The Future of Blockchain Technology in Enabling Digital Payments is no longer a futuristic fantasy; it’s rapidly becoming our reality. Forget slow, clunky, and expensive transactions – blockchain promises a faster, more secure, and transparent way to move money globally. This isn’t just about crypto; it’s about fundamentally reshaping how we handle finances, from everyday purchases to international trade. We’re diving deep into the potential, the challenges, and the game-changing innovations that are set to define the future of digital payments.
This exploration will cover the current state of digital payments, comparing traditional methods with emerging blockchain solutions. We’ll then delve into blockchain’s unique capabilities – enhanced security, reduced transaction costs, and the magic of smart contracts. Naturally, we’ll also tackle the hurdles: scalability issues, regulatory complexities, and potential risks. Finally, we’ll look at future trends, from stablecoins to AI integration, and how blockchain might seamlessly integrate with other technologies to create a truly revolutionary payment ecosystem. Get ready to rethink everything you know about moving money.
Current State of Digital Payments
The global digital payment landscape is a dynamic and rapidly evolving ecosystem, characterized by both significant advancements and persistent challenges. From mobile wallets to online banking, consumers are increasingly embracing digital alternatives to traditional cash and checks. However, issues like security vulnerabilities, regulatory inconsistencies, and varying levels of accessibility across different regions continue to shape its development.
The rise of digital payments is driven by factors such as increased smartphone penetration, improved internet infrastructure, and a growing preference for contactless transactions. This shift has created a lucrative market attracting major players vying for dominance, leading to a complex interplay of innovation and competition.
Blockchain’s secure, transparent nature is poised to revolutionize digital payments, offering faster, cheaper transactions. This shift towards decentralized finance is further amplified by advancements in remote collaboration, like those explored in this insightful article on How Virtual Reality is Enhancing Remote Work and Collaboration , which shows how seamless global teamwork can boost innovation in fintech. Ultimately, improved collaboration speeds up the development and adoption of blockchain-based payment solutions.
Major Players and Market Share
Several companies dominate the global digital payment market, each with its unique strengths and geographical focus. PayPal, for instance, holds a substantial market share, particularly in e-commerce transactions. Other key players include Visa and Mastercard, whose networks process billions of transactions annually. Mobile payment platforms like Alipay (China) and PhonePe (India) hold significant regional dominance, reflecting the diverse nature of the global digital payment ecosystem. The exact market share of each player fluctuates, influenced by factors such as mergers and acquisitions, regulatory changes, and evolving consumer preferences. Reliable, up-to-date market share data requires consulting specialized financial analytics firms.
Traditional vs. Blockchain-Based Payment Methods
Traditional payment systems, such as credit and debit cards processed through networks like Visa and Mastercard, rely on centralized intermediaries like banks and payment processors. These intermediaries validate transactions, ensuring funds transfer between parties. While widely adopted and relatively efficient for many transactions, they often incur higher fees and are susceptible to fraud and chargebacks. Processing times can also vary depending on factors such as banking hours and international transfers.
Blockchain-based payment solutions, in contrast, aim to decentralize the process. Utilizing distributed ledger technology, they aim to eliminate the need for intermediaries, potentially reducing transaction fees and enhancing security through cryptographic methods. However, scalability and regulatory uncertainty remain significant hurdles for widespread adoption. Furthermore, the technological complexity of blockchain can create barriers to entry for both businesses and consumers.
