How Blockchain is Transforming Global Financial Services? Forget everything you think you know about slow, expensive, and insecure financial transactions. Blockchain is blowing the lid off the traditional system, promising a future where money moves faster, safer, and more transparently than ever before. We’re talking about a seismic shift, impacting everything from cross-border payments to investment management – and it’s happening now.
This revolutionary technology is streamlining processes, slashing costs, and boosting security in ways previously unimaginable. Imagine a world without intermediaries hogging fees, where your transactions are instantly verifiable and virtually tamper-proof. That’s the promise of blockchain, and this deep dive explores how it’s reshaping the global financial landscape.
Increased Efficiency and Reduced Costs in Global Financial Transactions
The global financial system, traditionally a labyrinth of intermediaries and paperwork, is undergoing a seismic shift thanks to blockchain technology. This revolutionary technology promises to streamline processes, slash costs, and enhance security in international transactions, creating a more efficient and transparent financial ecosystem. The inherent transparency and immutability of blockchain drastically reduce friction in cross-border payments and offer a compelling alternative to legacy systems.
Blockchain streamlines cross-border payments by eliminating intermediaries and automating verification processes. Instead of relying on multiple banks and correspondent accounts, which often lead to delays and high fees, blockchain facilitates direct peer-to-peer transactions. This drastically reduces processing time, often from days to mere seconds or minutes, and significantly lowers transaction costs. The reduction in processing time also benefits businesses by improving cash flow and enabling faster settlement of international trade deals.
Reduced Fraud and Reconciliation Costs
Fraudulent activities and reconciliation issues are major headaches in international finance. The decentralized and cryptographically secured nature of blockchain drastically minimizes these problems. Each transaction is recorded on a distributed ledger, making it virtually impossible to alter or delete information without detection. This enhanced transparency and immutability make it significantly harder to commit fraud, and the automated reconciliation process further reduces the need for manual checks and the associated costs. For example, Ripple’s blockchain-based payment system is already being used by several banks to improve cross-border payment efficiency and reduce reconciliation errors.
Real-World Applications Demonstrating Improved Efficiency
Several real-world applications showcase blockchain’s potential to revolutionize financial services. Ripple, mentioned above, facilitates faster and cheaper international payments for banks and financial institutions. Stellar, another blockchain platform, focuses on micropayments and cross-border remittances, empowering individuals and small businesses in developing countries. Furthermore, companies like IBM are using blockchain to streamline supply chain finance, improving transparency and reducing fraud in international trade. These examples demonstrate the practical application of blockchain in enhancing efficiency and cost reduction within the global financial landscape.
Comparison of Traditional and Blockchain-Based Payment Systems
| Feature | Traditional System | Blockchain System | Difference |
|---|---|---|---|
| Transaction Time | Days to weeks | Seconds to minutes | Significant reduction in processing time |
| Transaction Fees | High, varying by intermediary | Lower, potentially transparent | Significant cost reduction |
| Security | Vulnerable to fraud and errors | Highly secure, tamper-proof | Enhanced security and reduced fraud risk |
| Transparency | Limited, opaque | High, all transactions visible (depending on the blockchain’s design) | Increased transparency and accountability |
Enhanced Security and Transparency in Financial Markets
Blockchain technology is revolutionizing global finance by offering unprecedented levels of security and transparency. Its inherent design features, particularly its cryptographic security and immutable ledger, are addressing long-standing vulnerabilities in traditional financial systems, paving the way for a more trustworthy and efficient global financial ecosystem.
Blockchain’s cryptographic security mechanisms protect financial data from unauthorized access and manipulation. Unlike centralized databases vulnerable to single points of failure, blockchain utilizes cryptography to secure transactions and verify identities. This multi-layered security approach significantly reduces the risk of fraud and data breaches, fostering greater confidence in the integrity of financial transactions.
Cryptographic Security in Blockchain
Blockchain employs robust cryptographic techniques, including hashing and digital signatures, to ensure data integrity and authenticity. Each transaction is cryptographically hashed, creating a unique fingerprint that is linked to the previous transaction in the chain. Any attempt to alter a transaction would change its hash, making the alteration immediately detectable. Digital signatures, based on public-key cryptography, verify the identity of the transacting parties, preventing unauthorized access and ensuring accountability. This combination of hashing and digital signatures creates an incredibly secure and tamper-evident system.
