How Cloud Computing is Redefining Data Storage Solutions? It’s the question on everyone’s lips, especially in today’s data-saturated world. We’re ditching the dusty server rooms and embracing a future where data lives in the ethereal cloud. This isn’t just about convenience; it’s a complete overhaul of how we store, access, and manage our precious information. From cost-effectiveness to unprecedented scalability, the cloud is changing the game, and we’re diving deep into how.
This shift isn’t just a tech trend; it’s a fundamental change in how businesses operate. Imagine a world where remote teams seamlessly collaborate on massive datasets, where scaling up or down is as easy as flipping a switch, and where security measures are constantly evolving to protect against the ever-present threat of cyberattacks. That’s the promise of cloud-based data storage, and we’ll unpack every aspect, exploring its benefits, challenges, and the incredible potential it holds for the future.
The Evolution of Data Storage: How Cloud Computing Is Redefining Data Storage Solutions
The way we store data has undergone a dramatic transformation, moving from clunky on-premise systems to the nimble, scalable world of cloud computing. This shift reflects a fundamental change in how businesses and individuals approach data management, driven by factors ranging from cost to sheer capacity needs. Let’s delve into this fascinating evolution.
Limitations of On-Premise Data Storage
Traditional on-premise data storage, where servers and storage devices are housed within an organization’s own facilities, presented several significant challenges. High upfront capital expenditure was required for purchasing hardware, software licenses, and setting up the necessary infrastructure. This often meant a substantial initial investment that could strain budgets, especially for smaller businesses. Beyond the initial cost, ongoing maintenance, including system upgrades, security patches, and employing IT staff to manage the infrastructure, added a significant recurring expense. Scalability was also a major hurdle; expanding storage capacity meant costly hardware additions and complex system reconfigurations, often requiring significant downtime. Finally, ensuring robust security against cyber threats and physical damage required considerable investment in specialized personnel and security systems.
Drivers Behind the Cloud Migration
Several key factors propelled the shift towards cloud-based storage solutions. The most compelling is arguably cost-effectiveness. Cloud storage eliminates the need for massive upfront capital investments in hardware. Instead, businesses pay only for the storage they consume, on a pay-as-you-go basis, reducing the financial burden significantly. Scalability is another major driver; cloud storage offers seamless and virtually instantaneous expansion of storage capacity, adapting to fluctuating data needs without the complexities and downtime associated with on-premise solutions. Furthermore, cloud providers invest heavily in robust security measures, often exceeding the capabilities of individual organizations, offering better protection against data breaches and cyberattacks. Finally, the accessibility offered by cloud storage, allowing authorized personnel to access data from anywhere with an internet connection, enhances productivity and collaboration.
Cost-Effectiveness: On-Premise vs. Cloud Storage
The financial implications of choosing between on-premise and cloud storage are substantial. The following table offers a comparative analysis:
| Factor | On-Premise Storage | Cloud Storage |
|---|---|---|
| Initial Investment | High (hardware, software, setup) | Low (minimal upfront costs) |
| Ongoing Maintenance | High (staff, upgrades, repairs) | Low (managed by provider) |
| Scalability | Low (complex, costly upgrades) | High (easy, on-demand expansion) |
| Security | Variable (dependent on internal resources) | Generally High (robust provider security measures) |
For example, a small startup might find the initial investment for on-premise servers prohibitive, while a cloud solution allows them to begin with minimal cost and scale as they grow. Conversely, a large enterprise with highly sensitive data might initially invest heavily in on-premise security, but even they often leverage cloud storage for less critical data due to its cost-effectiveness and scalability.
Key Features of Cloud-Based Data Storage Solutions
The shift to cloud computing has fundamentally altered how we approach data storage. No longer confined to physical servers and on-site infrastructure, data now resides in vast, distributed networks, offering unprecedented flexibility and scalability. Understanding the key features of cloud-based storage is crucial for businesses and individuals alike, as it directly impacts efficiency, security, and cost-effectiveness.
