The Growth of E-commerce and Its Technological Drivers is a wild ride! From its humble beginnings, e-commerce has exploded, fueled by innovations that have completely reshaped how we shop. Think dial-up internet to lightning-fast 5G, clunky websites to sleek mobile apps – it’s a story of constant evolution, driven by tech’s relentless march forward. This deep dive explores the key players, pivotal moments, and game-changing tech that made this digital revolution possible.
We’ll unpack the historical context, examining the hurdles early e-commerce faced and how brilliant minds overcame them. We’ll then zoom in on the tech titans – mobile technology, big data, AI, and more – that supercharged this growth. Get ready for a rollercoaster ride through payment gateways, logistics nightmares (and their solutions!), the power of social media, and a glimpse into the mind-blowing future of online shopping.
The Rise of E-commerce
E-commerce, the buying and selling of goods and services over the internet, has exploded from a niche activity to a dominant force in the global economy. Its journey, marked by technological leaps and evolving consumer behavior, is a fascinating case study in rapid technological adoption and societal shift. This section details the key milestones in this transformative journey, highlighting the limitations of the past and the capabilities of today’s sophisticated platforms.
A Historical Overview of E-commerce Development
The evolution of e-commerce can be broadly categorized into distinct phases, each characterized by specific technological advancements and market shifts. Early attempts faced significant hurdles, ranging from limited internet access and security concerns to a lack of consumer trust in online transactions. However, continuous innovation and improved infrastructure gradually eroded these barriers, paving the way for the ubiquitous e-commerce landscape we see today.
Key Milestones in E-commerce History, The Growth of E-commerce and Its Technological Drivers
The following table illustrates the key events, technological advancements, and their impact on the growth of e-commerce:
| Year | Key Event | Technological Advancements | Impact on E-commerce |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1979 | Michael Aldrich demonstrates the first online shopping system. | Early computer networks, dial-up modems. | Conceptual foundation laid; extremely limited reach. |
| 1990s | Early online marketplaces emerge (e.g., Pizza Hut online ordering). | Development of the World Wide Web, secure sockets layer (SSL) encryption. | Increased accessibility, initial trust building through secure transactions. |
| 1995 | Amazon launches, pioneering online retail. | Improved web browsers, increased internet penetration. | Significant expansion of online retail possibilities; established a new business model. |
| Late 1990s – Early 2000s | Dot-com boom and bust. | Rapid growth of internet infrastructure, emergence of e-payment systems (PayPal). | Rapid expansion followed by a period of consolidation and increased focus on sustainable business models. |
| 2000s – Present | Mobile commerce (m-commerce) takes off, social commerce emerges. | Smartphones, mobile internet access, social media platforms, improved logistics and delivery systems. | Massive expansion of reach and accessibility; personalized shopping experiences; integration of social media into purchasing behavior. |
| Present | Rise of AI-powered personalization, voice commerce, and augmented reality in e-commerce. | Artificial intelligence, machine learning, natural language processing, augmented reality technologies. | Highly personalized shopping experiences, enhanced customer service, new ways to interact with products before purchase. |
Early Limitations vs. Modern Capabilities
Early e-commerce platforms were severely limited by slow internet speeds, security vulnerabilities, and a lack of sophisticated payment gateways. Consumers were hesitant to share sensitive information online, and the overall shopping experience was often clunky and unreliable. In contrast, modern e-commerce platforms offer seamless user experiences, robust security measures, diverse payment options, and advanced features like personalized recommendations, detailed product information, and integrated customer support. The shift from dial-up connections to high-speed broadband and the widespread adoption of smartphones have dramatically increased accessibility and convenience. The integration of AI and machine learning has further enhanced personalization and efficiency, creating a vastly superior shopping experience compared to its early predecessors.
