The Rise of Edge Computing and Its Role in Decentralized Networks is shaking things up. Forget the cloud – the future of data processing is happening right at the edge, closer to where it’s generated. This means faster speeds, enhanced security, and a whole new level of efficiency for decentralized systems. Think of it as giving data its own personal, hyper-speed highway, bypassing the usual traffic jams of centralized servers. This shift is impacting everything from finance and healthcare to the Internet of Things, promising a more responsive, secure, and ultimately, decentralized digital world.
This deep dive explores the synergy between edge computing and decentralized networks, examining the technological advancements, real-world applications, and future trends shaping this exciting landscape. We’ll unpack the key differences between edge and cloud computing, dissect the architecture of decentralized systems, and explore the challenges and opportunities that lie ahead. Get ready for a ride!
Defining Edge Computing and Decentralized Networks
The rise of edge computing and its symbiotic relationship with decentralized networks is reshaping the technological landscape. Understanding the core principles of each is crucial to grasping the potential of this powerful combination. This section will dissect both concepts, comparing their architectures and highlighting their key differences.
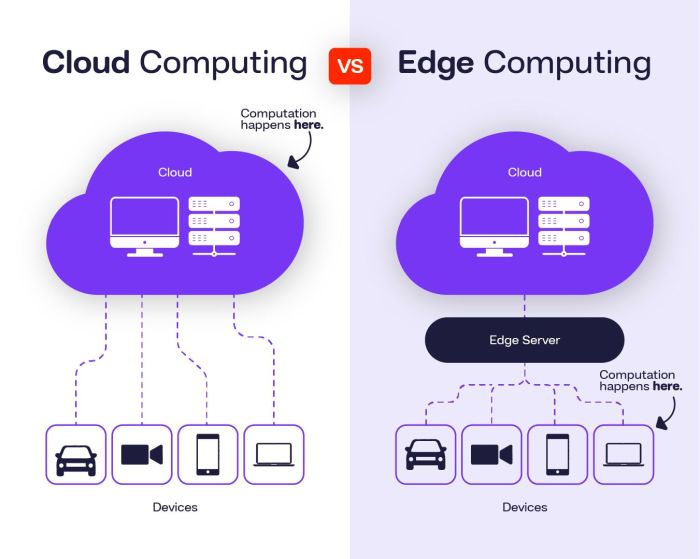
Edge computing, in a nutshell, brings computation and data storage closer to the source of data generation. Instead of relying solely on distant cloud servers, processing happens at the “edge” of the network – closer to devices like smartphones, IoT sensors, or even autonomous vehicles. This proximity significantly reduces latency and bandwidth consumption, enabling real-time applications and improved responsiveness.
Edge computing’s rise is crucial for decentralized networks, enabling faster data processing closer to the source. This is especially vital for applications like autonomous drone delivery systems, which demand real-time responsiveness. Check out how these systems are revolutionizing logistics in this insightful piece: How Autonomous Drones are Changing the Logistics Industry. The low-latency capabilities of edge computing are key to the success and safety of these increasingly complex drone operations, further solidifying its role in future decentralized networks.
Edge Computing Principles
Edge computing contrasts sharply with cloud computing’s centralized model. While cloud computing relies on massive data centers handling all processing and storage, edge computing distributes these tasks across multiple smaller nodes. This distributed approach offers several advantages, including reduced latency for time-sensitive applications, increased bandwidth efficiency, and enhanced data security through localized processing. Think of it like this: instead of sending every photo you take to a distant cloud server for processing, edge computing allows your phone to process the image locally, perhaps applying a filter or recognizing faces, before potentially uploading a smaller, processed version to the cloud.
Decentralized Networks: Characteristics and Architectures
Decentralized networks, unlike their centralized counterparts, don’t rely on a single point of control. Instead, they distribute control and data across multiple nodes, making them more resilient to failures and censorship. Think of Bitcoin’s blockchain – a decentralized ledger where transactions are verified across a network of computers, rather than by a single authority. This inherent resilience is a major benefit, but it also comes with challenges. Maintaining consensus across a large network can be complex and resource-intensive. Furthermore, security concerns arise from the need to ensure the integrity of each node within the network.
Centralized vs. Decentralized System Architectures
Centralized systems, exemplified by traditional client-server models, feature a central server that manages all data and processing. This creates a single point of failure – if the server goes down, the entire system fails. Decentralized systems, however, distribute control and data across numerous nodes. This distributed architecture increases resilience and fault tolerance. If one node fails, the system can continue functioning. However, this distributed nature also increases the complexity of managing and securing the network. The architectural difference lies in the flow of information and control; centralized systems have a hierarchical structure, while decentralized systems adopt a more peer-to-peer approach.