Cloud storage solutions are not a monolithic entity; rather, they encompass a range of service models, each tailored to specific needs and risk tolerances. These models offer diverse approaches to data management, security, and cost optimization, allowing users to choose the option best suited to their unique requirements.
Types of Cloud Storage Services, How Cloud Computing is Redefining Data Storage Solutions
Cloud storage services are broadly categorized into three main types: public, private, and hybrid clouds. Public cloud storage, like that offered by Amazon S3, Google Cloud Storage, or Microsoft Azure Blob Storage, utilizes shared infrastructure, providing cost-effectiveness and scalability. Private cloud storage, conversely, involves dedicated infrastructure managed either internally or by a third-party provider, offering enhanced control and security. Hybrid cloud storage combines elements of both, leveraging the benefits of each model—for example, using a private cloud for sensitive data and a public cloud for less critical information. This blended approach provides flexibility and optimized resource allocation.
Benefits of Cloud Storage
The advantages of cloud storage extend beyond simple data warehousing. Scalability allows businesses to effortlessly adjust storage capacity based on demand, eliminating the need for costly upfront investments and the potential for wasted resources. Accessibility ensures data is available from anywhere with an internet connection, fostering seamless collaboration and remote work capabilities. Data redundancy, through techniques like replication and mirroring, safeguards against data loss due to hardware failure or natural disasters. For instance, if one server fails in a cloud storage system, the data is automatically retrieved from a backup server, ensuring business continuity. This resilience is a key differentiator from traditional on-site storage solutions.
Security Measures in Cloud Storage Platforms
Security is paramount in cloud storage, and reputable providers implement robust measures to protect data. These include encryption (both in transit and at rest), access control lists (ACLs) that limit access based on user roles and permissions, and multi-factor authentication (MFA) to prevent unauthorized access. Regular security audits and penetration testing help identify and address vulnerabilities. Providers often employ advanced technologies such as intrusion detection and prevention systems (IDPS) and regularly update their security protocols to counter emerging threats. For example, Amazon S3 utilizes server-side encryption (SSE) with various key management options, while Google Cloud Storage offers customer-managed encryption keys (CMEK) for enhanced control. Best practices include regularly reviewing and updating security settings, using strong passwords, and employing a robust security awareness training program for users. Following these best practices significantly mitigates risks and ensures the confidentiality, integrity, and availability of stored data.
Impact on Data Management and Accessibility
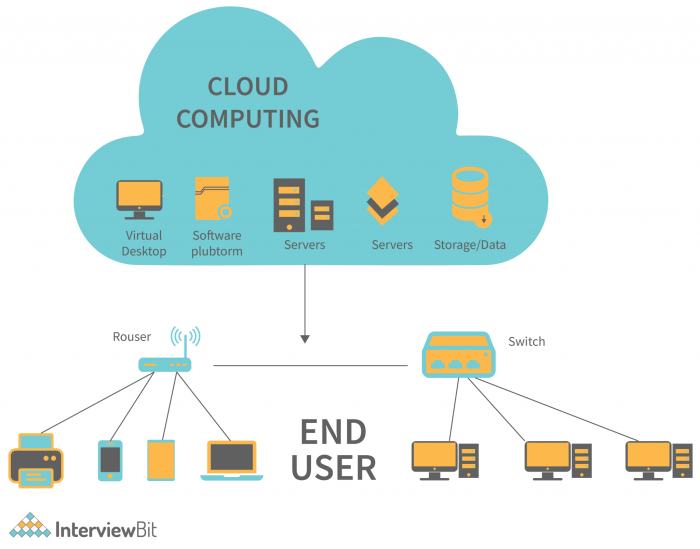
Source: interviewbit.com
Cloud computing’s scalability is revolutionizing data storage, handling the massive datasets needed for advanced analytics. This is especially crucial in fields like healthcare, where AI is transforming diagnostics and treatment; check out this insightful article on Artificial Intelligence and Its Applications in Healthcare to see how. Ultimately, the cloud’s flexible infrastructure is powering the AI revolution, making groundbreaking data analysis possible and paving the way for future innovations in data storage.
