How Machine Learning is Helping to Improve Traffic Management Systems? It’s a question that’s rapidly moving from the realm of futuristic fantasy to everyday reality. Imagine a city where traffic flows smoothly, accidents are predicted and prevented, and finding a parking spot is less of a quest and more of a breeze. That’s the promise of machine learning in traffic management – a tech revolution quietly reshaping how we navigate our urban jungles. This deep dive explores how algorithms are learning to untangle our traffic knots, one data point at a time.
From predicting rush hour bottlenecks to optimizing traffic light cycles in real-time, machine learning is transforming how we manage traffic. Sensors embedded in roads, cameras capturing traffic flow, and GPS data from millions of vehicles are feeding vast datasets into sophisticated algorithms. These algorithms then crunch the numbers, identifying patterns, predicting congestion, and suggesting solutions to optimize traffic flow. This isn’t just about reducing commute times; it’s about creating safer, more efficient, and ultimately, more sustainable urban environments.
Introduction
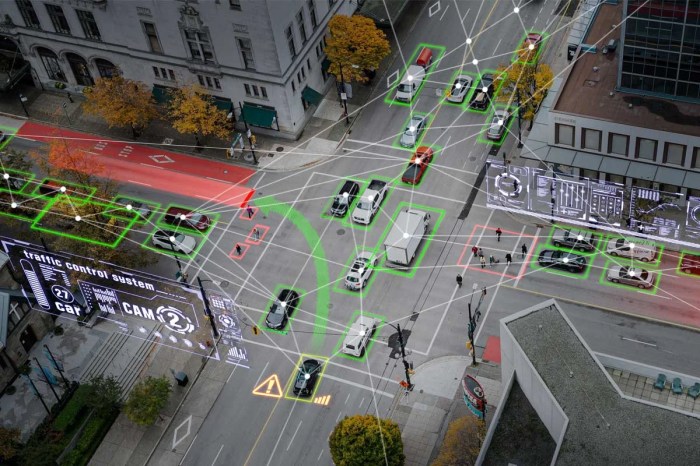

Source: ambiq.com
Navigating the urban jungle has become increasingly challenging. Rush hour traffic isn’t just a minor inconvenience; it’s a major economic and environmental drain, causing significant delays, wasted fuel, and increased pollution. Our roads, designed for a different era, are struggling to cope with the sheer volume of vehicles, leading to gridlock and frustration for commuters and businesses alike. Traditional methods of traffic management, often relying on static signal timings and human observation, are simply inadequate to address the complexities of modern traffic flow.
The limitations of traditional approaches are stark. Fixed-time traffic signals, for instance, are inflexible and often lead to unnecessary delays, especially during off-peak hours or when unexpected events occur. Manual adjustments by traffic controllers, while valuable, are reactive and can’t account for the dynamic and unpredictable nature of traffic patterns. Furthermore, collecting and analyzing traffic data traditionally involved manual processes, leading to delays in understanding traffic flow and implementing effective solutions. This lack of real-time data and adaptive control severely hinders efficient traffic management.
Integrating machine learning into traffic systems offers a transformative solution. By analyzing vast quantities of real-time data from various sources – such as traffic cameras, GPS devices, and smart sensors embedded in roads – machine learning algorithms can identify patterns, predict congestion hotspots, and optimize traffic flow in real-time. This allows for dynamic signal timing adjustments, improved route planning, and proactive interventions to mitigate congestion before it occurs. The potential benefits include reduced travel times, decreased fuel consumption, minimized emissions, and improved overall road safety.
Challenges of Modern Traffic Management
Modern traffic management faces numerous hurdles. Rapid urbanization leads to increased vehicle density, particularly in cities and suburbs. This increased density exacerbates existing infrastructure limitations, leading to congestion and delays. Unpredictable events, such as accidents, road closures, and special events, further disrupt traffic flow and necessitate swift and efficient responses. The sheer volume of data generated by traffic sensors and other sources also presents a significant challenge in terms of storage, processing, and analysis. Effective traffic management requires the ability to process and interpret this data in real-time to make informed decisions. For example, the city of Los Angeles struggles with severe congestion daily, requiring sophisticated systems to manage the flow of millions of vehicles.