Technological Drivers Fueling E-commerce Growth
The meteoric rise of e-commerce isn’t just about convenience; it’s a testament to groundbreaking technological advancements. These innovations have not only streamlined the buying process but have also fundamentally reshaped how businesses connect with consumers, fostering unprecedented levels of personalization and efficiency. From the ubiquitous smartphone to the power of data analytics, several key technologies have fueled this explosive growth.
The Role of Mobile Technology in E-commerce
Mobile technology has completely revolutionized the e-commerce landscape. The sheer portability and accessibility of smartphones have transformed how consumers shop, making purchasing a seamless part of daily life. This shift has driven businesses to prioritize mobile-first strategies, resulting in optimized websites and dedicated mobile apps. The impact is undeniable; more purchases are now made via mobile devices than ever before.
- Mobile-optimized websites: Websites designed for easy navigation and quick loading times on smaller screens are crucial for a positive user experience. This includes features like simplified layouts, tappable buttons, and intuitive search functions. A poorly designed mobile website can lead to immediate cart abandonment.
- In-app purchases: Mobile apps offer a more personalized and integrated shopping experience. Features like saved payment information, order tracking, and push notifications for deals and sales directly impact consumer behavior, encouraging repeat purchases and brand loyalty. For example, the Amazon app’s one-click ordering and personalized recommendations have significantly contributed to its success.
- Mobile payment systems: Services like Apple Pay, Google Pay, and PayPal have streamlined the checkout process, making online transactions quicker and more secure. This reduction in friction significantly increases conversion rates and encourages impulse buys.
- Location-based services: Features utilizing GPS data allow e-commerce businesses to provide location-specific services such as delivery tracking in real-time or finding nearby stores for click-and-collect options. This level of transparency and convenience increases customer satisfaction and trust.
The Impact of Big Data Analytics on E-commerce
Big data analytics is the unsung hero of personalized e-commerce. By collecting and analyzing vast amounts of consumer data, businesses can gain unparalleled insights into customer preferences, purchasing habits, and overall behavior. This data-driven approach allows for highly targeted marketing campaigns and the creation of more personalized shopping experiences.
- Personalized recommendations: Algorithms analyze past purchases and browsing history to suggest relevant products, significantly increasing sales conversion rates. Think of Netflix’s recommendation engine; the same principles apply to e-commerce platforms, offering tailored product suggestions to individual users.
- Targeted advertising: By identifying specific customer segments based on demographics, interests, and online behavior, businesses can deliver highly targeted advertisements through various channels, maximizing the effectiveness of their marketing spend. This allows for efficient resource allocation and improved ROI.
- Improved customer experience: Data analysis can help identify areas for improvement in the customer journey, such as website usability issues or bottlenecks in the checkout process. Addressing these pain points enhances overall customer satisfaction and reduces cart abandonment rates. For example, analyzing bounce rates on specific product pages can pinpoint areas requiring better product descriptions or clearer imagery.
The Impact of Payment Gateways and Security

Source: slideteam.net
The meteoric rise of e-commerce wouldn’t have been possible without the parallel development of secure and reliable online payment systems. Consumer trust is paramount in the digital marketplace, and the evolution of payment gateways has been instrumental in fostering this trust, transforming online shopping from a risky venture into a commonplace activity. The ability to seamlessly and securely transfer funds online is the bedrock upon which the entire e-commerce ecosystem is built.
The evolution of secure online payment systems has been a journey marked by increasing sophistication and robust security measures. Early online payment systems were relatively rudimentary, vulnerable to various forms of fraud. The introduction of SSL/TLS encryption protocols significantly improved security by encrypting sensitive data transmitted between the customer’s browser and the merchant’s server. The development of 3D Secure (Verified by Visa, Mastercard SecureCode) added another layer of protection by requiring additional authentication from the cardholder, significantly reducing the risk of unauthorized transactions. Today, advancements like tokenization, where sensitive card details are replaced with unique tokens, further enhance security and reduce the risk of data breaches. This continuous evolution of security protocols has been vital in building and maintaining consumer confidence in online transactions.
