How IoT is Shaping the Future of Connected Vehicles? It’s not just about fancy gadgets; it’s a total revolution. Imagine a world where your car anticipates your needs, communicates with other vehicles and infrastructure, and even diagnoses its own problems before they become major headaches. That’s the promise of the Internet of Things (IoT) in the automotive industry, and it’s happening faster than you think. This deep dive explores how IoT is transforming the driving experience, impacting the auto industry, and even reshaping our cities.
From enhanced safety features that practically drive themselves to predictive maintenance that keeps your car running smoothly, IoT is changing the game. We’ll unpack the tech behind connected cars, explore the communication protocols that make it all possible, and even delve into the crucial – and sometimes controversial – topics of data security and privacy. Buckle up, because this ride is going to be insightful.
Enhanced Safety and Driver Assistance
The Internet of Things (IoT) is revolutionizing the automotive industry, transforming vehicles from simple transportation devices into intelligent, interconnected ecosystems. This transformation significantly impacts safety and driver assistance, leading to fewer accidents and a smoother, more secure driving experience. The integration of numerous sensors, sophisticated algorithms, and constant data exchange allows for unprecedented levels of safety and convenience.
IoT sensors embedded within vehicles are instrumental in preventing accidents. These sensors constantly monitor various aspects of the vehicle and its surroundings, providing crucial data that can alert drivers to potential hazards or even autonomously intervene to mitigate risks. This proactive approach to safety goes far beyond traditional safety features.
Accident Prevention Through IoT Sensors
IoT sensors act as the eyes and ears of the connected car, providing a 360-degree view of the vehicle’s environment. For instance, blind-spot monitoring systems use radar sensors to detect vehicles in the driver’s blind spots, alerting them with visual or auditory warnings. Similarly, forward-collision warning systems utilize cameras and lidar to detect potential collisions and automatically apply the brakes if necessary. Tire pressure monitoring systems, another example, alert drivers to low tire pressure, preventing potential blowouts and improving handling. Advanced sensors also monitor driver behavior, detecting drowsiness or distraction and providing timely alerts.
Real-Time Traffic Updates and Navigation
Real-time traffic information is no longer a luxury but a necessity in today’s congested roads. IoT plays a crucial role in delivering this information. Connected vehicles constantly share data about their location, speed, and traffic conditions with a central server. This aggregated data is then used to generate real-time traffic maps and provide drivers with optimal routes, avoiding congestion and reducing travel time. Furthermore, these systems can predict potential traffic incidents based on historical data and current conditions, enabling proactive route adjustments.
Advanced Driver-Assistance Systems (ADAS)
ADAS features are becoming increasingly sophisticated thanks to the power of IoT. Examples include adaptive cruise control, which automatically adjusts the vehicle’s speed to maintain a safe following distance from the car ahead; lane-keeping assist, which gently steers the vehicle back into its lane if it starts to drift; and automatic emergency braking, which automatically applies the brakes if a collision is imminent. These systems, powered by a constant stream of data from various sensors, significantly enhance driver safety and reduce the likelihood of accidents.