Immutable Ledger and Enhanced Transparency
The immutable nature of the blockchain ledger is a key driver of increased transparency. Once a transaction is recorded on the blockchain, it cannot be altered or deleted, providing a permanent and auditable record of all financial activity. This transparency fosters accountability among all participants, reducing the potential for fraudulent activities and improving the overall trust in the financial system. Every participant has access to the same, verified record of transactions, eliminating information asymmetry and promoting fairness.
Combating Financial Crimes with Blockchain
Blockchain’s inherent transparency and security features are proving invaluable in combating money laundering and other financial crimes. The ability to trace the origin and flow of funds in real-time makes it significantly more difficult for criminals to obscure their activities. For example, some blockchain-based solutions are being used to track high-value transactions, flagging suspicious activity for further investigation by regulatory bodies. Furthermore, the use of smart contracts can automate compliance checks, ensuring that transactions adhere to anti-money laundering (AML) and know-your-customer (KYC) regulations.
Secure Transaction Process using Blockchain Technology
The following flowchart illustrates a simplified version of a secure transaction using blockchain technology:
Step 1: Transaction Initiation – User A initiates a transaction to send funds to User B. This transaction includes details like the amount, recipient’s address, and sender’s digital signature.
Step 2: Broadcasting – The transaction is broadcast to the network of nodes (computers validating the transaction).
Step 3: Verification – Nodes verify the transaction using cryptographic techniques. This includes checking the digital signatures, ensuring the sender has sufficient funds, and confirming the recipient’s address.
Step 4: Block Creation – Once verified, the transaction is added to a new block along with other validated transactions. This block is then cryptographically linked to the previous block in the chain.
Blockchain’s impact on global finance is undeniable, streamlining transactions and boosting transparency. But the tech’s potential extends beyond finance; consider how accurately predicting climate change impacts is crucial for responsible investing, a field greatly aided by advancements in AI, as detailed in this insightful article: The Role of AI in Advancing Predictive Models for Climate Change.
This data, in turn, can inform smarter blockchain-based financial strategies, mitigating climate-related risks and fostering sustainable growth.
Step 5: Block Addition to Blockchain – The new block is added to the blockchain, making the transaction permanently recorded and auditable.
Step 6: Transaction Confirmation – User B receives confirmation that the funds have been successfully transferred.
Decentralization and Disintermediation in Finance
The rise of blockchain technology is fundamentally reshaping the financial landscape, moving away from the traditional, centralized model towards a more decentralized and interconnected system. This shift, often referred to as disintermediation, promises to revolutionize how we conduct financial transactions, manage assets, and interact with financial institutions. Let’s dive into how blockchain facilitates this paradigm shift.
Traditional centralized financial systems, like banks and payment processors, act as intermediaries, controlling the flow of money and information. This centralized control offers a degree of stability and regulation but also introduces bottlenecks, high fees, and single points of failure. In contrast, decentralized blockchain-based systems leverage distributed ledger technology to create a transparent and secure environment where transactions are verified by a network of participants rather than a central authority. This eliminates the need for intermediaries in many cases, leading to faster, cheaper, and more efficient transactions.
Comparison of Centralized and Decentralized Financial Systems
Centralized systems rely on trusted third parties (like banks) to validate and process transactions, creating a hierarchical structure. This structure, while familiar, can be slow, expensive, and susceptible to fraud or single points of failure. A bank failure, for example, can disrupt access to funds for countless customers. Conversely, decentralized systems use distributed consensus mechanisms, such as proof-of-work or proof-of-stake, to verify transactions. This distributes trust across the network, making the system more resilient and less vulnerable to single points of failure. The absence of a central authority also reduces the risk of censorship or manipulation. Imagine a global payment system unaffected by geopolitical events or regulatory restrictions – that’s the potential of blockchain.
Benefits and Challenges of Disintermediation in Financial Services
Disintermediation, the removal of intermediaries, offers several compelling advantages. Lower transaction fees are a major draw, as are increased speed and efficiency. Blockchain’s transparency also improves accountability and reduces the risk of fraud. However, challenges remain. Regulatory uncertainty surrounding decentralized finance (DeFi) is a significant hurdle. The technical complexity of blockchain technology can also be a barrier to widespread adoption, particularly for less tech-savvy users. Furthermore, the lack of robust consumer protection mechanisms in many DeFi platforms poses a risk to users. The scalability of some blockchain networks also presents a challenge, particularly when handling high transaction volumes.
