How Quantum Computing is Enabling Faster Drug Discovery? Forget slow, painstaking research. Imagine a world where new drugs are developed at warp speed, thanks to the mind-bending power of quantum computers. This isn’t science fiction; it’s the cutting edge of pharmaceutical innovation. We’re diving deep into how this revolutionary technology is poised to completely transform drug discovery, from identifying promising drug targets to optimizing the molecules themselves.
Quantum computing, with its ability to process information in ways classical computers can’t, is tackling some of the biggest challenges in drug development. Think exponentially faster simulations of complex molecules, more accurate predictions of drug efficacy, and the potential to unlock entirely new drug candidates. This isn’t just about speeding things up; it’s about unlocking breakthroughs that were previously impossible.
Introduction to Quantum Computing and Drug Discovery
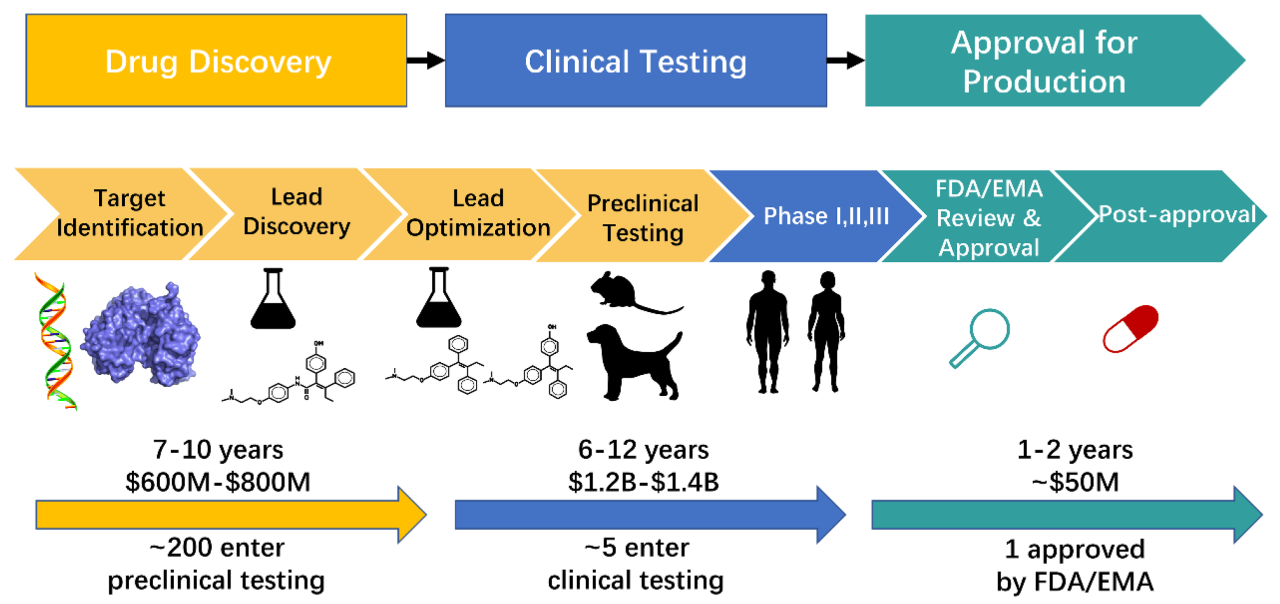
The pharmaceutical industry faces a persistent challenge: developing effective drugs is a lengthy, expensive, and often unsuccessful process. Traditional methods rely heavily on trial and error, leading to high failure rates and significant financial losses. Quantum computing, however, offers a potential game-changer, leveraging the bizarre laws of quantum mechanics to tackle these complexities with unprecedented speed and efficiency. This transformative technology promises to revolutionize drug discovery by accelerating various stages of the process, from identifying potential drug candidates to optimizing their properties.
Quantum computing differs fundamentally from classical computing in its approach to information processing. Classical computers store information as bits, representing either a 0 or a 1. Quantum computers, on the other hand, utilize qubits. Qubits leverage quantum phenomena like superposition (existing in multiple states simultaneously) and entanglement (linking the fates of multiple qubits), allowing them to perform calculations far beyond the capabilities of even the most powerful classical supercomputers. This inherent parallelism opens up possibilities for tackling problems previously considered intractable.