Comparison of Traditional and IoT-Enhanced Safety Features
| Feature | Traditional Safety Feature | IoT-Enhanced Safety Feature | Description of Enhancement |
|---|---|---|---|
| Braking | Anti-lock Braking System (ABS) | Automatic Emergency Braking (AEB) | AEB adds automatic braking functionality triggered by sensors detecting imminent collisions, going beyond ABS’s basic skid prevention. |
| Collision Warning | None | Forward Collision Warning (FCW) | FCW uses sensors to detect potential collisions and alerts the driver, providing a proactive warning absent in traditional systems. |
| Blind Spot Detection | Driver’s awareness (limited) | Blind Spot Monitoring (BSM) | BSM utilizes radar or cameras to detect vehicles in blind spots, offering a far superior level of detection compared to driver reliance. |
| Navigation | GPS Navigation (static data) | Real-time Navigation with Traffic Updates | Real-time navigation dynamically adjusts routes based on live traffic data, significantly improving efficiency and travel time compared to static GPS. |
Improved Vehicle Connectivity and Communication
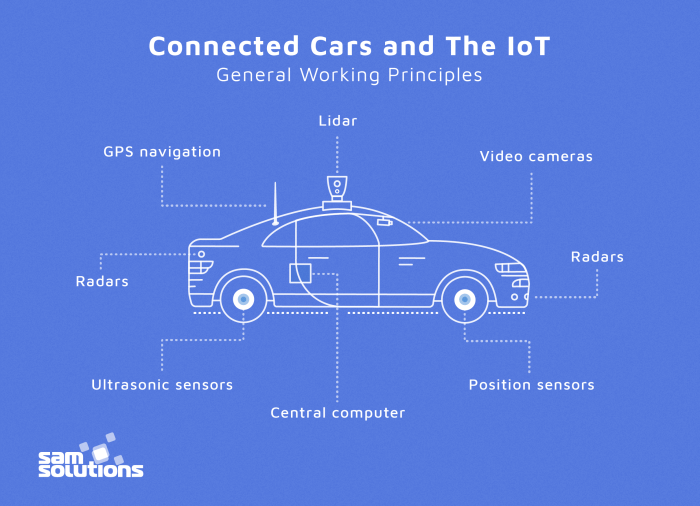
Source: sam-solutions.com
IoT’s impact on connected vehicles is massive, transforming them into rolling data centers. This data fuels advancements in autonomous driving, heavily reliant on AI’s ability to process and react to information in real-time. To truly grasp the potential, check out this insightful piece on The Future of Artificial Intelligence in Everyday Life , which highlights how AI is reshaping our world.
Ultimately, the future of driving is inextricably linked to AI’s continued development and integration within the IoT ecosystem of connected cars.
The rise of the Internet of Things (IoT) has fundamentally reshaped how vehicles communicate, paving the way for a safer, more efficient, and more convenient driving experience. Connected vehicles are no longer isolated entities; they’re active participants in a vast network, exchanging information with each other, infrastructure, and cloud services in real-time. This interconnectedness is driven by advancements in communication protocols and the ever-increasing processing power embedded within vehicles themselves.
This enhanced connectivity isn’t just about convenience; it’s about transforming the very fabric of transportation. Imagine a world where traffic jams are minimized, accidents are predicted and prevented, and logistics are streamlined with unprecedented efficiency. This is the promise of IoT-enabled vehicle communication, and it’s rapidly becoming a reality.
Communication Protocols in Connected Vehicles
Connected vehicles leverage a variety of communication protocols to achieve seamless information exchange. 5G cellular networks provide high-bandwidth, low-latency communication, ideal for streaming data-intensive applications like real-time video feeds and high-resolution map updates. However, 5G’s range can be limited in certain areas, necessitating the use of other technologies like Dedicated Short-Range Communications (DSRC) for vehicle-to-everything (V2X) communication. DSRC operates on a dedicated frequency band, ensuring reliable short-range communication between vehicles, infrastructure, and pedestrians. Other protocols, such as Wi-Fi and Bluetooth, also play a role, particularly for in-car connectivity and infotainment systems. The interplay of these different protocols ensures robust and adaptable communication capabilities across diverse scenarios.
IoT Enabling Seamless Communication
IoT acts as the connective tissue, allowing vehicles to seamlessly communicate with each other (V2V), infrastructure (V2I), and the cloud (V2C). For instance, a vehicle equipped with V2X technology can receive real-time alerts about accidents or traffic congestion ahead, allowing drivers to adjust their routes accordingly. Simultaneously, data collected from the vehicle, such as speed, location, and engine diagnostics, can be transmitted to the cloud for analysis and predictive maintenance. This continuous flow of information optimizes traffic management, improves fleet efficiency, and enhances overall road safety. Imagine a scenario where a vehicle detects a pothole and automatically reports its location to the relevant authorities, allowing for swift repairs and preventing further damage to other vehicles. This is the power of IoT in action.
