The Evolution of Cloud Storage Solutions in Data Management: From clunky mainframes to the sprawling cloud empires of today, the journey of data storage is a wild ride. We’ll unpack how we went from limited, expensive storage to the scalable, accessible solutions that power the modern digital world. Get ready to dive into the tech history, the different players, and the future of how we handle our ever-growing data deluge.
This deep dive explores the various cloud storage models – public, private, hybrid, you name it – and how giants like AWS, Azure, and Google Cloud Storage stack up. We’ll also unravel the tech behind the scenes, from object storage to clever data deduplication techniques. Plus, we’ll see how cloud storage has totally revamped data management in every industry imaginable, from healthcare to finance.
Early Stages of Cloud Storage
Source: domaonline.com
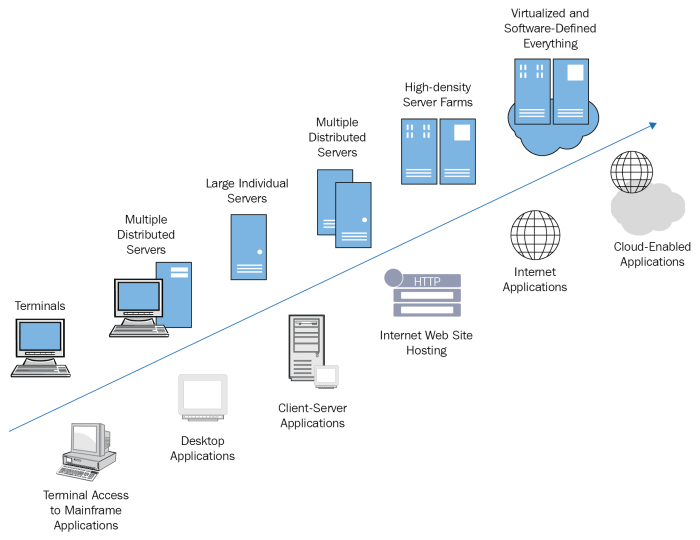
The journey to today’s ubiquitous cloud storage wasn’t a sudden leap; it was a gradual evolution from cumbersome, localized systems to the interconnected networks we rely on now. Before the cloud, data resided primarily on individual machines or within large, expensive mainframe systems. This era presented significant challenges for businesses and individuals alike, paving the way for the innovations that would define the cloud computing landscape.
Traditional data storage methods, before the rise of cloud computing, were characterized by high costs, limited accessibility, and significant maintenance burdens. Imagine massive, room-sized mainframes requiring specialized staff for operation and maintenance. Data backups were a complex, time-consuming process, often involving physical tape drives and intricate procedures. The sheer expense of hardware, software, and skilled personnel made data storage a privilege primarily accessible to large corporations. Accessibility was also severely limited; accessing data often required physical proximity to the machine, hindering collaboration and remote work.
Technological Advancements Enabling Cloud Storage
Several key technological advancements converged to make cloud storage a reality. The development of high-speed internet infrastructure was paramount, providing the necessary bandwidth to transmit large amounts of data efficiently. The miniaturization of computing hardware led to the creation of powerful yet affordable servers, forming the backbone of modern cloud data centers. Advances in virtualization technology allowed multiple virtual servers to run on a single physical machine, optimizing resource utilization and lowering costs. Finally, the emergence of robust software architectures, such as distributed file systems and object storage, ensured data reliability, scalability, and accessibility across geographically dispersed locations.
Chronological Overview of Early Cloud Storage Services
The earliest forms of cloud storage were not what we recognize today. They emerged gradually, often as ancillary services to other computing offerings. Early examples include network attached storage (NAS) devices, which provided centralized storage accessible across a local network. These were a significant step towards shared storage, but still lacked the scalability and accessibility of true cloud solutions. The late 1990s and early 2000s witnessed the rise of early commercial cloud storage services. These initial offerings often focused on specific niches, such as online backup or file sharing. Companies began experimenting with offering storage as a utility, laying the groundwork for the industry’s future growth.
