The Future of Autonomous Drones in Surveillance and Security is rapidly unfolding, transforming how we monitor and protect our world. From bustling cityscapes to remote border regions, these unmanned aerial vehicles (UAVs) are poised to revolutionize security and surveillance operations. But this technological leap isn’t without its complexities; ethical considerations, legal frameworks, and societal impacts all demand careful consideration as we navigate this exciting, yet challenging, new frontier.
This exploration delves into the cutting-edge technology driving autonomous drone capabilities, examining advancements in AI, sensor technology, and battery life. We’ll explore real-world applications, from crime prevention and disaster response to infrastructure monitoring, and weigh the potential economic benefits against the potential displacement of human workers. Crucially, we’ll dissect the ethical and legal dilemmas surrounding privacy, bias, and the need for robust regulations to ensure responsible deployment.
Technological Advancements in Autonomous Drone Surveillance
The world of autonomous drone surveillance is rapidly evolving, driven by advancements in artificial intelligence, sensor technology, and power systems. These improvements are transforming how drones are used in security and surveillance, leading to more efficient, precise, and versatile applications across various sectors. From border patrol to infrastructure inspection, the impact is undeniable.
Current autonomous drone technology boasts impressive capabilities. Navigation systems utilize GPS, inertial measurement units (IMUs), and computer vision to enable precise flight paths, even in challenging environments. Advanced sensors, including high-resolution cameras, thermal imagers, and LiDAR, provide comprehensive data collection for analysis. However, limitations remain in areas like battery life, AI processing power onboard the drone, and the robustness of autonomous navigation in complex or unpredictable situations.
Autonomous drones are poised to redefine surveillance and security, offering unparalleled real-time monitoring capabilities. This technological leap mirrors the advancements happening in other sectors, like the energy industry, which is undergoing a massive transformation as detailed in this insightful article: How Emerging Tech is Revolutionizing the Energy Industry. The efficiency gains seen in energy management through tech innovation are directly applicable to optimizing drone operations for enhanced security solutions.
Ultimately, smarter tech leads to smarter security.
AI-Powered Image Recognition and Object Tracking Advancements
Within the next five years, we can expect significant leaps in AI-powered image recognition and object tracking for drones. Deep learning algorithms are rapidly improving their ability to identify and track multiple objects in real-time, even in low-light conditions or amidst visual clutter. This will lead to more accurate threat detection, improved situational awareness, and more effective response capabilities for security personnel. For example, imagine a drone autonomously identifying and tracking a suspicious vehicle in a crowded city center, instantly alerting authorities. Furthermore, advancements in edge computing will allow drones to process more data onboard, reducing latency and improving the speed of response. The integration of advanced analytics will enable drones to not just identify objects but also predict potential threats based on observed patterns of behavior.
Impact of Improved Battery Technology and Charging Infrastructure
Improved battery technology and charging infrastructure are crucial for expanding the operational capabilities of autonomous drones. Current limitations in flight time significantly restrict the scope of surveillance operations. The development of higher-energy-density batteries, coupled with advancements in fast-charging technologies, will enable drones to stay airborne for longer periods, increasing their coverage area and operational endurance. The development of drone-specific charging stations and even autonomous charging systems will further enhance operational efficiency, allowing for continuous monitoring without the need for frequent manual intervention. Consider the impact on border patrol: longer flight times mean drones can patrol larger areas, effectively deterring illegal crossings and enhancing security.
Performance Characteristics of Leading Autonomous Drone Models
The following table compares the performance characteristics of three leading autonomous drone models currently available. Note that specifications can vary based on configurations and payloads.
| Drone Model | Speed (km/h) | Payload (kg) | Flight Time (minutes) | Sensor Resolution (pixels) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| DJI Matrice 300 RTK | 72 | 2.7 | 55 | 20MP |
| Autel EVO II Pro | 72 | 1.5 | 40 | 48MP |
| Skydio X2 | 80 | 1.0 | 38 | 5472×3648 |
Applications of Autonomous Drones in Security and Surveillance
The integration of autonomous drones into security and surveillance operations is rapidly transforming how we protect infrastructure, monitor public spaces, and respond to emergencies. These unmanned aerial vehicles (UAVs) offer a unique combination of mobility, versatility, and cost-effectiveness, making them increasingly attractive to various sectors. Their capabilities extend far beyond simple visual observation, encompassing advanced sensor technologies and sophisticated data analysis.
