How Robotics is Transforming the Future of Surgical Assistance? Forget the shaky hands of old – robotic surgery is revolutionizing the operating room, offering unparalleled precision and minimally invasive techniques. From the da Vinci system’s initial forays into the field to the cutting-edge AI-powered tools of today, the journey has been nothing short of extraordinary. We’re diving deep into this technological marvel, exploring its impact on surgeons, patients, and the future of healthcare.
This isn’t just about fancy gadgets; it’s about fundamentally changing how we approach surgery. We’ll unpack the different robotic systems, analyze their pros and cons, and examine how they’re improving outcomes for a range of procedures. Get ready to see how robotic surgery is not just a technological advancement, but a game-changer for the entire medical landscape.
The Rise of Robotic Surgery
Robotic surgery, once a futuristic fantasy, is rapidly transforming the surgical landscape. From its humble beginnings as a research project to its current widespread adoption, the journey of robotic surgery has been marked by significant technological leaps and a steady increase in its application across various surgical fields. This evolution has not been without its challenges, but the advancements have undeniably reshaped how surgeons approach minimally invasive procedures.
The initial development of robotic surgery systems can be traced back to the late 20th century. Early iterations were bulky and lacked the dexterity and precision of today’s systems. Key milestones include the FDA approval of the da Vinci Surgical System in 2000, a pivotal moment that propelled robotic surgery into mainstream medical practice. Subsequent advancements have focused on refining the technology, enhancing image quality, and increasing the system’s versatility and ease of use. Miniaturization, improved haptic feedback, and the integration of advanced imaging technologies have contributed significantly to the evolution of robotic surgical platforms.
Current Adoption of Robotic Surgery Across Surgical Specialties
Robotic surgery has found its most prominent applications in urology, particularly in prostatectomies, and in gynecology, where it’s used for hysterectomies and other minimally invasive procedures. Cardiac surgery, colorectal surgery, and thoracic surgery are also increasingly incorporating robotic techniques. The adoption rate varies across specialties and geographical regions, largely influenced by factors like the availability of trained surgeons, the cost of the technology, and the level of reimbursement from healthcare providers. For instance, while widespread in developed countries, the accessibility of robotic surgery in less developed regions remains limited due to economic constraints. The increasing demand for minimally invasive procedures and the proven benefits of robotic surgery are, however, driving broader adoption globally.
Initial Limitations and Challenges in Robotic Surgery
The early days of robotic surgery presented several significant hurdles. High initial costs were a major barrier to entry for many hospitals and surgical centers. The steep learning curve for surgeons required extensive training and practice to master the intricate controls of the robotic system. Furthermore, the initial systems were limited in their range of motion and dexterity compared to the human hand, which restricted the types of procedures that could be performed. Technological limitations also resulted in longer operation times and higher complication rates in some early cases, causing concerns about its overall efficacy. Addressing these challenges has been a central focus of ongoing research and development, resulting in significant improvements in system design, training protocols, and surgical techniques.
Types of Robotic Surgical Systems
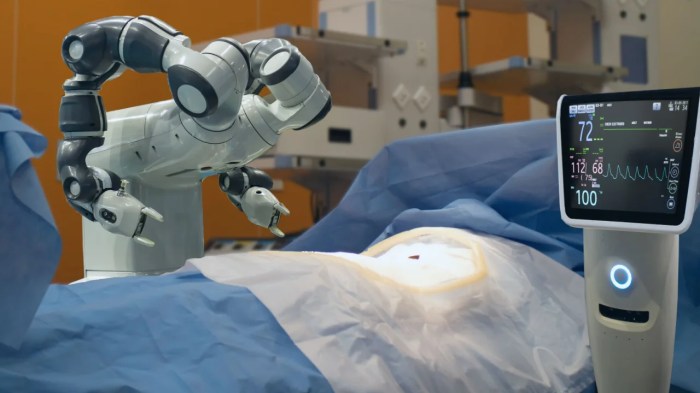
Source: medicaldevice-network.com
Robotic surgery is already revolutionizing healthcare, offering minimally invasive procedures and enhanced precision. But imagine the possibilities if AI controlling these robots became exponentially smarter, thanks to advancements like those detailed in this article on How Quantum Computing Will Enable Breakthroughs in AI. This leap in AI could lead to robotic surgeons capable of performing even more complex operations with unparalleled accuracy and speed, further transforming the future of surgical assistance.