Payment Gateway Technologies: A Comparison
Several prominent payment gateways cater to the diverse needs of e-commerce businesses. Each offers a unique blend of features, security protocols, and transaction fees, influencing their suitability for specific businesses and customer bases. Understanding these differences is crucial for merchants to optimize their online payment processing.
Security Features, Transaction Fees, and User Experience of Major Payment Gateways
| Feature | PayPal | Stripe | Apple Pay |
|---|---|---|---|
| Security Features | SSL/TLS encryption, fraud prevention tools, buyer and seller protection programs | SSL/TLS encryption, tokenization, fraud detection algorithms, PCI DSS compliance | Tokenization, biometric authentication (Touch ID, Face ID), device encryption |
| Transaction Fees | Varies depending on the plan and transaction type; generally higher fees for international transactions. | Varies depending on the plan and transaction type; typically lower fees than PayPal for domestic transactions. | Fees vary depending on the merchant’s agreement with Apple and the payment processor used; generally lower than PayPal and Stripe. |
| User Experience | Widely recognized and user-friendly interface; supports various payment methods. | Developer-friendly API; customizable checkout experience; integrates well with various e-commerce platforms. | Seamless and fast checkout experience for users with Apple devices; utilizes existing Apple ID credentials. |
E-commerce Logistics and Supply Chain Management
Source: magenest.com
The explosive growth of e-commerce has placed unprecedented pressure on logistics and supply chain management. Meeting consumer expectations for fast, affordable, and reliable delivery is no longer a luxury but a necessity for survival in the competitive online marketplace. This requires a sophisticated and adaptable system capable of handling everything from warehousing and inventory management to last-mile delivery and returns. The efficiency of this system directly impacts customer satisfaction, brand reputation, and ultimately, profitability.
E-commerce logistics presents unique challenges compared to traditional retail. The sheer volume of individual orders, the need for precise tracking and handling of diverse products, and the geographically dispersed nature of deliveries demand innovative solutions. Meeting these challenges involves optimizing every stage of the supply chain, from sourcing and manufacturing to storage, transportation, and final delivery. Failure to do so results in increased costs, delayed deliveries, and frustrated customers – all detrimental to a business’s bottom line.
Warehousing and Inventory Management in E-commerce
Efficient warehousing is the backbone of successful e-commerce logistics. This involves strategically locating warehouses to minimize shipping distances, implementing advanced inventory management systems to track stock levels in real-time, and optimizing warehouse layout to streamline order fulfillment. Modern warehouses utilize robotics and automation to automate tasks such as picking, packing, and sorting, significantly increasing efficiency and reducing human error. For instance, Amazon’s massive fulfillment centers employ robotic systems that move shelves to workers, drastically speeding up the picking process. This level of automation allows for the handling of a much larger volume of orders with greater speed and accuracy than traditional manual methods. Furthermore, sophisticated software systems predict demand and optimize inventory levels, minimizing storage costs and preventing stockouts.
Last-Mile Delivery Solutions
The last mile – the final leg of delivery from a distribution center to the customer’s doorstep – is often the most expensive and challenging part of the e-commerce logistics chain. Congestion, traffic, and the need for flexible delivery options (e.g., same-day, evening, or weekend delivery) create significant hurdles. Innovative solutions include the use of micro-fulfillment centers located closer to urban areas to reduce delivery times and costs, the expansion of delivery networks to include more delivery partners (like independent contractors), and the exploration of alternative delivery methods such as drone delivery. Companies like Zipline are already using drones to deliver medical supplies in developing countries, demonstrating the potential for wider application in e-commerce. While drone delivery faces regulatory hurdles, it promises to significantly reduce delivery times and costs in certain contexts.