Autonomous drones are already proving their worth in a range of security and surveillance applications, significantly enhancing operational efficiency and effectiveness. The following sections detail some key examples across different sectors and explore the potential for future development.
Current Applications of Autonomous Drones in Security and Surveillance
Autonomous drones are currently deployed across numerous sectors. Law enforcement agencies utilize them for crime scene investigation, search and rescue operations, and monitoring large-scale public gatherings. Border patrol agencies employ drones to monitor borders, detect illegal crossings, and track suspicious activity. Infrastructure monitoring companies leverage drones for inspecting bridges, pipelines, and power lines, identifying potential safety hazards before they escalate into major incidents. Similarly, agricultural businesses utilize them for crop monitoring and pest control. These applications highlight the versatility and adaptability of autonomous drone technology. The data collected by these drones is often processed using sophisticated algorithms, allowing for efficient analysis and timely responses to potential threats or issues.
Enhancing Security in Public Spaces with Autonomous Drones
The potential for autonomous drones to enhance security in high-traffic public areas is considerable. Airports could use them for perimeter surveillance, detecting unauthorized intrusions or potential threats. Stadiums could deploy drones to monitor crowds, identify potential troublemakers, and ensure the safety of attendees. Shopping malls could utilize drones for security patrols, deterring theft and providing a rapid response to incidents. In each case, the drones could be programmed with specific flight paths and equipped with sensors to detect anomalies or suspicious activity, alerting security personnel in real-time. This proactive approach can significantly improve response times and enhance overall safety.
Autonomous Drones in Disaster Response and Emergency Management
Autonomous drones play a vital role in disaster response and emergency management. Following natural disasters like earthquakes or floods, drones can quickly assess the extent of damage, locate survivors, and deliver essential supplies to affected areas. Their ability to navigate challenging terrain and operate in hazardous conditions makes them invaluable assets in such scenarios. They can also be equipped with thermal imaging cameras to detect survivors trapped under debris, providing crucial information for rescue teams. Furthermore, drones can monitor the spread of wildfires, providing real-time data to firefighters and enabling more effective containment strategies. The speed and efficiency of drone-based assessments significantly aid in efficient allocation of resources and improved response times.
Hypothetical Deployment Strategy for Autonomous Drones at a Large-Scale Public Event
Consider a large-scale music festival. A comprehensive deployment strategy would involve establishing a dedicated drone control center, equipped with sophisticated software for real-time monitoring and data analysis. Multiple drones, equipped with high-resolution cameras and thermal imaging, would be strategically positioned to cover the entire festival grounds. Pre-programmed flight paths would ensure complete coverage, while manual overrides would be available for emergency situations. Strict safety protocols would be implemented, including no-fly zones and designated drone landing areas. Clear communication channels between drone operators and ground security personnel would be crucial for coordinating responses to any incidents. The data collected by the drones would be analyzed to identify potential threats, manage crowd flow, and ensure the overall safety and security of attendees. The success of such a deployment relies heavily on meticulous planning, robust technology, and well-trained personnel.