Edge Computing vs. Cloud Computing: A Comparison
| Feature | Edge Computing | Cloud Computing | Key Difference |
|---|---|---|---|
| Data Processing Location | Closer to data source (edge devices) | Centralized data centers | Proximity to data source |
| Latency | Low latency | Higher latency | Speed of data processing and response |
| Bandwidth Usage | Reduced bandwidth consumption | Higher bandwidth consumption | Efficiency of data transmission |
| Scalability | Can be challenging to scale massively | Highly scalable | Ease of expanding capacity |
The Synergy Between Edge Computing and Decentralized Networks
Edge computing and decentralized networks are a match made in digital heaven. They complement each other beautifully, creating a more robust, efficient, and secure system than either could achieve alone. Essentially, edge computing provides the horsepower to make decentralized networks truly scalable and responsive.
Edge computing enhances decentralized networks by bringing processing power closer to the data source. This proximity drastically reduces latency, improves bandwidth efficiency, and strengthens data security – all critical aspects of a smoothly functioning decentralized system. Think of it like this: instead of sending every little piece of information across the globe to a central server, edge devices handle the processing locally, then only transmit the necessary results. This streamlined approach is the key to unlocking the full potential of decentralized technologies.
Reduced Latency in Decentralized Applications
Lower latency is a major win for decentralized applications (dApps). Imagine a real-time gaming scenario within a decentralized network. Without edge computing, every action – a move, a shot, a chat message – would have to travel to a central server, be processed, and then sent back to all participants. This back-and-forth creates noticeable lag. However, with edge computing, these actions are processed on nearby edge servers or even directly on the players’ devices, resulting in a significantly smoother and more responsive gaming experience. This is particularly crucial in applications demanding immediate feedback, such as augmented reality overlays or collaborative design tools.
Improved Bandwidth Usage in Decentralized Networks, The Rise of Edge Computing and Its Role in Decentralized Networks
By processing data closer to its source, edge computing drastically reduces the amount of data that needs to be transmitted across a network. This is particularly beneficial for decentralized networks, which often involve numerous devices and large volumes of data. Consider a smart city scenario using IoT devices. Instead of each sensor sending raw data to a central server for processing, edge devices can pre-process the data, identifying only critical events or anomalies before transmitting the condensed information. This drastically reduces bandwidth consumption, making the network more efficient and scalable.
Enhanced Data Security in Decentralized Systems
Data security is paramount, especially in decentralized networks where data might be distributed across multiple locations and devices. Edge computing enhances security by minimizing the amount of sensitive data that needs to be transmitted across the network. For example, in a decentralized healthcare system, patient data can be processed and analyzed on edge devices located within the hospital or clinic, reducing the risk of data breaches during transmission. This localized processing allows for greater control over data privacy and compliance with regulations like HIPAA. Furthermore, the decentralized nature of the network itself adds another layer of security; if one edge server is compromised, the entire system is not necessarily at risk.
Technological Aspects of Edge Computing in Decentralized Networks
The rise of decentralized networks necessitates a robust and efficient infrastructure, and edge computing provides precisely that. By processing data closer to its source, edge computing addresses the latency and bandwidth limitations inherent in traditional cloud-centric architectures, enabling faster response times and enhanced scalability for decentralized applications. This section delves into the core technological components that underpin the integration of edge computing within decentralized networks.
Types of Edge Devices and Their Capabilities
Edge devices form the backbone of any edge computing system. These devices range widely in processing power, storage capacity, and connectivity options, reflecting the diverse needs of decentralized applications. Consider, for example, a smart city infrastructure. Here, low-power sensors embedded in streetlights might only transmit basic data like light levels, while more powerful edge gateways located at traffic intersections might process complex algorithms for traffic optimization, requiring significantly greater computational resources and storage. Similarly, in an industrial IoT setting, edge devices could range from simple sensors monitoring machine health to sophisticated programmable logic controllers (PLCs) controlling entire production lines. The selection of an appropriate edge device depends critically on the specific application’s requirements, balancing computational needs with power consumption, cost, and security considerations.
Communication Protocols and Network Topologies
Efficient communication is paramount in decentralized networks, particularly those leveraging edge computing. Common protocols include MQTT (Message Queuing Telemetry Transport) for lightweight messaging in IoT environments, CoAP (Constrained Application Protocol) for resource-constrained devices, and various blockchain protocols for secure and transparent data exchange. Network topologies commonly employed include mesh networks, where devices communicate directly with each other without relying on a central hub, enhancing resilience and scalability. Star topologies, while simpler to manage, might be used where a central gateway aggregates data from multiple edge devices before transmitting it to the wider network. The choice of protocol and topology is often determined by factors such as network size, device capabilities, and security requirements. For instance, a large-scale sensor network might benefit from a mesh topology for redundancy, while a smaller, more controlled environment might favor a star topology for ease of management.