Connected Vehicles and Fleet Management
The impact of IoT on fleet management and logistics is transformative. Real-time tracking of vehicles allows for optimized route planning, reducing fuel consumption and delivery times. Predictive maintenance, based on data analysis from connected vehicles, minimizes downtime and reduces maintenance costs. Furthermore, improved communication facilitates efficient dispatching and resource allocation, leading to significant cost savings and operational efficiencies. For example, a logistics company can monitor the location and status of its entire fleet in real-time, allowing for dynamic adjustments to delivery schedules based on unexpected events like traffic delays or road closures. This level of visibility and control is simply not possible without the interconnectedness enabled by IoT.
Benefits of Enhanced V2X Communication
The benefits of enhanced vehicle-to-everything (V2X) communication are numerous and far-reaching. Consider the following:
- Reduced traffic congestion through optimized traffic flow and route guidance.
- Improved road safety by providing drivers with real-time alerts about potential hazards.
- Enhanced emergency response capabilities through faster notification of accidents and incidents.
- Increased fuel efficiency through optimized driving patterns and reduced idling time.
- Improved infrastructure management by providing data on road conditions and maintenance needs.
Remote Diagnostics and Predictive Maintenance
Source: dreamstime.com
The Internet of Things (IoT) is revolutionizing vehicle maintenance, moving away from reactive fixes to proactive, predictive strategies. By embedding numerous sensors throughout the vehicle, manufacturers can collect real-time data on various components, providing unprecedented insights into vehicle health and performance. This allows for remote diagnostics, identifying potential problems before they lead to breakdowns, and enabling predictive maintenance schedules to maximize vehicle lifespan and minimize downtime.
IoT sensors embedded within connected vehicles constantly monitor a vast array of parameters. These include engine temperature, tire pressure, oil levels, brake pad wear, and even the subtle vibrations that can indicate impending mechanical failures. This continuous stream of data is transmitted wirelessly to a central server for analysis, allowing technicians to remotely diagnose issues and potentially prevent costly repairs. For example, a sensor detecting abnormally high engine temperature could alert the owner and service center to a potential coolant leak before it causes catastrophic engine damage.
Remote Diagnostics Using IoT Sensors
IoT sensors act as the eyes and ears of the vehicle, providing a constant flow of diagnostic information. These sensors detect anomalies in various vehicle systems and relay this information to a central system, enabling remote troubleshooting. This remote access eliminates the need for physical inspections in many cases, speeding up diagnosis and repair times. For instance, a sudden drop in tire pressure detected by a tire pressure monitoring system (TPMS) can trigger an alert, allowing the driver to take immediate action or schedule a service appointment before a flat tire occurs. The data collected also helps identify recurring issues across a fleet of vehicles, enabling manufacturers to improve designs and address systemic problems proactively.
Predictive Maintenance Using IoT Data Analysis
Predictive maintenance leverages the power of data analytics to forecast potential failures before they happen. By analyzing the continuous stream of data from IoT sensors, sophisticated algorithms can identify patterns and predict when a component is likely to fail. This allows for scheduled maintenance to be performed proactively, minimizing downtime and preventing unexpected breakdowns. For example, if an algorithm detects a gradual increase in engine vibration over time, it might predict an impending bearing failure and recommend a preventative maintenance visit. This allows for the replacement of the bearing before it fails completely, avoiding costly repairs and potential roadside breakdowns. This contrasts sharply with reactive maintenance, where repairs are only undertaken after a failure has occurred.
IoT’s Contribution to Reduced Downtime and Improved Vehicle Lifespan
The shift from reactive to predictive maintenance, facilitated by IoT, significantly reduces vehicle downtime. By identifying and addressing potential problems before they escalate into major failures, vehicles spend less time in the repair shop and more time on the road. This is particularly crucial for commercial fleets, where downtime translates directly into lost revenue. Furthermore, proactive maintenance contributes to a longer vehicle lifespan. By addressing minor issues before they become major problems, the overall health and longevity of the vehicle are significantly improved. Regular maintenance based on predictive analytics prevents cascading failures, which often result from neglecting smaller problems.