Comparison of Digital Payment Systems
The following table compares the transaction speeds, fees, and security levels of various digital payment systems. Note that these values are generalized and can vary based on specific circumstances, such as transaction amount and location.
| System Name | Transaction Speed | Transaction Fee | Security Level |
|---|---|---|---|
| Visa/Mastercard | Near real-time (seconds to minutes) | Variable, typically low for smaller transactions | High (robust fraud detection systems) |
| PayPal | Minutes to hours | Variable, dependent on transaction type and location | Medium (subject to account security breaches) |
| Alipay | Near real-time | Generally low | High (extensive security measures within the Alipay ecosystem) |
| Bitcoin | Variable (minutes to hours, dependent on network congestion) | Variable, can be significant during periods of high network activity | High (cryptographically secure, but vulnerable to user error) |
Blockchain’s Potential in Revolutionizing Digital Payments: The Future Of Blockchain Technology In Enabling Digital Payments

Source: cloudinary.com
Blockchain technology is poised to disrupt the digital payments landscape, offering solutions to long-standing challenges related to security, efficiency, and cost. Its decentralized and transparent nature presents a compelling alternative to traditional, centralized payment systems, promising a faster, cheaper, and more secure future for online transactions.
Enhanced Security and Transparency in Digital Transactions
Blockchain’s inherent security stems from its cryptographic architecture and decentralized ledger. Every transaction is recorded on a distributed network, making it incredibly difficult to alter or delete individual entries. This immutable record provides a high level of transparency, allowing all participants to view the transaction history, enhancing trust and accountability. The use of cryptographic hashing ensures the integrity of each block, preventing tampering and maintaining the overall system’s security. This contrasts sharply with centralized systems, which are vulnerable to single points of failure and potential manipulation.
Reduced Transaction Costs and Processing Times
Traditional payment systems often involve intermediaries like banks and payment processors, each adding fees and processing delays. Blockchain eliminates many of these intermediaries, significantly reducing transaction costs. The decentralized nature of blockchain also allows for faster processing times, as transactions are verified by a network of nodes rather than a single entity. This speed improvement is particularly beneficial for international payments, which typically take several days to clear using traditional methods. For example, a cross-border payment that might take days through a bank could be processed in minutes using a blockchain-based system.
The Role of Smart Contracts in Automating Payment Processes and Reducing Fraud
Smart contracts are self-executing contracts with the terms of the agreement directly written into lines of code. On a blockchain, these contracts automatically execute payments upon the fulfillment of pre-defined conditions. This automation reduces the need for intermediaries, minimizes processing delays, and significantly lowers the risk of fraud. For instance, a smart contract could automatically release payment to a supplier upon confirmation of goods delivery, eliminating the need for manual verification and reducing the potential for disputes. The immutability of the blockchain ensures that the terms of the smart contract are enforced transparently and reliably.
Benefits of Decentralized Payment Systems Compared to Centralized Ones
Decentralized payment systems, built on blockchain, offer several advantages over centralized systems. They are more resilient to censorship and single points of failure, ensuring continuous operation even in the event of attacks or disruptions. They also provide greater user control over their funds, eliminating the reliance on intermediaries who might freeze or seize assets. Furthermore, the transparency of blockchain enhances accountability and reduces the potential for fraud and manipulation. This increased trust and security can lead to wider adoption and greater participation in the global economy.
Examples of Existing or Emerging Blockchain-Based Payment Systems and Their Functionalities
Several blockchain-based payment systems are already operational or under development, each with unique features and functionalities.
- Ripple (XRP): A real-time gross settlement system that enables fast and low-cost international money transfers. It uses a distributed ledger to track transactions and facilitate cross-border payments between banks and financial institutions.
- Stellar (XLM): A decentralized platform for building financial applications, including payment systems. It offers fast and inexpensive transactions with a focus on connecting different currencies and payment networks.
- Bitcoin (BTC): While primarily known as a cryptocurrency, Bitcoin’s underlying blockchain technology also serves as a decentralized payment system, enabling peer-to-peer transactions without intermediaries.
These examples demonstrate the growing potential of blockchain to revolutionize digital payments, offering a more efficient, secure, and transparent alternative to traditional systems.