The world of surgical robotics is far from monolithic. Several systems, each with its own strengths and weaknesses, are vying for dominance in operating rooms worldwide. Understanding the nuances of these different platforms is crucial for appreciating the ongoing revolution in minimally invasive surgery. This section will explore some of the key players in the field, comparing their capabilities and applications.
Robotic Surgical System Comparison
The following table provides a comparison of some prominent robotic surgical systems. Note that the field is constantly evolving, with new iterations and competitors emerging regularly. This table reflects the current state of the art, but should not be considered exhaustive.
| Name | Manufacturer | Key Features | Applications |
|---|---|---|---|
| da Vinci Surgical System | Intuitive Surgical | High-definition 3D vision, articulated instruments with seven degrees of freedom, endoscopic capabilities, intuitive surgeon console | General surgery, urology, gynecology, cardiothoracic surgery, head and neck surgery |
| Versius Surgical Robot | CMR Surgical | Modular design, compact size, flexible deployment options, intuitive user interface, 3D vision | General surgery, urology, gynecology |
| Renaissance Robotic System | Vicarious Surgical | AI-assisted surgery, single-port access, flexible robotic arms, haptic feedback | General surgery (currently in clinical trials) |
da Vinci Surgical System: A Detailed Look
The da Vinci system, the current market leader, is characterized by its sophisticated console and intuitive controls. Surgeons operate using a console that provides a magnified, three-dimensional view of the surgical field. The system’s articulated instruments allow for precise movements, mimicking the dexterity of the human hand, but with enhanced capabilities in terms of range of motion and tremor reduction. Its widespread adoption stems from years of refinement and a substantial body of clinical data demonstrating its safety and efficacy across a wide range of surgical procedures. However, the system’s high cost and significant training requirements represent significant barriers to entry for many hospitals.
Versius Surgical Robot: A Modular Approach
In contrast to the da Vinci system’s integrated design, the Versius robot boasts a modular architecture. This allows for greater flexibility in configuring the system to meet the specific needs of a given procedure or operating room setup. Its smaller size and portability are significant advantages, making it potentially more accessible to hospitals with limited space or resources. While it offers many of the same advantages as the da Vinci system in terms of precision and dexterity, its relative newcomer status means that the long-term clinical data supporting its widespread use is still accumulating. Ease of use is touted as a key selling point, but the learning curve still represents a hurdle for surgeons accustomed to traditional techniques.
Advantages and Disadvantages of Robotic Surgical Systems
Precision and dexterity are key advantages offered by robotic systems. The magnified 3D vision and articulated instruments allow surgeons to perform complex procedures with greater accuracy and control than with traditional laparoscopic techniques. However, the systems are not without their drawbacks. The high cost of acquisition and maintenance, coupled with the need for specialized training, represents a significant barrier. Furthermore, while robotic systems offer enhanced dexterity, they can lack the tactile feedback that surgeons rely on during open surgery. This can impact the surgeon’s ability to assess tissue tension and other critical aspects of the procedure. The ease of use varies depending on the system and the surgeon’s experience, with a significant learning curve associated with mastering the technology.
Impact on Surgical Procedures
Robotic surgery has revolutionized the surgical landscape, significantly impacting the precision, dexterity, and overall effectiveness of minimally invasive procedures. The enhanced capabilities offered by robotic systems have led to improved patient outcomes and expanded the possibilities for complex surgical interventions. This section explores the profound influence of robotic assistance on various surgical procedures.
Robotic surgery enhances the precision and dexterity of minimally invasive procedures primarily through its advanced features. The surgeon controls the robotic arms from a console, benefiting from magnified 3D high-definition vision, increased range of motion, and tremor filtration. This translates to smaller incisions, reduced trauma to surrounding tissues, less blood loss, and faster recovery times for patients. The intuitive interface allows for intricate maneuvers that would be difficult or impossible to achieve with traditional laparoscopic techniques.
Minimally Invasive Procedures Enhanced by Robotic Surgery
Robotic surgery has significantly improved several minimally invasive procedures. The benefits often include smaller incisions, reduced pain, shorter hospital stays, and quicker recovery times.
- Prostatectomy: Robotic-assisted prostatectomy offers improved precision in removing the prostate gland, minimizing damage to surrounding nerves and muscles responsible for urinary and sexual function. This results in better continence and potency outcomes compared to traditional open surgery.