Comparison of Predictive and Reactive Maintenance Costs and Benefits
| Feature | Predictive Maintenance | Reactive Maintenance |
|---|---|---|
| Cost of Maintenance | Higher initial investment in sensors and analytics software, but lower overall cost due to fewer major repairs. | Lower initial investment, but higher overall cost due to expensive emergency repairs and downtime. |
| Downtime | Significantly reduced downtime due to proactive repairs. | Significant downtime due to unexpected breakdowns and lengthy repair times. |
| Vehicle Lifespan | Extended vehicle lifespan due to proactive maintenance and prevention of cascading failures. | Shorter vehicle lifespan due to accumulated damage from neglected issues. |
| Efficiency | Improved overall efficiency due to minimized downtime and maximized vehicle uptime. | Reduced efficiency due to frequent breakdowns and unexpected repairs. |
Enhanced In-Vehicle Infotainment and Services
The Internet of Things (IoT) is revolutionizing the in-vehicle experience, transforming the car from a simple mode of transportation into a personalized entertainment and communication hub. This shift is driven by the seamless integration of various apps and services, creating a connected ecosystem that caters to individual driver preferences and needs. The possibilities are vast, extending far beyond the traditional radio and CD player.
Imagine a world where your car anticipates your needs. Before you even start the engine, your preferred playlist is queued, the navigation system is ready with your daily commute route, and your smart home system is accessible through the central dashboard. This is the promise of IoT-enabled in-vehicle infotainment. The integration of diverse apps, personalized settings, and seamless connectivity creates a truly customized and enjoyable driving experience.
Personalized In-Vehicle Experiences Enabled by IoT
IoT allows for the creation of highly personalized in-vehicle experiences. For example, a driver’s preferred climate settings, seat position, and even the ambient lighting can be automatically adjusted based on their profile. Furthermore, the system can learn driving habits and preferences over time, proactively suggesting routes, adjusting the audio system based on road noise levels, and even providing personalized news and information tailored to the driver’s interests. Consider a scenario where the car automatically adjusts the temperature based on the weather forecast and the driver’s past preferences, or suggests a different route based on real-time traffic conditions learned from the car’s connected sensors and external data sources. This level of personalization elevates the driving experience significantly.
Integration of Entertainment and Communication Apps
IoT facilitates the seamless integration of various entertainment and communication apps within the vehicle ecosystem. Popular streaming services like Spotify and Netflix can be accessed directly through the car’s infotainment system, providing passengers with a wide range of entertainment options. Furthermore, hands-free calling and messaging capabilities, integrated with platforms like WhatsApp or Messenger, ensure safe and convenient communication while driving. This integration eliminates the need for drivers to fumble with their phones, improving safety and enhancing the overall driving experience. The car’s operating system acts as a central hub, managing access to these various apps and services while prioritizing safety features.
Security Implications of Connected Infotainment Systems
The increased connectivity offered by IoT-enabled infotainment systems also presents significant security challenges. Connected cars are vulnerable to hacking, with potential consequences ranging from data theft to complete control of the vehicle. Malicious actors could gain access to personal information stored within the system, such as location data and contact details, or even remotely disable critical vehicle functions. This necessitates robust security measures, including strong encryption, regular software updates, and multi-factor authentication, to protect against these threats. Implementing secure coding practices during development is also crucial to prevent vulnerabilities from emerging in the first place.
Data Flow within a Connected Vehicle’s Infotainment System
A simplified representation of the data flow might look like this: The driver interacts with the infotainment system through the touchscreen or voice commands. This input triggers requests for data (e.g., music, navigation directions) which are sent to the cloud via a cellular or Wi-Fi connection. The cloud processes these requests, accessing data from various sources like streaming services or map providers. The processed data is then transmitted back to the vehicle’s infotainment system and displayed to the driver. This process involves various security protocols to ensure data integrity and confidentiality. Real-time data, such as traffic updates, is also fed into the system from external sensors and sources, constantly updating the driver’s experience. Finally, the system might send data back to the cloud, such as usage patterns and preferences, for analysis and personalization. This entire process is designed to be seamless and secure, ensuring a smooth and safe driving experience.
