments. Overcoming these obstacles requires a multi-faceted approach involving technological advancements, robust policy frameworks, and a proactive societal dialogue.
Technological Challenges in Implementing AI-Powered Solutions
Implementing AI in urban environments presents unique technological challenges. These range from the sheer scale and complexity of data management to the need for robust and reliable AI systems capable of operating in dynamic and unpredictable real-world conditions.
- Data Integration and Interoperability: Smart cities generate massive amounts of data from diverse sources. Integrating this data, often residing in disparate systems with varying formats and levels of quality, is a major hurdle. Solutions involve developing standardized data formats and APIs, as well as employing advanced data fusion techniques to create a unified and consistent data landscape. For example, integrating traffic camera data with weather forecasts and public transport schedules requires standardized interfaces and data transformation processes.
- Computational Resources and Energy Consumption: Training and deploying sophisticated AI models, especially deep learning algorithms, demands significant computational power and energy. This poses challenges for resource-constrained municipalities. Solutions include leveraging cloud computing, exploring energy-efficient hardware designs, and optimizing AI algorithms for lower computational demands. For instance, the city of Barcelona is exploring the use of edge computing to process data closer to its source, reducing the need for extensive data transmission and energy consumption.
- Algorithm Bias and Fairness: AI algorithms are trained on data, and if that data reflects existing societal biases, the resulting AI systems can perpetuate and even amplify those biases. This is particularly concerning in applications like crime prediction or resource allocation. Solutions involve carefully curating training data to ensure representativeness and employing techniques to detect and mitigate bias in algorithms. Regular audits and independent evaluations of AI systems are also essential.
- Robustness and Reliability in Dynamic Environments: AI systems in smart cities must operate reliably in unpredictable real-world conditions. They need to be resilient to noise, anomalies, and adversarial attacks. Solutions include developing more robust and fault-tolerant algorithms, incorporating human-in-the-loop mechanisms for oversight and error correction, and implementing comprehensive security measures to prevent malicious interference.
Societal Implications of Widespread AI Adoption
The widespread adoption of AI in smart cities raises crucial societal concerns. Addressing these issues requires careful planning, ethical considerations, and robust regulatory frameworks.
- Data Privacy and Security: Smart city systems collect vast amounts of personal data, raising concerns about privacy violations and data breaches. Solutions include implementing strong data anonymization and encryption techniques, adhering to strict data governance policies, and ensuring transparency and accountability in data handling practices. The implementation of GDPR-like regulations across different jurisdictions is crucial.
- Job Displacement: Automation driven by AI could lead to job displacement in various sectors, requiring proactive measures to mitigate this impact. Solutions include investing in retraining and upskilling programs for workers affected by automation, exploring alternative employment models, and fostering the growth of new industries related to AI development and deployment. Examples include retraining programs focusing on data science and AI maintenance.
- Algorithmic Accountability and Transparency: The decisions made by AI systems can have significant consequences for individuals and communities. It’s crucial to ensure accountability and transparency in the design, deployment, and operation of these systems. Solutions include establishing clear lines of responsibility for AI-driven decisions, implementing mechanisms for auditing and explaining AI outcomes, and fostering public understanding of AI technologies and their limitations.
Future Developments and Advancements in AI for Smart Cities
The future of AI in smart cities promises significant advancements across various domains. A phased approach is likely, with incremental improvements leading to transformative changes over time.
| Timeline | Expected Advancements | Examples |
|---|---|---|
| 2024-2027 | Improved data integration and interoperability; wider adoption of edge computing; enhanced AI algorithms for traffic management and resource optimization. | More seamless integration of various smart city sensors and systems; decentralized AI processing for faster response times in emergency situations; optimized traffic flow using predictive modeling. |
| 2028-2032 | Increased focus on AI ethics and fairness; development of explainable AI (XAI) systems; widespread use of AI for predictive maintenance and environmental monitoring. | Algorithms designed to mitigate bias in decision-making; improved transparency in AI-driven recommendations; proactive infrastructure maintenance reducing downtime and costs. |
| 2033-2037 | Emergence of truly autonomous systems for transportation and logistics; advanced AI for personalized urban services; development of AI-driven urban planning tools. | Self-driving vehicles integrated into public transportation networks; customized recommendations for public services based on individual needs; simulations for urban planning optimizing resource allocation. |
Closure

Source: datafloq.com
The integration of AI into our cities presents a complex but ultimately promising future. While challenges remain – from addressing potential biases in algorithms to ensuring data privacy – the potential benefits are undeniable. From smarter grids and streamlined public transport to proactive crime prevention and improved emergency response, AI offers a powerful toolkit for building more resilient, equitable, and thriving urban environments. The journey toward truly smart and safe cities is ongoing, but the potential, driven by AI, is undeniably exciting.