Cloud computing has revolutionized data management, shifting from complex, on-premise systems to streamlined, accessible solutions. This transition simplifies various aspects of data handling, offering increased efficiency and scalability for businesses of all sizes. The ease of use and powerful features make it a game-changer for organizations struggling with traditional data storage limitations.
Cloud storage dramatically improves data accessibility, especially for geographically dispersed teams. Imagine a global marketing team needing to access and collaborate on high-resolution campaign assets. With cloud storage, everyone, regardless of location, can access the latest versions simultaneously, fostering real-time collaboration and eliminating the delays associated with file transfers and version control issues. This accessibility extends to individual users as well, providing seamless access to their data from any device with an internet connection.
Simplified Data Management Tasks
Cloud platforms offer intuitive interfaces and automated tools that simplify complex data management tasks. Features like automated backups, data encryption, and version control significantly reduce the administrative burden associated with traditional data storage. For instance, scheduling backups becomes a simple click of a button, eliminating the need for manual intervention and minimizing the risk of data loss. Similarly, automated data encryption ensures the security of sensitive information, relieving IT teams from the complexities of implementing and managing encryption protocols. The streamlined nature of these processes frees up IT personnel to focus on more strategic initiatives.
Improved Data Accessibility for Remote Teams and Users
Cloud storage facilitates seamless data sharing and collaboration among remote teams. Centralized repositories allow multiple users to access and modify data simultaneously, fostering real-time collaboration and accelerating project timelines. This is particularly beneficial for businesses with remote employees or distributed teams, enabling efficient communication and information exchange regardless of geographical location. Furthermore, accessibility extends beyond teams; individual users can access their data from any device with an internet connection, enhancing productivity and flexibility.
Business Scenario: Enhanced Collaboration and Efficiency
Imagine a small architectural firm, “DesignSpark,” using cloud storage to manage project files, blueprints, and client communications. Previously, they relied on local servers and email attachments, leading to version control issues, slow file sharing, and difficulties in team collaboration. By transitioning to a cloud-based solution, DesignSpark centralizes all project-related data in a secure, accessible location. Architects can access and update files in real-time, fostering seamless collaboration. Client communications are also centralized, streamlining the approval process and reducing delays. The automated backup feature ensures data security and reduces the risk of data loss due to hardware failure or accidental deletion. This improved workflow leads to increased efficiency, reduced project timelines, and enhanced client satisfaction. The firm’s IT needs also significantly decrease, as they no longer require dedicated personnel to manage on-premise servers.
Addressing Data Security and Privacy Concerns in the Cloud
The shift to cloud computing, while offering unparalleled scalability and accessibility, introduces legitimate concerns about data security and privacy. The very nature of entrusting sensitive information to a third-party provider necessitates a thorough understanding of the potential risks and the robust mitigation strategies available. Failing to address these concerns can lead to significant financial losses, reputational damage, and legal repercussions.
The potential for data breaches, unauthorized access, and loss of control over sensitive data are significant risks associated with cloud storage. Malicious actors constantly seek vulnerabilities, while accidental data exposure through human error remains a persistent threat. Moreover, compliance with evolving data privacy regulations, such as GDPR and CCPA, demands a proactive and comprehensive approach to data security.
Data Breach Prevention Strategies
Effective data security in the cloud relies on a multi-layered approach. Encryption, both in transit and at rest, is paramount. This ensures that even if data is intercepted, it remains unreadable without the decryption key. Robust access control mechanisms, including role-based access control (RBAC), limit access to sensitive data based on individual roles and responsibilities. Regular security audits, both internal and external, are crucial for identifying and addressing vulnerabilities before they can be exploited. These audits should encompass penetration testing and vulnerability assessments to simulate real-world attacks and pinpoint weaknesses in the system.
Best Practices for Cloud Data Security and Compliance
Implementing a comprehensive security strategy requires a proactive and multifaceted approach. Here are some best practices to ensure data security and compliance:
- Employ strong encryption: Utilize both data-in-transit (using HTTPS/TLS) and data-at-rest encryption to protect data at all stages.
