How Technology is Changing the Landscape of Global Trade: Forget dusty shipping manifests and snail-mail invoices. The world of international commerce is undergoing a digital revolution, fueled by e-commerce giants, AI-powered supply chains, and the lightning-fast speed of fintech. This isn’t just about making things faster; it’s about reshaping the entire global economic landscape, creating new opportunities while simultaneously disrupting traditional business models. From the rise of digital marketplaces to the transformative power of blockchain, we’re diving deep into how technology is rewriting the rules of global trade.
This seismic shift impacts everyone, from multinational corporations to small businesses operating across borders. We’ll explore how innovative technologies are streamlining processes, boosting efficiency, and opening up previously unimaginable market access. But it’s not all smooth sailing. We’ll also address the challenges – cybersecurity risks, ethical concerns surrounding data, and the need for adaptable regulations – that accompany this rapid technological advancement.
E-commerce and Digital Marketplaces: How Technology Is Changing The Landscape Of Global Trade

Source: entrepreneur.com
The rise of e-commerce has fundamentally reshaped global trade, creating a borderless marketplace accessible to businesses of all sizes. This shift has democratized international commerce, allowing smaller enterprises to compete with larger corporations on a global scale and fostering unprecedented economic interconnectedness. The impact is profound, affecting everything from supply chains to consumer behavior.
E-commerce platforms have dramatically lowered the barriers to entry for international trade. Previously, reaching global markets required significant investment in logistics, infrastructure, and international marketing. Now, businesses can establish an online presence and reach customers worldwide with relatively minimal upfront costs. This accessibility has spurred innovation, increased competition, and led to a more diverse range of products and services available globally.
E-commerce Platforms and Their Impact on Global Trade
| Platform | Impact on Trade | Business Examples | Disruptive Strategies |
|---|---|---|---|
| Amazon | Facilitated massive growth in cross-border B2C e-commerce; provided a global marketplace for sellers of all sizes; streamlined logistics and fulfillment for international shipping. | Amazon itself (global reach, diverse product offerings); numerous third-party sellers leveraging Amazon’s infrastructure to reach international markets; small businesses using Fulfillment by Amazon (FBA) to compete globally. | Utilizing data analytics for personalized recommendations and targeted advertising; offering competitive pricing and a wide selection of products; investing heavily in logistics and fulfillment to ensure fast and reliable delivery; leveraging its vast customer base for feedback and product development. |
| Alibaba | Dominates B2B e-commerce, connecting businesses globally; enables small and medium-sized enterprises (SMEs) in developing countries to access international markets; offers a range of services including payment processing and logistics. | Alibaba itself (providing a platform for millions of businesses); numerous Chinese manufacturers and exporters using Alibaba to reach international buyers; SMEs leveraging Alibaba’s ecosystem to expand their reach beyond their local markets. | Focusing on building trust and transparency within its ecosystem; offering a range of services to support businesses, including financing and logistics; leveraging its vast network of suppliers and manufacturers; developing specialized platforms for different industries. |
| Shopify | Empowered millions of small and medium-sized businesses to create their own online stores and sell globally; provided easy-to-use tools and resources for managing online sales and marketing; facilitated integration with various payment gateways and shipping providers. | Numerous independent businesses using Shopify to sell products internationally; direct-to-consumer brands leveraging Shopify’s platform to build global audiences; artisans and small manufacturers using Shopify to bypass traditional retail channels. | Providing user-friendly tools and resources; offering a wide range of apps and integrations; focusing on mobile commerce; providing marketing and sales tools to help businesses grow their online presence. |
Examples of E-commerce Disrupting Traditional Trade Practices
The impact of e-commerce on traditional trade practices is undeniable. For example, the rise of e-commerce has significantly reduced the reliance on physical intermediaries such as wholesalers and distributors. Businesses can now connect directly with consumers worldwide, eliminating the need for these middlemen and reducing costs. This direct-to-consumer (DTC) model has empowered smaller businesses and fostered greater competition.
Furthermore, e-commerce has accelerated the shift towards a globalized supply chain. Businesses can source materials and manufacture products from anywhere in the world, leveraging global networks of suppliers and manufacturers. This has led to increased efficiency and lower production costs, but also raises concerns about ethical sourcing and labor practices.
