How Technology Is Helping Us Adapt to a Post-Pandemic World – it’s a story of resilience, reinvention, and the unexpected silver linings of a global crisis. From remote work revolutionizing our professional lives to telehealth transforming healthcare access, technology stepped up in ways we couldn’t have imagined. This isn’t just about surviving; it’s about thriving in a new normal shaped by digital innovation. We’ll dive into how everything from online learning to supply chain logistics has been reshaped, exploring both the triumphs and the challenges along the way.
The pandemic forced a rapid acceleration of technological adoption across every facet of life. Businesses scrambled to implement remote work solutions, educators embraced online learning platforms, and healthcare providers discovered the potential of telehealth. This rapid shift revealed both the power and the limitations of technology, highlighting the need for equitable access and responsible innovation. This exploration will uncover how technology is not just a tool for adaptation, but a catalyst for a fundamentally changed world.
Remote Work and Collaboration
The pandemic forced a rapid shift to remote work, fundamentally altering the landscape of professional life. While initially met with uncertainty, the widespread adoption of remote work technologies has revealed both challenges and remarkable opportunities for businesses and employees alike. This shift has spurred innovation in communication and collaboration tools, leading to a more flexible and, in many cases, more productive work environment.
The impact of remote work technologies on post-pandemic work culture is multifaceted. Companies have discovered that productivity doesn’t necessarily hinge on physical presence. Employees, meanwhile, have gained greater autonomy and work-life balance, although this comes with its own set of adjustments. The lines between work and personal life have blurred, requiring conscious effort to establish healthy boundaries. Furthermore, the rise of remote work has expanded the talent pool, allowing companies to recruit from a global workforce and fostering a more diverse and inclusive environment.
Successful Remote Collaboration Tools, How Technology Is Helping Us Adapt to a Post-Pandemic World
Several tools have proven crucial for effective remote collaboration. These platforms offer a range of features designed to streamline communication, project management, and file sharing. Choosing the right tools depends on team size, project complexity, and individual preferences.
For example, Slack, a popular communication platform, allows for instant messaging, file sharing, and the creation of channels for specific projects or teams. Its intuitive interface and robust features make it a go-to choice for many organizations. Microsoft Teams, another widely used platform, integrates seamlessly with other Microsoft Office applications, providing a centralized hub for communication, collaboration, and project management. Features like video conferencing, screen sharing, and task assignment contribute to efficient teamwork. Asana and Trello, on the other hand, are project management tools that help teams organize tasks, track progress, and collaborate on projects using Kanban boards or lists. These tools promote transparency and accountability, ensuring everyone stays on the same page.
Post-pandemic life? Tech’s got our backs, from remote work setups to telehealth. But its impact extends far beyond; consider the game-changer that is global education, where tech’s leveling the playing field. Check out this insightful piece on The Role of Technology in Global Education Accessibility to see how it’s bridging divides. Ultimately, tech’s helping us build a more connected, accessible future, one digital classroom at a time.
Best Practices for Maintaining Team Cohesion and Productivity in Remote Settings
Maintaining a strong team dynamic while working remotely requires a proactive approach. Regular communication is key, but it’s not just about sending emails. Scheduled virtual meetings, both formal and informal, help foster a sense of community and allow for open dialogue. These meetings shouldn’t just focus on work; incorporating social elements can significantly improve team cohesion. Clear communication protocols, including response times and preferred communication methods, are also essential. Furthermore, providing employees with the necessary resources and training to effectively use remote work technologies is crucial for maximizing productivity. Regular check-ins with individual team members to gauge their well-being and address any challenges they might be facing also demonstrate care and support.