- Hysterectomy: Robotic-assisted hysterectomies provide superior visualization and dexterity, allowing surgeons to precisely remove the uterus with minimal disruption to adjacent structures. This leads to reduced blood loss, less postoperative pain, and faster recovery.
- Cholecystectomy (Gallbladder Removal): Robotic assistance allows surgeons to navigate the complex anatomy of the biliary tract with enhanced precision, reducing the risk of bile duct injury. Smaller incisions contribute to improved cosmetic results and faster recovery.
- Cardiothoracic Surgery: Robotic systems are increasingly used in minimally invasive heart surgeries, enabling surgeons to perform complex procedures with greater precision and control. This leads to reduced trauma, faster recovery times, and improved patient outcomes.
Robotic Surgery in Complex and High-Risk Interventions
The capabilities of robotic surgery extend beyond minimally invasive procedures. It plays a crucial role in complex and high-risk surgical interventions where precision and dexterity are paramount. The benefits are often life-altering for patients facing challenging surgical scenarios.
- Complex Cancer Surgeries: Robotic surgery allows for more precise resection of tumors, especially in difficult-to-reach areas, minimizing damage to surrounding healthy tissue and vital organs. This is particularly beneficial in cases of pancreatic, esophageal, and colorectal cancers.
- Minimally Invasive Spine Surgery: Robotic assistance enhances the precision and accuracy of spinal procedures, leading to less trauma, reduced blood loss, and faster recovery times. It allows for more targeted placement of implants and correction of spinal deformities.
- Transplants: Robotic surgery has shown promise in minimally invasive transplant procedures, potentially reducing surgical trauma and improving patient outcomes. The dexterity and precision of robotic systems are particularly beneficial in complex transplant operations.
Benefits for Surgeons and Patients
Robotic surgery isn’t just a technological marvel; it’s a game-changer for both surgeons and their patients. The precision and capabilities offered by robotic systems translate into significant advantages across the board, leading to improved outcomes and a more streamlined surgical experience. Let’s delve into the specific benefits.
The benefits extend far beyond simply having a robot in the operating room. It’s about leveraging technology to enhance the surgeon’s abilities and improve the patient’s overall journey.
Benefits for Surgeons
Robotic surgery significantly improves the surgical experience for surgeons, leading to increased efficiency and reduced strain. The enhanced precision and control offered by robotic systems allow for more intricate procedures to be performed with greater accuracy.
Improved ergonomics, a key benefit, minimizes physical stress during long and complex operations. The surgeon sits comfortably at a console, controlling the robotic arms with intuitive controls, reducing the fatigue and strain associated with traditional open surgery. Enhanced visualization, provided by high-definition 3D cameras and magnified views, offers a clearer and more detailed perspective of the surgical field. This enhanced visualization allows surgeons to work with greater precision and confidence, resulting in improved surgical outcomes.
Benefits for Patients, How Robotics is Transforming the Future of Surgical Assistance
The advantages for patients undergoing robotic surgery are numerous and impactful. These benefits often lead to a faster and smoother recovery process.
Smaller incisions are a hallmark of robotic surgery. These smaller incisions translate to less trauma to surrounding tissues, leading to reduced pain and scarring. This minimizes the risk of infection and allows for quicker healing. Shorter hospital stays are another significant benefit, reducing the overall cost of care and allowing patients to return to their normal lives sooner. Faster recovery times, coupled with reduced pain, significantly improve the patient’s quality of life in the post-operative period. The overall patient experience is enhanced, resulting in higher satisfaction rates.
Comparative Patient Outcomes: Prostatectomy
Let’s compare patient outcomes for radical prostatectomy, a common procedure, using traditional open surgery versus robotic-assisted laparoscopic surgery. While individual results can vary, general trends show significant advantages for robotic surgery.
| Outcome | Traditional Open Prostatectomy | Robotic-Assisted Laparoscopic Prostatectomy |
|---|---|---|
| Hospital Stay (Days) | 3-7 | 1-3 |
| Blood Loss (ml) | 500-1000 | 100-200 |
| Pain Score (Post-operative) | Moderate to High | Low to Moderate |
| Recovery Time (Weeks) | 6-8 | 4-6 |
Note: These are general comparisons and individual results may vary. Consult with your physician for specific information.
