How Robotics is Changing the Future of Emergency Response? It’s not science fiction anymore. From earthquake zones to underwater disasters, robots are rapidly becoming indispensable first responders, dramatically reshaping how we tackle emergencies. Think drones zipping through rubble, robotic dogs sniffing out survivors in collapsed buildings, and underwater vehicles exploring submerged wreckage – the possibilities are mind-blowing.
This isn’t just about speed and efficiency; it’s about minimizing human risk in incredibly dangerous situations. Robots can handle hazardous materials, assess damage with incredible precision, and even deliver vital medical supplies to hard-to-reach areas. This evolution isn’t just improving response times; it’s saving lives and changing the very nature of emergency response forever.
Improved Search and Rescue Operations
The integration of robotics into search and rescue (SAR) operations is revolutionizing how we respond to disasters, significantly improving efficiency and safety. Faster response times, wider coverage areas, and the ability to access hazardous environments previously unreachable by humans are just some of the benefits. This section explores the specific ways robotic technologies are transforming SAR efforts.
Drones in Search and Rescue
Drones, or unmanned aerial vehicles (UAVs), are rapidly becoming indispensable tools in SAR operations. Their speed and maneuverability allow them to quickly survey large disaster zones, providing rescuers with a real-time aerial view of the affected area. High-resolution cameras and thermal imaging capabilities enable drones to locate survivors even in challenging conditions, such as collapsed buildings or dense forests. Modern drones also incorporate sophisticated obstacle avoidance systems, using sensors like LiDAR and radar to navigate complex terrains safely and efficiently, minimizing the risk of damage or loss of the drone itself. For instance, after the 2010 Haiti earthquake, drones were instrumental in mapping the rubble and identifying areas where survivors might be trapped, significantly speeding up rescue efforts. The coverage area a single drone can achieve in a short timeframe vastly surpasses what human teams can accomplish on foot, leading to faster victim location.
Robotic Dogs in Hazardous Environments
Robotic dogs, such as those developed by Boston Dynamics, are proving their worth in navigating hazardous environments that are too dangerous or unstable for humans to enter. These quadrupedal robots can traverse uneven terrain, climb stairs, and squeeze through narrow spaces, making them ideal for searching collapsed buildings or disaster areas with unstable ground. Equipped with cameras, sensors, and communication systems, they can relay real-time information to rescuers, allowing them to assess the situation remotely and make informed decisions. However, their limitations include battery life and the potential for damage in extremely harsh conditions. Their size also limits access to very confined spaces. Despite these limitations, their ability to access areas inaccessible to humans makes them invaluable assets in SAR missions. A notable example is their deployment in Fukushima following the nuclear disaster, where they were used to assess radiation levels in dangerous areas.
Autonomous Underwater Vehicles (AUVs) and Remotely Operated Vehicles (ROVs)
Underwater search and rescue operations benefit greatly from both AUVs and ROVs. AUVs are autonomous, meaning they operate independently without a direct human operator, making them suitable for extensive underwater searches. They can cover large areas efficiently, mapping the seabed and detecting objects of interest. ROVs, on the other hand, are remotely controlled by a human operator, providing more precise control and maneuverability in complex underwater environments. This makes them ideal for tasks requiring delicate manipulation, such as retrieving objects or inspecting damaged structures. The choice between AUVs and ROVs depends on the specific needs of the mission. AUVs are better suited for large-scale surveys, while ROVs excel in situations requiring precise control and manipulation. In the aftermath of the Titanic’s discovery, ROVs were used to explore the wreckage and recover artifacts. AUVs played a key role in mapping the seafloor surrounding the disaster site.