Potential Benefits of Machine Learning in Traffic Systems
Machine learning offers several key advantages in addressing these challenges. Real-time traffic prediction is a major benefit; by analyzing historical data and current conditions, machine learning models can accurately forecast congestion and recommend optimal routes to drivers. Dynamic traffic signal control, adapting signal timings based on real-time traffic conditions, significantly improves traffic flow efficiency. An example of this is the adaptive traffic control systems implemented in cities like Singapore, which have demonstrably reduced congestion and travel times. Furthermore, machine learning can help optimize traffic flow in construction zones and other areas with temporary disruptions, minimizing delays and improving safety. Improved incident detection and response, through the analysis of data from various sources, enables faster responses to accidents and other unforeseen events. Finally, machine learning facilitates better urban planning, allowing city planners to make data-driven decisions about infrastructure improvements and traffic management strategies. Cities like Amsterdam are already using this approach to proactively manage their road networks and improve traffic flow.
Real-time Traffic Prediction and Optimization
Imagine a city where traffic flows smoothly, without the frustrating standstills we’re all too familiar with. That’s the promise of real-time traffic prediction and optimization, powered by the magic of machine learning. By analyzing vast amounts of data, these systems can anticipate congestion hotspots, adjust traffic signals dynamically, and even suggest alternative routes to drivers, leading to reduced commute times and improved overall traffic efficiency.
Machine learning algorithms achieve this predictive power by analyzing historical traffic patterns, current sensor data, and even weather forecasts. They identify recurring congestion patterns, predict future traffic flow based on these patterns, and account for unforeseen events like accidents or road closures. This allows for proactive adjustments to traffic management strategies, rather than simply reacting to already existing congestion.
Traffic Prediction Models
Several machine learning models are employed for accurate traffic prediction. The choice of model often depends on the specific application, the type of data available, and the desired level of accuracy. Below is a comparison of some popular models:
| Model Name | Description | Advantages | Disadvantages |
|---|---|---|---|
| Time Series Analysis (e.g., ARIMA) | Analyzes historical traffic data to identify patterns and trends, forecasting future values based on these patterns. | Relatively simple to implement, requires less data than other models. | Can struggle with complex, non-linear relationships in traffic data; assumes stationarity in the data. |
| Neural Networks (e.g., Recurrent Neural Networks (RNNs), Long Short-Term Memory (LSTM)) | Complex models capable of learning intricate patterns and relationships in data, even non-linear ones. RNNs and LSTMs are particularly well-suited for time-series data. | High accuracy in predicting complex traffic patterns; can handle large datasets and non-stationary data. | Require significant computational resources and large datasets for training; can be difficult to interpret and tune. |
| Support Vector Machines (SVM) | Effective in classifying and predicting traffic conditions based on various features like time of day, weather, and day of the week. | Relatively robust to outliers and high-dimensional data. | Can be computationally expensive for very large datasets. |
Real-time Prediction Applications
Real-time traffic predictions significantly enhance traffic signal timing and routing decisions. For example, in cities using adaptive traffic control systems, predictions of upcoming congestion allow traffic signals to be adjusted dynamically, prioritizing traffic flow on congested routes and minimizing delays. Imagine a scenario where an accident is predicted to cause a significant bottleneck in 15 minutes. The system could proactively adjust signal timings in the surrounding area to divert traffic, mitigating the impact of the accident.
Similarly, real-time predictions are crucial for navigation apps. By incorporating these predictions, apps can provide drivers with alternative routes that avoid congested areas, leading to faster and more efficient commutes. For instance, a navigation app might suggest a slightly longer route that avoids a predicted traffic jam, ultimately saving the driver significant time.
Sensor Data Integration
The accuracy of these predictive models heavily relies on the quality and quantity of sensor data. A wide array of sensors, including cameras, GPS devices embedded in vehicles, and loop detectors embedded in roads, collect real-time traffic information such as speed, density, and flow. This data is crucial for training and validating the machine learning models, ensuring they accurately reflect real-world traffic conditions. For example, camera data can be used to detect incidents like accidents or stalled vehicles, while GPS data provides information on individual vehicle movements. Combining these diverse data sources provides a comprehensive view of the traffic network, enabling more precise predictions and optimizations.