Quantum Computing’s Role in Addressing Drug Discovery Challenges
The drug discovery pipeline is notoriously long and complex, involving several stages, each fraught with challenges. High attrition rates are common, with many promising drug candidates failing in clinical trials due to factors such as lack of efficacy, toxicity, or poor bioavailability. Quantum computing aims to address these challenges by significantly improving the speed and accuracy of several crucial steps. For instance, the process of identifying potential drug candidates, typically involving extensive screening of vast chemical libraries, can be dramatically accelerated using quantum algorithms. Similarly, quantum simulations can accurately predict the behavior of molecules and their interactions with biological targets, reducing the need for extensive and costly laboratory experiments. Finally, quantum machine learning algorithms can analyze massive datasets of biological information, identifying patterns and insights that could lead to the discovery of novel drug targets.
Specific Applications of Quantum Computing in Drug Discovery, How Quantum Computing is Enabling Faster Drug Discovery
Quantum computing’s impact on drug discovery is anticipated across multiple areas. One key application is in accelerating molecular simulations. Traditional methods struggle to accurately model the complex interactions within molecules, especially large and complex biomolecules like proteins. Quantum computers, however, can simulate these interactions with much greater accuracy and speed, allowing researchers to predict the properties of potential drug candidates with higher confidence. This reduces the reliance on time-consuming and expensive experimental validation.
Another area where quantum computing shows significant promise is in materials discovery. The search for novel materials with specific properties for drug delivery systems, such as targeted nanoparticles, can be significantly expedited using quantum algorithms. These algorithms can efficiently explore the vast chemical space of possible materials, identifying those with optimal properties for drug delivery.
Furthermore, quantum machine learning algorithms can be employed to analyze large genomic datasets, identifying potential drug targets and predicting the efficacy and safety of drug candidates. This data-driven approach can significantly accelerate the drug discovery process, leading to faster development of effective treatments. For example, quantum algorithms could analyze the vast amounts of genomic data associated with a disease like cancer, helping to identify specific genes or proteins that could be targeted by new drugs. This would significantly reduce the time and cost associated with identifying promising drug targets. Early successes in this area show promising results, although the field is still in its early stages of development.
Quantum Algorithms for Drug Discovery
Source: mdpi-res.com
Quantum computing isn’t just a futuristic concept; it’s rapidly becoming a game-changer in various fields, and drug discovery is no exception. The sheer complexity of biological systems and the vast amount of data involved in drug development make it an ideal candidate for the power of quantum algorithms. These algorithms offer the potential to accelerate the process significantly, leading to faster development of new and more effective treatments.
The application of quantum algorithms in drug discovery is multifaceted, tackling challenges from data security to complex molecular simulations. Let’s delve into some key areas.
Shor’s Algorithm and Data Security
Shor’s algorithm, a cornerstone of quantum computing, poses a significant threat to current encryption methods. It can efficiently factor large numbers, a process that underpins many widely used encryption algorithms like RSA. This has serious implications for the pharmaceutical industry, where sensitive data about drug candidates, clinical trials, and intellectual property is heavily reliant on robust encryption. A successful implementation of Shor’s algorithm by malicious actors could compromise this data, leading to significant financial losses and intellectual property theft. While large-scale quantum computers capable of breaking current encryption are still some years away, the pharmaceutical industry needs to proactively explore post-quantum cryptography solutions to safeguard its valuable data in the long term. This includes researching and implementing quantum-resistant cryptographic algorithms that are secure against attacks from both classical and quantum computers. For example, lattice-based cryptography is a promising candidate for post-quantum encryption.
Variational Quantum Eigensolver (VQE) and Quantum Approximate Optimization Algorithm (QAOA) for Molecular Simulations
Accurately simulating molecules is crucial for drug discovery. Classical computers struggle with this task for large molecules due to the exponential growth in computational complexity. Quantum algorithms offer a potential solution. Two prominent algorithms used for molecular simulations are the Variational Quantum Eigensolver (VQE) and the Quantum Approximate Optimization Algorithm (QAOA).