Comparison of Response Times
The following table compares the response times of traditional search and rescue methods with those employing robotic assistance:
| Method | Response Time (average) | Advantages | Disadvantages |
|---|---|---|---|
| Traditional Search and Rescue (Human Teams) | Hours to Days | Direct human interaction, adaptable to unforeseen circumstances. | Limited reach, slower coverage, safety risks for rescuers. |
| Drone-Assisted Search and Rescue | Minutes to Hours | Rapid aerial survey, wide coverage area, enhanced situational awareness. | Susceptible to weather conditions, limited payload capacity. |
| Robotic Dog-Assisted Search and Rescue | Hours to Days (depending on environment) | Access to hazardous environments, improved safety for human rescuers. | Limited battery life, potential for mechanical failure. |
| AUV/ROV-Assisted Underwater Search and Rescue | Hours to Days (depending on depth and area) | Exploration of inaccessible underwater areas, detailed data collection. | High initial cost, specialized operator training required. |
Enhanced Disaster Assessment and Monitoring
Robots are revolutionizing disaster response, moving beyond simple search and rescue to provide comprehensive assessment and monitoring capabilities. Equipped with an array of sensors and advanced computing power, these machines offer unprecedented speed and accuracy in gathering crucial data, leading to faster and more effective relief efforts. This enhanced data collection significantly improves decision-making during and after catastrophic events.
Robot-Based Damage Assessment in Natural Disasters
Robots equipped with a variety of sensors are transforming how we assess damage after natural disasters like earthquakes, floods, and wildfires. These sensors gather diverse data, providing a much more comprehensive picture than traditional methods. For example, visual sensors (cameras) capture high-resolution images and videos of the affected areas, documenting the extent of destruction to buildings and infrastructure. LiDAR (Light Detection and Ranging) sensors create detailed 3D maps, revealing ground deformation caused by earthquakes or the extent of flooding. Thermal sensors detect heat signatures, useful for identifying hotspots in wildfires or locating survivors trapped in collapsed structures. Gas sensors can detect leaks of hazardous materials, crucial for prioritizing safety measures. This multifaceted data collection paints a clear picture of the disaster’s impact, allowing for better resource allocation and more effective rescue operations.
Aerial Robotics and 3D Mapping of Disaster Zones
Drones, or aerial robots, play a vital role in rapidly creating 3D maps of disaster-stricken areas. Their maneuverability allows them to access difficult-to-reach locations, providing a bird’s-eye view that is impossible to obtain otherwise. These aerial robots typically utilize LiDAR and high-resolution cameras to capture data. This data is then processed using specialized software to generate detailed 3D models, showing the topography of the affected area, the extent of damage to buildings and infrastructure, and the location of debris fields. The speed and accuracy of this process are remarkable, providing emergency responders with critical information within hours of a disaster, enabling quicker decision-making regarding rescue and relief efforts. For instance, a visualization might show a color-coded map highlighting areas with severe structural damage in red, moderate damage in yellow, and minimal damage in green. This visual representation allows for efficient allocation of resources to the most affected areas.
Robotic Monitoring of Hazardous Materials and Radiation
Following disasters, the presence of hazardous materials, such as chemical spills or radiation leaks from damaged nuclear facilities, poses significant risks to both rescue workers and the affected population. Robots equipped with specialized sensors are deployed to monitor these hazardous areas remotely, providing real-time data on radiation levels, chemical concentrations, and other environmental hazards. This data is transmitted to a safe location, allowing experts to assess the risks and develop appropriate safety protocols. The use of robots in these situations significantly reduces the risk to human life and allows for more informed decision-making regarding evacuation and cleanup operations. Safety protocols typically involve redundant systems, remote operation from a safe distance, and the use of robots capable of withstanding extreme conditions. For example, robots equipped with radiation-shielding materials could be deployed to assess radiation levels in a nuclear power plant after an earthquake.
Flowchart: Robot Deployment for Disaster Assessment and Monitoring
The process of deploying robots for disaster assessment and monitoring involves several key steps. A simplified flowchart could be represented as follows:
[Imagine a flowchart here. The flowchart would begin with “Disaster Event,” leading to “Needs Assessment and Robot Selection.” This would branch to “Robot Deployment (Aerial and Ground),” followed by “Data Acquisition (Visual, LiDAR, Thermal, Gas Sensors).” This leads to “Data Transmission and Processing,” then to “Data Analysis and Visualization,” finally concluding with “Decision Making and Resource Allocation.”]
