How Blockchain Technology is Enabling Decentralized Cloud Storage? Forget the big brother cloud – we’re talking about a future where your data lives on a distributed network, controlled by you, not some mega-corp. This shift is powered by blockchain, offering a revolutionary approach to data security, privacy, and accessibility. Imagine a world free from data breaches and single points of failure; that’s the promise of decentralized cloud storage.
This new paradigm uses blockchain’s inherent immutability and transparency to create a secure and resilient storage ecosystem. Smart contracts automate access control, while cryptographic techniques ensure data integrity. This isn’t just theoretical; real-world applications are already emerging, transforming industries and empowering individuals to reclaim ownership of their digital lives. Let’s dive into the details.
Introduction to Decentralized Cloud Storage
Centralized cloud storage, while convenient, presents several vulnerabilities. Think of all your precious photos, documents, and videos residing on servers controlled by a single entity – a potential single point of failure. This reliance on a central authority introduces risks like data breaches, censorship, and vendor lock-in, leaving users vulnerable to the whims of the provider. Decentralized cloud storage offers a compelling alternative, aiming to address these limitations and empower users with greater control over their data.
Decentralized cloud storage operates on the principle of distributing data across a network of independent nodes rather than relying on a single central server. This distributed architecture enhances resilience, security, and availability. Imagine a vast, interconnected web of computers, each holding a piece of the puzzle. No single point of failure exists; even if some nodes go offline, the data remains accessible through other nodes in the network. This inherent redundancy is a significant advantage over traditional centralized systems. Furthermore, this distributed model reduces the risk of censorship, as no single entity controls the entire dataset.
Blockchain technology plays a crucial role in securing and managing this decentralized storage infrastructure. Blockchain, a distributed ledger technology, provides a transparent and immutable record of all data transactions. Each data block is cryptographically linked to the previous one, creating a chain of records that is incredibly difficult to tamper with. In the context of decentralized storage, the blockchain acts as a trusted registry, tracking the ownership and location of data across the network. This ensures data integrity and prevents unauthorized access or modification. For example, Filecoin, a decentralized storage network, utilizes blockchain to incentivize users to store and share data, creating a robust and reliable storage ecosystem. The blockchain tracks storage deals, ensuring that providers are compensated fairly for their services, and users have verifiable proof of data storage.
Blockchain’s Role in Decentralized Cloud Storage

Source: freemanlaw.com
Blockchain’s decentralized nature is revolutionizing cloud storage, offering enhanced security and data ownership. This secure infrastructure is particularly crucial for sensitive data, like the genomic information increasingly vital in biotech. Check out this insightful piece on The Future of Biotechnology and Its Relationship with Technology to see how this intersects. Ultimately, blockchain-powered decentralized storage promises a future where biotech data is both secure and accessible.
Blockchain technology acts as the backbone for decentralized cloud storage, offering a revolutionary approach to data management that prioritizes security, transparency, and user control. Unlike traditional centralized systems controlled by a single entity, blockchain-based storage distributes data across a network of nodes, enhancing resilience and minimizing single points of failure. This distributed ledger technology fundamentally alters how we think about data ownership and accessibility.
Blockchain ensures data immutability in decentralized storage through its inherent design. Once data is recorded on the blockchain, it becomes virtually impossible to alter or delete. Each block in the chain contains a cryptographic hash of the previous block, creating a tamper-evident record. Any attempt to modify data would result in a broken chain, immediately alerting the network to the tampering. This cryptographic linking ensures the integrity and authenticity of the stored information, providing a high level of trust and reliability. Think of it like a digitally signed, chronologically ordered, and globally distributed record book – changing one entry would be instantly obvious.
Data Immutability through Cryptographic Hashing
The core of blockchain’s data immutability lies in cryptographic hashing. Each data block is assigned a unique cryptographic hash – a complex, one-way function that transforms data into a fixed-length string of characters. This hash is then linked to the hash of the previous block, forming the chain. Any alteration to the data, however small, will result in a completely different hash, breaking the chain and revealing the tampering. This mechanism provides a verifiable and auditable trail of all data modifications, ensuring data integrity and preventing unauthorized changes. The computational difficulty of reversing the hash function further strengthens the security.
