The Future of AI in Optimizing Global Supply Chains and Logistics is no longer a futuristic fantasy; it’s the present and rapidly shaping the future of how goods move across the globe. Imagine a world where predictive analytics flawlessly anticipate demand, robots dance through warehouses with balletic efficiency, and AI-powered systems ensure every package arrives on time, every time. This isn’t science fiction; it’s the dawn of a new era in logistics, driven by the power of artificial intelligence.
From forecasting demand fluctuations to optimizing transportation routes and enhancing supply chain visibility, AI is revolutionizing every aspect of the industry. This transformation promises unprecedented efficiency, resilience, and sustainability, but also presents challenges related to job displacement, data security, and ethical considerations. Let’s dive into how AI is reshaping the global supply chain landscape and what that means for businesses and consumers alike.
AI-Driven Predictive Analytics in Supply Chain Management: The Future Of AI In Optimizing Global Supply Chains And Logistics
Predictive analytics, powered by artificial intelligence, is revolutionizing global supply chains by enabling businesses to anticipate market changes and optimize their operations with unprecedented accuracy. This allows for more efficient inventory management, reduced waste, and improved customer satisfaction. By leveraging vast datasets and sophisticated algorithms, AI can identify patterns and trends that would be impossible for humans to detect, leading to significant cost savings and competitive advantages.
AI algorithms analyze historical sales data, economic indicators, weather patterns, social media trends, and even geopolitical events to forecast future demand with remarkable precision. This forecasting capability allows businesses to optimize their inventory levels, ensuring they have enough stock to meet demand without tying up excessive capital in excess inventory. The ability to accurately predict demand fluctuations is crucial for minimizing stockouts, which can lead to lost sales and damaged customer relationships, and preventing overstocking, which results in wasted resources and storage costs.
AI Algorithms for Demand Forecasting and Inventory Optimization
AI uses various sophisticated algorithms to achieve accurate demand forecasting and optimized inventory levels. These algorithms learn from historical data, identifying complex relationships and patterns that traditional statistical methods often miss. For example, machine learning models like ARIMA (Autoregressive Integrated Moving Average) can identify seasonal trends and cyclical patterns, while deep learning models, such as recurrent neural networks (RNNs), are particularly effective at handling time-series data with complex dependencies. Furthermore, advanced algorithms can integrate external data sources, such as weather forecasts or social media sentiment, to improve forecast accuracy even further.
Hypothetical Scenario: Preventing Stockouts and Overstocking with Predictive Analytics
Imagine a global retailer selling winter coats. Using traditional forecasting methods, they might overestimate demand in certain regions due to an unusually cold previous winter, leading to overstocking and subsequent markdowns. Conversely, they might underestimate demand in other regions, resulting in stockouts and lost sales. However, with AI-powered predictive analytics, the retailer can analyze various data points – past sales, weather forecasts, social media buzz around fashion trends, and economic indicators – to generate a more accurate demand forecast. This enables them to optimize their inventory levels for each region, ensuring sufficient stock to meet demand while avoiding unnecessary overstocking. For example, if a region is predicted to have a milder winter than usual, the AI system would advise reducing the inventory of winter coats in that area, preventing potential losses from overstocking.
Comparison of AI-Powered Forecasting Models
Different AI models offer unique strengths and weaknesses depending on the specific characteristics of the data and the business context. For instance, while ARIMA models excel in capturing linear trends and seasonality, they might struggle with non-linear relationships or sudden shifts in demand. On the other hand, deep learning models, such as Long Short-Term Memory (LSTM) networks, can handle complex non-linear relationships and long-term dependencies more effectively, making them suitable for forecasting in volatile markets. However, deep learning models often require significantly more data and computational resources than simpler models. The choice of the most suitable model depends on factors such as data availability, computational resources, and the complexity of the demand patterns.
