The Rise of Digital Health Technologies and Their Impact on Healthcare Systems is reshaping how we experience and deliver healthcare. From telehealth appointments bridging geographical divides to AI-powered diagnostics catching diseases earlier, the digital revolution is fundamentally altering the landscape. This isn’t just about convenience; it’s about accessibility, efficiency, and ultimately, better patient outcomes. We’ll delve into the transformative power of digital health, exploring its benefits, challenges, and the exciting future it promises.
This exploration will cover the spectrum of digital health innovations, from wearable health trackers providing personalized insights to electronic health records streamlining administrative processes. We’ll examine how these technologies are improving patient care, transforming healthcare systems, and even raising important ethical questions around data privacy and security. Get ready to see how the future of healthcare is being written, one digital byte at a time.
Defining Digital Health Technologies

Source: ryanjamesmankowski.com
The rise of digital health technologies is revolutionizing healthcare, offering unprecedented opportunities to improve patient care, streamline processes, and reduce costs. From remote consultations to AI-powered diagnostics, these tools are transforming how we interact with and manage our health. Understanding the scope and evolution of these technologies is crucial to appreciating their impact on healthcare systems worldwide.
Digital health technologies encompass a broad range of tools and applications that leverage digital technologies to improve health outcomes. This includes everything from simple health apps tracking daily steps to sophisticated AI systems analyzing medical images for early disease detection. The integration of these technologies is fundamentally changing the landscape of healthcare delivery, making it more accessible, efficient, and personalized.
Categorization of Digital Health Technologies
The diverse field of digital health can be categorized into several key areas, each playing a vital role in modern healthcare. The following table provides a structured overview:
| Category | Description | Examples | Impact on Healthcare |
|---|---|---|---|
| Telehealth | Remote delivery of healthcare services using technology. | Video conferencing for consultations, remote patient monitoring. | Improved access to care, especially in rural areas; reduced travel time and costs. |
| Wearable Sensors | Devices worn on the body that collect health data. | Smartwatches tracking heart rate and activity levels, continuous glucose monitors. | Real-time health monitoring, early detection of health issues, personalized health management. |
| Electronic Health Records (EHRs) | Digital versions of patients’ medical records. | Systems storing patient history, medications, allergies, and test results. | Improved data management, reduced medical errors, enhanced care coordination. |
| Health Apps | Mobile applications designed to support health and wellness. | Apps for medication reminders, mental health support, fitness tracking. | Increased patient engagement, personalized health information, improved adherence to treatment plans. |
| AI-driven Diagnostics | Artificial intelligence used to analyze medical data and assist in diagnosis. | AI algorithms analyzing medical images for early cancer detection, AI-powered diagnostic tools for various diseases. | Faster and more accurate diagnosis, improved efficiency, potential for earlier intervention. |
Evolution of Digital Health Technologies
The evolution of digital health has been marked by significant milestones and technological advancements. Early stages focused on basic data management with the introduction of EHRs. The advent of the internet enabled telehealth, expanding access to care. Subsequently, the proliferation of smartphones and wearable technology has driven the development of a vast ecosystem of health apps and remote patient monitoring devices. Recent breakthroughs in artificial intelligence and machine learning have further accelerated innovation, leading to AI-powered diagnostic tools and personalized medicine approaches. For example, the development of sophisticated algorithms for analyzing medical images has significantly improved the accuracy and speed of cancer detection, while AI-powered chatbots are increasingly used for providing basic medical advice and support. The continuous advancements in computing power, data storage, and connectivity are driving the ongoing evolution of this field, promising even more transformative applications in the future.
Impact on Patient Care
Digital health technologies are revolutionizing patient care, offering unprecedented opportunities to improve access, engagement, and ultimately, health outcomes. This transformation is driven by a convergence of factors, including advancements in mobile technology, increased internet penetration, and a growing demand for more convenient and personalized healthcare experiences. The impact is particularly profound for patients in remote areas and those managing chronic conditions, where traditional models often fall short.
The integration of digital health tools has significantly altered the landscape of patient care, leading to more efficient and effective healthcare delivery. This section will explore how digital health improves patient access, enhances engagement in self-management, and influences overall patient outcomes compared to traditional methods.