Smart Contracts for Access Control and Data Management
Smart contracts automate data access control and management within decentralized cloud storage systems. These self-executing contracts define the rules and conditions for data access, sharing, and usage. For example, a smart contract could specify that only authorized users with a specific digital key can access a particular data set. This eliminates the need for centralized intermediaries, empowering users to control their data directly. Imagine a scenario where a medical record is stored on a decentralized platform; a smart contract could govern who (doctor, patient, insurer) can access what specific parts of the record, and under what circumstances. This enhances privacy and security by eliminating the risk of unauthorized access or data breaches associated with centralized systems.
Data Encryption and Security Mechanisms, How Blockchain Technology is Enabling Decentralized Cloud Storage
Blockchain-based decentralized storage incorporates robust encryption techniques to protect data at rest and in transit. Data encryption transforms data into an unreadable format, protecting it from unauthorized access even if a node is compromised. Various encryption algorithms, like AES (Advanced Encryption Standard) and RSA (Rivest-Shamir-Adleman), can be employed. Furthermore, the decentralized nature of the system enhances security. Because data is distributed across multiple nodes, the compromise of a single node doesn’t necessarily lead to data loss or exposure. The redundancy inherent in the distributed architecture offers significant resilience against attacks and failures. For example, if one node is compromised, the data remains accessible through other nodes in the network. This redundancy increases data availability and minimizes the impact of potential security breaches.
Key Technologies and Architectures
Decentralized cloud storage, while conceptually elegant, relies heavily on the interplay of various technologies to achieve its goals of security, scalability, and availability. Understanding these underlying technologies is crucial to grasping the full potential – and limitations – of this emerging paradigm. This section dives into the key players: blockchain consensus mechanisms and distributed file systems like IPFS, exploring their strengths and weaknesses in the context of decentralized storage.
The choice of blockchain consensus mechanism significantly impacts the performance and security of a decentralized storage system. Different mechanisms offer trade-offs between speed, energy efficiency, and security.
Blockchain Consensus Mechanisms in Decentralized Storage
Proof-of-Work (PoW) and Proof-of-Stake (PoS) are two prominent consensus mechanisms. PoW, famously used by Bitcoin, requires miners to solve complex computational puzzles to validate transactions and add blocks to the blockchain. This process is energy-intensive but provides a high level of security due to the computational cost of attacking the network. However, its energy consumption is a major drawback, making it less suitable for environmentally conscious decentralized storage solutions. In contrast, PoS selects validators based on their stake in the network, reducing energy consumption significantly. Validators are chosen probabilistically based on the amount of cryptocurrency they hold, making the process more efficient. However, PoS systems can be vulnerable to attacks from large stakeholders who control a significant portion of the stake. Other mechanisms, such as Delegated Proof-of-Stake (DPoS) and Practical Byzantine Fault Tolerance (PBFT), offer further variations with their own sets of advantages and disadvantages regarding speed, security, and energy efficiency. The optimal choice depends on the specific requirements of the decentralized storage system.
IPFS and Distributed File Systems in Decentralized Storage
IPFS (InterPlanetary File System) is a popular distributed file system often used in conjunction with blockchain technology for decentralized storage. IPFS allows for the decentralized storage and retrieval of data by creating a peer-to-peer network where files are addressed using content hashing, rather than location. This eliminates single points of failure and improves resilience. By integrating IPFS with a blockchain, the system gains verifiable provenance and tamper-proof data integrity. The blockchain acts as a ledger, recording the hashes of files stored on the IPFS network, ensuring that any changes to the files are immediately detectable. However, relying solely on IPFS for data availability can be challenging, as it relies on the participation of peers to maintain data accessibility. A combination with a blockchain provides an extra layer of trust and accountability, but introduces the complexities associated with blockchain technology, such as transaction fees and latency.
Conceptual Architecture of a Blockchain-Enabled Decentralized Cloud Storage System
The following table illustrates a simplified architecture:
| Component | Description | Interaction with other components | Technology |
|---|---|---|---|
| User | Uploads and downloads files | Interacts with the client application to store and retrieve data. | Web browser, mobile app |
| Client Application | Interfaces with the blockchain and IPFS | Receives requests from the user, interacts with the blockchain to record file hashes and with IPFS to store/retrieve file data. | Software application |
| Blockchain Network | Records file hashes and metadata | Provides tamper-proof record of file existence and integrity, verifying data through cryptographic hashing. | Blockchain (e.g., using PoS consensus) |
| IPFS Network | Stores and distributes file data | Receives and distributes file data based on content addressing, providing decentralized storage. | IPFS |
Data Integrity and Security
Decentralized cloud storage, while offering exciting possibilities, faces inherent security challenges. Traditional centralized systems rely on a single point of control for security, making them vulnerable. Blockchain technology, however, offers a compelling solution by leveraging its immutable ledger and cryptographic techniques to enhance data integrity and bolster security against various threats. This section explores how blockchain achieves this.