VQE is a hybrid quantum-classical algorithm that uses a classical optimizer to find the lowest energy state of a molecule. This ground state energy is crucial for understanding the molecule’s stability and reactivity. VQE works by iteratively adjusting parameters on a quantum computer to minimize the energy of the molecule, leveraging the quantum computer’s ability to handle the complex wave functions involved. QAOA, on the other hand, is designed to find approximate solutions to combinatorial optimization problems, which are frequently encountered in drug design, such as finding the optimal conformation of a molecule or identifying potential drug targets. Both algorithms have shown promise in early experiments, though their practical applicability is still under development and faces challenges related to noise and scalability. For instance, researchers have used VQE to simulate the electronic structure of small molecules, paving the way for larger and more complex simulations in the future. The accuracy and efficiency of these algorithms are heavily dependent on the quality of the quantum hardware and the development of improved algorithms and classical optimization techniques.
Quantum Machine Learning for Drug Target Identification
Drug discovery often involves sifting through massive datasets of biological information to identify potential drug targets. Quantum machine learning (QML) algorithms hold the potential to accelerate this process by analyzing these datasets more efficiently than classical machine learning methods. QML leverages the unique capabilities of quantum computers to process and analyze complex data patterns, potentially leading to the identification of novel drug targets that might be missed by classical approaches. For example, QML algorithms could be trained on genomic data to identify specific genes or proteins associated with a disease, thus identifying potential drug targets. Additionally, QML could be used to predict the efficacy and safety of drug candidates, reducing the time and cost associated with drug development. While still in its early stages, QML is a rapidly evolving field with the potential to revolutionize drug target identification and lead optimization. Examples of early applications include using quantum support vector machines (QSVMs) to classify biological data and using quantum neural networks to model protein interactions. The success of these applications will depend on the development of more powerful and robust quantum computers and more sophisticated QML algorithms.
Applications of Quantum Computing in Drug Design and Development

Source: medium.com
Quantum computing, still in its nascent stages, holds the potential to revolutionize the pharmaceutical industry by significantly accelerating and improving the drug discovery process. The sheer complexity of biological systems and the vast chemical space to explore make traditional methods slow and expensive. Quantum algorithms offer a powerful new toolkit to tackle these challenges, leading to faster development of safer and more effective drugs.
Quantum Computing’s Impact on Key Drug Discovery Stages
The drug discovery pipeline is a lengthy and complex process. Quantum computing can significantly impact several crucial stages. The table below illustrates how quantum approaches compare to classical methods and the potential advantages they offer.
| Stage | Classical Approach | Quantum Approach | Potential Benefits |
|---|---|---|---|
| Target Identification & Validation | High-throughput screening, bioinformatics analysis of large datasets. Often slow and computationally intensive. | Quantum machine learning algorithms can analyze vast genomic and proteomic datasets to identify promising drug targets more efficiently. Quantum simulations can model protein-ligand interactions with higher accuracy. | Faster identification of targets, reduced reliance on expensive and time-consuming experimental screening. Increased accuracy in target selection. |
| Lead Discovery & Optimization | Virtual screening of large compound libraries, experimental synthesis and testing of potential drug candidates. A significant bottleneck due to the vast chemical space. | Quantum algorithms can efficiently explore the chemical space, predicting the properties of millions of molecules simultaneously. Quantum simulations can accurately predict binding affinities and other crucial properties. | Faster identification of promising lead compounds, reduced experimental workload, improved prediction accuracy leading to fewer failed clinical trials. |
| Preclinical Development | Extensive in vitro and in vivo testing to assess safety, efficacy, and pharmacokinetics. Time-consuming and expensive. | Quantum simulations can predict drug metabolism, toxicity, and other pharmacokinetic properties with greater accuracy. This reduces the need for extensive animal testing. | Reduced reliance on animal testing, faster and more cost-effective preclinical development, improved prediction of drug safety and efficacy. |
| Clinical Trials | Large-scale clinical trials to assess efficacy and safety in humans. Expensive and time-consuming. | Quantum machine learning algorithms can analyze patient data to identify optimal patient subgroups for clinical trials, potentially reducing the size and cost of trials. Improved prediction of individual patient responses to drugs. | More efficient and cost-effective clinical trials, personalized medicine approaches, faster regulatory approval. |
Improving the Accuracy of Molecular Property Prediction
Quantum simulations, leveraging algorithms like Variational Quantum Eigensolver (VQE) and Quantum Approximate Optimization Algorithm (QAOA), can dramatically improve the accuracy of predicting crucial molecular properties. For example, accurately predicting binding affinity—how strongly a drug molecule interacts with its target—is critical for drug efficacy. Classical methods often rely on approximations and simplifications, leading to inaccuracies. Quantum simulations, however, can model the complex interactions between molecules with greater precision, leading to more reliable predictions of binding affinity and reducing the need for extensive experimental validation. Similarly, predicting toxicity is crucial for drug safety. Quantum simulations can help identify potential toxicities early in the drug development process, minimizing risks and saving resources. For instance, by simulating the interaction of a drug molecule with cellular components, quantum computing can predict potential adverse effects with greater accuracy than classical methods.