Blockchain’s Facilitation of Peer-to-Peer Transactions
Blockchain technology facilitates peer-to-peer (P2P) transactions by enabling direct transfers of assets between participants without the need for intermediaries. This is achieved through smart contracts, self-executing contracts with the terms of the agreement directly written into code. These contracts automate the execution of transactions, reducing reliance on intermediaries and ensuring transparency and security. For example, instead of relying on a bank to transfer funds internationally, individuals can use blockchain-based platforms to send money directly to each other, significantly reducing transaction times and fees. This increased efficiency and lower cost directly benefits both individuals and businesses.
Advantages and Disadvantages of Decentralized Finance (DeFi)
The potential benefits of DeFi are substantial, but it’s crucial to understand both sides of the coin.
- Advantages: Increased accessibility to financial services, particularly in underserved communities; lower transaction fees; greater transparency and security; faster transaction speeds; increased financial innovation and competition.
- Disadvantages: Regulatory uncertainty and lack of consumer protection; high technical complexity; potential for smart contract vulnerabilities; risks associated with volatile cryptocurrencies; scalability issues on some platforms.
Blockchain’s Impact on Investment and Asset Management
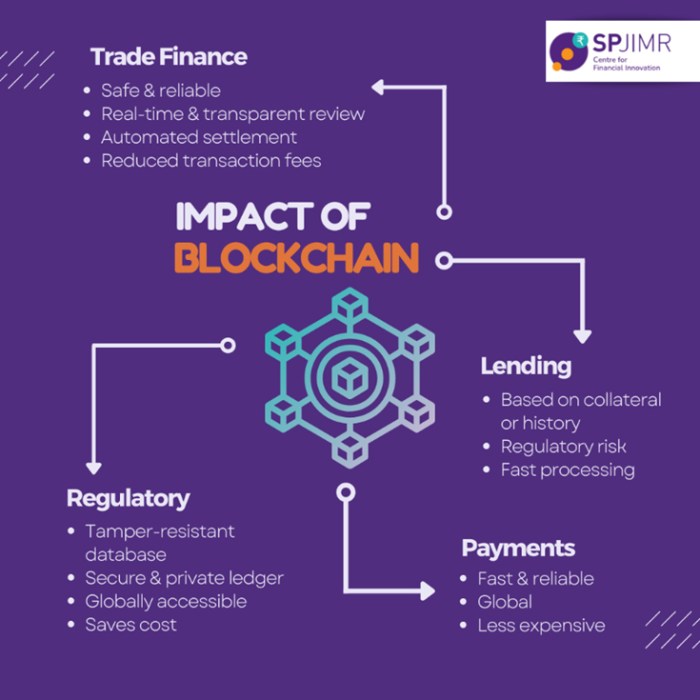
Source: spjimr.org
The financial world is ripe for disruption, and blockchain technology is shaking things up in the investment and asset management sectors. Its potential to streamline processes, enhance security, and unlock new investment opportunities is rapidly transforming how we handle everything from securities issuance to fractional ownership. This isn’t just about hype; real-world applications are already proving the transformative power of this technology.
Blockchain is revolutionizing the way securities are issued and managed, offering significant improvements over traditional methods. The inherent transparency and immutability of blockchain drastically reduce the risk of fraud and errors, while simultaneously speeding up the process.
Securities Issuance and Management on Blockchain
Traditional methods of issuing and managing securities are often slow, expensive, and opaque. They involve multiple intermediaries, leading to delays and increased costs. Blockchain streamlines this by creating a secure, transparent, and efficient digital ledger for recording and managing securities. This allows for faster settlement times, reduced operational costs, and improved tracking of ownership. For instance, companies can issue and manage their own securities directly, bypassing the need for intermediaries like clearing houses and custodians, leading to significant cost savings and increased efficiency. The automation facilitated by smart contracts further accelerates the process, triggering automatic payments and other actions based on pre-defined conditions. This enhanced efficiency is particularly valuable in the issuance of complex securities, where traditional methods often involve significant delays and administrative overhead.