Impact on the Automotive Industry and Infrastructure
The Internet of Things (IoT) isn’t just revolutionizing cars; it’s reshaping the entire automotive landscape and the infrastructure that supports it. From manufacturing processes to city planning, the impact is profound and far-reaching, demanding adaptation and innovation across the board. This shift necessitates a reimagining of traditional business models and a collaborative approach to building smarter, more efficient urban environments.
The integration of IoT is fundamentally altering the business models of automotive manufacturers. Traditionally, the automotive industry operated on a linear model: design, manufacture, sell, and service. Now, with connected vehicles, manufacturers are moving towards a more service-oriented model, generating revenue streams beyond initial vehicle sales. Data collected from connected vehicles provides invaluable insights into driver behavior, vehicle performance, and potential maintenance needs. This data-driven approach allows manufacturers to offer personalized services, predictive maintenance programs, and even subscription-based features, creating recurring revenue streams and fostering stronger customer relationships. For example, Tesla’s over-the-air software updates and subscription-based features like premium connectivity exemplify this shift.
Transformation of Automotive Business Models
IoT allows car manufacturers to transition from a product-centric to a service-centric business model. Instead of solely focusing on vehicle sales, manufacturers can leverage data from connected cars to offer a range of value-added services. This includes personalized insurance packages based on driving behavior, predictive maintenance alerts that minimize downtime, and remote diagnostics that streamline servicing. This shift towards recurring revenue streams enhances profitability and strengthens customer loyalty. The ability to constantly improve vehicles through software updates also extends the lifespan of vehicles and reduces the need for complete replacements, creating a more sustainable ecosystem.
IoT’s Role in Smart City Infrastructure
Smart city initiatives heavily rely on IoT to optimize urban transportation and enhance safety. Connected vehicles play a crucial role in this by providing real-time data on traffic flow, road conditions, and potential hazards. This data can be used to optimize traffic signal timing, improve public transportation scheduling, and even alert emergency services to accidents more quickly. For instance, sensors embedded in roads and vehicles can detect potholes or icy patches, allowing for proactive maintenance and improved road safety. The integration of connected vehicles with smart city infrastructure creates a synergistic effect, improving the overall efficiency and livability of urban areas.
Challenges and Opportunities of Widespread Connected Vehicle Adoption
The widespread adoption of connected vehicles presents both significant opportunities and challenges. Opportunities include enhanced safety, improved traffic flow, and the development of new services. However, challenges include data security and privacy concerns, the need for robust infrastructure, and the potential for increased costs. Ensuring the security of vehicle data is paramount, as breaches could have serious consequences. The development of standardized communication protocols and data sharing mechanisms is crucial to facilitate seamless interoperability between different vehicle manufacturers and infrastructure providers. Addressing these challenges proactively is essential for the successful integration of connected vehicles into our urban environments.
A Future City with Integrated Connected Vehicle Infrastructure
Imagine a city where traffic jams are a thing of the past. Self-driving vehicles seamlessly navigate streets, communicating with each other and the city’s infrastructure to optimize traffic flow. Smart traffic signals adjust in real-time based on traffic conditions, minimizing delays. Sensors embedded in roads detect potholes and other hazards, automatically alerting maintenance crews. Emergency vehicles receive priority access, ensuring rapid response times. Parking is effortless, with intelligent systems guiding drivers to available spaces and even autonomously parking vehicles. The air is cleaner due to the increased efficiency of electric vehicles and optimized traffic management. Citizens enjoy a safer, more efficient, and more sustainable urban environment, all thanks to the seamless integration of connected vehicles and smart city infrastructure.