Improved Medical Assistance and Evacuation: How Robotics Is Changing The Future Of Emergency Response
The integration of robotics into emergency medical services is revolutionizing how we respond to crises, offering unprecedented capabilities to deliver timely and effective care, even in the most challenging environments. From delivering vital supplies to performing complex surgeries in the field, robots are transforming the landscape of emergency medicine, improving patient outcomes and saving lives.
Robotic systems are significantly enhancing the speed and efficiency of medical assistance and evacuation in emergency situations. This advancement is particularly crucial in disaster zones or remote areas where access is limited or infrastructure is damaged. The use of robots mitigates risks to human responders, allows for faster delivery of critical supplies, and enables remote medical expertise to be leveraged effectively.
Robotic Delivery of Medical Supplies and Equipment
In disaster scenarios, the timely delivery of essential medical supplies and equipment is paramount. Drones, for instance, equipped with GPS and autonomous navigation systems, are proving invaluable. Imagine a scenario where an earthquake has rendered roads impassable. A swarm of drones, each carrying a payload of medical kits, can navigate the debris field and deliver critical supplies— bandages, medications, and even blood—directly to injured individuals or temporary medical facilities. Similarly, ruggedized robots on wheels or tracks can traverse difficult terrain, delivering heavier equipment like ventilators or portable X-ray machines to remote locations unreachable by traditional ambulances.
Robotic Surgery Platforms in Field Hospitals
The deployment of robotic surgery platforms in temporary field hospitals is a game-changer. These systems, typically consisting of a surgeon’s console and a robotic arm at the patient’s side, allow surgeons to perform minimally invasive procedures remotely or with enhanced precision. Advantages include smaller incisions leading to less scarring, reduced blood loss, and faster recovery times for patients. However, limitations exist. The high cost of the equipment and the need for specialized training for surgeons represent significant hurdles to widespread adoption. Furthermore, reliable communication infrastructure is essential for remote surgery, which may be lacking in disaster areas. Successful implementation requires careful planning and coordination.
Robotic Ambulances and Transport Systems
The concept of robotic ambulances is gaining traction. While fully autonomous ambulances are still largely experimental, several projects are exploring semi-autonomous systems that can navigate pre-programmed routes, assisting paramedics in reaching patients quickly and safely. These robotic systems could incorporate features like advanced sensors to detect obstacles and optimize routes, as well as integrated communication systems for real-time updates to emergency dispatch centers. Furthermore, robotic systems can be designed to transport patients, particularly in challenging environments, providing a more stable and controlled transport than traditional methods. For example, a robotic stretcher system could navigate uneven terrain or confined spaces with greater ease and precision, reducing the risk of further injury to the patient during transport.
Ethical Considerations in Robotic Emergency Medical Response
The increasing use of robots in emergency medical situations raises several important ethical considerations that must be carefully addressed.
From search-and-rescue robots navigating disaster zones to drones delivering vital medical supplies, robotics is revolutionizing emergency response. This is just one facet of how technology is boosting public safety, a broader trend explored in detail here: How Technology is Shaping the Future of Public Safety and Security. Ultimately, faster response times and improved outcomes are the key benefits of this robotic revolution in emergency services.
- Algorithmic Bias: Ensuring that robotic systems do not perpetuate or exacerbate existing biases in healthcare access and delivery is crucial.
- Data Privacy and Security: Protecting patient data collected by robotic systems is paramount. Robust security measures must be in place to prevent breaches and misuse of sensitive information.
- Accountability and Liability: Determining liability in cases of malfunction or error involving robotic systems is a complex legal and ethical challenge.
- Human Oversight and Control: Maintaining appropriate levels of human oversight and control over robotic systems is essential to ensure safety and prevent unintended consequences.
- Access and Equity: Ensuring equitable access to robotic-assisted emergency medical services for all populations, regardless of socioeconomic status or geographic location, is critical.