Addressing Challenges and Limitations
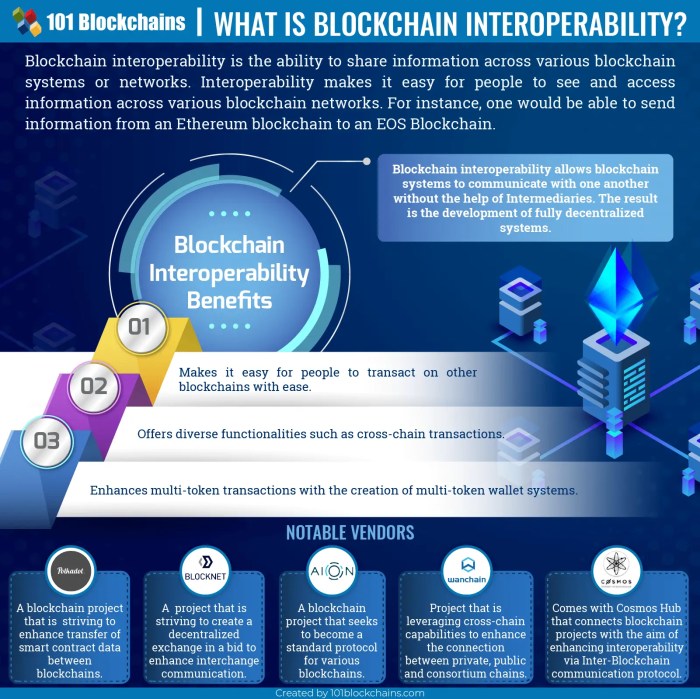
Source: 101blockchains.com
While the potential of blockchain in revolutionizing digital payments is undeniable, several hurdles stand in the way of widespread adoption. These challenges span technological limitations, regulatory uncertainties, and inherent risks within the system itself. Overcoming these obstacles requires a multi-pronged approach involving technological innovation, clear regulatory frameworks, and robust security measures.
Technological Challenges
The current state of blockchain technology presents several significant technological bottlenecks that hinder its wider application in digital payment systems. These challenges impact the efficiency, scalability, and overall usability of blockchain-based payment solutions. Addressing these is crucial for mainstream acceptance.
- Scalability: Many existing blockchain networks struggle to handle a high volume of transactions simultaneously. This limitation directly impacts transaction speeds and costs, making them impractical for large-scale adoption, especially in high-traffic payment systems. For example, Bitcoin’s relatively low transaction throughput compared to traditional payment processors like Visa creates a significant barrier to entry for widespread use in daily transactions.
- Interoperability: Different blockchain networks often operate in isolation, lacking the ability to seamlessly communicate and exchange data. This lack of interoperability prevents the creation of a unified, interconnected payment ecosystem. Imagine trying to send money from a Bitcoin wallet to an Ethereum wallet – the process is complex and often requires intermediaries.
- Transaction Speed: The time it takes to confirm a transaction on some blockchain networks can be slow, making them unsuitable for real-time payments. This delay can be a significant drawback for applications requiring immediate transaction finality, such as point-of-sale payments.
Regulatory Hurdles and Concerns
The regulatory landscape surrounding blockchain and cryptocurrencies remains largely undefined in many jurisdictions. This uncertainty creates a significant barrier to entry for businesses considering blockchain-based payment solutions.
- Lack of Clear Regulatory Frameworks: The absence of consistent and comprehensive regulations creates legal ambiguity and risks for businesses. This uncertainty can deter investment and hinder the development of robust and compliant blockchain payment systems. The varied approaches taken by different governments globally exacerbate this issue.
- Anti-Money Laundering (AML) and Know Your Customer (KYC) Compliance: Blockchain’s pseudonymous nature presents challenges in complying with AML and KYC regulations designed to prevent financial crime. Ensuring traceability and transparency within blockchain transactions while preserving user privacy is a key challenge.
- Taxation of Cryptocurrencies: The taxation of cryptocurrencies and blockchain-based transactions varies significantly across countries, creating complexity and uncertainty for both businesses and individuals.
Security Risks and Mitigation
While blockchain technology offers inherent security advantages, it is not immune to vulnerabilities. Addressing these risks is crucial for building trust and ensuring the integrity of blockchain-based payment systems.