Ethical and Legal Considerations of Autonomous Drone Surveillance: The Future Of Autonomous Drones In Surveillance And Security
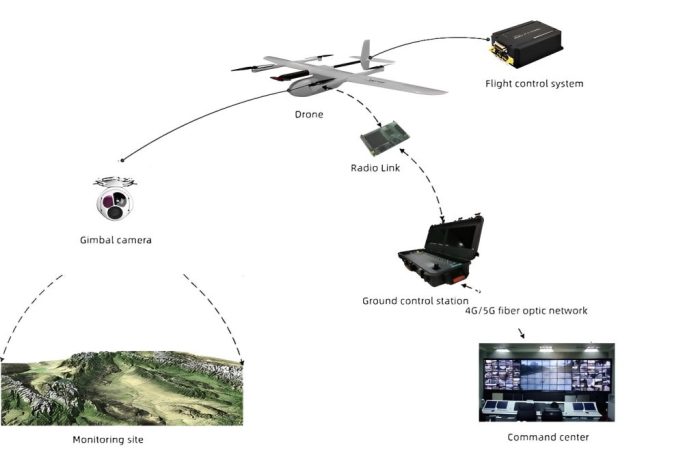
Source: jouav.com
The rise of autonomous drones capable of sophisticated surveillance presents a complex interplay of technological advancement and ethical, legal challenges. While offering significant benefits in security and efficiency, their widespread deployment raises serious concerns about privacy infringement, algorithmic bias, and the potential for misuse. Navigating this landscape requires a careful consideration of existing legal frameworks and the development of robust regulatory mechanisms to ensure responsible innovation.
The ethical dilemmas surrounding autonomous drone surveillance are multifaceted and deeply intertwined with the very nature of the technology. The capacity for continuous, widespread monitoring raises significant privacy concerns. Unlike human surveillance, which is often limited by physical constraints and human oversight, autonomous drones can operate 24/7, potentially capturing vast amounts of data about individuals without their knowledge or consent. This constant monitoring can chill free speech and assembly, creating a chilling effect on public life. Furthermore, the algorithms driving these drones’ decision-making processes are susceptible to biases present in the data they are trained on, leading to discriminatory outcomes. For example, an algorithm trained on biased data might disproportionately target certain demographics, exacerbating existing social inequalities.
Privacy Violations and Algorithmic Bias, The Future of Autonomous Drones in Surveillance and Security
The potential for privacy violations is arguably the most pressing ethical concern. Autonomous drones equipped with high-resolution cameras and other sensors can capture highly sensitive personal information, including images of individuals in their homes, workplaces, and public spaces. The sheer volume of data collected and the potential for its misuse represent a significant threat to individual privacy. The lack of transparency in how these algorithms operate further compounds this concern, making it difficult to identify and address biases or errors. Consider, for instance, a facial recognition system trained primarily on images of one ethnic group; its accuracy in identifying individuals from other groups would likely be significantly lower, leading to misidentification and potential wrongful accusations. This lack of accountability and transparency makes it challenging to hold developers and users accountable for the consequences of biased algorithmic decisions.
Current Legal Frameworks and Their Gaps
The legal landscape governing the use of drones varies significantly across countries. Some nations have established comprehensive regulations, while others lag behind, creating inconsistencies and loopholes that can be exploited. Many jurisdictions have regulations concerning drone operation, including airspace restrictions, licensing requirements, and limitations on data collection. However, these regulations often fail to address the unique challenges posed by autonomous drones, particularly those with advanced surveillance capabilities. For example, the rules concerning data storage, access, and retention are often inadequate to protect against unauthorized surveillance or the misuse of collected data. The legal frameworks often struggle to keep pace with the rapid technological advancements in drone technology and artificial intelligence, creating a regulatory gap that needs urgent attention.
Balancing National Security and Individual Privacy
The use of autonomous drones for surveillance often presents a conflict between national security interests and individual privacy rights. Governments may argue that widespread drone surveillance is necessary to prevent terrorism, crime, and other threats. However, such surveillance must be carefully balanced against the fundamental right to privacy. Finding this balance requires careful consideration of proportionality, necessity, and transparency. Surveillance should only be undertaken when it is proportionate to the threat, necessary to achieve a legitimate objective, and conducted in a transparent manner that allows for public scrutiny. The absence of clear guidelines and oversight mechanisms can lead to abuses of power and violations of fundamental rights. For example, the deployment of autonomous drones for mass surveillance without proper judicial oversight raises serious concerns about potential human rights violations.