Minimizing Human Risk in Hazardous Environments
Robots are increasingly vital in emergency response, not just for their efficiency, but crucially, for their ability to protect human life in situations far too dangerous for people. Deploying robots allows us to tackle hazardous situations while minimizing the risk to first responders and potentially saving countless lives. This section explores how robotic technology is revolutionizing emergency response in high-risk environments.
Robots Handling Hazardous Materials and Explosives, How Robotics is Changing the Future of Emergency Response
Specialized robots are designed to handle hazardous materials, including chemical spills, radioactive contamination, and unexploded ordnance (UXO). These robots are equipped with a range of safety features, such as remote operation, radiation shielding, and explosion-proof casings. For instance, bomb disposal robots often utilize manipulator arms with various tools to safely disarm explosive devices. These robots often feature advanced sensors to detect the presence of hazardous materials and provide real-time data to operators, ensuring safe handling procedures. Their robust construction and remote control capabilities eliminate the need for human personnel to directly engage with potentially lethal substances. One example is the PackBot, a small, tracked robot that has been deployed in numerous hazardous material scenarios, providing invaluable assistance in assessing and neutralizing threats. Its compact size allows it to access confined spaces, while its durable design withstands harsh conditions.
Robots in Structural Collapses and Dangerous Environments
Following structural collapses, such as earthquakes or building implosions, the environment becomes incredibly dangerous. Debris, unstable structures, and the potential for secondary collapses pose significant risks to rescue workers. Robots can navigate these treacherous terrains, searching for survivors and assessing the stability of the structures. These robots are often equipped with cameras, sensors, and even gripping mechanisms to move debris and clear paths for human rescuers. For example, robots with advanced imaging capabilities can penetrate rubble to locate survivors, providing crucial information for targeted rescue efforts. This allows rescue teams to focus their efforts on areas with the highest probability of finding survivors, improving efficiency and minimizing the risk to their own safety. Their ability to work tirelessly in hazardous conditions, without the need for rest or protection, makes them indispensable tools.
Robotic Systems vs. Human Teams in Nuclear/Chemical Spills
In the event of a nuclear or chemical spill, the risks to human life are extremely high. Robotic systems offer a significant advantage over human teams in these situations. Robots can be deployed to assess the extent of contamination, collect samples, and even assist in cleanup efforts, all while minimizing human exposure to harmful substances. While human expertise is still essential for strategic decision-making and complex tasks, robots can perform the dangerous and time-consuming tasks, such as initial site assessment and decontamination. The effectiveness of robotic systems lies in their ability to operate continuously in hazardous environments, performing repetitive tasks without fatigue or risk of injury. This reduces the overall exposure time for human personnel, improving their safety and minimizing long-term health risks. Human teams remain crucial for complex decision-making and oversight, but robots provide a layer of safety and efficiency previously unattainable.
Types of Robots Used in Hazardous Environments
The following table Artikels several types of robots used in hazardous environments, highlighting their capabilities and limitations.
| Robot Type | Capability | Risk Mitigated | Limitations |
|---|---|---|---|
| Bomb disposal robot | Disarming explosive devices, handling hazardous materials | Exposure to explosives, hazardous materials | Limited dexterity in some tasks, range limitations |
| Search and rescue robot | Navigating rubble, locating survivors, assessing structural integrity | Exposure to unstable structures, hazardous environments | Limited maneuverability in extremely tight spaces, susceptibility to damage |
| Unmanned aerial vehicle (UAV) | Aerial surveillance, mapping hazardous areas, delivering supplies | Exposure to hazardous environments, risk of ground-based operations | Weather dependent, limited payload capacity, range limitations |
| Teleoperated manipulator | Handling radioactive materials, performing remote tasks in contaminated areas | Exposure to radiation, hazardous chemicals | Requires skilled operator, limited dexterity, range limitations |
Future Trends and Challenges in Robotics for Emergency Response
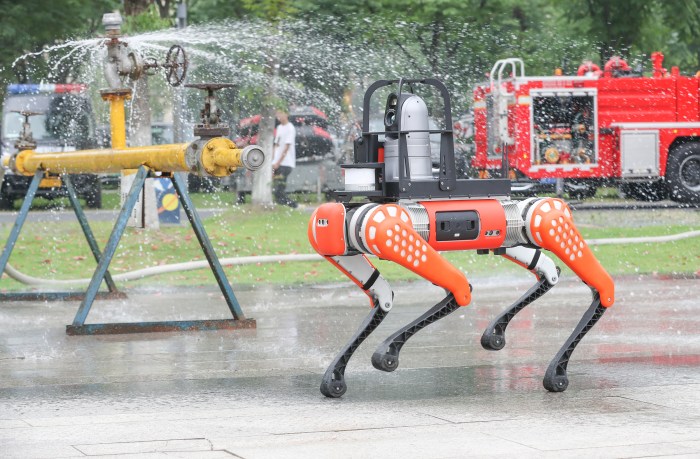

Source: stdaily.com
The integration of robotics into emergency response is rapidly evolving, promising a future where rescue operations are faster, safer, and more efficient. However, realizing this potential requires navigating significant technological and logistical hurdles. The path forward involves embracing cutting-edge technologies while simultaneously addressing the practical challenges of implementation and integration.