Global trade’s undergoing a serious tech makeover, with digital platforms streamlining everything from logistics to payments. But this new efficiency brings new challenges, especially for intellectual property. Securing digital copyrights is crucial, and that’s where innovation steps in; check out this article on The Role of Blockchain in Digital Copyright Protection to see how it’s changing the game.
Ultimately, stronger IP protection paves the way for smoother, more trustworthy global commerce.
Finally, e-commerce has changed consumer behavior. Consumers now expect greater convenience, transparency, and choice when making purchases. This has put pressure on traditional retailers to adapt their business models to compete in the digital marketplace. Those who fail to adapt risk being left behind.
Supply Chain Optimization and Logistics
Global trade is no longer a game of slow boats and snail mail. Technology is revolutionizing how goods move across borders, making supply chains faster, more efficient, and far more transparent than ever before. This shift is driven by advancements in areas like artificial intelligence, the Internet of Things (IoT), and blockchain technology, all working together to streamline the complex process of getting products from origin to consumer.
The integration of AI and IoT is dramatically reshaping supply chain efficiency. AI-powered predictive analytics can forecast demand with remarkable accuracy, allowing businesses to optimize inventory levels, reducing storage costs and minimizing waste from unsold goods. IoT sensors embedded in shipping containers, trucks, and warehouses provide real-time data on location, temperature, and other crucial factors. This constant stream of information enables proactive problem-solving, preventing delays and losses due to unforeseen circumstances like extreme weather or equipment malfunction. For instance, a temperature-sensitive pharmaceutical shipment can be rerouted immediately if a sensor detects a breach in the ideal temperature range, ensuring the integrity of the product and preventing significant financial losses.
AI and IoT Enhance Supply Chain Efficiency
AI algorithms analyze vast datasets to identify bottlenecks and inefficiencies in the supply chain. This allows businesses to optimize routes, improve warehouse management, and streamline logistics operations. IoT devices provide real-time visibility into the movement of goods, allowing for immediate responses to disruptions. Consider a scenario where a shipment is delayed due to unexpected traffic congestion. Real-time tracking data from IoT sensors alerts the logistics team, who can then reroute the shipment or take other necessary steps to minimize the impact of the delay. This proactive approach reduces costs associated with late deliveries and customer dissatisfaction.
Blockchain Technology and Supply Chain Transparency
Blockchain technology, the backbone of cryptocurrencies, is transforming supply chain transparency and traceability. Its decentralized and immutable ledger provides a secure record of every step in a product’s journey, from raw material sourcing to final delivery. This enhanced visibility combats counterfeiting, ensures product authenticity, and allows for better accountability across the entire supply chain. For example, a luxury handbag manufacturer can use blockchain to verify the authenticity of its leather, ensuring that it comes from ethically sourced suppliers and hasn’t been tampered with during transportation. Consumers can scan a QR code on the product to access its complete history on the blockchain, building trust and confidence in the brand.
Traditional vs. Modern Logistics: A Comparison
Traditional logistics methods often rely on manual processes, paper-based documentation, and limited real-time visibility. This can lead to delays, errors, and increased costs. Modern, technology-driven approaches leverage AI, IoT, and blockchain to automate many aspects of the supply chain, improving efficiency and reducing errors.
- Traditional Shipping: Often involves manual data entry, slower communication, and less precise tracking, leading to potential delays and increased risk of errors.
- Automated Shipping Systems: Utilize AI-powered route optimization, real-time tracking, and automated warehousing, resulting in faster delivery times and improved accuracy.
Speed, Cost, and Reliability Comparison
The following table summarizes the key differences between traditional and automated shipping systems:
| Feature | Traditional Shipping | Automated Shipping Systems |
|---|---|---|
| Speed | Slower, subject to delays | Faster, optimized routes |
| Cost | Higher due to inefficiencies and errors | Lower due to automation and optimization |
| Reliability | Lower due to manual processes and lack of visibility | Higher due to real-time tracking and predictive analytics |
Fintech and International Payments
The globalized marketplace thrives on seamless cross-border transactions. However, traditional banking systems often present significant hurdles, characterized by high fees, lengthy processing times, and complex regulatory landscapes. Fintech, with its innovative solutions, is rapidly transforming this landscape, offering faster, cheaper, and more transparent international payment options. This shift is not just about convenience; it’s fundamentally altering how businesses operate and compete on a global scale.