Comparison of Remote Work Models
Different remote work models offer varying degrees of flexibility and control. Understanding the advantages and disadvantages of each is crucial for making informed decisions.
| Remote Work Model | Advantages | Disadvantages | Suitable For |
|---|---|---|---|
| Fully Remote | Increased flexibility, reduced commute time, wider talent pool | Potential for isolation, challenges in team building, requires strong self-discipline | Teams that can operate independently, roles that don’t require physical presence |
| Hybrid | Combines benefits of both in-office and remote work, allows for in-person collaboration when needed | Requires careful planning and coordination, potential for inequities between in-office and remote employees | Teams that require a mix of in-person and remote collaboration, roles that benefit from both environments |
| In-Office | Stronger team cohesion, easier communication, better supervision | Limited flexibility, increased commute time, higher overhead costs | Teams that require constant in-person interaction, roles that involve hands-on tasks |
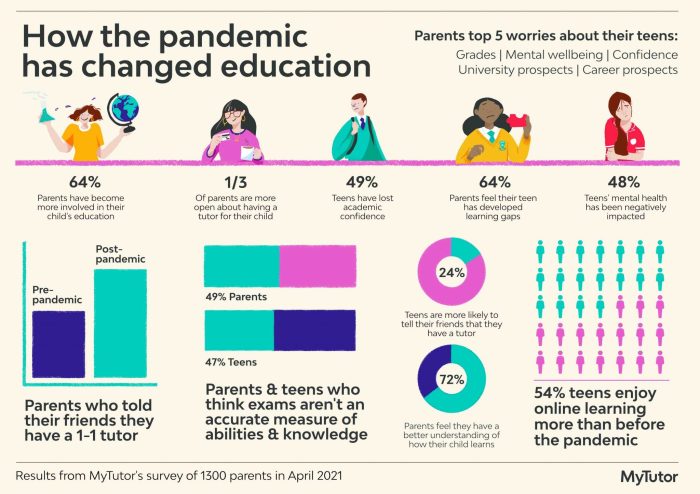
E-learning and Online Education
The pandemic acted as a brutal but effective catalyst, catapulting online education from a niche option to a mainstream necessity. Overnight, classrooms went digital, forcing a rapid evolution of online learning platforms and pedagogical approaches. This shift, while initially chaotic, has ultimately reshaped the educational landscape, presenting both unprecedented challenges and exciting opportunities.
The evolution of online learning platforms since the pandemic has been nothing short of astonishing. Pre-pandemic platforms, often clunky and lacking interactive features, underwent a significant upgrade. We saw a surge in user-friendly interfaces, improved video conferencing capabilities, and the integration of more sophisticated learning management systems (LMS). Features like interactive quizzes, collaborative document editing, and personalized learning pathways became commonplace, addressing some of the limitations of traditional online learning. The market also saw the rise of new platforms specifically designed for remote learning, offering tailored solutions for different educational needs and age groups. This rapid innovation ensured that the abrupt shift to online learning wasn’t completely disruptive, even if it was initially bumpy.
Challenges and Opportunities in Online Education
The transition to online learning presented significant challenges for both students and educators. Students faced issues with digital literacy, access to reliable internet and technology, and the lack of face-to-face interaction with peers and teachers. The isolating nature of online learning contributed to feelings of loneliness and disengagement for some. Educators, on the other hand, had to rapidly adapt their teaching methods, mastering new technologies and developing engaging online content while navigating the technical challenges of virtual classrooms. However, the pandemic also revealed opportunities. Online learning fostered greater flexibility and accessibility, allowing students to learn at their own pace and access educational resources from anywhere with an internet connection. Educators discovered innovative ways to engage students online, utilizing interactive tools and collaborative projects to create dynamic learning environments. The increased use of data analytics also allowed for personalized learning experiences, catering to individual student needs and learning styles.
Technology’s Role in Enhancing Accessibility and Inclusivity
Technology has played a crucial role in making education more accessible and inclusive. Online learning platforms break down geographical barriers, enabling students in remote areas or with disabilities to access quality education. Assistive technologies, such as screen readers and text-to-speech software, are seamlessly integrated into many online learning environments, catering to students with visual or auditory impairments. Subtitles and transcripts enhance accessibility for students with hearing difficulties. Furthermore, online learning allows for personalized learning experiences, catering to diverse learning styles and needs, making education more equitable for all students. For example, students with learning disabilities can benefit from the tailored pace and support offered by online platforms.