Key Performance Indicators (KPIs) Improved by Predictive Analytics, The Future of AI in Optimizing Global Supply Chains and Logistics
Predictive analytics significantly impacts several key performance indicators within supply chain management.
| KPI | Description | Improvement with Predictive Analytics | Example |
|---|---|---|---|
| Inventory Turnover | Measures how efficiently inventory is managed. | Increased turnover, indicating faster sales and reduced storage costs. | Improved from 4 times per year to 6 times per year. |
| Stockout Rate | Percentage of orders that cannot be fulfilled due to lack of stock. | Significant reduction, leading to increased sales and customer satisfaction. | Reduced from 5% to 1%. |
| Fill Rate | Percentage of orders fulfilled from available stock. | Increased fill rate, reflecting improved inventory management and reduced lost sales. | Increased from 90% to 98%. |
| Holding Costs | Costs associated with storing and managing inventory. | Reduced costs due to optimized inventory levels and reduced waste. | Decreased by 15%. |
Automation and Robotics in Warehousing and Logistics
The warehousing and logistics industry is undergoing a massive transformation, driven by the relentless pursuit of efficiency and cost reduction. Automation and robotics are at the forefront of this change, revolutionizing how goods are handled, stored, and moved. From automated guided vehicles navigating warehouse floors to robotic arms meticulously picking and packing items, the impact is profound and far-reaching. This section delves into the specifics of this technological shift and its implications for the industry.
The integration of automated systems is no longer a futuristic concept; it’s a current reality reshaping the logistics landscape. Companies are increasingly adopting automation to streamline operations, enhance speed, and improve accuracy, ultimately boosting their bottom line. This shift towards automation involves a complex interplay of technologies, including sophisticated software, advanced sensors, and powerful robotic systems, all working in concert to optimize warehouse efficiency.
Automated Guided Vehicles (AGVs) and Robots in Warehouse Operations
Automated Guided Vehicles (AGVs) are self-navigating vehicles that transport materials within a warehouse or distribution center. They follow pre-programmed routes or use advanced sensors to navigate dynamically around obstacles. These vehicles can carry significant loads, reducing the need for manual handling and significantly improving efficiency. Robots, on the other hand, perform a variety of tasks, from picking and packing to sorting and palletizing. They are often equipped with advanced vision systems and artificial intelligence (AI) to handle complex tasks with speed and precision.
AI’s impact on global supply chains is huge, promising smoother, faster logistics. This efficiency boost isn’t limited to shipping; the same principles are revolutionizing other sectors, like healthcare, where advancements in robotics are transforming patient care, as detailed in this insightful article: The Role of Robotics in Supporting the Healthcare Industry. Ultimately, the core theme is automation driving optimization, whether it’s streamlining deliveries or enhancing medical procedures.
For example, Amazon utilizes thousands of robots in its fulfillment centers. These robots move shelves of products to human pickers, drastically reducing the time workers spend walking to retrieve items. Similarly, companies like Ocado have implemented highly automated warehouses where robots pick, pack, and sort groceries with minimal human intervention. These systems use a combination of AGVs, robotic arms, and sophisticated software to orchestrate the entire process.
AI-Powered Robots Improving Picking, Packing, and Sorting Efficiency
AI plays a crucial role in enhancing the capabilities of warehouse robots. AI-powered vision systems allow robots to identify and grasp items of varying shapes and sizes with greater accuracy than traditional robotic systems. This is particularly important for picking tasks, where the ability to handle fragile or irregularly shaped items is essential. AI algorithms also optimize picking routes, minimizing travel time and maximizing throughput. In packing, AI helps robots choose the optimal packaging materials and techniques, reducing waste and improving efficiency. Sorting is another area where AI shines, enabling robots to quickly and accurately sort items based on size, weight, destination, or other criteria.
For instance, a clothing retailer might use AI-powered robots to sort garments by size and color, preparing them for shipment to individual customers. This significantly reduces the time and labor required for manual sorting, allowing for faster order fulfillment and improved customer satisfaction. Another example could be a logistics company using AI-powered robots to sort packages based on their destination zip code, optimizing delivery routes and reducing transit times.