Potential Regulations for Autonomous Drone Surveillance
Addressing the ethical and legal implications of widespread autonomous drone use requires a comprehensive regulatory framework. Such a framework should encompass the following:
- Strict data protection regulations: These regulations should govern the collection, storage, use, and sharing of data collected by autonomous drones, ensuring compliance with privacy laws and providing individuals with control over their personal information.
- Transparency and accountability mechanisms: Clear guidelines should be established regarding the algorithms used in autonomous drone surveillance systems, ensuring transparency and accountability for algorithmic decisions. Independent audits of these systems should be conducted to identify and mitigate potential biases.
- Robust oversight and judicial review: The use of autonomous drones for surveillance should be subject to strict oversight and judicial review, ensuring that such deployments are proportionate, necessary, and comply with human rights standards.
- Clear guidelines on data retention and disposal: Regulations should specify the duration for which data collected by autonomous drones can be retained and the procedures for its secure disposal once it is no longer needed.
- Licensing and certification requirements: Strict licensing and certification requirements should be implemented for operators of autonomous drones used for surveillance, ensuring that they possess the necessary expertise and adhere to established safety and ethical standards.
Economic and Societal Impacts of Autonomous Drone Surveillance
The rise of autonomous drones in surveillance and security presents a complex interplay of economic opportunities and societal challenges. While offering significant potential for cost reduction and efficiency gains, the technology also raises concerns about job displacement and the implications of increased surveillance on individual privacy and freedom. Understanding these multifaceted impacts is crucial for responsible development and deployment of this transformative technology.
Economic Benefits of Autonomous Drone Surveillance
Autonomous drones promise substantial economic benefits across various sectors. In infrastructure inspection, for example, drones can replace costly and time-consuming manual inspections of bridges, power lines, and pipelines, leading to significant cost savings and reduced risk to human inspectors. Similarly, in agriculture, drones equipped with sensors can monitor crop health and optimize irrigation, resulting in increased yields and reduced resource waste. The security industry also stands to benefit from reduced labor costs associated with patrolling and monitoring large areas. These cost savings translate into increased profitability and efficiency for businesses, ultimately contributing to economic growth. For instance, a recent study by the University of California, Berkeley, estimated that using drones for infrastructure inspection could save the US economy billions of dollars annually.
Job Displacement in Security and Surveillance
The automation potential of autonomous drones inevitably raises concerns about job displacement. Security guards, surveillance personnel, and inspectors whose tasks can be automated by drones may face redundancy. This is particularly true for repetitive, routine tasks that require less specialized human skills. The transition will require retraining and upskilling initiatives to equip affected workers with the skills needed for new roles in drone operation, maintenance, data analysis, and other related fields. The integration of humans and autonomous systems, emphasizing human oversight and intervention, will become increasingly important to mitigate potential job losses.
Social Benefits and Drawbacks of Increased Surveillance
The widespread adoption of autonomous drone surveillance presents a double-edged sword for society. On one hand, increased surveillance can enhance public safety by deterring crime, providing rapid response to emergencies, and assisting in search and rescue operations. Improved monitoring of infrastructure could prevent costly accidents and ensure public safety. However, the potential for increased surveillance raises significant concerns about privacy violations, potential misuse of data, and the chilling effect on freedom of expression and assembly. The balance between security and liberty needs careful consideration and the implementation of robust regulatory frameworks to safeguard individual rights.
Hypothetical Scenario: Autonomous Drone Surveillance in a Major City
Imagine a major city deploying a network of autonomous drones for surveillance purposes. Positive impacts could include a significant reduction in crime rates due to increased police presence and faster response times. Real-time traffic monitoring could optimize traffic flow, reducing congestion and improving commute times. Disaster response could be significantly improved with drones quickly assessing damage and delivering aid. However, negative consequences could include widespread public unease over constant surveillance, leading to a chilling effect on public gatherings and freedom of expression. Data privacy concerns could arise from the potential for misuse of collected data. The possibility of algorithmic bias in drone-based surveillance systems, leading to unfair targeting of specific demographics, is another significant concern. Balancing the benefits of increased security with the protection of individual liberties would be a major challenge in such a scenario.