Innovative Technologies in Online Education
The adoption of innovative technologies has significantly enhanced the online learning experience.
- Virtual Reality (VR) and Augmented Reality (AR): VR and AR technologies offer immersive learning experiences, allowing students to explore historical sites, dissect virtual organs, or participate in simulated experiments, fostering deeper engagement and understanding.
- Gamification: Incorporating game mechanics like points, badges, and leaderboards into online learning platforms increases student motivation and engagement, turning learning into a fun and rewarding experience.
- Artificial Intelligence (AI): AI-powered tools can personalize learning paths, provide instant feedback, and automate administrative tasks, freeing up educators’ time to focus on individual student needs.
- Adaptive Learning Platforms: These platforms adjust the difficulty level and content based on individual student performance, ensuring that each student is challenged appropriately and receives the support they need.
- Interactive Whiteboards and Collaborative Tools: These tools facilitate real-time collaboration and interaction among students and teachers, mimicking the collaborative aspects of traditional classrooms.
Telehealth and Remote Healthcare
Source: co.uk
The pandemic dramatically accelerated the adoption of telehealth, transforming how we access and receive healthcare. No longer a niche service, telehealth is now a vital component of a modern, accessible healthcare system, offering convenience and potentially improved outcomes for patients and providers alike. This section delves into the technological advancements driving this growth, compares telehealth’s effectiveness to traditional care, and explores its impact on healthcare access and affordability.
Technological Advancements in Telehealth
Several technological advancements have fueled the rapid expansion of telehealth. High-speed internet access, coupled with increasingly sophisticated smartphones and other mobile devices, has made remote consultations readily available to a wider population. Secure video conferencing platforms, such as Zoom and dedicated telehealth platforms, provide reliable and HIPAA-compliant channels for communication between patients and healthcare providers. Furthermore, the development of wearable health monitoring devices allows for continuous data collection, enabling proactive intervention and personalized care. Remote patient monitoring (RPM) systems transmit vital signs and other health data directly to healthcare professionals, facilitating early detection of potential problems and reducing hospital readmissions. Artificial intelligence (AI) is also playing an increasingly significant role, assisting with diagnosis, treatment planning, and administrative tasks. For example, AI-powered chatbots can answer patient queries, schedule appointments, and provide basic health information, freeing up clinicians’ time for more complex tasks.
Effectiveness of Telehealth Compared to In-Person Care
The effectiveness of telehealth varies depending on the specific condition being treated. For routine check-ups, medication management, and mental health counseling, telehealth often provides comparable or even superior outcomes to in-person care. The convenience and reduced travel time can improve adherence to treatment plans. However, for conditions requiring physical examination or complex procedures, in-person care remains essential. Studies have shown that telehealth can be particularly effective for managing chronic conditions like diabetes and hypertension, where regular monitoring and remote support are crucial. For example, remote monitoring of blood glucose levels in diabetic patients can lead to better glycemic control and reduced complications. On the other hand, diagnosing a complex fracture or performing surgery still necessitates a face-to-face encounter. The optimal approach often involves a blended model, integrating telehealth with in-person visits as needed.