Accelerating Lead Optimization and Drug Candidate Selection
A hypothetical workflow using quantum computing to accelerate lead optimization could look like this: First, a vast library of virtual molecules is generated. Quantum algorithms then rapidly screen these molecules, predicting their binding affinity to the target protein using quantum simulations. The top candidates are then further analyzed using quantum simulations to predict their pharmacokinetic and pharmacodynamic properties, including absorption, distribution, metabolism, excretion, and toxicity. Finally, based on these predictions, a smaller set of optimized lead compounds is selected for experimental synthesis and testing. This process significantly reduces the time and cost associated with traditional lead optimization, focusing resources on the most promising candidates. For example, instead of synthesizing and testing thousands of compounds, a quantum-assisted approach might allow researchers to narrow down the field to a few dozen, dramatically accelerating the process and saving substantial resources.
Quantum Computing for Drug Target Identification
The quest for effective treatments hinges on identifying the right molecular targets within the body’s complex machinery. Traditional methods, while successful, often prove time-consuming and resource-intensive. Quantum computing, with its potential to handle vast datasets and complex calculations, offers a revolutionary approach to drug target identification, accelerating the process and potentially uncovering targets previously inaccessible. This new frontier promises to significantly impact the pharmaceutical industry, leading to faster development of life-saving medications.
Quantum computing’s power lies in its ability to analyze intricate biological systems at an unprecedented scale. By leveraging quantum algorithms, researchers can simulate molecular interactions with greater accuracy, leading to a more precise understanding of disease mechanisms and the identification of promising drug targets. This approach significantly reduces the reliance on lengthy and expensive experimental trials, streamlining the overall drug discovery process.
Quantum Algorithms for Protein-Protein Interaction Analysis
Understanding protein-protein interactions (PPIs) is crucial for identifying drug targets, as many diseases arise from disruptions in these interactions. Traditional methods for analyzing PPIs are often limited by computational complexity, hindering the ability to explore the vast landscape of potential interactions. Quantum algorithms, however, offer a pathway to overcome these limitations. For instance, Variational Quantum Eigensolver (VQE) and Quantum Approximate Optimization Algorithm (QAOA) can be employed to simulate PPIs with higher accuracy and efficiency than classical algorithms, providing insights into the dynamics of these interactions and identifying potential points of intervention for drug development. Imagine simulating the interaction of a viral protein with a human cell receptor; a quantum computer could provide a detailed, highly accurate model of this interaction, revealing potential vulnerabilities for drug targeting. This level of detail is difficult, if not impossible, to achieve with classical methods.
Advantages and Disadvantages of Quantum Computing in Drug Target Identification
The application of quantum computing to drug target identification presents both significant advantages and challenges.
It’s important to weigh the benefits against the limitations before fully embracing this technology.
Quantum computing’s power to accelerate drug discovery is seriously game-changing, allowing scientists to simulate molecular interactions with unprecedented speed. This efficiency boost is mirrored in other industries; for example, consider the logistical revolution underway, as detailed in this insightful article on How Autonomous Vehicles are Set to Disrupt the Logistics Industry. Ultimately, both these advancements highlight the transformative potential of cutting-edge technology in solving complex real-world problems, leading to faster breakthroughs in medicine and beyond.
- Advantages: Increased accuracy in molecular simulations, faster identification of novel drug targets, potential for discovering targets inaccessible to traditional methods, reduced reliance on extensive experimental trials, and the ability to analyze large datasets of biological information efficiently.