Impact of Automation on Labor Costs and Job Displacement
The increasing adoption of automation in warehousing and logistics has a significant impact on labor costs and employment. While automation can lead to substantial cost savings by reducing the need for human labor, it also raises concerns about job displacement. The nature of jobs in the sector is shifting; while some roles may be eliminated, new roles focused on the maintenance, programming, and management of automated systems are being created. The long-term impact will depend on several factors, including the pace of technological advancement, the ability of workers to adapt to new skills, and the implementation of effective retraining programs.
It’s important to note that while some jobs may be lost, others will be created. The focus should be on reskilling and upskilling the workforce to meet the evolving demands of the automated warehouse environment. For example, warehouse workers might transition into roles overseeing robotic systems or specializing in data analysis related to warehouse optimization. This requires proactive planning and investment in education and training programs.
Benefits and Challenges of Robotic Automation in Warehouses
The decision to implement robotic automation in a warehouse involves careful consideration of both the benefits and challenges involved. A balanced assessment is crucial for successful implementation and realizing the full potential of this technology.
- Benefits: Increased efficiency and productivity, reduced labor costs (in the long term), improved accuracy and reduced error rates, enhanced safety for workers by automating hazardous tasks, greater scalability and flexibility to adapt to fluctuating demand.
- Challenges: High initial investment costs, potential for job displacement, need for skilled personnel to operate and maintain systems, integration complexities with existing systems, potential for system downtime and maintenance issues.
AI-Powered Optimization of Transportation Networks
The global supply chain relies heavily on efficient transportation networks. Optimizing these networks is crucial for on-time delivery, reduced costs, and enhanced customer satisfaction. AI is revolutionizing this process, offering solutions that were previously unimaginable. By leveraging vast datasets and advanced algorithms, AI systems can analyze complex logistical challenges and provide data-driven solutions for improved efficiency and profitability.
AI significantly enhances route optimization, scheduling, and fleet management, leading to substantial improvements in delivery times and cost savings. This is achieved through the intelligent analysis of various factors, including real-time traffic conditions, weather patterns, fuel prices, and driver availability. The result is a more dynamic and responsive transportation network capable of adapting to unforeseen circumstances.
Real-time Traffic Monitoring and Route Adjustments
AI-driven solutions for real-time traffic monitoring and route adjustments are transforming the way goods are transported. Systems utilize GPS data, traffic cameras, and other sensor networks to create a dynamic picture of traffic flow. When unexpected delays occur, such as accidents or road closures, the AI system immediately recalculates optimal routes, minimizing disruptions and ensuring timely deliveries. For example, a logistics company using an AI-powered route optimization platform might reroute a truck around a sudden traffic jam, avoiding a potential delay of several hours. This real-time adaptation is impossible to achieve with traditional methods.
Comparison of AI Algorithms for Transportation Network Optimization
Several AI algorithms are used in optimizing transportation networks, each with its strengths and weaknesses. Genetic algorithms, for instance, are effective in exploring a vast solution space to find near-optimal routes. However, they can be computationally expensive for extremely large networks. Reinforcement learning algorithms, on the other hand, learn through trial and error, adapting to changing conditions over time. They are particularly well-suited for dynamic environments, such as those with fluctuating traffic patterns. Finally, machine learning algorithms can predict future traffic conditions based on historical data and current trends, allowing for proactive route planning and scheduling. The choice of algorithm depends on the specific needs of the transportation network and the available computational resources.
Visualization of Improved Delivery Times and Fuel Efficiency
Imagine a bar graph comparing average delivery times before and after implementing an AI-powered transportation management system. The pre-AI bar might show an average delivery time of, say, 48 hours, while the post-AI bar displays a significantly reduced average of 36 hours. A second bar graph alongside this could illustrate fuel efficiency. This graph could show a percentage increase in fuel efficiency, perhaps from 10% to 15% or even higher, reflecting the optimization of routes and reduction in idle time. A line graph could further illustrate the impact over time, demonstrating a steady decrease in delivery times and a steady increase in fuel efficiency as the AI system learns and adapts to the changing conditions. The visualization would clearly demonstrate the substantial improvements achieved through AI-powered optimization, showcasing the tangible benefits in terms of both speed and cost savings. For instance, a hypothetical scenario might show a 20% reduction in delivery times and a 12% improvement in fuel efficiency for a large logistics company operating across multiple regions. This would represent significant cost savings and a substantial boost to their bottom line.