Telehealth Applications and Benefits
| Application | Benefits | Technology Used | Patient Population |
|---|---|---|---|
| Chronic Disease Management (e.g., diabetes, hypertension) | Improved adherence to treatment plans, reduced hospitalizations, early detection of complications | Remote patient monitoring devices, telehealth platforms, wearable sensors | Patients with chronic conditions |
| Mental Healthcare | Increased access to care, reduced stigma, improved convenience | Video conferencing, secure messaging platforms | Individuals with mental health concerns |
| Primary Care Consultations | Convenient access to primary care physicians, reduced wait times | Video conferencing, electronic health records | Patients needing routine check-ups or minor ailment consultations |
| Specialist Consultations | Access to specialists regardless of geographical location | Video conferencing, secure file sharing | Patients requiring specialized care |
Impact of Telehealth on Healthcare Access and Affordability
Telehealth has the potential to significantly improve healthcare access, particularly for individuals in rural or underserved areas with limited access to healthcare facilities. By eliminating geographical barriers, telehealth makes specialized care more readily available. Furthermore, telehealth can contribute to increased affordability by reducing transportation costs, time off work, and the need for frequent in-person visits. However, the digital divide remains a significant challenge, as access to reliable internet and technology is not universally available. Efforts to bridge this gap are crucial to ensuring equitable access to telehealth services. Telehealth also presents opportunities for cost savings for healthcare providers through increased efficiency and reduced overhead costs associated with physical facilities. However, the long-term financial impact of telehealth is still evolving and requires further investigation.
Digital Transformation in Businesses
The COVID-19 pandemic acted as a powerful catalyst, forcing businesses worldwide to rapidly embrace digital technologies to survive and thrive. Those that successfully navigated this period leveraged technology not just for immediate crisis management, but also for long-term strategic advantage, reshaping their operations and forging new paths to growth. This section explores how businesses adapted, highlighting successful examples and best practices for digital transformation across various industries.
Businesses across the globe were compelled to rethink their operations almost overnight. The sudden shift to remote work, the closure of physical stores, and the disruption of supply chains forced companies to rely heavily on technology to maintain operations, connect with customers, and adapt to the changing landscape. This rapid adoption of digital tools and strategies led to a significant acceleration of the digital transformation process that was already underway in many industries.
Business Adaptation Strategies and Examples
Many companies successfully leveraged technology to maintain business continuity and even achieve growth during the pandemic. For example, grocery stores rapidly expanded their online ordering and delivery services, partnering with third-party delivery platforms or investing in their own logistics networks. Restaurants shifted to online ordering and contactless delivery, utilizing apps and platforms to reach customers who were staying home. Retailers that already had a strong online presence saw significant increases in sales, while those that lagged behind scrambled to catch up. Companies like Zoom experienced explosive growth as video conferencing became essential for remote work and communication. Meanwhile, Netflix saw a surge in subscribers as people sought entertainment during lockdowns. These examples demonstrate the critical role of technology in ensuring business survival and even capitalizing on unexpected opportunities.
Best Practices for Digital Transformation
Implementing a successful digital transformation strategy requires a holistic approach. It’s not simply about adopting new technologies; it’s about fundamentally changing how a business operates and interacts with its customers. Key best practices include:
* Prioritizing Customer Experience: Digital transformation should always start with the customer. Businesses need to understand how technology can improve the customer journey, from initial engagement to post-purchase support.
* Data-Driven Decision Making: Harnessing data analytics to gain insights into customer behavior, market trends, and operational efficiency is crucial. This data can inform strategic decisions and drive continuous improvement.
* Investing in Employee Training and Development: Digital transformation requires a skilled workforce. Businesses need to invest in training and development programs to equip employees with the skills they need to effectively utilize new technologies.
* Building a Strong Digital Infrastructure: A reliable and scalable digital infrastructure is essential to support the demands of a digitally transformed business. This includes investing in cloud computing, cybersecurity, and other essential technologies.
* Agile and Iterative Approach: Digital transformation is an ongoing process, not a one-time project. Adopting an agile approach allows businesses to adapt to changing needs and continuously improve their digital capabilities.