Fractional Ownership and Tokenization of Assets
Blockchain technology facilitates the creation of fractional ownership and tokenization of assets, opening up new investment opportunities for a wider range of participants. Tokenization represents assets as digital tokens on a blockchain, making them easily divisible and tradable. This allows investors to gain exposure to assets they might not otherwise be able to afford, such as real estate or fine art. For example, a valuable piece of artwork can be tokenized, with each token representing a fraction of ownership. This allows multiple investors to collectively own the artwork, making it more accessible and liquid. Similarly, real estate can be tokenized, allowing investors to buy and sell fractional shares of properties with greater ease and efficiency than traditional methods. This democratizes access to previously illiquid asset classes, potentially boosting market liquidity and driving economic growth.
Improved Transparency and Efficiency of Investment Funds
The use of blockchain in investment funds is boosting transparency and efficiency. Investors can track their investments in real-time, gaining a clearer picture of fund performance and asset allocation. This enhanced transparency increases accountability and builds trust between fund managers and investors. Blockchain’s automation capabilities also reduce administrative overhead, streamlining operations and lowering costs. For example, smart contracts can automate the distribution of dividends and other payments, minimizing errors and delays. The immutability of the blockchain ledger also enhances auditability, providing a reliable record of all fund transactions.
- Enhanced Transparency and Auditability: A transparent, immutable record of all fund transactions, simplifying audits and increasing investor confidence.
- Automated Processes: Smart contracts automate tasks such as dividend distribution, reducing administrative costs and errors.
- Improved Security: Blockchain’s cryptographic security features minimize the risk of fraud and unauthorized access.
- Increased Efficiency: Faster settlement times and reduced operational costs through automation.
- Enhanced Liquidity: Tokenization of assets increases liquidity and accessibility for investors.
- Reduced Regulatory Burden: Streamlined compliance processes through automated reporting and record-keeping.
The Role of Blockchain in Regulatory Compliance
Source: medium.com
Blockchain technology, with its inherent transparency and immutability, presents both challenges and opportunities for financial regulators worldwide. While its decentralized nature can complicate oversight, the technology’s potential to enhance data integrity and streamline compliance processes is undeniable. This section explores how blockchain can revolutionize regulatory compliance in financial services.
Blockchain’s impact on regulatory compliance stems from its ability to create a shared, immutable ledger of transactions. This shared record significantly reduces the need for manual reconciliation and verification, leading to increased efficiency and accuracy in reporting. Furthermore, the transparent nature of blockchain allows regulators to monitor transactions in real-time, facilitating early detection of potentially suspicious activities.
Enhanced Regulatory Reporting through Blockchain
The use of blockchain can drastically improve the accuracy and efficiency of regulatory reporting. Currently, financial institutions spend significant resources compiling and submitting reports to various regulatory bodies. This process is often time-consuming, error-prone, and involves multiple intermediaries. A blockchain-based system could automate the reporting process, ensuring data consistency and reducing the risk of human error. For example, imagine a system where all relevant transaction data is automatically recorded on a shared blockchain and then aggregated into standardized reports, automatically submitted to the relevant regulatory authorities. This eliminates manual data entry, reduces the potential for errors, and frees up resources for other crucial tasks. The automated nature of this system also allows for real-time monitoring of compliance, allowing regulators to identify potential issues promptly.
Blockchain’s Influence on KYC and AML Processes, How Blockchain is Transforming Global Financial Services
Know Your Customer (KYC) and Anti-Money Laundering (AML) processes are critical for preventing financial crime. These processes are currently often cumbersome and involve significant manual verification. Blockchain can streamline these processes by providing a secure and transparent platform for identity verification and transaction monitoring. A blockchain-based KYC system could allow customers to securely share their identity information with financial institutions, eliminating the need for repeated verification across different platforms. Similarly, blockchain’s ability to track transactions in real-time can significantly improve AML compliance by flagging suspicious activities immediately. The immutable nature of the blockchain ensures that any attempt to alter transaction data is easily detectable.
A Hypothetical Scenario: Blockchain in Securities Trading
Consider a hypothetical scenario in the securities trading sector. Currently, verifying the legitimacy of securities and tracking their ownership involves a complex and often opaque process. Multiple intermediaries, such as custodians and clearinghouses, are involved, leading to delays and potential for errors. A blockchain-based system could revolutionize this process. Each security could be represented by a unique token on a blockchain, with ownership automatically recorded and updated on the ledger. This eliminates the need for manual record-keeping and reduces the risk of fraud. Regulators could access the blockchain to monitor transactions in real-time, ensuring compliance with securities regulations and quickly identifying any suspicious activities, such as insider trading or market manipulation. This transparency and efficiency would enhance market integrity and investor confidence. For instance, the Securities and Exchange Commission (SEC) could instantly verify the ownership of a specific security, significantly streamlining investigations and enforcement actions. The system’s inherent audit trail would also simplify the process of demonstrating compliance with regulations, reducing the burden on financial institutions.