Improved Patient Access to Care in Remote and Underserved Areas
Digital health technologies are bridging geographical divides and overcoming access barriers for patients in remote or underserved communities. Telemedicine, for instance, allows specialists to consult with patients in geographically isolated areas, eliminating the need for extensive travel. Mobile health (mHealth) apps provide access to health information, appointment scheduling, and medication reminders, empowering patients to actively participate in their care regardless of location. Consider the example of a rural community with limited access to cardiologists. Through telehealth platforms, patients can receive consultations and monitoring from specialists hundreds of miles away, improving early diagnosis and treatment of heart conditions. Similarly, remote patient monitoring (RPM) devices, such as wearable sensors and home blood pressure monitors, transmit vital signs to healthcare providers, enabling proactive interventions and reducing the need for frequent hospital visits, particularly beneficial for patients with chronic conditions living far from medical centers.
Enhanced Patient Engagement and Self-Management of Chronic Conditions
Digital health plays a crucial role in empowering patients to actively manage their health, especially those with chronic conditions. Patient portals allow patients to access their medical records, communicate with their providers, and schedule appointments online, fostering a sense of ownership and control over their care. Furthermore, mHealth apps provide personalized reminders for medication adherence, track vital signs, and offer educational resources, enabling patients to better understand their conditions and actively participate in their treatment plans.
- Medication Adherence Apps: These apps send reminders and track medication intake, improving adherence rates for patients with conditions like hypertension or diabetes.
- Diabetes Management Apps: These apps allow patients to log their blood glucose levels, track their diet and exercise, and receive personalized feedback and support.
- Mental Health Apps: These apps provide tools for stress management, cognitive behavioral therapy (CBT) exercises, and connect users with mental health professionals, expanding access to care.
These tools promote self-efficacy and improve patient outcomes by encouraging consistent engagement in self-care activities. The result is better disease management, reduced hospital readmissions, and improved quality of life.
Impact of Telehealth on Patient Outcomes Compared to Traditional In-Person Care
Numerous studies have demonstrated the effectiveness of telehealth in improving patient outcomes, often comparable to or even exceeding those achieved through traditional in-person care. In many cases, telehealth offers increased convenience and accessibility, leading to improved adherence to treatment plans and better overall health management. For example, studies have shown that telehealth interventions for chronic conditions like diabetes and heart failure can lead to significant reductions in hospitalizations and emergency room visits. While telehealth may not be suitable for all conditions requiring hands-on physical examination, its effectiveness in managing many chronic diseases is well-documented, making it a valuable tool in enhancing healthcare delivery and improving patient outcomes. The convenience and reduced travel time associated with telehealth can also lead to improved patient satisfaction and engagement in care.
Transformation of Healthcare Systems
Source: silvertouch.com
Digital health technologies are revolutionizing healthcare, moving beyond simply improving patient care to fundamentally reshaping the very structure and function of healthcare systems. This transformation isn’t just about shiny new gadgets; it’s about streamlining processes, improving efficiency, and ultimately, making healthcare more accessible and affordable. The impact is far-reaching, affecting everything from administrative tasks to the delivery of care itself.
The integration of digital tools is streamlining administrative tasks, reducing costs, and freeing up valuable time for healthcare professionals to focus on what matters most: patient care. This shift is leading to a more efficient and responsive healthcare system, better equipped to handle the increasing demands of a growing and aging population.
Streamlining Administrative Processes, The Rise of Digital Health Technologies and Their Impact on Healthcare Systems
Digital health technologies offer significant opportunities to streamline the often-cumbersome administrative processes within healthcare systems. This leads to increased efficiency, reduced costs, and improved patient experience.
- Electronic Health Records (EHRs): EHRs replace paper-based systems, allowing for easier access to patient information, improved care coordination, and reduced medical errors. Imagine a scenario where a doctor can instantly access a patient’s complete medical history, including allergies and past treatments, from any location with internet access – a huge improvement over searching through physical files.
- Automated Appointment Scheduling and Reminders: Online appointment booking and automated reminders reduce no-shows and improve scheduling efficiency. This frees up administrative staff to focus on other tasks, while patients benefit from a more convenient experience.
- Automated Billing and Claims Processing: Digital systems automate billing and claims processing, reducing delays and administrative overhead. This translates to faster reimbursements for providers and less hassle for patients.
- Telehealth Platforms for Administrative Tasks: Remote consultations and administrative tasks, such as virtual check-ins, can be managed through telehealth platforms. This reduces the need for in-person visits, saving time and resources for both patients and providers.
Challenges and Opportunities in Integrating Digital Health Technologies
While the potential benefits are substantial, integrating digital health technologies into existing healthcare infrastructure presents significant challenges and opportunities. Successful implementation requires careful planning, investment, and a commitment to ongoing adaptation.
