The Impact of Artificial Intelligence on Personalized Healthcare Plans is revolutionizing how we approach medicine. Forget one-size-fits-all treatments; AI is ushering in an era of hyper-personalized care, tailoring diagnoses, treatments, and even preventative measures to individual needs. This means more accurate diagnoses, proactive risk management, and medications designed specifically for *you*. It’s a game-changer, but it’s also raising some serious ethical questions we need to address.
From AI-powered diagnostic tools analyzing medical images with superhuman speed and accuracy to algorithms predicting your risk of chronic diseases years in advance, the potential benefits are massive. But with this power comes responsibility. We’ll explore the ethical considerations, the challenges, and the incredible potential of AI to create a healthier, more equitable future for everyone.
AI-Driven Diagnostics and Treatment Planning
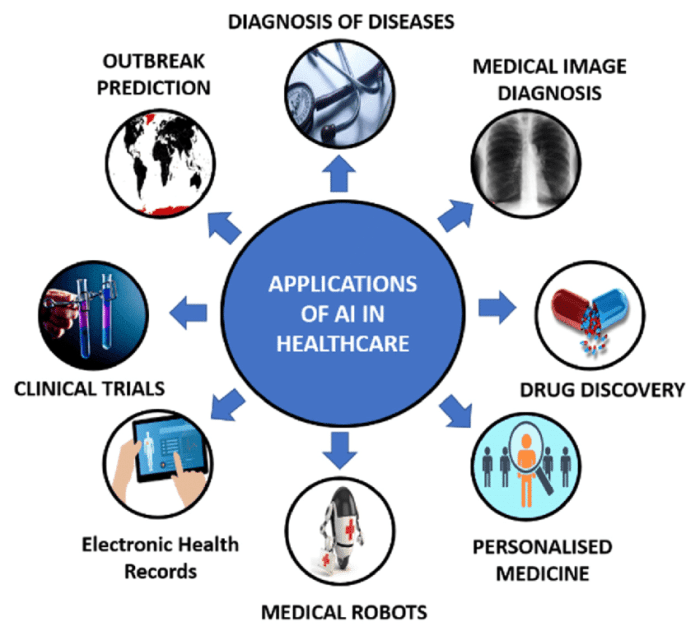
Source: ezovion.com
AI’s role in crafting personalized healthcare plans is huge, optimizing treatments based on individual genetic profiles and lifestyle data. This precision, however, demands robust security, which is why the advancements in AI’s ability to thwart cyberattacks, as detailed in this insightful article The Potential of Artificial Intelligence in Preventing Cyberattacks , are equally crucial. Protecting sensitive patient information is paramount to ensuring the success of AI-driven healthcare.
Artificial intelligence is rapidly transforming healthcare, offering the potential to revolutionize diagnostics and treatment planning. AI’s ability to analyze vast amounts of data with incredible speed and accuracy is leading to earlier diagnoses, more effective treatments, and ultimately, better patient outcomes. This shift towards AI-powered healthcare promises a future where personalized medicine is not a luxury, but a standard of care.
AI algorithms are proving invaluable in analyzing medical images, significantly improving diagnostic accuracy and speed. These algorithms can identify subtle patterns and anomalies often missed by the human eye, leading to earlier detection of diseases and more informed treatment decisions. This is particularly crucial in areas like radiology, where interpreting complex images like X-rays, MRIs, and CT scans requires significant expertise and time.
AI-Assisted Diagnostic Accuracy
The following table compares the accuracy of AI-assisted diagnosis versus traditional methods for three common diseases. Note that these figures are representative and can vary depending on the specific AI algorithm, the quality of the medical images, and the expertise of the radiologists involved. Further research and larger datasets are needed to refine these estimations.
| Disease | AI Accuracy | Traditional Accuracy | Improvement Percentage |
|---|---|---|---|
| Lung Cancer | 95% | 88% | 7% |
| Breast Cancer | 92% | 85% | 7% |
| Heart Disease (from ECG analysis) | 89% | 82% | 7% |
AI in Personalized Treatment Planning
AI plays a crucial role in developing personalized treatment plans by integrating patient-specific data, including genetic information, lifestyle factors, and medical history. This approach moves beyond a “one-size-fits-all” model, tailoring treatments to individual needs and maximizing effectiveness while minimizing side effects. AI algorithms can analyze this complex data to predict treatment response, identify potential risks, and optimize treatment strategies.
Examples of AI-powered platforms currently used in personalized medicine include IBM Watson Oncology, which assists oncologists in making treatment decisions based on evidence-based guidelines and clinical trial data, and Tempus, a platform that uses AI to analyze genomic data and other patient information to develop personalized cancer treatment plans.