Technology’s Role in Business Adaptation
The following table illustrates the specific technologies used by businesses to adapt to the post-pandemic world:
| Technology | Application in Business Adaptation | Industry Examples | Benefits |
|---|---|---|---|
| Cloud Computing | Enabling remote work, scalability, cost reduction | Software companies, financial institutions, healthcare providers | Increased flexibility, reduced IT infrastructure costs, enhanced collaboration |
| Data Analytics | Improving decision-making, optimizing operations, personalizing customer experiences | Retail, e-commerce, marketing agencies | Data-driven insights, improved efficiency, enhanced customer engagement |
| Automation | Automating repetitive tasks, improving efficiency, reducing costs | Manufacturing, logistics, customer service | Increased productivity, reduced operational costs, improved accuracy |
| Artificial Intelligence (AI) | Improving customer service, enhancing security, automating processes | Banking, healthcare, retail | Enhanced customer experience, improved security, increased efficiency |
The Changing Landscape of Social Interaction: How Technology Is Helping Us Adapt To A Post-Pandemic World

Source: vox-cdn.com
The pandemic forced a dramatic shift in how we connect, accelerating the already rapid integration of technology into our social lives. While physical distancing became the norm, technology stepped in, bridging the gap and offering alternative avenues for maintaining social bonds. This wasn’t simply a matter of convenience; it was a lifeline for many, highlighting both the potential and the pitfalls of technology’s role in shaping our social interactions.
The reliance on digital communication platforms during lockdowns demonstrated technology’s remarkable ability to facilitate social connections even amidst physical separation. Video calls became commonplace, allowing families and friends to maintain visual contact and share moments, albeit remotely. Online gaming communities thrived, providing virtual spaces for social interaction and shared experiences. Social media platforms, for better or worse, became even more central to our social lives, acting as digital town squares where individuals could connect, share updates, and participate in online discussions. However, this increased reliance also raised concerns about the impact of constant digital connection on mental health and well-being.
The Impact of Social Media on Mental Health
The impact of social media on mental well-being is a complex and multifaceted issue. While platforms like Facebook and Instagram can foster a sense of community and connection, they can also contribute to feelings of inadequacy, anxiety, and depression. Curated online personas often present an unrealistic portrayal of others’ lives, leading to social comparison and feelings of envy. The constant stream of information and notifications can also be overwhelming, contributing to stress and burnout. Conversely, platforms emphasizing positive interactions and shared interests, such as niche hobby groups or supportive online communities, can offer significant mental health benefits, providing a sense of belonging and shared experience. Research consistently highlights the correlation between excessive social media use and negative mental health outcomes, emphasizing the need for mindful and balanced engagement with these platforms. For example, studies have linked high social media usage to increased rates of anxiety and depression in young adults.
Combating Social Isolation Through Technology
Technology offers powerful tools to combat social isolation and loneliness, particularly for vulnerable populations like the elderly or individuals with disabilities. Video conferencing platforms can facilitate regular contact with loved ones, reducing feelings of isolation. Online support groups and communities provide spaces for individuals to connect with others facing similar challenges, fostering a sense of belonging and shared understanding. Apps designed to connect individuals based on shared interests or location can help combat loneliness by facilitating new social connections. Furthermore, virtual reality (VR) technologies are emerging as promising tools for creating immersive social experiences, allowing individuals to interact with others in virtual environments, potentially mitigating the negative impacts of physical isolation. For instance, VR therapy is being explored as a means to treat social anxiety and phobias by providing a safe and controlled environment to practice social interactions.
The Evolution of Social Interaction: A Visual Representation
Imagine a timeline stretching across a canvas. At the far left, a small, isolated figure represents pre-technological social interaction, characterized by close-knit communities and limited reach. As the timeline progresses, the figure grows larger, surrounded by increasingly complex networks of connection. The first stage shows the introduction of the telephone, represented by a thin, connecting line between the figure and a few other distant figures. The next stage depicts the emergence of the internet, represented by a web of interconnected lines expanding outward, symbolizing the increased accessibility of communication and the formation of online communities. The final stage depicts the figure surrounded by a vibrant, multi-layered network of connections, symbolizing the current era of hyper-connectivity through various social media platforms and digital communication tools. The colours shift from muted tones at the beginning to a vibrant array of colours, reflecting the diverse and dynamic nature of modern social interaction. The overall visual suggests a continuous evolution, highlighting the expanding reach and complexity of social connection facilitated by technology, while also acknowledging the potential challenges and complexities that accompany this evolution.