Challenges include the high initial investment costs of new technologies, the need for robust cybersecurity measures to protect sensitive patient data, the potential for widening the digital divide among patients with limited access to technology, and the need for staff training and support to ensure effective adoption. Furthermore, interoperability issues between different digital health systems can create significant hurdles.
Opportunities lie in increased efficiency, improved patient outcomes, reduced costs, and enhanced access to care, particularly in underserved areas. The potential for data-driven insights to improve healthcare delivery and research is also significant. The key is to address the challenges proactively and strategically to fully realize the transformative potential of digital health.
Hypothetical Scenario: A Rural Hospital’s Digital Transformation
Consider a rural hospital struggling with limited resources and staffing shortages. Implementing a fully integrated digital health system could dramatically improve its capabilities.
This system would include EHRs allowing specialists in distant urban centers to remotely consult on complex cases. Telehealth would enable patients to access specialists without long and expensive trips. Automated appointment scheduling would optimize limited staff time, and remote patient monitoring would allow for proactive care management of chronic conditions. Automated billing and claims processing would improve cash flow. The result would be improved patient care, increased efficiency, and a more sustainable and resilient healthcare system for the rural community, bridging the gap in access to specialized care often experienced in remote areas. This is not just a hypothetical scenario; many rural hospitals are already seeing similar positive impacts from strategic digital health investments.
Data Security and Privacy Concerns
The digital revolution in healthcare, while promising incredible advancements, introduces a Pandora’s Box of ethical dilemmas, particularly concerning patient data. The sheer volume of sensitive information collected, stored, and transmitted – from medical records and genetic data to lifestyle choices and wearable device readings – necessitates a robust and comprehensive approach to data security and privacy. The potential for breaches, misuse, and unauthorized access is a significant hurdle that must be addressed to ensure public trust and the ethical deployment of digital health technologies.
The ethical implications of utilizing patient data in digital health applications are multifaceted. While data aggregation can lead to groundbreaking research and personalized treatments, the potential for discrimination, stigmatization, and exploitation looms large. For example, an insurance company accessing a patient’s genetic predisposition to a specific disease could lead to discriminatory pricing practices. Similarly, unauthorized access to sensitive mental health information could have devastating consequences for an individual’s personal and professional life. Balancing the benefits of data-driven healthcare with the imperative to protect individual rights is a crucial challenge for policymakers, developers, and healthcare providers alike.
Data Security Measures in Digital Health Systems
Protecting patient information requires a multi-layered approach. Various security measures are employed, each with its strengths and weaknesses. The following table compares some common methods:
| Security Measure | Description | Advantages | Disadvantages |
|---|---|---|---|
| Encryption | Converting data into an unreadable format, requiring a decryption key for access. | Strong protection against unauthorized access; protects data both in transit and at rest. | Can be computationally expensive; requires careful key management to avoid vulnerabilities. |
| Access Control | Restricting access to data based on user roles and permissions. | Limits access to authorized personnel only; reduces the risk of accidental or malicious data exposure. | Requires careful planning and implementation; can be complex to manage in large systems. |
| Data Anonymization/De-identification | Removing or altering identifying information from data sets. | Facilitates research and data sharing while protecting patient privacy. | Can be difficult to achieve complete anonymity; residual identifying information may remain. |
| Intrusion Detection/Prevention Systems | Monitoring network traffic and system activity for suspicious behavior. | Detects and prevents unauthorized access attempts; provides real-time alerts. | Can generate false positives; requires ongoing maintenance and updates. |
Best Practices for Ensuring Data Security and Patient Privacy
A proactive and comprehensive approach to data security and privacy is crucial. Several best practices can significantly reduce the risk of breaches and misuse:
Implementing robust security measures, including encryption, access controls, and intrusion detection systems, is paramount. Regular security audits and penetration testing should be conducted to identify vulnerabilities. Furthermore, staff training on data security protocols and ethical considerations is essential. Finally, transparent data governance policies, including clear guidelines on data collection, storage, use, and disposal, are vital for building trust and complying with regulations like HIPAA (in the US) or GDPR (in Europe). These policies should be easily accessible and understandable to patients, fostering a culture of accountability and transparency.
The Future of Digital Health
The digital revolution in healthcare is far from over. We’re only scratching the surface of what’s possible. The next decade promises a breathtaking acceleration in innovation, transforming how we prevent, diagnose, and treat illnesses, fundamentally reshaping the healthcare landscape. This isn’t just about incremental improvements; it’s a paradigm shift driven by converging technologies and a growing demand for more accessible, efficient, and personalized care.