Fintech’s Role in Streamlining International Payments and Reducing Transaction Costs
Fintech companies are leveraging technology to drastically reduce the friction associated with international payments. They achieve this through automation, improved data analytics, and the use of alternative payment rails. For example, platforms offering real-time payment processing eliminate the delays inherent in traditional correspondent banking networks. By automating much of the verification and compliance process, fintech also minimizes manual intervention, reducing processing times and costs. The use of APIs allows for seamless integration with existing business systems, further enhancing efficiency. This streamlining translates directly into lower transaction fees for businesses, freeing up capital for growth and investment. Companies like Wise (formerly TransferWise) and PayPal have demonstrated the effectiveness of this approach, significantly undercutting traditional banking fees for international transfers.
Cryptocurrencies and Blockchain’s Impact on Cross-Border Payments
Cryptocurrencies and blockchain technology hold the potential to revolutionize cross-border payments by offering decentralized, secure, and transparent alternatives to traditional systems. Blockchain’s distributed ledger technology eliminates the need for intermediaries, reducing transaction costs and processing times. Cryptocurrencies, with their inherent global accessibility, further facilitate international transfers, bypassing geographical limitations. However, the volatility of cryptocurrency prices and regulatory uncertainties remain significant challenges. Despite these challenges, several companies are already exploring the use of stablecoins (cryptocurrencies pegged to fiat currencies) to mitigate volatility risks. The potential for faster, cheaper, and more secure cross-border payments using blockchain technology is undeniable, even if widespread adoption still requires addressing regulatory and technological hurdles. Ripple, for instance, is actively developing solutions for cross-border payments using its XRP cryptocurrency.
Challenges and Opportunities Associated with Using New Financial Technologies in Global Trade
The adoption of fintech in global trade presents both exciting opportunities and significant challenges. While fintech offers the potential for increased efficiency and reduced costs, concerns remain regarding data security, regulatory compliance, and the potential for fraud. Ensuring the secure handling of sensitive financial data is paramount, and robust cybersecurity measures are crucial. Navigating the complex regulatory landscape varies across jurisdictions, creating compliance challenges for businesses operating internationally. Furthermore, the lack of standardized regulations for cryptocurrencies and other emerging technologies adds another layer of complexity. However, the opportunities are immense. Fintech can unlock access to global markets for smaller businesses, facilitate faster payment cycles, and improve transparency throughout the supply chain. The key lies in addressing the challenges proactively and fostering collaboration between fintech companies, regulators, and businesses to create a secure and efficient global financial ecosystem.
Illustrative Comparison: Traditional Banking vs. Fintech Solution for International Transactions
The following flowchart illustrates the differences between a traditional bank transfer and a fintech solution for an international transaction:
Traditional Banking:
[Start] –> [Initiate Transfer (Bank)] –> [Verification & Compliance Checks (Multiple Banks)] –> [Intermediary Banks (Multiple)] –> [Currency Conversion (Multiple Banks)] –> [Funds Arrive (Recipient Bank)] –> [End]
Fintech Solution:
[Start] –> [Initiate Transfer (Fintech Platform)] –> [Verification & Compliance Checks (Automated)] –> [Direct Transfer (Single Platform)] –> [Currency Conversion (Automated)] –> [Funds Arrive (Recipient Account)] –> [End]
This simplified comparison highlights the reduced number of intermediaries and the automated nature of fintech solutions, leading to faster processing and lower costs. The complexity of traditional banking is evident in the multiple steps and the involvement of numerous intermediaries, each adding to the overall transaction time and cost.
Data Analytics and Market Insights
In today’s hyper-connected world, global trade isn’t just about shipping goods; it’s about leveraging data to understand and conquer markets. Data analytics has become the secret weapon for businesses navigating the complexities of international commerce, providing unparalleled insights that drive smarter decisions and boost profitability. This isn’t about guesswork anymore; it’s about evidence-based strategies.