- Smart Contract Vulnerabilities: Bugs or flaws in smart contracts, the self-executing contracts that govern transactions on some blockchains, can be exploited by malicious actors, leading to significant financial losses. Thorough auditing and testing of smart contracts are essential to mitigate these risks.
- 51% Attacks: A 51% attack occurs when a single entity controls more than half of the computing power of a blockchain network. This gives them the ability to reverse transactions and manipulate the network, undermining its security and integrity. This risk is more pronounced in smaller, less decentralized networks.
- Exchange Hacks and Security Breaches: While blockchain itself is secure, exchanges and other intermediaries handling cryptocurrency can be vulnerable to hacking and security breaches. Robust security measures are necessary to protect user funds and prevent theft.
Potential Solutions, The Future of Blockchain Technology in Enabling Digital Payments
Overcoming the challenges and mitigating the risks associated with blockchain-based digital payments requires a multifaceted approach.
- Technological advancements such as layer-2 scaling solutions, improved consensus mechanisms, and cross-chain communication protocols can address scalability and interoperability issues.
- Clearer regulatory frameworks that provide legal certainty and address AML/KYC compliance will encourage wider adoption.
- Robust security practices including thorough smart contract audits, decentralized exchange architectures, and multi-signature wallets will enhance security.
- Industry collaboration and the development of standardized protocols will foster interoperability and streamline the integration of blockchain into existing financial systems.
Future Trends and Innovations
The future of blockchain in digital payments isn’t just about incremental improvements; it’s about a fundamental shift in how we transact. Emerging technologies are poised to catapult blockchain beyond its current capabilities, creating a faster, more secure, and more inclusive global payment system. This section explores the key trends shaping this exciting evolution.
The convergence of blockchain with other innovative technologies promises to redefine the landscape of digital finance. We’ll examine the impact of stablecoins and CBDCs, the role of AI and machine learning, and paint a picture of a future where blockchain-powered payments are the norm, not the exception.
Stablecoins and Central Bank Digital Currencies (CBDCs)
Stablecoins, cryptocurrencies pegged to a stable asset like the US dollar, and CBDCs, digital versions of fiat currencies issued by central banks, are set to significantly impact blockchain-based payments. Stablecoins offer a solution to the volatility inherent in many cryptocurrencies, making them more attractive for everyday transactions. Meanwhile, CBDCs promise to enhance efficiency and security in cross-border payments, potentially bypassing traditional banking systems and reducing transaction costs. Imagine a world where international remittances happen instantly and cheaply, powered by a globally interoperable CBDC network built on blockchain. This could have a transformative effect on global trade and financial inclusion, particularly in underserved regions. The integration of stablecoins and CBDCs into existing blockchain payment infrastructure will likely lead to a more robust and user-friendly system.
Artificial Intelligence and Machine Learning in Blockchain Payment Systems
AI and machine learning are not just buzzwords; they’re crucial for enhancing the security and efficiency of blockchain payment systems. AI-powered fraud detection systems can analyze vast amounts of transaction data in real-time, identifying suspicious activity and preventing fraudulent payments. Machine learning algorithms can optimize transaction routing, reducing latency and improving overall system efficiency. For instance, an AI could predict network congestion and automatically reroute transactions to less congested pathways, ensuring faster processing times. This proactive approach, powered by AI and ML, will be crucial as blockchain payment volumes increase exponentially. Furthermore, AI can personalize user experiences, making blockchain-based payment platforms more intuitive and accessible to a wider audience.
A Hypothetical Future Scenario: Blockchain-Powered Payments in 2035
Imagine 2035. Your phone, equipped with a built-in digital wallet linked to your CBDC account, allows you to seamlessly make payments anywhere in the world. You purchase groceries using a decentralized payment network, the transaction verified instantly and securely on a blockchain. Micro-payments for streaming services are handled automatically, and international remittances to family overseas arrive in seconds, with minimal fees. Businesses leverage blockchain’s transparency and immutability to track supply chains, ensuring authenticity and combating counterfeiting. The entire financial system operates with greater efficiency, transparency, and security, thanks to the widespread adoption of blockchain technology. This isn’t science fiction; it’s a plausible future based on current technological advancements and trends. This scenario highlights the potential for a more inclusive and efficient global financial system.