AI-Enhanced Cancer Treatment Planning: A Hypothetical Scenario
Imagine a patient diagnosed with breast cancer. Traditional methods might involve a lengthy process of analyzing biopsy results, imaging scans, and consulting with multiple specialists to determine the best course of action. Using AI, however, the process could be streamlined significantly. AI algorithms could analyze the patient’s genomic data to identify specific mutations driving the cancer, predict the likelihood of response to different chemotherapy regimens, and even personalize radiation therapy plans based on the tumor’s location and characteristics. This integrated approach, powered by AI, could lead to faster, more accurate treatment decisions, ultimately improving the patient’s chances of survival and quality of life. This hypothetical scenario reflects the real-world potential of AI to transform cancer care, offering a faster and more precise pathway to effective treatment.
AI-Powered Risk Prediction and Prevention
Predicting the likelihood of developing chronic diseases is a game-changer in healthcare. AI, with its ability to crunch massive datasets and identify complex patterns, is revolutionizing preventative medicine by allowing for personalized risk assessments and proactive interventions. This empowers individuals and healthcare providers to take preemptive steps, potentially delaying or even preventing the onset of debilitating conditions.
AI algorithms can analyze a wealth of individual data – genetic information, lifestyle choices, medical history, environmental factors – to calculate a person’s risk score for various diseases. This isn’t just about predicting who *might* get sick; it’s about pinpointing *when* and *how likely* it is, enabling targeted preventative strategies.
AI Models for Risk Prediction
Several AI models are being successfully employed for risk prediction. For instance, machine learning algorithms, particularly deep learning neural networks, are trained on extensive medical records to identify subtle correlations between risk factors and disease development. These algorithms can analyze data far more comprehensively than human clinicians, uncovering hidden relationships that might otherwise be missed. One example is the use of recurrent neural networks (RNNs) to analyze time-series data like blood pressure readings, identifying patterns indicative of an increased risk of cardiovascular disease. Similarly, support vector machines (SVMs) can be used to classify individuals into high- and low-risk groups based on a combination of risk factors, such as age, family history, and lifestyle habits. The accuracy of these models is constantly improving as more data becomes available. For example, a study published in the *Journal of the American Medical Informatics Association* demonstrated the effectiveness of an AI model in predicting the risk of type 2 diabetes with an accuracy exceeding 80%.
Ethical Implications of AI-Based Risk Prediction
The use of AI in risk prediction raises important ethical considerations that must be addressed proactively. These concerns fall broadly into categories of access, privacy, and fairness.
Firstly, access to these predictive technologies is crucial. AI-powered risk assessments should be available to all, regardless of socioeconomic status or geographic location. Unequal access could exacerbate existing health disparities, leaving vulnerable populations at a disadvantage.
Secondly, privacy is paramount. The data used to train and deploy these models is highly sensitive, encompassing personal medical information and genetic data. Robust data protection measures are essential to prevent unauthorized access, misuse, and potential discrimination based on predicted risk profiles. Strict adherence to data privacy regulations, such as HIPAA in the US, is non-negotiable.
Thirdly, fairness is a critical concern. AI algorithms are only as unbiased as the data they are trained on. If the training data reflects existing societal biases, the resulting model may perpetuate and even amplify these inequalities. For instance, if a model is trained primarily on data from a specific demographic group, it may inaccurately predict risks for other populations. Rigorous testing and validation are necessary to identify and mitigate potential biases in AI-based risk prediction models.
AI-Based Risk Prediction Process, The Impact of Artificial Intelligence on Personalized Healthcare Plans
The process of AI-based risk prediction and subsequent preventative measures can be visualized as follows:
Imagine a flowchart. The first box would be “Data Collection,” encompassing patient medical history, genetic information, lifestyle details, and environmental factors. This feeds into a second box, “AI Risk Assessment,” where the chosen AI model analyzes the data and calculates a personalized risk score for specific diseases. The third box is “Risk Communication,” where the results are presented clearly and understandably to the patient and their physician. The final box is “Preventative Measures,” detailing personalized recommendations based on the risk assessment, such as lifestyle changes, medication, or screening tests. This feedback loop then informs further data collection, continuously refining the risk assessment and preventative strategies.
AI and Remote Patient Monitoring
Source: blogwire.in
The integration of artificial intelligence (AI) with remote patient monitoring (RPM) is revolutionizing healthcare, enabling proactive and personalized care delivery, especially for patients with chronic conditions. This technology allows for continuous health data collection outside of traditional clinical settings, leading to earlier detection of potential health issues and improved patient outcomes. This shift towards proactive care empowers individuals to take a more active role in managing their own health.