Data analytics empowers businesses to understand global market trends by analyzing vast quantities of information from diverse sources. This allows for accurate forecasting of demand, identification of emerging markets, and precise targeting of customer segments. By processing this information, companies can identify profitable opportunities and mitigate potential risks, leading to a more efficient and effective global trade strategy.
Utilizing Big Data for Global Trade Optimization
Companies are increasingly using big data to refine their global trade strategies. For instance, Amazon utilizes massive datasets to predict consumer demand, optimize its logistics network, and personalize customer experiences across borders. This allows them to efficiently manage inventory, streamline delivery times, and ultimately enhance customer satisfaction. Similarly, logistics companies like DHL employ predictive analytics to anticipate potential supply chain disruptions, enabling them to proactively adjust routes and mitigate delays. This kind of proactive management minimizes costs and ensures timely delivery, a critical factor in international trade. Analyzing consumer behavior data allows companies to tailor their products and marketing efforts to specific regional preferences, boosting sales and market share.
Ethical Considerations in International Data Usage
The collection and use of data in international trade present significant ethical considerations. Data privacy regulations vary widely across countries, creating challenges for businesses operating globally. Ensuring compliance with different data protection laws, such as GDPR in Europe or CCPA in California, is paramount. Transparency in data collection practices is crucial to build trust with customers and partners. The potential for bias in algorithms used to analyze data must also be addressed to avoid discriminatory outcomes. Finally, the responsible use of data should prioritize fairness and avoid exploiting vulnerable populations. Navigating these ethical complexities is vital for maintaining a positive reputation and fostering long-term sustainable growth.
Data Sources, Applications, Benefits, and Risks in Global Trade
The effective use of data in global trade hinges on accessing and interpreting relevant information from diverse sources. Below is a table illustrating various data sources, their applications, benefits, and potential risks:
| Data Source | Application in Global Trade | Benefits | Potential Risks |
|---|---|---|---|
| Customs Data | Tracking import/export volumes, identifying trade patterns, assessing tariff impacts. | Improved forecasting, risk management, compliance. | Data accuracy, accessibility, timeliness. |
| Consumer Behavior Data (e.g., online purchasing, social media activity) | Understanding consumer preferences, tailoring marketing campaigns, optimizing product development. | Increased sales, improved customer satisfaction, enhanced market penetration. | Privacy concerns, data bias, interpretation challenges. |
| Supply Chain Data (e.g., inventory levels, transportation times, logistics costs) | Optimizing logistics, reducing delays, minimizing costs. | Improved efficiency, cost savings, enhanced supply chain resilience. | Data integration challenges, security breaches, system failures. |
| Economic Indicators (e.g., GDP growth, inflation rates, exchange rates) | Assessing market stability, identifying investment opportunities, managing financial risks. | Informed decision-making, risk mitigation, improved profitability. | Data volatility, forecasting inaccuracies, geopolitical uncertainty. |
Automation and Robotics in Manufacturing and Logistics
Source: isurajitroy.com
The rise of automation and robotics is fundamentally reshaping global trade, impacting everything from manufacturing processes to the intricate dance of global supply chains. This technological shift isn’t just about increased efficiency; it’s about a complete reimagining of how goods are produced, moved, and delivered across the world. The integration of intelligent machines is leading to a new era of speed, precision, and cost-effectiveness, but also presents challenges that need careful consideration.
Automation is significantly improving efficiency, reducing labor costs, and boosting productivity across diverse sectors. From the assembly lines of car factories to the vast warehouses of e-commerce giants, robots are taking on repetitive and physically demanding tasks, freeing up human workers for more complex and strategic roles. This increased productivity translates directly into lower production costs and faster delivery times, benefiting both businesses and consumers.