Emerging Technologies Revolutionizing Emergency Response
The next generation of emergency response robots will leverage advancements in artificial intelligence (AI) and swarm robotics to enhance their capabilities significantly. AI will empower robots with improved decision-making, enabling them to autonomously navigate complex environments, assess damage more accurately, and even perform tasks requiring a high degree of dexterity, such as delicate medical procedures in the field. Swarm robotics, where multiple robots collaborate on a task, offers the potential for greater efficiency and redundancy in search and rescue operations, covering larger areas and handling diverse challenges simultaneously. Imagine a swarm of small, agile robots searching a collapsed building, communicating their findings in real-time and coordinating their efforts to locate survivors. This level of coordination and adaptability is currently beyond the capabilities of individual robots.
Challenges of Integrating Robotic Systems into Existing Infrastructure
Integrating robots into the existing emergency response infrastructure presents substantial challenges. One key issue is interoperability: ensuring that different robotic systems from various manufacturers can communicate and share data seamlessly. This requires the development of standardized communication protocols and data formats. Another challenge is the need for robust and reliable communication networks in disaster zones, where infrastructure may be severely damaged. Furthermore, the cost of acquiring, maintaining, and training personnel to operate sophisticated robotic systems can be prohibitive for many emergency response agencies, demanding innovative financing models and collaborative efforts. The complexity of integrating these new systems into established workflows also requires careful planning and training.
Standardized Protocols and Training for Emergency Response Robot Operators
The effective use of emergency response robots hinges on the availability of well-trained operators. Standardized training protocols are crucial to ensure consistency in operation and minimize the risk of errors. This training should encompass not only technical skills in operating the robots but also crucial aspects like situational awareness, ethical considerations, and decision-making under pressure. A standardized certification process could help establish minimum competency levels for operators, guaranteeing a consistent level of skill and safety across different agencies. Furthermore, ongoing professional development programs are essential to keep operators updated on the latest technologies and best practices.
Increased Collaboration Between Human Responders and Robots
The future of emergency response is not about robots replacing human responders, but rather about creating a synergistic partnership. Robots can handle dangerous tasks, such as entering unstable structures or navigating hazardous environments, while human responders leverage their expertise, judgment, and emotional intelligence to make critical decisions and interact with survivors. Effective collaboration requires the development of intuitive human-robot interfaces that allow for seamless communication and control. This includes developing systems that can accurately interpret human instructions and provide clear and concise feedback to the operators. Furthermore, research into shared autonomy, where robots and humans share control over tasks, could lead to more effective and efficient emergency response.
Final Wrap-Up
Source: seepositive.in
The integration of robotics into emergency response isn’t just a technological advancement; it’s a humanitarian revolution. As technology continues to evolve, so too will our ability to respond to crises. The future of emergency response is collaborative, efficient, and, most importantly, safer, thanks to the tireless work of robots on the front lines. It’s a future where technology and human ingenuity work hand-in-hand to protect lives and rebuild communities in the aftermath of disaster.