Comparison of Early Cloud Storage Solutions
The table below compares some of the early cloud storage solutions, highlighting their key features and limitations. Note that precise figures for storage capacity and pricing may be difficult to obtain due to the evolving nature of these early offerings.
| Provider | Approximate Storage Capacity (Early Stages) | Pricing Model (Illustrative) | Key Limitations |
|---|---|---|---|
| Early Network Attached Storage (various vendors) | Variable, typically limited by the NAS device’s capacity (e.g., terabytes) | One-time purchase of the device | Limited scalability, single point of failure, restricted access to the local network |
| Early online backup services (e.g., some ISP offerings) | Variable, often limited by subscription tier (e.g., gigabytes) | Subscription-based, often tiered | Limited functionality, often focused solely on backup, potential bandwidth limitations |
| Early file sharing services (e.g., early versions of popular services) | Variable, often limited by free tier or subscription (e.g., gigabytes) | Free tier with limitations, subscription-based for increased capacity | Security concerns, limited collaboration features, often lacked robust version control |
| Early dedicated cloud storage providers (emerging in early 2000s) | Variable, depending on service and subscription (e.g., terabytes) | Subscription-based, often tiered based on storage and features | Relatively high cost compared to later solutions, limited feature set compared to modern services |
The Rise of Cloud Storage as a Service (CaaS)
The evolution of data storage didn’t stop with the early days of networked drives. The true game-changer arrived with Cloud Storage as a Service (CaaS), offering scalable, accessible, and often cost-effective solutions for individuals and businesses alike. This shift marked a pivotal moment, transforming how we think about and manage data. The flexibility and on-demand nature of CaaS propelled its adoption across various sectors, from startups to multinational corporations.
Cloud Storage Service Models: Public, Private, Hybrid, and Multi-Cloud
Understanding the different models of CaaS is crucial for choosing the right fit. Each model presents unique advantages and disadvantages, impacting security, cost, and control. Public clouds, like AWS S3, offer accessibility and scalability at a potentially lower upfront cost, but data security and control are shared. Private clouds, on the other hand, provide greater control and security, but often come with higher infrastructure and maintenance costs. Hybrid clouds combine elements of both, offering a balance between cost and control. Finally, multi-cloud strategies utilize multiple public cloud providers to mitigate risk and leverage specialized services. This diversification can improve resilience and reduce vendor lock-in.
Major Cloud Storage Providers: A Comparison
The CaaS landscape is dominated by a few key players, each with its own strengths and weaknesses. Choosing the right provider depends heavily on specific needs and priorities. While features and pricing models are constantly evolving, understanding the core offerings is vital.
Here’s a look at three major providers:
- Amazon Web Services (AWS) S3: Known for its extensive feature set, mature ecosystem, and global reach. It offers a wide range of storage classes optimized for different access patterns and cost considerations. Its integration with other AWS services is seamless.
- Key Features: Scalability, durability, security features (encryption, access control), diverse storage classes (S3 Standard, S3 Intelligent-Tiering, S3 Glacier), cost-effective options, extensive integration with other AWS services.
- Microsoft Azure Blob Storage: A robust and scalable storage solution tightly integrated with the Azure ecosystem. It provides various storage tiers to cater to different performance and cost requirements. Its strong enterprise focus makes it a popular choice for large organizations.
- Key Features: Scalability, high availability, security features (encryption, access control), different storage tiers (hot, cool, archive), cost-effective options, seamless integration with other Azure services.
- Google Cloud Storage (GCS): A highly scalable and reliable object storage solution offering competitive pricing and strong integration with Google Cloud Platform (GCP) services. Its focus on machine learning and big data analytics makes it attractive for data-intensive workloads.
- Key Features: Scalability, high availability, security features (encryption, access control), various storage classes (standard, nearline, coldline, archive), competitive pricing, strong integration with GCP services, machine learning capabilities.