Blockchain Integration with Other Technologies
Blockchain’s true potential lies not in isolation, but in its integration with other technologies. Combining blockchain with Internet of Things (IoT) devices could create automated payment systems for smart homes and connected cars. Integration with biometric authentication systems could enhance security, while integration with decentralized identity platforms could streamline user verification and KYC/AML processes. The synergistic effect of these integrations promises to create a more seamless and secure payment ecosystem, where transactions are faster, cheaper, and more secure than ever before. This interconnectedness will be key to unlocking the full potential of blockchain in the digital payment space.
Specific Use Cases and Applications

Source: robots.net
Blockchain technology, with its inherent security and transparency, is poised to revolutionize various industries beyond simple cryptocurrency transactions. Its decentralized nature and immutable ledger offer solutions to long-standing problems related to trust, efficiency, and security in digital payments. Let’s explore some key applications.
Cross-Border Payments
Cross-border payments often involve multiple intermediaries, leading to high fees, slow processing times, and a lack of transparency. Blockchain can streamline this process by creating a decentralized network for transferring funds directly between parties, eliminating the need for intermediaries. Imagine a system where you could send money to someone in another country instantly, with minimal fees and complete visibility of the transaction’s progress. This would be particularly beneficial for remittances, where billions of dollars are sent annually across borders, often at exorbitant costs. For example, a blockchain-based platform could use smart contracts to automate the process of verifying identities and complying with regulatory requirements, making cross-border payments faster and cheaper.
Supply Chain Finance
Blockchain’s ability to track assets and transactions throughout a supply chain offers significant benefits for businesses. Consider a scenario involving the import of goods: each step, from raw material sourcing to manufacturing and delivery, could be recorded on a shared, immutable ledger. This provides complete transparency, allowing all stakeholders to view the status of the goods at any point in the process. This enhanced visibility reduces fraud, improves efficiency, and enables faster payment cycles. For instance, a coffee roaster could track their beans from the farm to the consumer, ensuring quality and authenticity while streamlining payment to farmers upon delivery verification. Smart contracts could automatically trigger payments upon delivery confirmation, eliminating delays and disputes.
Micropayments
Micropayments, small-value transactions, are often impractical with traditional payment systems due to high transaction fees. Blockchain can facilitate micropayments by reducing these fees significantly. This opens up new possibilities for digital content creators, who can be paid directly for their work, even for small amounts. Imagine a scenario where a blogger receives micropayments from readers for accessing premium content, or an artist receiving micro-donations for their work. The low transaction costs and efficient processing of blockchain make this viable.
Table of Use Cases
| Industry | Use Case | Benefits | Challenges |
|---|---|---|---|
| Finance | Cross-border Payments | Reduced fees, faster processing, increased transparency | Regulatory hurdles, scalability, interoperability |
| Supply Chain Management | Tracking Goods and Payments | Improved transparency, reduced fraud, faster payment cycles | Integration with existing systems, data security, standardization |
| Media & Entertainment | Micropayments for Digital Content | Direct payments to creators, increased revenue streams for content providers, accessibility for consumers | Scalability, user adoption, payment gateway integration |
| Healthcare | Secure Data Sharing and Payment | Enhanced data privacy and security, streamlined payments for medical services | Data privacy regulations, interoperability with existing healthcare systems, user adoption |
End of Discussion
The future of digital payments is undeniably intertwined with the evolution of blockchain technology. While challenges remain, the potential benefits – increased security, reduced costs, and enhanced transparency – are too significant to ignore. As blockchain matures and regulations adapt, we can expect to see a gradual but significant shift towards decentralized, blockchain-powered payment systems. This isn’t just about faster transactions; it’s about building a more efficient, secure, and inclusive global financial system. The journey is just beginning, and the possibilities are limitless.