Order Fulfillment Process Flowchart
The following flowchart depicts a typical e-commerce order fulfillment process:
[Imagine a flowchart here. The flowchart would begin with “Customer Places Order,” branching to “Order Received and Processed,” then to “Inventory Check,” then to “Order Picking and Packing,” then to “Shipping Label Generation,” then to “Dispatch to Carrier,” then to “Delivery to Customer,” and finally to “Order Complete.” There would be feedback loops for potential issues like “Out of Stock” leading back to “Inventory Check” and “Delivery Failure” leading back to “Dispatch to Carrier” for redelivery. The flowchart would visually represent the sequential steps and potential branching paths in the process.]
The Role of Social Media and Influencer Marketing
The rise of e-commerce has been inextricably linked to the explosive growth of social media. No longer a supplementary marketing channel, social media platforms have become integral to the entire e-commerce ecosystem, shaping consumer behavior, driving sales, and fundamentally altering how brands connect with their audiences. This integration isn’t just about advertising; it’s about building communities, fostering engagement, and creating seamless shopping experiences directly within the platforms themselves.
Social media’s impact on e-commerce is multifaceted. It provides businesses with unprecedented access to potential customers, allowing for targeted advertising campaigns and real-time engagement. The ability to track metrics, analyze user behavior, and adapt strategies accordingly offers a level of precision previously unimaginable. Furthermore, the rise of social commerce – the ability to buy products directly through platforms like Instagram and Facebook – has streamlined the purchasing process, making it quicker and more convenient for consumers.
The Impact of Influencer Marketing on E-commerce Sales and Brand Awareness
Influencer marketing, leveraging the reach and credibility of individuals with significant online followings, has become a cornerstone of successful e-commerce strategies. These influencers, ranging from mega-influencers with millions of followers to micro-influencers with highly engaged niche audiences, act as trusted advocates for brands, driving sales and enhancing brand perception. For example, a beauty brand partnering with a popular makeup artist on Instagram can see a significant surge in sales and website traffic as the influencer promotes their products to their dedicated audience. Similarly, a clothing brand collaborating with a fashion blogger can experience increased brand awareness and a boost in online sales through targeted promotions and affiliate links. The success of influencer marketing hinges on authenticity and a genuine connection between the influencer and their audience. A forced or inauthentic endorsement can be detrimental to a brand’s image.
Advantages and Disadvantages of Using Social Media for E-commerce
The decision to leverage social media for e-commerce requires careful consideration of both its benefits and drawbacks.
The advantages are numerous and compelling:
- Increased Brand Awareness and Reach: Social media allows brands to reach a vast audience beyond traditional marketing channels.
- Targeted Advertising: Sophisticated targeting options allow for precise audience segmentation, maximizing the effectiveness of advertising spend.
- Enhanced Customer Engagement: Direct interaction with customers through comments, messages, and live sessions fosters brand loyalty and valuable feedback.
- Cost-Effective Marketing: Compared to traditional advertising, social media marketing can be significantly more cost-effective, especially when leveraging organic reach.
- Improved Customer Service: Social media provides a platform for addressing customer inquiries and resolving issues promptly and publicly.
- Data-Driven Insights: Detailed analytics provide valuable insights into customer behavior, campaign performance, and overall marketing effectiveness.
However, it’s crucial to acknowledge the potential downsides:
- Negative Feedback and Brand Reputation Management: Negative comments and reviews can quickly spread, potentially damaging a brand’s reputation. Effective monitoring and response strategies are essential.
- Algorithm Changes and Reach Limitations: Social media algorithms are constantly evolving, impacting organic reach and potentially requiring increased advertising spend to maintain visibility.
- Time and Resource Commitment: Managing social media presence effectively requires a significant investment of time and resources for content creation, engagement, and community management.
- Competition: The highly competitive nature of social media requires consistent effort and innovation to stand out from the crowd.
- Measuring ROI: While analytics provide data, accurately measuring the return on investment (ROI) for social media marketing can be challenging.