Supply Chain and Logistics Innovations
The pandemic threw a wrench into global supply chains, exposing vulnerabilities and forcing businesses to rethink their logistics strategies. However, it also accelerated the adoption of technologies that improved efficiency, resilience, and transparency. This wasn’t just about surviving the crisis; it was about building a more robust and adaptable system for the future.
The reliance on just-in-time inventory models, once lauded for efficiency, proved brittle in the face of lockdowns, port congestion, and unpredictable demand. Companies scrambled to find alternative suppliers, optimize transportation routes, and enhance visibility across their supply networks. This urgency spurred innovation and a faster-than-expected adoption of digital solutions.
Technological Solutions Addressing Supply Chain Disruptions
The pandemic highlighted the critical need for real-time data visibility and predictive analytics. Companies that leveraged technologies like blockchain for tracking goods, AI for demand forecasting, and IoT sensors for monitoring inventory levels were better positioned to navigate disruptions. For instance, using blockchain to track shipments provided transparency and accountability, reducing delays and improving traceability. AI-powered predictive models helped anticipate demand fluctuations and optimize inventory levels, minimizing stockouts and waste. The implementation of IoT sensors in warehouses and transportation hubs enabled real-time monitoring of goods, alerting businesses to potential problems before they escalated.
Best Practices for Building Robust and Adaptable Supply Chains
Building a resilient supply chain requires a multi-faceted approach that prioritizes diversification, visibility, and agility. Diversifying sourcing to multiple suppliers mitigates the risk of relying on a single point of failure. Real-time data visibility across the entire supply chain allows for proactive identification and mitigation of potential disruptions. Finally, agile supply chains are able to quickly adapt to changing conditions, such as fluctuating demand or unexpected events. This agility can be achieved through flexible manufacturing processes, responsive logistics networks, and strong collaboration with suppliers and partners. Investing in advanced analytics and digital technologies is crucial for achieving these goals. Companies should consider adopting a risk management framework that incorporates scenario planning and contingency strategies to prepare for a wide range of potential disruptions.
Key Technological Advancements in Logistics and Transportation
The following advancements significantly impacted logistics and transportation during and after the pandemic:
- Advanced Analytics and AI: Predictive modeling for demand forecasting, route optimization, and risk management. This allows for proactive adjustments to inventory levels and shipping routes, minimizing disruptions.
- Blockchain Technology: Enhanced transparency and traceability of goods throughout the supply chain, improving accountability and reducing fraud.
- Internet of Things (IoT): Real-time monitoring of goods, vehicles, and infrastructure, providing insights into potential bottlenecks and delays.
- Robotics and Automation: Increased efficiency and reduced labor costs in warehousing and transportation, particularly in handling and sorting goods.
- Drone Delivery and Autonomous Vehicles: The potential for faster and more efficient delivery, especially in remote or congested areas, is significant though still in early stages of widespread adoption.
- Digital Twins: Virtual representations of physical assets and processes, enabling simulation and optimization of supply chain operations. This allows for testing different scenarios and identifying potential vulnerabilities before they occur in the real world.
Closing Summary
The post-pandemic world is undeniably a tech-driven one. While challenges remain – digital divides, ethical considerations, and the ever-evolving landscape of cybersecurity – the undeniable truth is that technology has been instrumental in our collective adaptation. From fostering remote connections to revolutionizing healthcare and business, the innovations we’ve witnessed are reshaping our lives in profound ways. The future isn’t just digital; it’s a future where technology’s role in shaping our society continues to evolve, demanding our ongoing attention and thoughtful engagement.