Enhancing Supply Chain Visibility and Transparency with AI
The quest for efficient and resilient global supply chains is driving the adoption of advanced technologies, with AI playing a pivotal role in boosting visibility and transparency. No longer are businesses reliant on sporadic updates and delayed information; AI empowers real-time tracking and monitoring, leading to improved decision-making and reduced risks. This enhanced visibility translates directly into cost savings, improved customer satisfaction, and a more agile response to market fluctuations.
AI-powered platforms achieve this through the integration of various data sources, from IoT sensors on goods in transit to enterprise resource planning (ERP) systems and customer relationship management (CRM) data. This comprehensive data aggregation provides a holistic view of the entire supply chain, allowing businesses to pinpoint bottlenecks, anticipate disruptions, and proactively mitigate potential problems. The result is a more streamlined and responsive supply chain, capable of adapting to the ever-changing demands of the global market.
Real-Time Tracking and Monitoring of Goods
AI algorithms analyze data from diverse sources – GPS trackers, RFID tags, and barcode scanners – to provide continuous updates on the location and status of goods throughout their journey. Machine learning models can predict potential delays based on historical data, weather patterns, and traffic conditions, enabling proactive interventions. For example, a company shipping perishable goods could receive an alert about an unexpected traffic jam, allowing them to reroute the shipment and prevent spoilage. This level of precision minimizes delays, reduces waste, and ensures timely delivery, ultimately enhancing customer satisfaction.
Blockchain Technology and Enhanced Transparency
Blockchain, a decentralized and immutable ledger, adds another layer of security and transparency to the AI-powered supply chain. By recording all transactions and events on a shared, verifiable ledger, blockchain ensures the integrity of data and prevents tampering. AI algorithms can analyze this blockchain data to identify anomalies, such as counterfeit products or fraudulent activities, and trigger appropriate responses. Consider a pharmaceutical company using blockchain to track the movement of its drugs from manufacturing to the end consumer. This guarantees the authenticity of the product and protects against counterfeiting, significantly enhancing consumer trust and safety.
Risks and Challenges of Increased Data Sharing and AI Reliance
While AI offers immense benefits, the increased reliance on data sharing and AI algorithms also presents potential risks. Data breaches, cybersecurity threats, and the potential for algorithmic bias are significant concerns. Ensuring data privacy and security through robust encryption and access controls is paramount. Furthermore, the complexity of AI algorithms can make it difficult to understand their decision-making processes, potentially leading to unforeseen consequences. Rigorous testing and validation of AI models are crucial to mitigate these risks. For instance, an AI system predicting demand based on biased historical data might lead to overstocking or understocking of certain products, resulting in financial losses.
System Architecture of an AI-Powered Supply Chain
A typical AI-powered supply chain architecture involves several key components interacting seamlessly. Imagine a central data hub collecting data from various sources: IoT sensors on shipments (providing real-time location and condition data), ERP systems (managing inventory and orders), CRM systems (tracking customer interactions), and weather APIs (providing real-time weather updates). This data is then fed into AI algorithms, including predictive analytics models for demand forecasting and anomaly detection, and optimization algorithms for route planning and resource allocation. The insights generated by these algorithms are then used to inform decision-making across the supply chain, from procurement to delivery. The system also includes a visualization dashboard providing real-time insights and alerts to stakeholders. This architecture ensures that information flows smoothly and efficiently throughout the supply chain, enhancing visibility and transparency at every stage. The system would also incorporate robust security measures to protect sensitive data and ensure compliance with data privacy regulations.
The Impact of AI on Supply Chain Resilience and Risk Management
AI is revolutionizing supply chain management, moving beyond simple optimization to proactively bolster resilience and mitigate risks. Traditional methods often react to disruptions, while AI allows for predictive analysis and proactive intervention, leading to significant improvements in overall supply chain stability and profitability. This proactive approach is crucial in today’s volatile global landscape.