Artificial Intelligence and Machine Learning in E-commerce
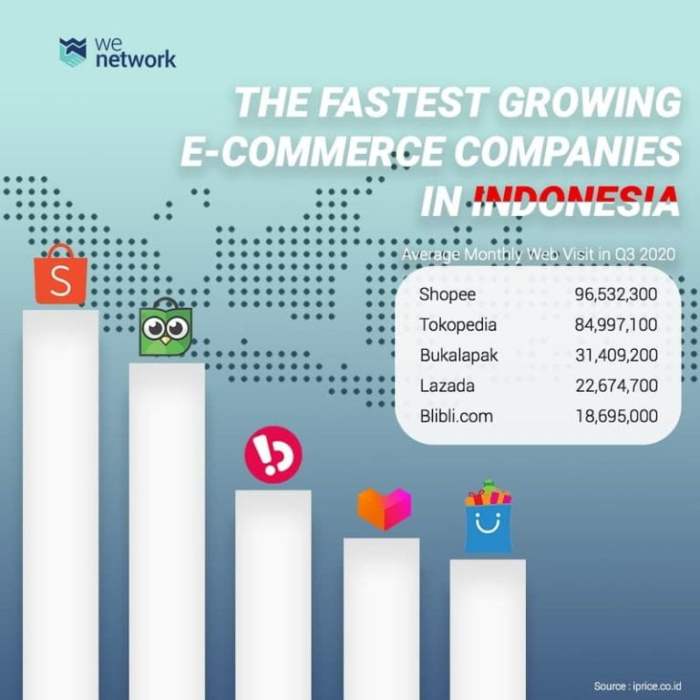
Source: wenetworkasia.com
The rise of e-commerce has been inextricably linked to advancements in technology, and arguably none has been more transformative than the integration of artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning (ML). These powerful tools are no longer futuristic fantasies; they’re actively shaping the customer experience and streamlining operations for businesses of all sizes, from startups to global giants. This section explores the diverse applications of AI and ML within the e-commerce landscape, highlighting both their benefits and the ethical considerations they raise.
AI and ML are revolutionizing e-commerce by automating tasks, personalizing experiences, and improving decision-making. This is achieved through sophisticated algorithms that analyze vast amounts of data to identify patterns, predict behavior, and optimize outcomes. The impact spans across various aspects of the online shopping journey, from the initial product discovery to post-purchase customer service.
Personalized Recommendations
Personalized recommendations are arguably the most visible application of AI in e-commerce. By analyzing browsing history, purchase patterns, and other user data, AI algorithms can suggest products that are highly relevant to individual customers. This significantly increases the likelihood of a purchase and enhances customer satisfaction. For example, Amazon’s recommendation engine, famously effective, uses a collaborative filtering approach, suggesting items frequently bought together or items similar to those previously purchased by the user. Netflix utilizes a similar system to suggest movies and TV shows based on viewing history and ratings. These systems aren’t simply suggesting random items; they’re leveraging complex algorithms to understand individual preferences and predict future behavior.
Fraud Detection
The increasing volume of online transactions makes fraud detection a critical concern for e-commerce businesses. AI and ML algorithms excel at identifying fraudulent activities by analyzing transactional data, identifying anomalies, and flagging suspicious patterns. These systems can analyze factors such as IP addresses, payment methods, shipping addresses, and purchase history to detect unusual activity and prevent fraudulent transactions. This not only protects businesses from financial losses but also enhances customer trust and security. For instance, PayPal employs AI-powered systems to detect and prevent fraudulent transactions in real-time, minimizing financial risks for both buyers and sellers.
AI-Powered Chatbots
AI-powered chatbots are transforming customer service in e-commerce. These virtual assistants can handle a wide range of customer inquiries, from order tracking and returns to product information and technical support. By providing instant responses and 24/7 availability, chatbots significantly improve customer satisfaction and reduce the burden on human customer service agents. Companies like Sephora and H&M utilize sophisticated chatbots that can understand natural language, providing a seamless and personalized interaction. These chatbots can also learn and improve over time, adapting to changing customer needs and providing increasingly accurate and helpful responses.