Advantages and Disadvantages of Cloud Storage Service Models
The optimal choice among public, private, hybrid, and multi-cloud models depends heavily on specific needs. For example, a small startup might benefit from the cost-effectiveness and scalability of a public cloud, while a financial institution might prioritize the enhanced security of a private cloud or a hybrid approach. A large multinational corporation might adopt a multi-cloud strategy to avoid vendor lock-in and optimize resource utilization.
Consider these factors:
| Model | Advantages | Disadvantages |
|---|---|---|
| Public Cloud | Cost-effective, scalable, readily available | Security concerns, vendor lock-in potential, less control |
| Private Cloud | Enhanced security, greater control, customization | Higher upfront costs, complex management, less scalability |
| Hybrid Cloud | Balance of cost and control, flexibility | Complexity in management, potential integration challenges |
| Multi-Cloud | Improved resilience, reduced vendor lock-in, optimized resource utilization | Increased complexity in management, potential integration challenges |
Technological Advancements in Cloud Storage

Source: dataentryoutsourced.com
From floppy disks to the cloud, data management’s journey has been wild. The sheer volume of data generated, especially in creative fields, demands robust solutions. This explosion is directly linked to the rise of AI, as explored in this fascinating article: How Artificial Intelligence is Redefining Creative Industries. Ultimately, the evolution of cloud storage is crucial for handling the massive datasets fueling AI’s creative revolution, ensuring efficient access and collaboration.
The early days of cloud storage were, let’s be honest, a bit…rustic. Think dial-up speeds and storage limitations that would make a modern smartphone blush. But the relentless march of technology has transformed cloud storage into the powerhouse we know today, offering unprecedented scalability, security, and performance. This evolution is driven by advancements in underlying storage technologies, robust security measures, and innovative approaches to data management.
This section dives into the key technological advancements that have propelled cloud storage from a niche technology to the backbone of modern data management. We’ll explore how innovations in storage architectures, security protocols, and performance optimization have shaped the landscape of cloud storage, enabling businesses and individuals alike to leverage the power of the cloud with confidence.
Object Storage, Distributed File Systems, and Data Deduplication, The Evolution of Cloud Storage Solutions in Data Management
The evolution of storage technologies has been pivotal in enhancing cloud storage capabilities. Early cloud storage solutions often relied on traditional file systems, which struggled to scale effectively to handle massive datasets. The advent of object storage, a key innovation, changed the game. Object storage treats data as independent objects, each identified by a unique identifier, metadata, and the actual data itself. This approach allows for massive scalability and high availability, as objects can be distributed across multiple servers and data centers. Simultaneously, distributed file systems emerged, enabling parallel access to large datasets across multiple nodes. These systems offer high performance and fault tolerance, crucial for handling demanding workloads. Finally, data deduplication techniques, which identify and eliminate redundant data copies, significantly reduce storage costs and improve efficiency. Imagine storing terabytes of data with many duplicated files; deduplication drastically reduces that footprint. Netflix, for instance, relies heavily on these techniques to manage its vast library of video content.
Advancements in Data Security and Encryption
Security is paramount in cloud storage, and advancements in encryption techniques have played a crucial role. Early cloud storage solutions often relied on simple encryption methods, but modern solutions utilize sophisticated encryption algorithms, such as AES-256, to protect data both in transit and at rest. Beyond encryption, cloud providers have implemented multi-layered security measures, including access control lists (ACLs), role-based access control (RBAC), and intrusion detection systems (IDS), to prevent unauthorized access and data breaches. These measures, combined with regular security audits and penetration testing, ensure the integrity and confidentiality of stored data. The financial industry, for example, relies heavily on robust cloud security measures to protect sensitive customer data.