- Disadvantages: The technology is still in its early stages of development, requiring significant investment in hardware and software. Expertise in quantum computing is limited, and the interpretation of quantum computational results requires specialized skills. Furthermore, the cost of accessing quantum computing resources can be prohibitive for many research groups.
Examples of Successful Applications
While still in its nascent stages, quantum computing has already shown promise in drug target identification. Although large-scale, publicly available examples of completely novel drug targets discovered solely through quantum computing are currently limited due to the technology’s relative infancy and the proprietary nature of much pharmaceutical research, there are promising developments in specific areas. For instance, researchers are using quantum simulations to study the binding affinities of potential drug candidates to their target proteins, leading to a more efficient screening process. Another example lies in the improved prediction of protein folding using quantum algorithms. Accurate prediction of protein structure is crucial for understanding their function and identifying potential drug targets. Early successes in this area suggest a promising future for quantum computing in drug discovery. These initial successes highlight the potential of quantum computing to revolutionize the process of identifying effective drug targets, although more widespread, publicly available results are expected as the technology matures.
Challenges and Future Outlook of Quantum Computing in Drug Discovery: How Quantum Computing Is Enabling Faster Drug Discovery
Quantum computing holds immense promise for revolutionizing drug discovery, but its journey from theoretical potential to practical application is paved with significant hurdles. While early successes hint at a future where drug development is faster, cheaper, and more effective, several key challenges need to be addressed before quantum computers become a standard tool in pharmaceutical labs.
Current technological limitations significantly hamper the widespread adoption of quantum computers in drug discovery. The field is still in its nascent stages, and the technology faces considerable obstacles in terms of scalability, stability, and error correction. The delicate nature of quantum bits (qubits), the fundamental units of quantum computation, makes them highly susceptible to noise and decoherence – essentially, they lose their quantum properties quickly, leading to inaccurate calculations. This necessitates complex error correction techniques that currently add significant overhead and limit the size and complexity of problems that can be tackled. Furthermore, building and maintaining quantum computers is incredibly expensive, restricting access to a select few research institutions and companies.
Technological Limitations of Quantum Computers
The fragility of qubits is a major bottleneck. Current quantum computers have a limited number of qubits, and their coherence time – the period during which they maintain their quantum state – is relatively short. This restricts the complexity of simulations that can be performed. For instance, accurately simulating a large protein molecule, a crucial step in drug design, requires a significantly larger number of qubits and longer coherence times than are currently available. Improvements in qubit technology, such as the development of more stable and scalable qubit architectures (e.g., trapped ions, superconducting circuits), are crucial for overcoming this limitation. Another significant challenge lies in the development of efficient quantum algorithms specifically tailored for drug discovery problems. While some promising algorithms exist, their practical implementation and optimization remain an active area of research.
Ethical Considerations in Quantum Drug Discovery
The transformative potential of quantum computing in drug discovery also raises important ethical considerations. Access to this powerful technology could exacerbate existing inequalities in the pharmaceutical industry, potentially widening the gap between wealthy and developing nations in terms of access to new drugs and therapies. The potential for misuse of quantum computing in drug development, such as the design of novel bioweapons or the creation of highly addictive substances, also requires careful consideration and proactive regulatory frameworks. Ensuring equitable access to the benefits of quantum-enhanced drug discovery and establishing ethical guidelines for its application are paramount to realizing its full potential responsibly.
Future Advancements in Quantum Computing for Drug Discovery
The future of quantum computing in drug discovery is bright, contingent upon overcoming the current technological hurdles. Several advancements are anticipated to revolutionize the field:
- Improved Qubit Technology: Development of more stable and scalable qubits with longer coherence times will allow for larger and more complex simulations, enabling the modeling of increasingly intricate biological systems.
- Advanced Error Correction Codes: More efficient error correction techniques will mitigate the effects of noise and decoherence, increasing the accuracy and reliability of quantum computations.
- Development of Specialized Quantum Algorithms: The creation of novel quantum algorithms specifically designed for drug discovery tasks, such as molecular dynamics simulations and quantum machine learning for drug target identification, will enhance the efficiency and effectiveness of the process.
- Increased Computational Power: The development of larger-scale quantum computers with thousands or even millions of qubits will enable the simulation of significantly more complex biological systems, leading to a deeper understanding of disease mechanisms and the design of more effective drugs.