Blockchain significantly improves data integrity by creating a tamper-evident record of all data modifications. Each transaction, representing a change to a file or data set, is cryptographically linked to the previous one, forming a chain. Any attempt to alter past data would break this chain and be immediately detectable, ensuring data authenticity and preventing unauthorized changes. This is unlike traditional cloud storage where a single compromised server could lead to widespread data corruption.
Cryptographic Hashing and Data Authenticity
Cryptographic hashing plays a crucial role in maintaining data integrity within a blockchain-based decentralized cloud storage system. Each data block is assigned a unique hash value – a fingerprint generated through a one-way cryptographic function. This hash is then included in the subsequent block’s metadata. Even a tiny change to the data will result in a completely different hash value, instantly revealing any tampering. This system ensures that the data remains unaltered and verifiable. For example, imagine a file with a specific hash value; if that value changes, it immediately flags a potential breach or corruption. The system can then be examined to determine the cause.
Security Mechanisms Against Data Breaches and Denial-of-Service Attacks
Blockchain’s decentralized nature provides inherent resilience against data breaches. Since data isn’t stored in a single location, a successful attack on one node won’t compromise the entire system. Data is replicated across numerous nodes, making it far more difficult for malicious actors to access and modify information. Moreover, cryptographic techniques like encryption further protect data at rest and in transit, safeguarding against unauthorized access even if a node is compromised. Consider the scenario of a large corporation using a blockchain-based system. If one storage node is attacked, the data remains accessible from the other nodes, minimizing downtime and data loss.
The inherent redundancy of blockchain also mitigates the impact of denial-of-service (DoS) attacks. Unlike centralized systems that can be overwhelmed by a flood of requests, a distributed network can better absorb and distribute the load, preventing service disruptions. This distributed nature makes it significantly more challenging to disable the entire system with a single attack. For instance, if a malicious actor attempts a DoS attack on a specific node, the other nodes in the network continue to function normally, ensuring continuous service availability.
Real-World Applications and Case Studies
Decentralized cloud storage, powered by blockchain technology, is moving beyond theoretical possibilities and finding practical applications across various sectors. Its inherent security, transparency, and data ownership features are proving invaluable in solving real-world problems, leading to the emergence of innovative platforms and projects. Let’s explore some examples of how this technology is transforming industries.
The potential of decentralized cloud storage is vast, impacting businesses and individuals alike. Its impact spans diverse fields, each benefiting from its unique properties. The following examples showcase the breadth of its applicability.
Examples of Decentralized Cloud Storage Platforms
Several platforms are already leveraging blockchain to offer decentralized cloud storage solutions. These platforms offer varying features and target different user needs, from individuals seeking secure file storage to businesses requiring robust and scalable solutions. Here are a few prominent examples:
- Storj: Storj uses a decentralized network of nodes to store data, offering encryption and redundancy for enhanced security. Users pay only for the storage they use, making it a cost-effective option. Its open-source nature fosters community involvement and transparency.
- Sia: Sia employs a similar decentralized architecture to Storj, focusing on secure and affordable storage. It utilizes smart contracts to ensure payment reliability and data availability. Sia’s focus on competitive pricing makes it attractive to users seeking cost-effective storage solutions.
- IPFS (InterPlanetary File System): While not strictly a blockchain-based solution, IPFS is a decentralized storage system often used in conjunction with blockchain for enhanced security and data management. It offers content addressing and versioning, providing robust data integrity.
Industries Benefiting from Decentralized Cloud Storage
The benefits of decentralized cloud storage extend far beyond individual users. Various industries are adopting this technology to improve efficiency, security, and data management.
- Healthcare: Secure storage and sharing of sensitive patient data, ensuring compliance with regulations like HIPAA.
- Finance: Improved security for financial transactions and records, reducing the risk of data breaches and fraud. This also allows for greater transparency and auditability.