Integration with Existing Security Systems
The seamless integration of autonomous drones into existing security infrastructure is crucial for maximizing their effectiveness. This isn’t just about adding another surveillance tool; it’s about creating a synergistic system where drones enhance and complement existing technologies, leading to a more comprehensive and responsive security network. Successful integration requires careful consideration of data formats, communication protocols, and overall system architecture.
Autonomous drones can significantly enhance existing security systems like CCTV networks and alarm systems by providing a mobile, aerial perspective. Drones can act as roving cameras, expanding the coverage area of fixed CCTV cameras, accessing areas difficult for ground-based systems to reach, and providing real-time aerial views of incidents. When integrated with alarm systems, drones can be automatically dispatched to investigate triggered alarms, providing immediate visual confirmation and valuable situational awareness. This rapid response capability can be vital in emergency situations.
Data Integration Challenges
Integrating data from autonomous drones with other security systems presents several significant challenges. Firstly, the data formats differ considerably. Drones typically generate high-resolution video streams, thermal imagery, and potentially other sensor data (e.g., LiDAR, acoustic sensors), while existing systems might primarily handle lower-resolution video feeds and structured data from alarm systems. Converting and correlating this diverse data requires robust data processing and management capabilities. Secondly, real-time data processing and transmission are critical for effective response, requiring high bandwidth communication networks and efficient data compression techniques. Network latency and reliability can also significantly impact the effectiveness of the integrated system. Finally, ensuring data security and privacy is paramount. Sensitive information captured by drones needs to be securely stored, transmitted, and accessed, adhering to relevant data protection regulations.
Hypothetical System Architecture for City-Wide Integration
Imagine a city-wide security system integrating autonomous drones with existing CCTV networks, alarm systems, and emergency response services. The system would consist of a central command center housing a powerful data processing and management system. This center would receive data feeds from various sources, including fixed CCTV cameras, alarm sensors (intrusion, fire, etc.), and the autonomous drones. The drones would be equipped with high-resolution cameras, thermal imaging, and GPS for precise location tracking. They would communicate with the central command center via a secure, high-bandwidth wireless network (e.g., 5G or dedicated private network). The system would utilize advanced algorithms for real-time data analysis, including object recognition, threat assessment, and anomaly detection. Automated alerts and incident reports would be generated, routing information to relevant emergency services based on the severity and location of the incident. Human operators in the command center would monitor the system, intervene when necessary, and manage drone deployments. The system would incorporate robust cybersecurity measures to protect against unauthorized access and data breaches.
Integrated System Data Flow and Communication Pathways
A visual representation of this system would show a central command center at the heart of the network. Lines radiating outwards would represent data streams flowing from various sources: fixed CCTV cameras, alarm sensors, and multiple autonomous drones operating throughout the city. These data streams would converge at the central command center, where they are processed and analyzed. Feedback loops would show information flowing back to the drones, guiding their movements and adjusting their tasks based on the overall situational awareness. For instance, if an alarm is triggered in a specific location, the system would automatically dispatch the nearest drone to provide visual confirmation and real-time video feed to the command center. Another line would show the communication pathway between the command center and emergency response services, enabling the rapid deployment of first responders. The diagram would visually demonstrate the complex interplay of data flow and communication pathways within this integrated security system, highlighting the synergy between autonomous drones and existing infrastructure. The use of different colors and line thicknesses could visually represent the different data types (video, sensor data, commands) and their bandwidth requirements. The overall visual would emphasize the seamless integration and collaborative nature of the system.
Outcome Summary
Autonomous drones are undeniably reshaping the landscape of surveillance and security, offering unprecedented capabilities for monitoring and protection. However, realizing their full potential requires a proactive approach to addressing the ethical, legal, and societal implications. By fostering open dialogue, developing comprehensive regulations, and prioritizing responsible innovation, we can harness the power of autonomous drones while mitigating potential risks, ensuring a future where security and privacy coexist harmoniously.