AI’s ability to process vast datasets, identify patterns, and predict future trends empowers businesses to anticipate and neutralize potential disruptions before they significantly impact operations. This predictive capability is particularly valuable in mitigating the effects of unforeseen events, allowing companies to minimize losses and maintain operational continuity.
AI-Driven Disruption Prediction and Mitigation
AI algorithms can analyze historical data, real-time information from various sources (weather patterns, geopolitical events, social media sentiment), and even incorporate external economic forecasts to identify potential disruptions. For instance, by analyzing historical shipping data alongside weather forecasts, an AI system can predict port congestion caused by an impending hurricane, allowing businesses to reroute shipments and avoid delays. Similarly, analyzing social media trends can help anticipate potential labor disputes or supply shortages before they escalate. The ability to proactively identify and address these issues minimizes downtime, reduces costs associated with delays, and safeguards against significant financial losses.
AI’s Response to Unforeseen Events: Case Studies
The COVID-19 pandemic highlighted the vulnerabilities of traditional supply chains. However, companies leveraging AI were better positioned to adapt. For example, some businesses used AI-powered demand forecasting to adjust production levels based on changing consumer behavior, preventing stockouts and minimizing waste. Others utilized AI to optimize their logistics networks, rerouting shipments around affected regions and ensuring the timely delivery of essential goods. Similarly, AI helped in predicting the impact of natural disasters, such as earthquakes or floods, on supply chains by analyzing historical data and real-time information from various sources, allowing companies to activate contingency plans in advance.
Comparison of Traditional and AI-Powered Risk Management
Traditional risk management relies heavily on historical data and expert judgment, often resulting in reactive responses to disruptions. This approach is inherently limited in its ability to predict unforeseen events or adapt to rapidly changing circumstances. AI-powered risk management, on the other hand, leverages advanced analytics and machine learning to identify previously unseen patterns and predict future risks with greater accuracy. This proactive approach allows businesses to develop more robust contingency plans, allocate resources more efficiently, and ultimately build more resilient supply chains. Imagine comparing a weather forecast based solely on past weather patterns to one incorporating complex meteorological models and real-time satellite data – the AI-powered approach offers a significantly clearer and more accurate picture.
Ethical Considerations in AI-Driven Supply Chain Risk Management
The use of AI in supply chain risk management raises important ethical considerations. Data privacy is paramount; ensuring the responsible collection, storage, and use of sensitive data is crucial. Algorithmic bias is another concern; AI models trained on biased data may perpetuate inequalities or lead to unfair outcomes. Transparency and explainability are also essential; businesses need to understand how AI systems arrive at their risk assessments and ensure that these assessments are fair and unbiased. Furthermore, the potential displacement of human workers through automation needs careful consideration and proactive mitigation strategies, such as retraining and reskilling initiatives. Responsible implementation requires a careful balancing of efficiency gains with ethical considerations.
AI and Sustainability in Global Supply Chains
The race to net-zero is on, and global supply chains, notorious for their environmental impact, are under intense scrutiny. Fortunately, artificial intelligence offers a powerful toolkit to drastically reduce the carbon footprint of logistics and manufacturing, paving the way for a more sustainable future. AI’s ability to analyze massive datasets, predict outcomes, and optimize processes makes it uniquely suited to tackling the complexities of green supply chain management.
AI’s contribution to a greener supply chain isn’t just about reducing emissions; it’s about building a more resilient and ethical system. By optimizing logistics, reducing waste, and promoting sustainable sourcing, AI helps companies meet growing consumer demand for environmentally and socially responsible products while improving their bottom line.
AI-Driven Reduction of Carbon Emissions
AI can significantly reduce carbon emissions across various stages of the supply chain. Sophisticated algorithms analyze real-time data on weather patterns, traffic conditions, and fuel prices to optimize delivery routes, minimizing fuel consumption and associated emissions. For instance, a logistics company using AI-powered route optimization might discover a 15% reduction in fuel usage compared to traditional methods, translating directly into lower CO2 emissions. Furthermore, AI can predict potential disruptions like extreme weather events, allowing companies to proactively adjust their operations and avoid unnecessary emissions caused by delays or rerouting. Predictive maintenance, powered by AI, also minimizes downtime and extends the lifespan of vehicles, further reducing emissions associated with manufacturing and replacing equipment.