Intelligent Transportation Systems (ITS) and Machine Learning

Source: teledataict.com
Intelligent Transportation Systems (ITS) are revolutionizing how we manage traffic, and machine learning is the engine driving this transformation. By analyzing vast amounts of data from various sources, machine learning algorithms can optimize the performance of ITS components, leading to smoother traffic flow, reduced congestion, and improved safety. This synergy allows for a more responsive and efficient transportation network.
Machine learning’s role in optimizing ITS components is multifaceted and powerful. It allows for a level of responsiveness and predictive capability previously unimaginable. The algorithms aren’t just reacting to current conditions; they’re anticipating future needs and proactively adjusting the system accordingly.
Machine Learning’s Optimization of ITS Components
Machine learning algorithms are increasingly vital to the effective functioning of adaptive traffic control systems. These systems dynamically adjust traffic signal timings based on real-time traffic conditions, minimizing delays and optimizing throughput. Machine learning models can analyze data from various sources – traffic cameras, loop detectors, GPS data from vehicles – to predict traffic patterns and adjust signal timings accordingly. This dynamic optimization surpasses the capabilities of traditional, fixed-time traffic signal systems. Similarly, advanced traveler information systems (ATIS) benefit greatly from machine learning. By analyzing historical traffic data and real-time information, machine learning models can predict travel times, suggest optimal routes, and provide drivers with accurate and timely information, reducing congestion and improving overall travel efficiency.
Examples of Successful ITS Deployments Leveraging Machine Learning
Several cities have successfully deployed machine learning-powered ITS solutions. For instance, some cities use machine learning to predict accident hotspots based on historical data and environmental factors like weather conditions. This predictive capability allows for proactive measures such as increased police patrols or targeted safety campaigns, reducing accident rates. Other cities use machine learning to optimize public transportation scheduling, adjusting routes and frequencies in real-time to meet changing demand. This dynamic approach ensures efficient service and reduces wait times for commuters. Imagine a city where bus routes adjust automatically based on real-time passenger demand, predicted using machine learning – reducing overcrowding and improving on-time performance.
Machine Learning’s Enhancement of Communication and Coordination Between ITS Components, How Machine Learning is Helping to Improve Traffic Management Systems
Effective communication and coordination between different ITS components are crucial for optimal performance. Machine learning plays a key role in facilitating this communication by integrating data from various sources and enabling seamless information exchange. For example, data from traffic cameras can be integrated with data from GPS devices to provide a comprehensive view of traffic conditions. Machine learning algorithms can then analyze this integrated data to identify patterns, predict congestion, and coordinate the actions of different ITS components, such as adaptive traffic control systems and ATIS. This coordinated approach ensures a more responsive and efficient transportation network.
Hypothetical Scenario: Machine Learning Integrated Within an ITS Framework
Imagine a city implementing a comprehensive ITS framework powered by machine learning. The system integrates data from various sources, including traffic cameras, loop detectors, GPS devices, and weather sensors. Machine learning algorithms analyze this data to predict traffic patterns, identify potential congestion points, and dynamically adjust traffic signal timings. Simultaneously, the system provides drivers with real-time traffic information and suggests optimal routes through a mobile app. In case of an unexpected incident, such as an accident or road closure, the system automatically reroutes traffic and notifies drivers through the app. This integrated approach, driven by machine learning, leads to significant improvements in traffic flow, reduced congestion, and enhanced safety. The system could even learn and adapt to seasonal variations in traffic patterns or even anticipate changes based on large public events.
Anomaly Detection and Incident Management
Source: open-pr.com
Machine learning is revolutionizing traffic management by enabling systems to not only predict traffic flow but also to identify and respond to unexpected events. Anomaly detection, a key application of machine learning in this field, allows for proactive incident management, leading to smoother traffic flow and reduced congestion. This is achieved by analyzing vast amounts of traffic data to identify unusual patterns that signal potential problems.
Machine learning algorithms excel at identifying unusual traffic patterns that signify accidents, road closures, or other incidents. These algorithms analyze various data points, including speed variations, traffic density fluctuations, and travel time discrepancies, comparing them against established baselines. Significant deviations from these baselines trigger alerts, enabling rapid response and mitigation efforts. For example, a sudden and significant drop in average speed within a specific road segment, coupled with increased traffic density upstream, could strongly indicate an accident. The system can then automatically trigger alerts to emergency services and provide real-time updates to drivers via navigation apps.