Impact on Manufacturing Processes and Global Supply Chains
The integration of automation and robotics is streamlining manufacturing processes worldwide. Robots are now capable of performing tasks with incredible speed and accuracy, leading to fewer errors and higher-quality products. This precision is particularly important in industries requiring intricate assembly or delicate handling. Furthermore, automated systems can operate 24/7, maximizing production output and minimizing downtime. In global supply chains, automation enhances visibility and traceability, allowing companies to monitor goods in real-time and respond quickly to disruptions. Automated warehousing and logistics systems optimize inventory management, reduce storage costs, and ensure timely delivery. The result is a more efficient and resilient global supply chain.
Efficiency Improvements and Cost Reductions
Automation leads to dramatic efficiency gains in various sectors. For example, in the automotive industry, robotic welding and painting systems have significantly increased production speed and reduced defects. In electronics manufacturing, automated assembly lines ensure consistent quality and high throughput. The reduction in labor costs is another key benefit, though this should be viewed in the context of potential job displacement and the need for retraining initiatives. Moreover, automation minimizes waste by optimizing material usage and reducing errors, leading to significant cost savings. The overall impact is a more competitive global marketplace with faster production cycles and lower prices for consumers.
Advantages and Disadvantages of Automation Implementation
Implementing automation presents both advantages and disadvantages. On the positive side, increased productivity, reduced labor costs, and improved product quality are significant benefits. However, the high initial investment cost can be a barrier for smaller businesses. Moreover, the need for skilled workers to program, maintain, and troubleshoot automated systems necessitates investment in training and development. The potential for job displacement also requires careful consideration and proactive strategies for workforce adaptation. The specific advantages and disadvantages vary depending on the stage of the global trade process, with implementation in manufacturing differing from its impact on logistics.
Examples of Successful Automation Integration
Amazon’s vast network of fulfillment centers exemplifies the successful integration of automation in logistics. Automated guided vehicles (AGVs) transport goods across warehouses, robotic arms pick and pack items, and sophisticated software manages inventory and order fulfillment. This highly automated system enables Amazon to fulfill millions of orders daily with incredible speed and efficiency. Similarly, Tesla’s Gigafactories utilize extensive robotics in car manufacturing, achieving a level of automation unprecedented in the automotive industry. These examples showcase how advanced automation can transform operations, enhancing efficiency and scalability. The key is strategic planning and a phased approach to implementation, allowing companies to adapt to the changing landscape and maximize the benefits of automation.
Cybersecurity and Data Protection in Global Trade
The digital revolution has fundamentally reshaped global trade, creating unprecedented opportunities but also exposing businesses to a wider range of cybersecurity threats. As more transactions move online, the volume of sensitive data exchanged across borders increases exponentially, making robust cybersecurity measures paramount for the survival and success of any internationally operating company. The cost of a data breach, including financial losses, reputational damage, and legal penalties, can be devastating. Therefore, understanding and implementing effective cybersecurity strategies is no longer a luxury but a necessity for businesses engaged in global commerce.
The interconnected nature of global trade means that a single vulnerability in one part of the supply chain can have cascading effects across the entire network. This interconnectedness makes data protection a shared responsibility, requiring collaboration between businesses, governments, and international organizations. Failure to adequately address cybersecurity risks can lead to significant disruptions, financial losses, and damage to brand reputation, ultimately undermining the efficiency and competitiveness of global trade.
Major Cybersecurity Threats in Global Trade, How Technology is Changing the Landscape of Global Trade
Businesses involved in global trade face a diverse range of cybersecurity threats, many of which are amplified by the cross-border nature of their operations. These threats can be broadly categorized into several key areas, each requiring a distinct approach to mitigation. Understanding these threats is the first step towards building a robust security posture.
- Data breaches: Hackers may target companies to steal sensitive customer data, intellectual property, or financial information. This can lead to significant financial losses, legal penalties, and reputational damage. For example, a breach affecting a logistics company could expose customer shipping details and potentially lead to identity theft.
- Phishing and social engineering attacks: These attacks manipulate employees into revealing sensitive information or granting access to company systems. Sophisticated phishing campaigns can exploit vulnerabilities in human psychology to gain unauthorized access to networks and data. A successful attack could allow hackers to steal trade secrets or disrupt operations.
- Malware and ransomware attacks: Malware can infect systems and steal data, while ransomware can encrypt critical data and demand payment for its release. The impact of ransomware attacks can be particularly devastating, potentially halting operations and causing significant financial losses. The NotPetya ransomware attack in 2017, which disrupted global supply chains, serves as a stark reminder of the potential consequences.