The future of digital health hinges on several key technological advancements and their synergistic impact. We’re moving beyond simply digitizing existing processes; we’re creating entirely new models of care, enabled by sophisticated data analysis, AI-powered diagnostics, and seamless integration of devices and platforms.
The boom in digital health tech is revolutionizing healthcare, creating both amazing opportunities and serious vulnerabilities. Protecting this sensitive data requires robust security measures, and that’s where AI steps in; learn more about its crucial role in The Role of Artificial Intelligence in Fraud Prevention to understand how it safeguards the digital health revolution. Ultimately, AI-powered fraud prevention is key to ensuring the long-term success and trustworthiness of digital healthcare.
Artificial Intelligence and Machine Learning in Diagnostics and Treatment
AI and machine learning are poised to revolutionize healthcare diagnostics and treatment. Imagine algorithms that can analyze medical images with superhuman accuracy, detecting subtle signs of disease long before they become clinically apparent. This is already happening. AI-powered systems are being used to analyze mammograms, CT scans, and pathology slides, improving the speed and accuracy of diagnosis for cancers and other diseases. Furthermore, AI is assisting in drug discovery, personalizing treatment plans based on individual patient data, and even predicting patient outcomes, allowing for proactive interventions. For instance, AI algorithms are being trained on vast datasets of patient records to identify individuals at high risk of developing heart failure, enabling early preventative measures. This leads to better patient outcomes and reduced healthcare costs. The integration of AI and machine learning is not merely an enhancement; it’s a fundamental transformation of the diagnostic and treatment process.
Emerging Technologies and Their Potential Impact
Beyond AI, several other emerging technologies are poised to reshape digital health. The Internet of Medical Things (IoMT) – the network of connected medical devices – will generate massive amounts of real-time patient data, providing continuous monitoring and enabling proactive interventions. Wearable sensors, implantable devices, and smart home technology will track vital signs, activity levels, and other health metrics, allowing for personalized health management and early detection of potential problems. Blockchain technology can enhance data security and privacy, creating a more trustworthy and transparent healthcare ecosystem. Telemedicine, already experiencing significant growth, will continue to expand, making healthcare more accessible, especially in remote areas. The combination of these technologies will create a holistic and interconnected healthcare ecosystem. For example, a patient with a chronic condition might use a wearable sensor to monitor their blood sugar levels, which are then transmitted to their doctor via a secure platform, triggering an alert if their levels become dangerously high. This proactive approach allows for timely intervention and prevents serious complications.
Projected Development and Adoption of Key Digital Health Innovations (2024-2034)
Predicting the future is always tricky, but based on current trends and technological advancements, we can project a timeline for the adoption of key digital health innovations over the next decade.
| Year | Innovation | Projected Development/Adoption |
|---|---|---|
| 2024-2026 | Widespread adoption of AI-powered diagnostic tools in radiology and pathology | Increased accuracy and efficiency in diagnosis, leading to earlier detection of diseases. Examples include wider implementation of AI in mammogram analysis and automated pathology slide review. |
| 2027-2029 | Expansion of IoMT and personalized medicine | Continuous patient monitoring using wearable sensors and implantable devices becomes more commonplace, leading to proactive interventions and personalized treatment plans. This includes wider availability of continuous glucose monitors and remote patient monitoring systems. |
| 2030-2034 | Mature integration of AI in treatment planning and drug discovery | AI algorithms become integral to developing personalized treatment plans and accelerating drug discovery processes. Examples include AI-driven clinical trial design and the development of targeted therapies based on individual patient genomics. |
Economic and Societal Impacts: The Rise Of Digital Health Technologies And Their Impact On Healthcare Systems
The rise of digital health technologies presents a complex interplay of economic and societal consequences. While initial investments can be substantial, the long-term potential for cost savings and improved health outcomes is significant. Furthermore, the increased accessibility afforded by digital health tools has the power to reshape healthcare equity, though careful consideration of potential disparities is crucial.
The economic implications of widespread digital health adoption are multifaceted. On one hand, there are substantial upfront costs associated with developing, implementing, and maintaining digital health infrastructure, including software, hardware, training, and cybersecurity measures. However, these costs are often offset by potential long-term savings. For instance, telehealth consultations can reduce travel expenses for both patients and healthcare providers, while remote patient monitoring can prevent costly hospital readmissions by allowing for early intervention. Improved efficiency through automation and data analysis can also lead to significant cost reductions in administrative tasks and resource allocation. The overall economic impact hinges on a delicate balance between initial investment and the realization of long-term benefits.