Machine learning is revolutionizing traffic flow, predicting congestion hotspots and optimizing signal timing for smoother commutes. This predictive power mirrors the advancements in personalized online experiences; check out this article on The Role of AI in Enhancing Personalized Online Shopping to see how similar AI-driven insights are used. Ultimately, both applications boil down to using data to anticipate needs and improve efficiency – whether that’s navigating rush hour or finding the perfect pair of shoes.
Identifying Traffic Anomalies Using Machine Learning
Machine learning models, specifically unsupervised learning techniques like clustering and outlier detection, are adept at identifying anomalies in traffic data. These models learn the typical patterns of traffic flow over time and then flag instances that deviate significantly from these learned patterns. Different algorithms are suited for different types of data and anomaly characteristics. For instance, k-means clustering could be used to group similar traffic patterns, with outliers representing potential incidents. One-class SVM can be effective in identifying anomalies when the data is primarily normal, and we are trying to identify the rare events (like accidents).
Predicting the Impact of Incidents on Traffic Flow
Once an anomaly is detected, the next step is to predict its impact on the broader traffic network. This involves using predictive modeling techniques, such as time series analysis and simulation, to forecast how the incident will affect travel times, congestion levels, and overall network performance. For instance, a model might predict that a highway closure will cause a 30-minute delay on alternative routes during peak hours, allowing authorities to implement diversions or adjust traffic light timings to mitigate the impact. This predictive capability allows for proactive traffic management strategies, reducing the severity and duration of traffic disruptions.
Types of Traffic Anomalies Detectable by Machine Learning
Machine learning can detect a wide range of anomalies in traffic data. These include:
Several types of anomalies can be detected. Understanding these different types allows for more tailored anomaly detection strategies and more effective incident response.
- Sudden speed drops: Indicative of accidents, road closures, or unexpected congestion.
- Unusual traffic density fluctuations: Significant increases or decreases in traffic volume compared to typical patterns for a given time and location.
- Prolonged travel time increases: Persistent delays exceeding normal variations, suggesting a persistent problem like construction or a recurring incident.
- Unusually high numbers of stopped vehicles: Detected through data from traffic cameras or GPS-enabled vehicles, this can signal a significant incident requiring immediate attention.
- Unusual traffic patterns on specific days or times: These may indicate special events, roadworks scheduled outside normal times, or recurring incidents in a particular location.
Implementing an Anomaly Detection System
Implementing a machine learning-based anomaly detection system involves a structured approach:
- Data Collection and Preprocessing: Gather data from various sources (e.g., traffic cameras, GPS devices, loop detectors) and clean, transform, and prepare the data for model training. This includes handling missing values and outliers and potentially normalizing the data.
- Model Selection and Training: Choose an appropriate machine learning algorithm (e.g., One-Class SVM, Isolation Forest, or clustering algorithms) based on the type of data and anomaly characteristics. Train the model using historical traffic data to learn typical traffic patterns.
- Anomaly Detection and Alerting: Deploy the trained model to continuously monitor real-time traffic data. When the model detects an anomaly, it triggers an alert to the relevant authorities or systems.
- Incident Response and Feedback: Develop a system to respond to alerts efficiently, potentially involving rerouting traffic, deploying emergency services, or updating drivers. Feedback from incident response can be used to improve the accuracy and effectiveness of the anomaly detection system over time.
- Model Evaluation and Refinement: Regularly evaluate the performance of the anomaly detection model and refine it as needed based on new data and feedback. This iterative process ensures the system remains accurate and effective over time.
Parking Management and Optimization
Parking woes are a common urban headache, contributing significantly to traffic congestion and wasted time. Smart cities are increasingly turning to machine learning (ML) to alleviate these problems, optimizing parking availability and improving the overall parking experience. ML algorithms can analyze vast amounts of data to predict demand, manage resources, and guide drivers to available spaces, ultimately making urban environments more efficient and less frustrating.
Machine learning offers several powerful tools for tackling parking challenges. By leveraging data from various sources – sensor networks, GPS data, and even social media – ML models can accurately predict parking demand and occupancy levels, enabling proactive management strategies. This predictive capability is crucial for optimizing pricing strategies, dynamically allocating parking spaces, and improving overall traffic flow around parking areas.