- Implement multi-factor authentication (MFA): MFA adds an extra layer of security by requiring multiple forms of authentication, making it significantly harder for unauthorized users to gain access.
- Utilize robust access control: Implement granular access control measures, such as role-based access control (RBAC), to limit user access to only the data they need.
- Regularly conduct security audits and penetration testing: Proactive vulnerability assessments and penetration testing help identify and address weaknesses before they can be exploited.
- Maintain comprehensive data loss prevention (DLP) measures: Implement DLP tools to monitor and prevent sensitive data from leaving the cloud environment without authorization.
- Establish a robust incident response plan: Having a well-defined plan in place to handle data breaches and other security incidents is crucial for minimizing damage and ensuring compliance.
- Stay updated on relevant regulations: Keep abreast of evolving data privacy regulations, such as GDPR and CCPA, and ensure your cloud security practices comply with all applicable laws.
- Choose reputable cloud providers: Select cloud providers with strong security track records and robust security certifications, such as ISO 27001.
- Regularly back up your data: Regular data backups provide a safety net in case of data loss or corruption, ensuring business continuity.
For example, a healthcare provider storing patient data in the cloud must comply with HIPAA regulations, requiring stringent security measures and data encryption. A financial institution storing customer financial information needs to meet stringent PCI DSS compliance standards. Failure to adhere to these regulations can result in hefty fines and severe reputational damage. Therefore, proactive security measures are not just good practice, they are a business imperative.
Cloud Storage and Emerging Technologies

Source: futurecdn.net
The synergy between cloud storage and emerging technologies is rapidly reshaping how we handle and interpret data. No longer a simple repository, cloud storage is becoming an integral part of sophisticated data processing pipelines, fueled by advancements in artificial intelligence, machine learning, and big data analytics. This integration unlocks unprecedented potential for businesses and researchers alike, allowing for more efficient data management, insightful analysis, and innovative applications.
Cloud storage provides the scalable and cost-effective infrastructure necessary for the computationally intensive tasks associated with these emerging technologies. The ability to store and access vast datasets quickly and easily is a fundamental requirement for AI and machine learning algorithms, which often require massive amounts of training data. Similarly, big data analytics relies heavily on the capacity and accessibility offered by cloud storage to process and analyze enormous datasets in a timely manner.
AI and Machine Learning Integration with Cloud Storage
The integration of AI and machine learning with cloud storage is revolutionizing various sectors. Cloud platforms offer pre-trained models and tools that simplify the development and deployment of AI applications. For example, image recognition systems can be trained on massive image datasets stored in the cloud, allowing for faster and more accurate identification. Similarly, natural language processing models benefit from the readily available text data stored in cloud environments, enabling more sophisticated chatbots and sentiment analysis tools. This seamless integration allows for rapid iteration and continuous improvement of AI models, as new data can be easily incorporated and analyzed.
Cloud Storage’s Role in Big Data Analytics and Processing
Big data analytics demands robust storage and processing capabilities, a need perfectly met by cloud storage solutions. Cloud platforms provide scalable storage solutions that can accommodate exponentially growing datasets, enabling businesses to store and analyze data from various sources, such as social media, sensor networks, and customer transactions. The parallel processing capabilities of cloud computing allow for faster data analysis and extraction of meaningful insights. For instance, a retail company could leverage cloud storage and analytics to analyze customer purchase patterns, predict future demand, and optimize inventory management. This real-time analysis empowers businesses to make data-driven decisions more effectively.
Future Trends in Cloud-Based Data Storage
The future of cloud-based data storage is marked by several key trends. We can expect to see continued growth in the adoption of serverless computing, which allows developers to focus on application logic without managing underlying infrastructure. This simplifies development and reduces operational overhead. Furthermore, advancements in edge computing will bring data processing closer to the source, reducing latency and improving real-time applications. The increasing use of blockchain technology will enhance data security and transparency, providing verifiable and immutable records. Finally, the development of more sophisticated data governance and compliance tools will address the growing concerns surrounding data privacy and security in the cloud. For example, the rise of decentralized storage solutions, built upon blockchain technology, promises greater user control and data sovereignty, potentially addressing some of the concerns associated with centralized cloud providers.