Strategies for Enhancing Scalability and Performance
To handle ever-increasing data volumes and user demands, cloud storage providers employ various strategies to enhance scalability and performance. These include horizontal scaling (adding more servers to a cluster), content delivery networks (CDNs) to distribute data closer to users, and advanced caching mechanisms to reduce latency. Furthermore, the use of solid-state drives (SSDs) instead of traditional hard disk drives (HDDs) has significantly improved performance, offering faster read and write speeds. Consider the example of a large e-commerce platform: horizontal scaling allows them to handle peak traffic during sales events, while CDNs ensure fast delivery of product images and videos to customers worldwide.
Hypothetical Scenario: The Benefits of Improved Scalability and Security
Imagine a rapidly growing online gaming company, “LevelUp Games,” which stores its game data, user profiles, and in-game assets in a cloud storage system. Initially, they utilize a smaller, less scalable solution. During a highly anticipated game launch, the system is overwhelmed by a massive influx of new users, leading to slowdowns, crashes, and ultimately, a negative user experience. However, by migrating to a cloud storage system with enhanced scalability and security features, LevelUp Games can seamlessly handle the increased load. The improved scalability ensures that the system can handle the surge in traffic without performance degradation, while robust security measures protect sensitive user data from unauthorized access or cyberattacks. This prevents data loss and maintains user trust, ensuring a positive brand reputation and continued growth. The improved system allows for a much smoother launch and avoids the costly consequences of a system failure.
Impact of Cloud Storage on Data Management Practices: The Evolution Of Cloud Storage Solutions In Data Management
Cloud storage has fundamentally reshaped how businesses and individuals manage their data. The shift from on-premise solutions to the cloud has brought about significant changes in efficiency, cost, and accessibility, impacting various industries in profound ways. This section explores the transformative effects of cloud storage on data management practices, comparing traditional methods with modern cloud-based approaches and highlighting the benefits in data sharing and collaboration.
Transformation of Data Management Practices Across Industries
Cloud storage has revolutionized data management across diverse sectors. In healthcare, for example, hospitals utilize cloud platforms to securely store and share patient medical records, facilitating better collaboration between doctors and specialists. This improves patient care and reduces the risk of data loss associated with physical storage. Financial institutions leverage cloud storage for secure transaction processing and regulatory compliance, benefiting from enhanced scalability and disaster recovery capabilities. The media and entertainment industry uses cloud storage for efficient content management, enabling seamless collaboration among production teams and quick delivery of content to global audiences. Even small businesses benefit from readily available, cost-effective storage solutions, freeing up valuable resources and time.
Comparison of Traditional and Cloud-Based Backup and Recovery
Traditional data backup and recovery methods often involved physical tapes, external hard drives, and on-site servers. This approach was cumbersome, time-consuming, and prone to data loss due to physical damage or theft. In contrast, cloud-based backup and recovery solutions offer automated backups, off-site storage, and quick recovery times. Data is replicated across multiple data centers, ensuring high availability and resilience against disasters. The cloud also offers versioning, allowing for easy retrieval of previous data versions, further minimizing the risk of data loss. For example, a small business using traditional methods might experience significant downtime and data loss if their on-site server fails, whereas a cloud-based solution would minimize disruption.
Cloud Storage and Enhanced Data Sharing and Collaboration
Cloud storage platforms inherently facilitate data sharing and collaboration. Centralized repositories allow multiple users to access, modify, and share data simultaneously, breaking down geographical barriers and fostering real-time teamwork. Features like shared folders, permission controls, and version history enhance collaboration while maintaining data security and accountability. For instance, a design team working on a project can access and modify design files stored in the cloud from anywhere in the world, promoting efficient teamwork and faster project completion. This streamlined workflow is unimaginable with traditional file-sharing methods.