Parking Demand Prediction and Occupancy Estimation
Different machine learning approaches are employed to predict parking demand and occupancy. Regression models, such as linear regression and support vector regression, are frequently used to establish relationships between parking demand and various factors like time of day, day of the week, events happening nearby, and weather conditions. More complex models, including neural networks, can capture non-linear relationships and handle high-dimensional data effectively, providing more accurate predictions. For example, a neural network model trained on historical parking data from a city center could accurately predict high occupancy during lunchtime and evening rush hours, allowing parking management to adjust pricing or direct drivers to less congested areas. Another approach uses time series analysis to forecast parking occupancy based on past trends and seasonality. The choice of model depends on the specific context, data availability, and desired accuracy.
Improving Parking Guidance Systems
Machine learning significantly enhances parking guidance systems by providing real-time information on available parking spaces. This information is relayed to drivers through mobile apps, in-car navigation systems, and dynamic signage. By reducing the time drivers spend circling for parking, ML contributes to reduced congestion and fuel consumption. For instance, a city implementing a smart parking system might use a combination of sensor data and ML-based prediction to provide drivers with accurate estimates of available spaces in different parking lots, enabling them to choose the most convenient and efficient option. This leads to smoother traffic flow and reduced environmental impact.
Image Recognition for Parking Space Detection
Image recognition technology, powered by deep learning, plays a vital role in detecting available parking spaces. Cameras strategically positioned in parking areas capture images, which are then processed by ML algorithms to identify occupied and vacant spaces. This automated process eliminates the need for manual monitoring and provides real-time updates to parking guidance systems.
- Image Acquisition: Cameras capture images of parking areas at regular intervals.
- Image Preprocessing: Images are cleaned and enhanced to improve the accuracy of object detection. This might include noise reduction, contrast adjustment, and perspective correction.
- Object Detection: Convolutional Neural Networks (CNNs) are trained to identify parking spaces and classify them as occupied or vacant. This involves training the CNN on a large dataset of labeled images of parking spaces.
- Data Transmission: The results of the object detection are transmitted to a central system, which updates the parking guidance system in real-time.
This technology is already being deployed in various cities worldwide, significantly improving parking efficiency and reducing the frustration associated with searching for parking. For example, a system in a large shopping mall might use this approach to provide real-time information to its mobile app, allowing shoppers to quickly locate available parking spots.
Public Transportation Optimization
Public transportation, the backbone of many cities, is constantly striving for improved efficiency and effectiveness. Machine learning offers a powerful toolkit to achieve this, moving beyond traditional scheduling and route planning to create truly dynamic and responsive systems. By leveraging real-time data and predictive analytics, cities can significantly improve the passenger experience and optimize resource allocation.
Machine learning algorithms are revolutionizing how public transit systems operate, offering solutions to long-standing challenges. These improvements translate to faster commutes, reduced wait times, and ultimately, a more sustainable and efficient transportation network.
Real-time Passenger Demand Analysis
Optimizing bus routes and schedules based on real-time passenger demand is a key area where machine learning shines. By analyzing data from various sources – smart card taps, GPS tracking of buses, and even social media trends – machine learning models can predict passenger volumes at specific times and locations. This allows transit authorities to dynamically adjust service levels, deploying more buses to high-demand areas during peak hours and reducing service in less utilized areas, ensuring optimal resource allocation. For example, a city might see a surge in ridership near a stadium after a major sporting event. A machine learning model, by analyzing historical data and real-time information, can predict this surge and proactively deploy additional buses to prevent overcrowding and long wait times.
Predictive Delay and Disruption Management
Machine learning excels at predicting potential delays and disruptions. By integrating data from various sources, such as weather forecasts, traffic conditions, and historical incident reports, machine learning algorithms can identify patterns and predict potential problems before they occur. This allows transit operators to proactively adjust schedules, reroute buses, or alert passengers to potential delays, minimizing disruption and improving overall service reliability. For instance, a model might predict significant delays due to an impending snowstorm, allowing the transit authority to preemptively adjust schedules and communicate potential delays to passengers.
Enhanced Passenger Information Through Mobile Applications
Integrating machine learning with mobile applications provides passengers with real-time information, enhancing their overall experience. Applications can provide accurate arrival times, real-time bus locations, and alternative route suggestions based on current conditions. This increased transparency and access to information empowers passengers to make informed decisions and improves their satisfaction with the public transportation system. Imagine an app that not only shows you the real-time location of your bus but also predicts its arrival time with remarkable accuracy, factoring in current traffic conditions and potential delays. This kind of predictive power, fueled by machine learning, transforms the passenger experience from frustrating uncertainty to informed convenience.