Future Trends and Challenges in Blockchain Adoption in Finance

Source: esoftskills.com
The integration of blockchain technology into global financial services is rapidly evolving, presenting both exciting opportunities and significant hurdles. While the potential benefits are undeniable, several technological and regulatory challenges need to be addressed for widespread adoption. The future of finance hinges on successfully navigating these complexities.
Technological Hurdles to Wider Adoption
Several key technological obstacles hinder the broader implementation of blockchain in financial services. Scalability remains a major concern; many current blockchain networks struggle to handle the high transaction volumes required by large-scale financial applications. Interoperability, or the ability of different blockchain networks to communicate and exchange data seamlessly, is another critical issue. The lack of standardized protocols and frameworks prevents the creation of a truly interconnected and efficient financial ecosystem. Furthermore, the complexity of blockchain development and implementation requires specialized skills and resources, creating a barrier to entry for smaller financial institutions. Finally, the energy consumption associated with some blockchain networks, particularly those using proof-of-work consensus mechanisms, raises environmental concerns.
Impact of Scalability and Interoperability Issues
Scalability limitations directly impact the efficiency and cost-effectiveness of blockchain-based financial transactions. Slow transaction speeds and high fees can make blockchain solutions impractical for high-volume applications like payment processing or securities trading. The lack of interoperability prevents the seamless integration of blockchain systems with existing financial infrastructure, hindering the development of truly integrated solutions. For example, a bank using one blockchain platform might struggle to interact efficiently with another bank using a different platform, creating friction and limiting the potential benefits of blockchain. Addressing these issues is crucial for unlocking the full potential of blockchain in finance. Solutions such as layer-2 scaling solutions and cross-chain communication protocols are actively being developed to mitigate these challenges.
Predictions for the Future Role of Blockchain in Reshaping Global Financial Services
Blockchain technology is poised to significantly reshape global financial services in the coming years. We anticipate a growing adoption of blockchain for cross-border payments, reducing transaction costs and processing times. Decentralized finance (DeFi) applications will continue to proliferate, offering innovative financial products and services outside traditional financial institutions. The use of blockchain for managing digital assets, such as securities and digital currencies, will become increasingly prevalent. Regulatory clarity and standardization will be key drivers of broader adoption, fostering trust and encouraging wider participation from financial institutions. The integration of blockchain with other emerging technologies, such as artificial intelligence and the Internet of Things, will create new opportunities for innovation and efficiency. For instance, we could see the emergence of blockchain-based supply chain finance solutions that enhance transparency and traceability, reducing fraud and improving efficiency. The evolution of central bank digital currencies (CBDCs) will further accelerate the integration of blockchain into the global financial system.
Comparison of Blockchain Platforms for Financial Applications
The following table compares several prominent blockchain platforms suitable for financial applications, highlighting their strengths and weaknesses:
| Platform | Scalability | Security | Features |
|---|---|---|---|
| Ethereum | Moderate (improving with layer-2 solutions) | High (proven track record) | Smart contracts, decentralized applications (dApps), large developer community |
| Hyperledger Fabric | High (permissioned network) | High (configurable security mechanisms) | Privacy features, modular architecture, suitable for enterprise applications |
| R3 Corda | Moderate | High (focus on privacy and security) | Focus on financial institutions, private and permissioned network |
| Ripple | High (optimized for payments) | Moderate | Real-time gross settlement (RTGS), focus on cross-border payments |
Epilogue: How Blockchain Is Transforming Global Financial Services
The blockchain revolution in finance isn’t just a futuristic fantasy; it’s a rapidly unfolding reality. While challenges remain – scalability, regulation, and widespread adoption among them – the potential benefits are undeniable. From enhanced security and transparency to increased efficiency and reduced costs, blockchain is poised to fundamentally alter how we conduct financial transactions globally. The future of finance is decentralized, secure, and undeniably…blockchain.