- Hybrid Quantum-Classical Computing: Combining the strengths of quantum and classical computers will allow researchers to leverage the power of quantum computing for specific tasks while relying on classical computers for other aspects of drug discovery, creating a more efficient and cost-effective workflow.
For example, imagine a future where quantum computers can accurately simulate the interaction of a drug molecule with its target protein, predicting its efficacy and potential side effects with unprecedented precision. This would drastically reduce the time and cost associated with drug development, leading to faster access to life-saving medications. Similarly, quantum machine learning algorithms could accelerate the identification of novel drug targets, paving the way for the development of therapies for currently incurable diseases.
Illustrative Examples
Quantum simulations are revolutionizing drug discovery by allowing scientists to explore the intricate interactions between drug molecules and their target proteins with unprecedented accuracy. This detailed understanding facilitates the design of more effective and safer drugs, ultimately accelerating the drug development process and improving patient outcomes. Let’s delve into a specific example to illustrate this transformative potential.
Quantum Simulation of the Interaction Between a Drug Molecule and a Target Protein
Consider the drug molecule imatinib, a tyrosine kinase inhibitor used to treat chronic myeloid leukemia (CML). Imatinib targets the BCR-ABL protein, a mutated enzyme responsible for uncontrolled cell growth in CML. Classical simulations struggle to accurately model the complex interactions between imatinib and BCR-ABL, especially the subtle conformational changes that occur upon binding. Quantum simulations, however, offer a higher level of accuracy, allowing researchers to probe these interactions at the atomic level. The simulation would involve modeling the electronic structure of both imatinib and the active site of BCR-ABL, using quantum mechanical methods to calculate the forces and energies involved in their interaction. This detailed analysis can reveal crucial insights into the binding affinity, specificity, and potential off-target effects of imatinib.
Quantum simulations provide a more accurate representation of the drug-protein interaction, revealing subtle conformational changes and predicting binding affinity with greater precision than classical methods. This leads to improved drug design and a better understanding of drug efficacy and potential side effects.
Designing Novel Drug Molecules with Improved Efficacy and Reduced Side Effects
By leveraging quantum simulations, scientists can explore a vast chemical space to design novel drug molecules with enhanced properties. Let’s imagine a scenario where researchers identify a specific aspect of imatinib’s interaction with BCR-ABL that could be optimized for improved efficacy or reduced toxicity. Using quantum algorithms, they can virtually screen millions of potential drug candidates, evaluating their binding affinity, selectivity, and other relevant properties. This process can lead to the identification of a redesigned imatinib molecule, let’s call it “Imatinib-X,” with superior characteristics.
| Property | Imatinib | Imatinib-X |
|---|---|---|
| Binding Affinity (Kd) | 1 nM | 0.1 nM |
| Selectivity (BCR-ABL vs. other kinases) | 10:1 | 100:1 |
| Toxicity (LD50 in mice) | 200 mg/kg | 500 mg/kg |
Visualization of a Quantum Simulation
Imagine a three-dimensional representation of the BCR-ABL protein, depicted as a complex network of atoms and molecules. The active site, where imatinib binds, is highlighted. Imatinib is then introduced into the simulation, its atoms represented as colorful spheres. As the simulation progresses, the atoms of imatinib and the active site of BCR-ABL interact, with the forces between them calculated using quantum mechanical principles. The simulation would show the dynamic rearrangement of atoms, revealing the precise binding mode and the energy changes associated with the interaction. Different colors could represent different energies or forces, illustrating regions of strong or weak interactions. The simulation would visually demonstrate how slight changes in the structure of imatinib could lead to significant alterations in binding affinity and selectivity. This visual representation allows scientists to understand the drug-protein interaction in a more intuitive way, guiding the design of more effective and safer drugs.
Outcome Summary

Source: biostrand.ai
The potential of quantum computing to revolutionize drug discovery is undeniable. While challenges remain—from the technology’s current limitations to ethical considerations—the future is bright. As quantum computers become more powerful and accessible, we can expect a wave of new drugs and treatments, developed faster and more efficiently than ever before. This isn’t just about faster drug development; it’s about a healthier future, powered by the incredible potential of quantum mechanics.