- Supply Chain Management: Enhanced traceability and transparency of goods throughout the supply chain, combating counterfeiting and improving efficiency.
- Government and Public Sector: Secure and transparent storage of public records, ensuring data integrity and accessibility.
- Media and Entertainment: Secure distribution and storage of digital content, protecting against piracy and unauthorized access.
Comparison of Decentralized Cloud Storage Solutions
To better understand the nuances of different decentralized cloud storage solutions, let’s compare three prominent platforms based on key features and benefits.
| Feature | Storj | Sia | IPFS |
|---|---|---|---|
| Data Encryption | End-to-end encryption | End-to-end encryption | Encryption supported, but not mandatory |
| Pricing Model | Pay-as-you-go | Pay-as-you-go | Variable, often community-supported |
| Scalability | Highly scalable | Highly scalable | Highly scalable |
| Data Availability | Redundancy through multiple nodes | Redundancy through multiple nodes | Redundancy depends on implementation |
| Open Source | Yes | Yes | Yes |
Scalability and Performance
Decentralized cloud storage, while offering exciting possibilities for data security and user control, faces significant hurdles when it comes to scalability and performance. The very nature of distributing data across a vast network of nodes introduces complexities that centralized systems don’t have to contend with. Achieving the speed and capacity needed to compete with traditional cloud providers requires innovative solutions and careful architectural design.
The challenge lies in balancing the decentralized ethos with the need for efficient data retrieval and storage. As the amount of data stored increases, so do the complexities of locating, accessing, and managing it across potentially thousands of independent nodes. This can lead to slower speeds, increased latency, and higher costs for users. Addressing these challenges is crucial for the widespread adoption of decentralized cloud storage.
Sharding for Enhanced Scalability
Sharding is a key technique used to improve the scalability of decentralized storage systems. Instead of storing all data on every node, sharding divides the data into smaller, manageable chunks called “shards.” These shards are then distributed across multiple nodes, reducing the load on any single node and improving overall system performance. Imagine a massive library; instead of having all books in one room, sharding is like distributing them across many smaller rooms, each specializing in a particular subject. This makes finding a specific book (data) much faster. Efficient shard management, including techniques for locating shards and ensuring data consistency across shards, is critical to the success of this approach. Implementing a robust shard management system is a complex undertaking that requires careful consideration of various factors, including network topology, data distribution algorithms, and fault tolerance mechanisms.
Data Retrieval Optimization
Efficient data retrieval is crucial for a positive user experience. In decentralized systems, locating the relevant data shards can be time-consuming. Techniques such as content-addressable storage (CAS), where data is identified by its cryptographic hash, can significantly improve retrieval speeds. CAS allows for quick verification of data integrity and efficient searching based on the hash value. Furthermore, caching mechanisms, where frequently accessed data is stored closer to users, can reduce latency and improve overall performance. For instance, a popular file might be cached on multiple geographically dispersed nodes, ensuring faster access times for users around the world. This is akin to having copies of popular books in multiple branches of the library.
Network Optimization and Bandwidth Management
The performance of decentralized cloud storage heavily relies on the underlying network infrastructure. Network congestion and bandwidth limitations can severely impact data transfer speeds and overall system performance. Careful network planning and efficient bandwidth management are essential for optimizing performance. This might involve employing techniques like content delivery networks (CDNs) to distribute data across geographically dispersed servers, reducing latency for users in different locations. Furthermore, implementing efficient routing protocols and load balancing strategies can ensure that data traffic is distributed evenly across the network, preventing bottlenecks and maximizing throughput. The use of peer-to-peer (P2P) technologies, where nodes share bandwidth and resources, can also contribute to improved network efficiency.