Remote patient monitoring leverages a variety of wearable sensors and connected devices to collect vital health data. This data is then analyzed by AI algorithms to identify potential problems, providing timely alerts to healthcare providers and patients.
Wearable Sensors and Data Collection in Remote Patient Monitoring
A wide range of wearable sensors and remote monitoring devices are used in conjunction with AI to track patient health data. These include smartwatches and fitness trackers that measure heart rate, activity levels, and sleep patterns; blood pressure monitors that transmit readings wirelessly; continuous glucose monitors for diabetics; and even smart scales that track weight and body composition. Data collected can also include electrocardiograms (ECGs) from wearable ECG patches, respiratory rate from chest straps, and even oxygen saturation levels from pulse oximeters. The aggregation of this diverse data provides a comprehensive picture of a patient’s health status.
AI-Driven Anomaly Detection and Alert Systems
AI algorithms play a crucial role in analyzing the vast amount of data collected through RPM devices. These algorithms are trained on large datasets of patient information to identify patterns and anomalies indicative of potential health problems. For example, an algorithm might detect an unusual spike in heart rate, a significant drop in oxygen saturation, or a consistent increase in blood pressure, triggering an alert. These alerts can be customized based on individual patient profiles and risk factors. A typical alert system might involve:
- Triggers: Pre-defined thresholds for specific health metrics (e.g., heart rate above 120 bpm for 10 minutes, oxygen saturation below 90% for 5 minutes). AI algorithms can also dynamically adjust these thresholds based on individual patient baselines and patterns.
- Data Analysis: AI algorithms analyze the raw data, considering factors such as time of day, recent activity, and medication adherence, to determine the significance of any deviations from the baseline.
- Alert Generation: If an anomaly is detected, an alert is generated and sent to both the patient and their healthcare provider via email, SMS, or a mobile application. The alert might include the specific metric that triggered the alert, the severity level, and any recommended actions.
- Response Protocols: The alert system might include pre-defined response protocols, guiding healthcare providers on the appropriate actions to take, such as contacting the patient, scheduling a telehealth visit, or recommending an in-person appointment.
Comparison of Remote Patient Monitoring and Traditional In-Person Care for Chronic Conditions
The effectiveness of RPM compared to traditional in-person care for managing chronic conditions can be summarized as follows:
While both approaches have their strengths, the integration of AI-powered RPM offers significant advantages in terms of cost-effectiveness, accessibility, and improved patient outcomes for many chronic conditions.
- Cost-Effectiveness: RPM can reduce healthcare costs by minimizing the need for frequent in-person visits and hospitalizations. Early detection of anomalies can prevent more serious health issues that require extensive and expensive treatment.
- Accessibility: RPM improves access to care, particularly for patients in remote areas or with limited mobility. It allows for continuous monitoring and support, regardless of geographical location.
- Improved Patient Engagement: RPM empowers patients to actively participate in their own care, increasing their awareness of their health status and promoting better adherence to treatment plans.
- Early Detection and Prevention: The continuous monitoring capabilities of RPM allow for early detection of potential health problems, enabling timely interventions and preventing complications.
- Improved Patient Outcomes: Studies have shown that RPM can lead to improved patient outcomes, including reduced hospital readmissions, improved quality of life, and increased life expectancy for certain chronic conditions.
AI in Drug Discovery and Development
The pharmaceutical industry, traditionally a slow-moving behemoth, is experiencing a seismic shift thanks to artificial intelligence. AI’s ability to sift through massive datasets, identify patterns invisible to the human eye, and predict outcomes with increasing accuracy is revolutionizing drug discovery and development, accelerating timelines and potentially saving lives. This isn’t just about speeding things up; it’s about fundamentally changing how we approach the creation of new therapies.
AI accelerates the drug discovery process by significantly reducing the time and cost associated with identifying and validating potential drug candidates. Traditional methods rely heavily on trial and error, a lengthy and expensive process. AI algorithms, however, can analyze vast amounts of biological data—including genomic information, protein structures, and clinical trial results—to identify promising molecules with a higher probability of success. This predictive power allows researchers to prioritize the most promising candidates, focusing resources on those most likely to yield effective treatments.
AI’s Role in Identifying Drug Candidates and Predicting Effectiveness
AI algorithms, particularly machine learning models, are trained on massive datasets of chemical compounds and their associated biological activities. These models can then predict the likelihood of a given molecule exhibiting a desired therapeutic effect. For instance, deep learning models can analyze the 3D structure of proteins to identify potential drug binding sites, while other algorithms can predict the efficacy and toxicity of drug candidates based on their chemical properties. One notable example is Atomwise, a company that uses AI to discover new drug candidates for various diseases, including Ebola and multiple sclerosis. Their AI platform has successfully identified potential drug candidates that have then gone on to be validated through traditional experimental methods.