Data Management and Security Protocols at the Edge
Data management and security are critical concerns in decentralized networks. Given the distributed nature of edge devices, ensuring data integrity, availability, and confidentiality becomes especially challenging. Implementing robust security measures at the edge is crucial to prevent unauthorized access and data breaches. This includes using encryption protocols like TLS/SSL to secure communication channels, employing access control mechanisms to restrict access to sensitive data, and implementing regular software updates to patch vulnerabilities. Data management strategies might involve local data storage on edge devices, combined with data replication and synchronization across multiple edge nodes to ensure data availability and resilience against device failures. Furthermore, techniques like differential privacy can be implemented to protect sensitive data while still allowing for useful analytics. Consider the example of a healthcare application using edge computing: patient data needs stringent protection, necessitating strong encryption, access control, and potentially anonymization techniques at the edge before any aggregation or transmission occurs.
Hypothetical Architecture Diagram of a Decentralized Network Utilizing Edge Computing
Imagine a smart agriculture system. The architecture would consist of numerous sensor nodes (soil moisture, temperature, humidity sensors) deployed across the farm. These nodes would communicate with local edge gateways, potentially using a mesh network topology via LoRaWAN (Long Range Wide Area Network). These gateways would pre-process data, performing initial analysis (e.g., identifying anomalies) before transmitting summarized data to a central cloud server via a secure connection (e.g., using TLS/SSL). The cloud server would aggregate data from multiple farms, enabling large-scale analysis and insights. Data integrity and security are maintained through blockchain technology, with each data transaction recorded on a distributed ledger, ensuring transparency and preventing tampering. The system would also include a mechanism for data redundancy and recovery, potentially using edge device replication and cloud backups. This distributed architecture ensures resilience, as failure of a single edge gateway or sensor would not compromise the entire system. The data flow would be from sensors to edge gateways, then to the cloud server, with feedback loops allowing for automated control actions based on the analyzed data.
Applications and Use Cases: The Rise Of Edge Computing And Its Role In Decentralized Networks
Edge computing’s decentralized nature unlocks a wave of innovative applications across various sectors. By processing data closer to its source, it dramatically improves speed, efficiency, and security, particularly within decentralized networks. This shift empowers industries to build more responsive, resilient, and user-centric systems.
The marriage of edge computing and decentralized networks offers compelling advantages in terms of scalability, resilience, and data privacy. Let’s dive into some real-world examples illustrating this powerful synergy.
Real-World Applications Across Industries
The following examples showcase how edge computing enhances decentralized applications across diverse industries. The benefits extend beyond mere technological improvements; they directly impact user experience, operational efficiency, and even societal well-being.
- Finance: Fraud detection in real-time. Decentralized financial platforms can leverage edge computing to analyze transaction data at the point of origin, instantly flagging suspicious activity and preventing fraudulent transactions before they are processed. This drastically reduces financial losses and enhances the security of the entire system. The speed and localized processing ensure minimal latency, improving the user experience and building trust.
- Healthcare: Remote patient monitoring. Wearable health devices transmit vital patient data to nearby edge servers for immediate analysis. This allows for quicker detection of anomalies, enabling timely interventions and potentially life-saving actions. The decentralized nature protects patient data privacy by limiting the reliance on centralized servers, enhancing user autonomy and compliance with regulations.
- Internet of Things (IoT): Smart city infrastructure management. Sensors deployed across a city collect vast amounts of data related to traffic, pollution, and energy consumption. Edge computing processes this data locally, optimizing traffic flow, reducing pollution levels, and improving energy efficiency. The decentralized network ensures robustness against single points of failure, enhancing the resilience of the city’s infrastructure. This approach also minimizes latency, leading to more effective real-time responses to changing conditions.
Impact on Scalability and Resilience
Edge computing significantly enhances the scalability and resilience of decentralized applications. By distributing processing power and data storage across multiple edge nodes, the system can handle a massive increase in data volume and user traffic without compromising performance. This distributed architecture mitigates the risk of single points of failure; if one edge node fails, the system continues to function seamlessly, ensuring high availability and resilience. This is especially crucial for applications requiring continuous operation, such as critical infrastructure monitoring or real-time financial transactions. For example, a decentralized supply chain management system using edge computing can adapt smoothly to unexpected disruptions, like natural disasters or logistical bottlenecks.