- Supply chain attacks: Hackers may target a company’s suppliers or partners to gain access to its systems. This type of attack can be difficult to detect and can have far-reaching consequences. A compromised supplier could unknowingly provide access to a company’s network, potentially leading to a wider breach.
- Denial-of-service (DoS) attacks: These attacks flood a company’s systems with traffic, making them unavailable to legitimate users. DoS attacks can disrupt operations and cause significant financial losses. A successful attack against an e-commerce platform could prevent customers from placing orders, leading to lost revenue.
Best Practices for Cybersecurity in Global Trade
Implementing a comprehensive cybersecurity strategy requires a multi-layered approach that incorporates both technical and non-technical measures. This proactive approach is crucial for mitigating risks and protecting sensitive data.
A robust cybersecurity framework should encompass several key elements, addressing vulnerabilities across the entire organization. Prioritizing these practices can significantly reduce the likelihood and impact of cyberattacks.
- Implement strong authentication and access controls: Use multi-factor authentication (MFA) to protect access to sensitive systems and data. Regularly review and update access permissions to ensure only authorized personnel have access to necessary information.
- Regularly update software and systems: Keep all software and systems patched and up-to-date to minimize vulnerabilities. This includes operating systems, applications, and network devices.
- Conduct regular security assessments and penetration testing: Identify vulnerabilities in systems and processes through regular security assessments and penetration testing. This allows businesses to proactively address potential weaknesses before they can be exploited by attackers.
- Implement data loss prevention (DLP) measures: Use DLP tools to monitor and prevent sensitive data from leaving the organization’s control. This can include measures to prevent data from being copied to unauthorized devices or sent via email.
- Develop and implement incident response plans: Have a plan in place to respond to security incidents quickly and effectively. This includes procedures for identifying, containing, and recovering from attacks.
- Invest in employee cybersecurity awareness training: Educate employees about cybersecurity threats and best practices. This includes training on phishing scams, malware, and social engineering attacks.
- Comply with relevant data protection regulations: Understand and comply with relevant data protection regulations, such as GDPR and CCPA. This includes implementing appropriate data governance and privacy measures.
- Utilize encryption for data in transit and at rest: Encrypt sensitive data both when it is being transmitted over networks and when it is stored on systems. This helps to protect data from unauthorized access even if a system is compromised.
Last Word
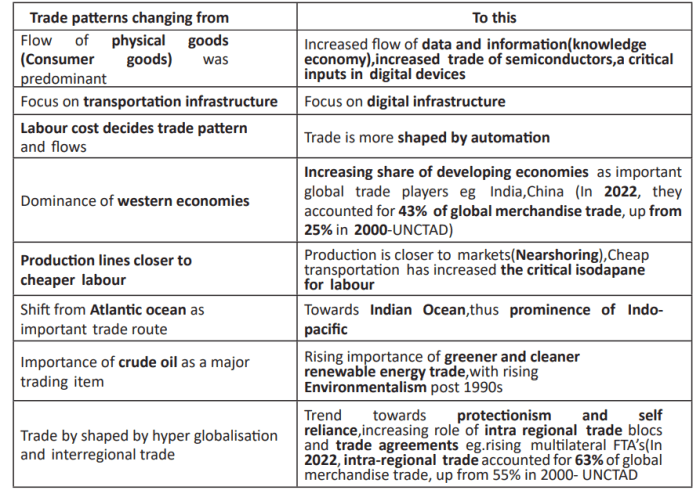
Source: edukemy.com
The technological transformation of global trade is undeniably reshaping our world. While challenges exist, the opportunities presented by e-commerce, AI, fintech, and data analytics are immense. The future of global trade isn’t just about faster shipping; it’s about smarter, more efficient, and more inclusive systems. Embracing innovation and addressing the inherent risks will be crucial for businesses and governments alike to navigate this new era and thrive in the increasingly interconnected global marketplace. The journey towards a truly digitalized global trade network is ongoing, but the direction is clear: technology is leading the charge.