AI-Optimized Logistics for Minimized Fuel Consumption and Waste
Beyond route optimization, AI contributes to minimizing fuel consumption and waste through intelligent warehouse management. AI-powered systems can optimize warehouse layouts, automate picking and packing processes, and predict demand fluctuations, minimizing wasted energy and reducing transportation needs. Imagine a smart warehouse using AI to predict peak demand periods and pre-position inventory strategically, reducing the need for last-minute, fuel-intensive deliveries. Similarly, AI-powered inventory management prevents overstocking, minimizing waste from expired or obsolete products. Real-time tracking of goods using IoT sensors and AI analytics also allows for efficient delivery scheduling and minimizes empty miles, contributing significantly to fuel savings and emissions reduction.
AI’s Role in Enhancing Sustainable Sourcing and Ethical Procurement
AI is revolutionizing sustainable sourcing and ethical procurement by providing unprecedented transparency and traceability. AI-powered platforms can analyze vast amounts of data from suppliers to assess their environmental and social performance, identifying those who adhere to sustainable practices and ethical labor standards. This enables companies to make informed decisions, selecting suppliers committed to responsible sourcing and minimizing their supply chain’s environmental and social impact. For example, an apparel company using AI could track the origin of its cotton, ensuring it’s sourced sustainably and ethically, reducing its environmental footprint and promoting fair labor practices throughout its supply chain.
Key Sustainability Metrics Trackable and Improvable with AI
AI significantly enhances the tracking and improvement of key sustainability metrics. The ability to collect, analyze, and interpret large datasets in real-time allows for continuous monitoring and adjustments.
- Carbon Footprint: AI can accurately measure and track CO2 emissions across the entire supply chain, from manufacturing to delivery.
- Fuel Consumption: AI optimizes routes and logistics to minimize fuel usage per unit transported.
- Waste Generation: AI reduces waste through optimized inventory management and efficient resource allocation.
- Sustainable Sourcing Compliance: AI monitors supplier adherence to environmental and social standards.
- Energy Consumption: AI optimizes energy usage in warehouses and manufacturing facilities.
- Transportation Efficiency: AI reduces empty miles and improves delivery schedules.
Last Point
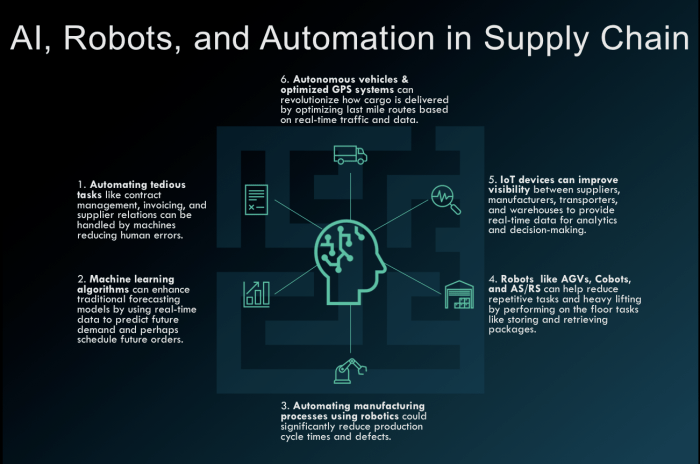
Source: supplychainrevolution.com
The integration of AI into global supply chains and logistics is not just a technological advancement; it’s a fundamental shift in how we manage the flow of goods. While challenges remain, the potential benefits—increased efficiency, enhanced resilience, and a more sustainable future—are undeniable. As AI technologies continue to evolve, we can expect even more sophisticated solutions that will further optimize supply chains, leading to a more streamlined, responsive, and ultimately, more efficient global marketplace. The future is intelligent, and it’s already here.