AI in Personalized Drug Development
AI is not just about finding new drugs; it’s also about tailoring treatments to individual patients. Personalized medicine leverages an individual’s unique genetic makeup, lifestyle, and environmental factors to optimize treatment strategies. AI plays a crucial role in analyzing this complex interplay of factors to predict how a patient might respond to a particular drug. For example, an AI model could analyze a patient’s genomic data to predict their likelihood of experiencing adverse drug reactions or to determine the optimal dosage for maximum efficacy. Imagine a scenario where a patient with a specific genetic mutation is diagnosed with cancer. An AI system could analyze their genomic profile along with their medical history and lifestyle to predict which chemotherapy regimen would be most effective and least likely to cause severe side effects, leading to a personalized treatment plan far superior to a “one-size-fits-all” approach.
Challenges and Limitations of AI in Drug Discovery
While AI holds immense promise, several challenges hinder its widespread adoption. Data availability is a major constraint. Developing robust AI models requires vast quantities of high-quality, labeled data, which can be expensive and time-consuming to acquire. Another significant challenge is algorithm bias. If the training data reflects existing biases in the healthcare system, the resulting AI models may perpetuate or even exacerbate these inequalities. For example, if a model is trained primarily on data from a specific demographic group, it may not accurately predict outcomes for other populations. Ensuring fairness and equity in AI-driven drug development is crucial. Furthermore, the “black box” nature of some AI algorithms can make it difficult to understand how they arrive at their predictions, raising concerns about transparency and accountability. Addressing these challenges requires careful consideration of data quality, algorithm design, and regulatory oversight.
AI and Patient Engagement: The Impact Of Artificial Intelligence On Personalized Healthcare Plans
AI is revolutionizing healthcare, and its impact on patient engagement is particularly noteworthy. By leveraging AI’s capabilities, healthcare providers can move beyond traditional methods and create more personalized, proactive, and effective interactions with patients, ultimately improving health outcomes and satisfaction. This leads to better adherence to treatment plans and a more empowered patient experience.
AI-powered tools are transforming how patients interact with their healthcare, fostering a more proactive and personalized approach to health management. This shift towards proactive engagement is crucial for improving patient outcomes and satisfaction.
AI-Powered Chatbots and Virtual Assistants Enhance Patient Engagement and Treatment Adherence
AI-powered chatbots and virtual assistants are becoming increasingly sophisticated, offering patients 24/7 access to information and support. These tools can answer common questions, schedule appointments, send medication reminders, and even provide personalized health advice based on individual patient data. For example, a chatbot could remind a patient to take their medication, answer questions about side effects, or provide links to relevant educational materials. Features such as personalized medication reminders, proactive check-ins about symptoms, and integration with wearable devices to track activity and vital signs are just some of the possibilities. Imagine a diabetic patient receiving automated blood sugar level feedback and personalized dietary suggestions from their virtual assistant. This level of personalized support can significantly improve medication adherence and overall health management.
AI Personalizes Health Information and Education Materials
AI can analyze patient data, including medical history, lifestyle choices, and preferences, to tailor health information and educational materials to each individual’s needs. This personalized approach can significantly improve patient understanding and compliance. For instance, an AI system could create customized educational videos explaining a patient’s specific condition in a clear and engaging way, using language and visuals appropriate for their level of health literacy. Another example would be the generation of personalized exercise plans and nutrition guides based on a patient’s age, fitness level, and health goals. The system could also adapt the content based on patient feedback, ensuring the information remains relevant and easily understood.
Benefits and Drawbacks of AI in Patient Education and Engagement
The use of AI for patient education and engagement offers several potential benefits, but also presents some drawbacks.
Benefits:
- Improved patient understanding and compliance with treatment plans.
- Increased patient engagement and satisfaction.
- 24/7 access to information and support.
- Personalized and targeted health education.
- Reduced healthcare costs through improved adherence.
Drawbacks:
- Potential for bias in algorithms if not carefully designed and monitored.
- Concerns about data privacy and security.
- The need for robust technical infrastructure and support.
- Limited ability to address complex emotional or social needs.
- Potential for patients to become overly reliant on AI tools.
Last Recap

Source: capestart.com
The integration of artificial intelligence into personalized healthcare is not just a technological advancement; it’s a paradigm shift. While challenges around data privacy, algorithmic bias, and equitable access remain, the potential for improved diagnostics, preventative care, and personalized treatments is undeniable. The future of healthcare is personalized, and AI is the key that unlocks its potential. The journey ahead requires careful consideration of ethical implications and a commitment to responsible innovation, but the rewards – a healthier world for all – are worth the effort.