Impact on Data Privacy and User Autonomy
Edge computing plays a pivotal role in safeguarding data privacy and enhancing user autonomy within decentralized systems. By processing sensitive data locally at the edge, the need to transmit large amounts of data to centralized servers is reduced. This minimizes the risk of data breaches and unauthorized access, bolstering user trust and compliance with data privacy regulations. Furthermore, the decentralized nature of the system empowers users with greater control over their own data, allowing them to decide which data is shared and how it is used. This aligns with the principles of data sovereignty and user agency, strengthening the ethical dimensions of decentralized applications. For instance, a healthcare application using edge computing can process patient data locally on a wearable device, minimizing the amount of data transmitted to the cloud and enhancing patient control over their health information.
Challenges and Future Trends
The rise of edge computing within decentralized networks, while promising, isn’t without its hurdles. Successfully integrating these two powerful technologies requires navigating a complex landscape of security concerns, management complexities, and interoperability issues. Overcoming these challenges will unlock the full potential of this transformative combination, paving the way for a truly decentralized and efficient digital future.
Implementing edge computing in a decentralized environment presents unique challenges that demand innovative solutions. The distributed nature of decentralized networks, coupled with the inherent security risks associated with edge devices, creates a complex problem that needs careful consideration. Furthermore, managing a vast network of edge nodes across geographically dispersed locations requires sophisticated tools and strategies. Finally, ensuring seamless interoperability between different edge devices and platforms remains a critical obstacle to widespread adoption.
Security Concerns in Decentralized Edge Computing
Security is paramount, especially when dealing with sensitive data processed at the edge of a decentralized network. Malicious actors could target vulnerable edge devices, compromising data integrity and confidentiality. For instance, a compromised IoT device on a smart city network could provide access to sensitive infrastructure data. Robust security protocols, including encryption, authentication, and access control mechanisms, are crucial. Furthermore, regular security audits and updates are essential to mitigate vulnerabilities. Blockchain technology, with its inherent security features, can play a significant role in securing edge devices and data transactions within decentralized networks. Implementing secure boot processes and employing hardware security modules (HSMs) can further enhance the security posture of edge devices.
Management and Orchestration of Decentralized Edge Networks
Managing a large-scale decentralized edge network is a complex undertaking. The sheer number of edge devices, their varying capabilities, and their geographical distribution pose significant management challenges. Centralized management approaches may not be suitable due to the decentralized nature of the network. Instead, decentralized or distributed management solutions are needed. This could involve using AI-powered tools for automated provisioning, monitoring, and scaling of edge resources. Self-organizing networks, where edge devices autonomously coordinate and manage themselves, represent a promising approach to this challenge. Employing containerization and orchestration technologies, similar to those used in cloud computing, can also streamline the management of decentralized edge deployments.
Interoperability and Standardization in Decentralized Edge
Interoperability between different edge devices, platforms, and protocols is essential for the seamless operation of a decentralized edge network. The absence of widely adopted standards can hinder the development and deployment of edge applications. Promoting open standards and developing interoperability frameworks are crucial steps towards addressing this challenge. Collaborative efforts between industry stakeholders, standardization bodies, and open-source communities can facilitate the creation of common protocols and interfaces. This would enable different edge devices and platforms to communicate and collaborate effectively, regardless of their vendor or technology.
Future Trends in Decentralized Edge Computing
The future of edge computing in decentralized networks is bright, with several exciting trends shaping its evolution. The increasing adoption of 5G and beyond 5G (B5G) networks will provide the necessary bandwidth and low latency connectivity to support the demanding requirements of edge applications. Artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning (ML) will play a crucial role in automating the management and optimization of decentralized edge networks. Blockchain technology will further enhance the security and trust in decentralized edge deployments.
Technological Advancements Shaping the Future
The future of edge computing in decentralized networks will be significantly influenced by several technological advancements:
- Advancements in AI and ML for Edge: More sophisticated AI and ML algorithms will enable autonomous edge devices to adapt to changing conditions and optimize resource utilization.
- Improved Network Technologies (5G/B5G, IoT): Faster and more reliable network connectivity will enable the deployment of more demanding edge applications.
- Blockchain Integration for Security and Trust: Blockchain technology will enhance the security and transparency of data transactions within decentralized edge networks.
- Serverless Computing at the Edge: Serverless architectures will further simplify the deployment and management of edge applications.
- Enhanced Edge Security Mechanisms: New security technologies will protect edge devices and data from increasingly sophisticated cyber threats.
Closure
Source: strapiapp.com
The convergence of edge computing and decentralized networks represents a paradigm shift in how we process and manage data. By bringing computation closer to the source, we unlock unprecedented levels of speed, security, and efficiency. While challenges remain in areas like security and interoperability, the potential benefits – from revolutionizing IoT applications to bolstering data privacy – are undeniable. The future is decentralized, and it’s happening at the edge.