Ethical Considerations and Future Trends: How Machine Learning Is Helping To Improve Traffic Management Systems
The integration of machine learning into traffic management systems, while promising significant improvements, also raises crucial ethical questions and presents unique challenges. Balancing the benefits of optimized traffic flow with the potential risks to individual privacy and fairness is paramount. The future of this technology hinges on addressing these concerns proactively and developing robust solutions.
Data Privacy Concerns
The effectiveness of machine learning in traffic management relies heavily on the collection and analysis of vast amounts of data, including vehicle location, speed, and travel patterns. This data can potentially reveal sensitive information about individuals, raising concerns about privacy violations. For example, detailed travel patterns could expose an individual’s home address, work location, or regular social activities. Addressing these concerns requires implementing strong data anonymization techniques, robust security measures, and transparent data governance policies that clearly Artikel how data is collected, used, and protected. Regulations like GDPR in Europe offer a framework for this, but continuous adaptation and improvement are crucial.
Algorithmic Bias and Fairness
Machine learning algorithms are trained on data, and if that data reflects existing societal biases, the resulting algorithms may perpetuate and even amplify those biases. For instance, an algorithm trained on data showing a disproportionate number of traffic violations in certain neighborhoods might lead to increased police surveillance in those areas, regardless of the actual crime rate. Mitigating algorithmic bias requires careful data curation, rigorous algorithm testing, and ongoing monitoring for unintended discriminatory outcomes. Regular audits and transparency in algorithmic decision-making processes are vital to ensuring fairness and equity.
Challenges and Limitations of Machine Learning in Traffic Management
Despite its potential, machine learning for traffic management faces several challenges. The accuracy of predictions depends heavily on the quality and quantity of data available. In areas with limited sensor coverage or unreliable data, the effectiveness of machine learning models can be significantly reduced. Furthermore, unforeseen events, such as major accidents or unexpected road closures, can disrupt even the most sophisticated prediction models. Robustness and adaptability to unexpected circumstances are crucial for the reliable deployment of these systems. Finally, the computational resources required to process and analyze large datasets in real-time can be substantial, potentially posing a barrier to implementation, especially in resource-constrained environments.
Emerging Trends: Reinforcement Learning and Federated Learning
Reinforcement learning (RL) is emerging as a powerful tool for optimizing traffic signal control. Unlike traditional methods, RL algorithms learn optimal control strategies through trial and error, adapting to dynamic traffic conditions in real-time. Imagine an RL agent learning to adjust signal timings based on real-time traffic flow data, leading to improved traffic flow and reduced congestion. Federated learning allows multiple traffic management systems to collaboratively train a shared model without directly sharing their individual data. This approach protects data privacy while still enabling the development of more accurate and robust models by leveraging data from diverse sources. This is particularly valuable for large metropolitan areas with multiple jurisdictions.
Visual Representation of Future Impact
Imagine a city’s transportation network depicted as a dynamic, interconnected web. Each node represents an intersection, with the flow of traffic represented by glowing lines, their intensity indicating traffic volume. Advanced machine learning algorithms, visualized as a central “brain” connected to the network, continuously monitor and adjust traffic signals in real-time, responding instantly to changing conditions. The lines representing traffic flow become smoother and more consistent, indicating reduced congestion and improved travel times. Autonomous vehicles, seamlessly integrated into the system, further optimize traffic flow, contributing to a more efficient and environmentally friendly transportation ecosystem. This visualization depicts a future where machine learning optimizes not just individual roadways, but the entire urban transportation network as a cohesive and intelligent system.
Closing Notes
The integration of machine learning into traffic management systems is no longer a futuristic concept; it’s a rapidly evolving reality with the potential to dramatically improve our daily lives. While challenges remain, particularly around data privacy and algorithmic bias, the benefits – from reduced congestion and improved safety to optimized public transport and smarter parking – are undeniable. As machine learning algorithms continue to learn and adapt, we can expect even more sophisticated and effective traffic management solutions in the years to come, paving the way for smoother commutes and a more efficient urban landscape. The future of traffic management is smart, it’s data-driven, and it’s here.