Impact of Cloud Storage on Data Management Aspects
| Aspect of Data Management | Traditional Approach | Cloud-Based Approach | Impact |
|---|---|---|---|
| Cost | High upfront investment in hardware and software, ongoing maintenance costs. | Pay-as-you-go model, reduced upfront investment, lower operational costs. | Significant cost reduction, improved scalability. |
| Efficiency | Manual backups, slow recovery times, limited accessibility. | Automated backups, quick recovery, anytime, anywhere access. | Increased efficiency, improved productivity. |
| Security | Vulnerable to physical damage, theft, and cyberattacks. | Robust security measures, data encryption, access controls, disaster recovery. | Enhanced security, reduced risk of data loss. |
| Scalability | Limited scalability, requires significant investment to expand capacity. | Easily scalable, capacity can be adjusted based on needs. | Improved scalability, ability to adapt to changing business needs. |
The Future of Cloud Storage in Data Management
The cloud storage landscape is constantly evolving, driven by the ever-increasing demands for data storage, processing power, and accessibility. We’re moving beyond simply storing data in the cloud; we’re entering an era where cloud storage is becoming increasingly intelligent, efficient, and integrated into the very fabric of data management. The future promises exciting advancements, but also presents significant challenges that need careful consideration.
Emerging trends like serverless computing and edge computing are reshaping how we interact with and manage data. The integration of artificial intelligence and machine learning is further optimizing storage solutions, making them more responsive, cost-effective, and secure. This leads to a future where data management is seamless, automated, and deeply integrated with business processes, leading to significant improvements in efficiency and decision-making.
Serverless and Edge Computing in Cloud Storage
Serverless computing removes the burden of managing servers, allowing developers to focus solely on code. In the context of cloud storage, this means developers can build applications that automatically scale based on demand, without worrying about infrastructure provisioning. Edge computing, on the other hand, brings computation and data storage closer to the source of data generation, reducing latency and improving responsiveness for applications that require real-time processing, such as IoT devices or autonomous vehicles. Imagine a network of smart streetlights: edge computing allows the data from each light to be processed locally, reducing the strain on the central cloud and ensuring faster responses to changing conditions, like traffic flow or pedestrian activity. The combination of serverless and edge computing offers a highly scalable and efficient solution for handling massive datasets generated by diverse sources.
Artificial Intelligence and Machine Learning in Cloud Storage Optimization
AI and ML are revolutionizing cloud storage management. AI-powered systems can predict storage needs, optimize data placement for faster retrieval, and automatically identify and address potential security threats. Machine learning algorithms can analyze usage patterns to identify redundancies and inefficiencies, automatically deleting or archiving unnecessary data. For example, an AI-powered system could automatically identify and delete duplicate files across a company’s cloud storage, freeing up valuable space and reducing storage costs. This proactive approach minimizes human intervention and maximizes efficiency. Furthermore, AI can enhance data security by detecting anomalies and potential breaches in real-time, providing a proactive defense against cyber threats.
A Futuristic Cloud Storage System: Project Chimera
Imagine “Project Chimera,” a futuristic cloud storage system. Chimera utilizes a hybrid architecture combining the scalability of serverless computing with the low-latency benefits of edge computing. Data is intelligently distributed across multiple data centers and edge nodes based on real-time demand and access patterns, ensuring optimal performance and redundancy. AI-powered analytics constantly monitor storage usage, automatically adjusting resource allocation to meet fluctuating demands. Advanced encryption and security protocols, integrated with AI-driven threat detection, ensure data integrity and confidentiality. Chimera seamlessly integrates with various applications and platforms, providing a unified data management solution. Its self-healing capabilities automatically recover from failures and ensure high availability. The system also incorporates advanced data compression and deduplication techniques, maximizing storage efficiency and minimizing costs. Chimera’s intuitive interface provides users with comprehensive visibility into their data, empowering them to make informed decisions about storage and data management strategies. This system represents a significant leap forward in data management, offering unprecedented scalability, efficiency, and security.
Closing Notes
Source: packt-cdn.com
The evolution of cloud storage isn’t just a tech story; it’s a story of how we manage, access, and protect the world’s information. From the limitations of the past to the exciting possibilities of AI-powered, serverless futures, the journey has been remarkable. As we navigate the challenges and embrace the opportunities ahead, one thing’s for sure: the cloud’s influence on data management will only grow stronger.