Technological Advancements and Future Trends
Robotic surgery, already a game-changer in the medical field, is poised for an even more dramatic evolution. Emerging technologies are rapidly enhancing its capabilities, promising a future where minimally invasive procedures are not only more precise but also more accessible and adaptable to a wider range of surgical needs. This next wave of innovation is driven by advancements in artificial intelligence, haptic feedback systems, and the exciting potential of tele-surgery.
The integration of these technologies is pushing the boundaries of what’s possible in the operating room, leading to improved patient outcomes and expanding the reach of surgical expertise. This section will explore these advancements and examine how they are shaping the future landscape of robotic surgery.
Artificial Intelligence in Robotic Surgery
AI is rapidly transforming robotic surgery, enhancing precision, efficiency, and safety. AI algorithms can analyze vast amounts of patient data, including medical images and surgical history, to create personalized surgical plans. This pre-operative planning improves the accuracy of incisions and reduces the risk of complications. During surgery, AI can assist surgeons by providing real-time feedback on instrument placement, tissue identification, and potential risks. For instance, AI-powered systems can identify and highlight critical structures like blood vessels or nerves during a procedure, minimizing the chance of accidental damage. This level of assistance not only improves the surgical outcome but also reduces the surgeon’s cognitive load, allowing for greater focus and efficiency. Furthermore, AI-powered robotic systems can learn from past procedures, constantly refining their performance and adapting to new challenges.
Enhanced Haptic Feedback Systems
One of the limitations of current robotic surgery systems is the lack of a fully realistic sense of touch. While surgeons can control the robotic instruments, they don’t experience the same tactile feedback as they would during a traditional open surgery. However, advancements in haptic feedback technology are changing this. New systems are being developed that provide surgeons with a more nuanced sense of touch, allowing them to feel the texture and consistency of tissues during the procedure. This improved tactile feedback enhances the surgeon’s precision and control, leading to more delicate and accurate movements. Imagine the difference between blindly sculpting with clay and sculpting while feeling the clay’s texture and consistency – that’s the transformative potential of advanced haptic feedback in robotic surgery. This is particularly important in delicate procedures such as neurosurgery or microsurgery, where precise control is paramount.
The Expanding Reach of Tele-surgery
Tele-surgery, the remote performance of surgical procedures using robotic systems, represents a significant frontier in the field. While still in its early stages of widespread adoption, it holds the potential to revolutionize healthcare access, especially in remote or underserved areas. The ability to perform complex surgeries remotely could significantly improve patient care in disaster zones, or areas with limited access to specialized surgeons.
Hypothetical Scenario: Robotic Surgery in a Disaster Zone
Imagine a scenario following a major earthquake in a remote mountainous region. Communication and transportation infrastructure is severely damaged, leaving many injured individuals without access to immediate surgical care. A team of surgeons, located hundreds of miles away in a well-equipped medical facility, utilize a state-of-the-art tele-surgery system. High-definition cameras and advanced robotic arms, controlled remotely by the surgeons, are deployed to the disaster zone. A local medical team, trained to assist, prepares the patient and manages the local aspects of the procedure while the remote surgeons skillfully perform the life-saving operation. The system uses AI-powered image analysis to provide real-time data and guidance to the surgeons, while advanced haptic feedback allows them to precisely manipulate the robotic instruments, effectively extending their surgical expertise across vast distances. This hypothetical scenario demonstrates the transformative potential of robotic surgery in crisis situations, bridging geographical barriers and ensuring timely access to critical care.
Ethical and Societal Implications
The rise of robotic surgery presents a fascinating paradox: a technology promising incredible advancements in patient care, yet simultaneously raising complex ethical and societal questions. Its increasing adoption necessitates a careful consideration of its impact on accessibility, cost, training, the surgical workforce, and the broader healthcare landscape. Failing to address these issues risks exacerbating existing inequalities and creating new challenges within the healthcare system.
Robotic surgery’s transformative potential is undeniable, but its benefits aren’t uniformly distributed. A critical examination of ethical considerations is paramount to ensure equitable access and responsible implementation.
Access and Cost of Robotic Surgery
The high cost of robotic surgical systems—including the initial purchase price, maintenance, and specialized training—creates significant barriers to access. Hospitals in underserved communities or those with limited budgets may struggle to afford this technology, potentially widening the healthcare disparity gap. This unequal access could lead to situations where patients in wealthier areas benefit from more advanced, minimally invasive procedures, while those in less affluent regions are left with less sophisticated options. For example, a rural hospital might lack the resources to invest in a da Vinci surgical robot, limiting the availability of robotic-assisted procedures for its patients compared to a large urban medical center. This disparity needs careful consideration in policy decisions and resource allocation.