Case Studies
Real-world applications showcase the transformative power of cloud storage across diverse sectors. These examples highlight how businesses are leveraging cloud solutions to streamline operations, improve efficiency, and gain a competitive edge in today’s data-driven world. The following case studies illustrate the practical benefits and diverse applications of cloud storage across various industries.
Healthcare: Enhanced Patient Care Through Cloud-Based Data Management
The healthcare industry is increasingly reliant on vast amounts of patient data, including medical records, imaging results, and genomic information. Efficient and secure storage is crucial for delivering quality care and complying with regulations. Cloud storage solutions are proving invaluable in addressing these challenges.
- Improved Collaboration and Access: Cloud platforms enable seamless sharing of patient data among healthcare providers, facilitating better coordination of care and reducing the risk of duplicated tests or conflicting treatments. Imagine a scenario where specialists across different hospitals can access a patient’s complete medical history in real-time, ensuring the most informed decisions are made.
- Enhanced Data Security and Compliance: Reputable cloud providers invest heavily in security infrastructure and comply with stringent regulations like HIPAA. This ensures that sensitive patient data remains protected from unauthorized access and breaches, while also simplifying compliance efforts.
- Scalability and Cost-Effectiveness: Cloud storage offers the flexibility to scale storage capacity as needed, accommodating fluctuating data volumes associated with patient growth and new technologies like telehealth. This eliminates the need for expensive on-premise infrastructure upgrades and reduces IT overhead.
Finance: Secure and Scalable Data Storage for Financial Institutions
The financial sector deals with massive datasets, including transactional data, customer information, and market analysis. Maintaining data integrity, security, and regulatory compliance are paramount. Cloud storage provides a robust and secure solution for managing this sensitive information.
- Disaster Recovery and Business Continuity: Cloud-based data replication and backup capabilities ensure business continuity in the event of a disaster, minimizing downtime and data loss. This is particularly critical for financial institutions where uninterrupted operations are essential.
- Enhanced Data Analytics and Insights: Cloud platforms provide the computational power necessary for advanced data analytics, enabling financial institutions to gain valuable insights from their data, improving risk management, fraud detection, and customer service.
- Compliance with Regulatory Requirements: Reputable cloud providers adhere to strict security and compliance standards, such as those mandated by financial regulatory bodies. This simplifies compliance efforts for financial institutions and minimizes the risk of penalties.
Retail: Streamlining Operations and Enhancing Customer Experience
Retailers generate vast quantities of data from point-of-sale systems, customer relationship management (CRM) platforms, and e-commerce websites. Efficient data management is crucial for optimizing inventory, personalizing customer experiences, and gaining a competitive advantage.
- Improved Inventory Management: Cloud-based solutions provide real-time visibility into inventory levels across multiple locations, enabling retailers to optimize stock levels, reduce waste, and improve supply chain efficiency. This can lead to significant cost savings and improved customer satisfaction.
- Personalized Customer Experiences: By leveraging cloud-based data analytics, retailers can gain insights into customer preferences and behavior, enabling them to personalize marketing campaigns, product recommendations, and customer service interactions. This can lead to increased customer loyalty and sales.
- Scalability for Peak Demand: Cloud storage offers the scalability needed to handle peak demand during promotional periods or holiday seasons, ensuring that e-commerce platforms remain responsive and customers can enjoy a seamless shopping experience.
Closing Notes
The cloud isn’t just a storage solution; it’s a catalyst for innovation. By streamlining data management, enhancing accessibility, and bolstering security, cloud computing empowers businesses and individuals alike to unlock the true potential of their data. As technology continues to evolve, the cloud will undoubtedly play an even more significant role, shaping the future of data storage and transforming how we interact with information. So, are you ready to embrace the cloud revolution?