Future Trends and Challenges: How Blockchain Technology Is Enabling Decentralized Cloud Storage
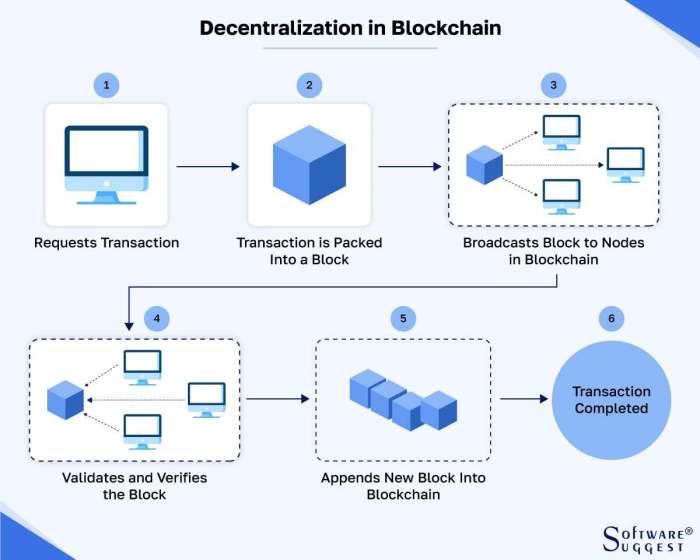
Source: softwaresuggest.com
The decentralized cloud storage landscape, while brimming with potential, faces significant hurdles in its journey towards mainstream adoption. Future developments will hinge on addressing these challenges while capitalizing on emerging technological advancements. The path forward involves a delicate balance between innovation and practicality, security and accessibility.
The next few years will witness a fascinating interplay between technological advancements and the practical realities of implementing and scaling decentralized storage solutions. We can expect refinements in existing blockchain architectures, the emergence of novel consensus mechanisms, and a greater focus on user experience to broaden appeal. However, several key obstacles remain, demanding creative solutions.
Technological Advancements and Refinements
The evolution of blockchain technology itself will be crucial. We’ll likely see the widespread adoption of more efficient and scalable consensus mechanisms beyond Proof-of-Work (PoW) and Proof-of-Stake (PoS), potentially incorporating innovations like Proof-of-Authority or Directed Acyclic Graphs (DAGs) to reduce energy consumption and increase transaction throughput. Furthermore, improvements in interoperability between different blockchain networks will be vital for creating a truly seamless decentralized storage ecosystem. This could involve the development of standardized protocols and cross-chain communication solutions. For example, imagine a future where data seamlessly moves between Filecoin and Arweave networks, optimizing storage costs and resilience.
Addressing Scalability and Performance Limitations
Current decentralized storage solutions often struggle with scalability and performance compared to centralized counterparts. Addressing this involves optimizing data sharding techniques, improving network bandwidth, and developing more efficient data retrieval mechanisms. This requires collaborative efforts from developers, researchers, and infrastructure providers. For instance, the development of more sophisticated sharding algorithms could allow for the efficient distribution of data across a vast network of nodes, significantly improving performance and resilience.
Enhanced Security and Data Integrity Mechanisms
While blockchain enhances data integrity, the underlying storage layer remains vulnerable. The integration of advanced cryptographic techniques, such as homomorphic encryption, could allow for computations on encrypted data without compromising its confidentiality. Furthermore, exploring the potential of zero-knowledge proofs could allow for verification of data integrity without revealing the data itself. Imagine a system where users can prove they possess a specific file without revealing its content, enhancing privacy and security.
Quantum Computing’s Potential Impact
The emergence of quantum computing presents both opportunities and threats. While quantum computers could potentially break current cryptographic algorithms used to secure data, this also necessitates a shift towards quantum-resistant cryptography. Proactive research and development in post-quantum cryptography are crucial to ensuring the long-term security of decentralized storage systems. The transition will require a significant investment in research and infrastructure upgrades, but the potential disruption warrants the effort. For example, migrating to lattice-based cryptography, which is considered resistant to quantum attacks, is a key step in preparing for this technological shift.
Challenges in User Adoption and Decentralization
Despite technological advancements, widespread adoption faces several obstacles. One major challenge is the complexity of interacting with decentralized systems. User-friendly interfaces and intuitive tools are needed to make decentralized storage accessible to a broader audience. Additionally, fostering trust and ensuring data availability require robust governance models and incentive mechanisms to prevent malicious actors from compromising the system. Clear regulatory frameworks are also necessary to address legal and compliance issues. For example, clear guidelines regarding data ownership, liability, and jurisdiction in a decentralized environment are needed to encourage broader participation.
Closing Notes
Decentralized cloud storage, fueled by blockchain technology, represents a paradigm shift in how we manage and protect our data. By eliminating single points of failure and empowering users with greater control, it promises a more secure, transparent, and resilient future. While challenges remain in scalability and widespread adoption, the potential benefits – from enhanced data privacy to increased resilience against attacks – are undeniable. The decentralized revolution is here, and it’s changing the game for cloud storage.