Data Security and Privacy in Connected Vehicles: How IoT Is Shaping The Future Of Connected Vehicles
The increasing connectivity of vehicles presents a double-edged sword. While offering incredible benefits like enhanced safety and convenience, it also introduces significant vulnerabilities to data breaches and privacy violations. The sheer volume of data collected—from driving habits to personal information—makes connected cars a prime target for cybercriminals and malicious actors. Understanding the potential risks and implementing robust security measures is paramount to maintaining trust and ensuring the safe adoption of this transformative technology.
Potential Vulnerabilities and Threats in Connected Vehicle Systems
Connected vehicles rely on a complex network of interconnected systems, each potentially a weak point. These vulnerabilities range from software flaws in the vehicle’s operating system to insecure communication protocols between the vehicle and external servers. Hackers could exploit these weaknesses to gain unauthorized access, potentially leading to serious consequences. For instance, a compromised system could allow remote control of vehicle functions, such as braking or steering, resulting in accidents. Data breaches could expose sensitive personal information like location history, driving patterns, and even biometric data collected by in-car sensors. Furthermore, denial-of-service attacks could render critical vehicle systems inoperable, creating safety hazards. The sophisticated nature of modern vehicles, with their many interconnected electronic control units (ECUs), makes comprehensive security a challenging but essential undertaking.
Best Practices for Securing Data Transmitted by IoT Devices in Vehicles, How IoT is Shaping the Future of Connected Vehicles
Securing data transmitted by IoT devices in vehicles requires a multi-layered approach. This includes employing strong encryption protocols to protect data in transit and at rest. Regular software updates are crucial to patching security vulnerabilities discovered after the vehicle’s initial release. Authentication mechanisms, such as strong passwords and multi-factor authentication, should be implemented to prevent unauthorized access. Secure coding practices are also vital to prevent vulnerabilities from being introduced into the vehicle’s software during its development. Furthermore, employing intrusion detection and prevention systems can help identify and mitigate potential attacks in real-time. Data minimization, only collecting the data strictly necessary for intended functionality, reduces the attack surface. Finally, rigorous testing and validation of security measures throughout the entire vehicle lifecycle are essential to ensure robust protection.
Regulatory Landscape Surrounding Data Privacy in Connected Vehicles
The regulatory landscape surrounding data privacy in connected vehicles is constantly evolving, with varying regulations across different jurisdictions. The General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR) in Europe, for example, sets a high bar for data protection, requiring explicit consent for data collection and providing individuals with control over their data. Similar regulations are emerging globally, focusing on transparency, accountability, and data subject rights. Automakers need to navigate these complex and often conflicting regulations to ensure compliance. Failure to comply can result in significant fines and reputational damage. International harmonization of these regulations is a significant ongoing challenge, but necessary to ensure consistent data protection standards across borders.
Measures Automakers Can Take to Protect User Data in Connected Vehicles
Automakers have a critical responsibility to protect the data of their customers. Implementing a robust security architecture, encompassing hardware, software, and network security, is paramount. This includes secure over-the-air (OTA) updates to address vulnerabilities quickly. Data anonymization and aggregation techniques can reduce the risk of identifying individual users from collected data. Transparency with users regarding data collection practices and providing clear and accessible privacy policies is essential to build trust. Regular security audits and penetration testing should be conducted to identify and address potential weaknesses. Investing in cybersecurity expertise and establishing a dedicated security team are also crucial steps. Finally, fostering collaboration with cybersecurity experts and other stakeholders is vital for continuous improvement in vehicle security and privacy.
Final Review

Source: edu.in
The integration of IoT into vehicles isn’t just a technological advancement; it’s a paradigm shift. It’s about creating a safer, more efficient, and more personalized driving experience. While challenges around data security and privacy remain, the potential benefits of connected vehicles are undeniable. As technology continues to evolve, we can expect even more innovative applications of IoT to emerge, paving the way for a future where driving is smarter, safer, and more connected than ever before. The road ahead is exciting, and the journey is just beginning.