Impact on Surgical Workforce and Training
The introduction of robotic surgery necessitates specialized training for surgeons, nurses, and other healthcare professionals. This training is often expensive and time-consuming, potentially creating a shortage of qualified personnel. Furthermore, the transition to robotic surgery might lead to concerns about job displacement for surgeons who are not trained in robotic techniques. The healthcare system needs to proactively address this by integrating robotic surgery training into existing medical curricula and developing support programs to ensure a smooth transition for existing surgical professionals. Investing in robust training programs and developing clear career pathways for professionals in this evolving field is crucial to prevent a shortage of skilled personnel.
Societal Benefits and Challenges
Widespread adoption of robotic surgery offers the potential for significant societal benefits. Improved surgical precision, reduced invasiveness, and faster recovery times can lead to better patient outcomes and reduced healthcare costs in the long run. However, challenges remain. The ethical dilemmas surrounding data privacy related to robotic surgical systems, algorithmic bias, and the potential for increased reliance on technology over human judgment all need careful consideration. For instance, ensuring that the data collected by robotic surgical systems is used responsibly and securely, while also mitigating potential biases in algorithms that control the robot’s movements, is paramount. Open and transparent discussions involving ethicists, policymakers, and healthcare professionals are essential to navigate these complex issues.
Illustrative Examples of Robotic Surgical Applications: How Robotics Is Transforming The Future Of Surgical Assistance
Robotic surgery, while still a relatively new field, has already amassed a significant body of evidence showcasing its transformative impact across various surgical specialties. The following case studies illustrate the practical applications and benefits of this technology, highlighting both the surgical procedures and the experiences of both surgeons and patients.
Robotic Prostatectomy Case Study
This case involved a 62-year-old male patient diagnosed with prostate cancer. The patient presented with symptoms including urinary frequency and nocturia. The surgical plan was a robotic-assisted radical prostatectomy (RARP). The surgical field encompassed the pelvic region, specifically the prostate gland and surrounding structures. The da Vinci Surgical System was employed, utilizing its miniature, articulated instruments to provide enhanced dexterity and precision within the confined surgical space. These instruments allowed for meticulous dissection and removal of the prostate gland, minimizing damage to nearby nerves and blood vessels responsible for erectile and urinary function. The procedure lasted approximately three hours. Post-operative recovery was remarkably smooth, with minimal blood loss and a shorter hospital stay compared to traditional open surgery. The patient reported significant improvement in urinary symptoms within weeks of the surgery, and nerve-sparing techniques employed during the RARP preserved his erectile function. The surgeon commented on the improved visualization and precision offered by the robotic system, enabling a more controlled and less invasive procedure. The enhanced dexterity allowed for the preservation of crucial anatomical structures, contributing to the excellent patient outcome.
Robotic-Assisted Cardiac Surgery Case Study
A 70-year-old female patient required a mitral valve repair due to severe mitral regurgitation. This condition, where the mitral valve doesn’t close properly, allows blood to leak back into the heart, leading to shortness of breath and fatigue. The surgery was performed using the da Vinci system, adapted for cardiac surgery. The surgical field involved the heart itself, requiring a precise and delicate approach. Specialized robotic instruments, designed for cardiac procedures, allowed the surgeon to access the heart through small incisions. The surgeon used the robotic system’s high-definition 3D vision to meticulously repair the mitral valve, restoring its proper function. The procedure was significantly less invasive than traditional open-heart surgery. The patient experienced a faster recovery, with reduced pain and a shorter hospital stay. Post-operative echocardiograms confirmed successful valve repair and improved cardiac function. The surgeon highlighted the enhanced visualization and precision of the robotic system, particularly its ability to manipulate delicate tissues within the heart, leading to a successful outcome with minimal trauma to the patient.
Conclusion
The rise of robotic surgery isn’t just a trend; it’s a paradigm shift. From enhanced precision and minimally invasive procedures to faster recovery times and improved patient outcomes, the benefits are undeniable. While ethical considerations and accessibility remain important discussions, the future of surgical assistance is undeniably robotic. As technology continues to advance, we can expect even more groundbreaking applications, paving the way for a future where surgery is safer, more efficient, and more accessible than ever before. The future of surgery is here, and it’s robotic.