Ethical Considerations: Data Privacy and Algorithmic Bias
While AI and ML offer significant advantages, their use in e-commerce also raises ethical considerations. Data privacy is a major concern, as AI algorithms rely on vast amounts of user data to function effectively. It is crucial for e-commerce businesses to be transparent about their data collection practices and to ensure that user data is handled responsibly and securely, complying with regulations such as GDPR. Furthermore, algorithmic bias is a significant risk. AI algorithms are trained on data, and if that data reflects existing societal biases, the algorithm may perpetuate and even amplify those biases, leading to unfair or discriminatory outcomes. For example, an AI-powered recommendation system trained on data that predominantly features male users might disproportionately recommend products to male users, neglecting the needs and preferences of female customers. Addressing these ethical challenges is essential for ensuring the responsible and equitable use of AI in e-commerce.
The Future of E-commerce: The Growth Of E-commerce And Its Technological Drivers
The digital landscape is constantly evolving, and e-commerce is no exception. What was once a novel way to shop is now deeply ingrained in our daily lives. But the future of online retail promises even more dramatic shifts, driven by technological advancements and changing consumer expectations. Prepare for a shopping experience unlike anything you’ve seen before.
Augmented Reality (AR) Shopping
Augmented reality is poised to revolutionize how we interact with products online. Imagine trying on clothes virtually, seeing how furniture would look in your living room without lifting a finger, or testing out makeup shades before purchasing. AR apps overlay digital information onto the real world, offering an immersive and personalized shopping experience. This technology drastically reduces the risk of buyer’s remorse, leading to increased customer satisfaction and potentially higher conversion rates. Companies like Warby Parker have already successfully implemented AR try-on features for eyeglasses, demonstrating the potential for wider adoption. The impact will be a more informed and confident consumer, leading to increased sales and reduced returns.
Voice Commerce
The rise of smart speakers and virtual assistants has opened the door to voice commerce – the ability to shop using voice commands. This hands-free shopping experience is particularly appealing for busy consumers who can add items to their carts or make purchases while multitasking. Amazon’s Alexa and Google Assistant are leading the charge, integrating seamlessly with e-commerce platforms. The convenience factor is key here; we’re seeing a steady increase in voice-activated purchases, especially for everyday items like groceries and household goods. This trend is expected to significantly impact how consumers discover and purchase products, potentially shifting the focus towards simpler, more conversational interfaces.
The Metaverse and Immersive Shopping
The metaverse, a persistent, shared virtual world, presents a completely new frontier for e-commerce. Imagine browsing virtual stores, interacting with digital representations of products, and even attending virtual fashion shows. Brands are already experimenting with virtual storefronts and digital collectibles (NFTs), creating immersive experiences that blur the lines between the physical and digital worlds. While still in its early stages, the metaverse has the potential to transform the entire shopping experience, offering unparalleled levels of engagement and personalization. This could lead to the creation of entirely new business models and revenue streams, attracting a younger, tech-savvy generation of consumers. For example, brands like Nike have already started selling virtual sneakers in the metaverse. This creates new avenues for brand building and customer engagement beyond traditional e-commerce models.
Emerging Trends Summary
The future of e-commerce is dynamic and multifaceted. The following list summarizes the key emerging trends and their projected impact:
- Augmented Reality (AR): Offers immersive product visualization, leading to increased customer satisfaction and reduced returns.
- Voice Commerce: Provides hands-free shopping convenience, boosting sales of everyday items.
- Metaverse Shopping: Creates immersive brand experiences and potentially new business models, attracting younger consumers.
Final Summary
The journey of e-commerce is far from over. The explosive growth we’ve witnessed is just the beginning. As technology continues its breakneck pace, expect even more radical shifts in how we buy and sell online. From AR shopping experiences to the immersive world of the metaverse, the future of e-commerce promises to be as dynamic and disruptive as its past. Buckle up, because this ride is only getting started!