Cost Savings and Efficiency Gains in Healthcare
Digital health technologies offer several avenues for cost reduction and increased efficiency within healthcare systems. Telemedicine, for example, drastically reduces travel time and costs for patients, especially those in rural or underserved areas. Remote patient monitoring systems enable proactive health management, minimizing the need for expensive emergency room visits and hospitalizations. Automated administrative tasks, such as appointment scheduling and billing, free up healthcare professionals to focus on patient care, boosting overall productivity. Consider the example of a large hospital system implementing a comprehensive electronic health record (EHR) system. While the initial investment might be considerable, the long-term savings from reduced paperwork, improved medication management, and decreased medical errors can significantly outweigh the initial expense. This leads to a more efficient use of resources and ultimately, a reduction in healthcare costs.
Improved Health Equity and Accessibility
Increased access to healthcare through digital means holds immense potential for improving health equity and accessibility, particularly for underserved populations. Telehealth platforms can bridge geographical barriers, connecting patients in remote areas with specialists who might otherwise be inaccessible. Mobile health (mHealth) applications can provide personalized health information and support, empowering individuals to take control of their health. Digital tools can also facilitate culturally sensitive care by providing multilingual resources and connecting patients with providers who understand their cultural background. However, it’s crucial to acknowledge that digital health technologies can exacerbate existing health disparities if not implemented thoughtfully. Unequal access to technology, digital literacy, and reliable internet connectivity can create barriers for certain populations. Therefore, strategies to address these disparities, such as providing subsidized internet access or digital literacy training, are essential to ensure equitable access to the benefits of digital health.
Visual Representation of Economic and Social Benefits
Imagine a two-sided bar graph. On one side, labeled “Costs,” shorter bars represent the initial investment in digital health infrastructure (software, hardware, training). Longer bars on the “Savings” side illustrate the cost reductions from reduced hospital readmissions, fewer emergency room visits, decreased administrative costs, and increased efficiency. Beneath the graph, a map of a country is shown. Darker shaded areas represent regions with limited access to healthcare, while lighter shaded areas represent regions with greater access. Overlaying this map are icons representing telehealth access points, mHealth applications usage, and digital literacy programs. The contrast between the darker and lighter areas demonstrates how digital health technologies can bridge geographical disparities and improve access to care. The overall visual conveys the message that while there are initial investment costs, the long-term economic and societal benefits – particularly in terms of improved health equity and accessibility – far outweigh the expenses.
Conclusion
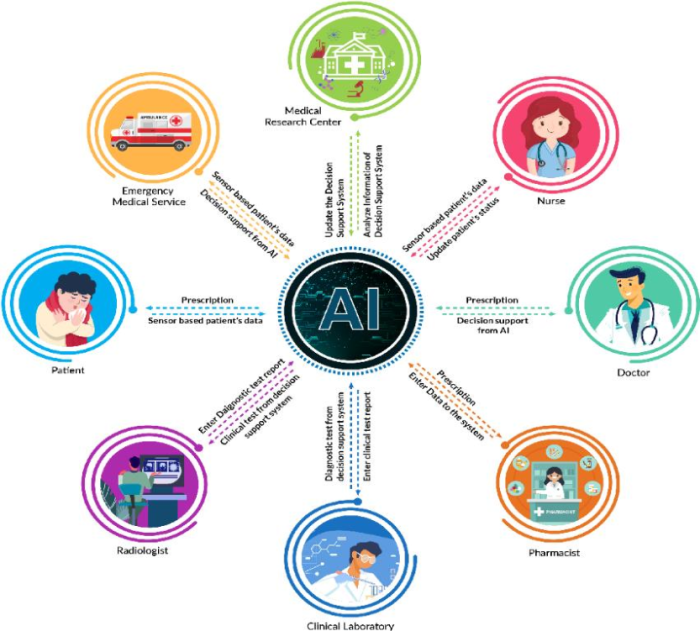
Source: researchgate.net
The rise of digital health technologies isn’t just a trend; it’s a fundamental shift in how healthcare is delivered and experienced. While challenges remain—particularly regarding data security and equitable access—the potential benefits are undeniable. From improving patient engagement and access to care in underserved areas to streamlining administrative processes and fostering earlier disease detection, digital health is poised to revolutionize the industry. As we move forward, navigating the ethical considerations and ensuring equitable access will be crucial to unlocking the full potential of this transformative force. The future of healthcare is undeniably digital, and the journey promises to be both exciting and transformative.
