How Blockchain is Transforming Digital Healthcare Records? Forget clunky, insecure systems – blockchain’s shaking up the healthcare world. Imagine a future where your medical records are instantly accessible, flawlessly secure, and shared seamlessly between doctors, hospitals, and even you. That’s the promise of blockchain, and it’s closer than you think. This revolutionary technology is poised to revolutionize data privacy, streamline processes, and ultimately, improve patient care.
From enhancing security and privacy to revolutionizing clinical trials and supply chain management, blockchain’s impact is far-reaching. We’ll dive deep into how this decentralized ledger technology is tackling long-standing healthcare challenges, offering a glimpse into a more efficient, transparent, and patient-centric future. Get ready for a deep dive into the tech that’s changing the game.
Enhanced Security and Privacy of Digital Health Records

Source: cryptoadventure.com
Secure, transparent healthcare records? That’s the blockchain promise. But the shift to digital also means AI-powered analysis is key, impacting jobs big time – check out this insightful piece on How Artificial Intelligence is Shaping the Future of the Job Market to see how. Ultimately, blockchain’s role in healthcare is inextricably linked to the evolving tech landscape, including AI’s influence on workforce dynamics.
The current system of managing digital health records (DHRs) faces significant challenges. Traditional methods often rely on centralized databases vulnerable to breaches, leaving sensitive patient information at risk. This vulnerability necessitates a more robust and secure approach, and blockchain technology offers a promising solution.
Blockchain’s decentralized and cryptographic nature offers a powerful counterpoint to the inherent weaknesses of traditional DHR systems. Unlike centralized databases, blockchain distributes patient data across a network of computers, making it significantly more difficult for hackers to access or alter information. Each transaction, or update to a record, is cryptographically secured, ensuring data integrity and traceability.
Cryptographic Hashing and Distributed Ledger Technology Enhance Security
Blockchain leverages cryptographic hashing to create a unique, immutable fingerprint for each data block. Any attempt to alter the data would change the hash, instantly flagging the tampering. This, coupled with the distributed ledger technology, makes it nearly impossible to manipulate records without detection. The distributed nature means no single point of failure exists; even if one node in the network is compromised, the remaining nodes maintain data integrity. This resilience contrasts sharply with traditional systems where a single database breach can compromise all patient data.
Blockchain-Based Access Control Mechanisms
Implementing access control on a blockchain requires careful design. Instead of relying on centralized user authentication, blockchain allows for granular permissioning. Each authorized individual, such as a doctor, nurse, or patient, receives a unique cryptographic key that grants them access only to the specific data they need. This permissioning can be programmed directly into the smart contracts governing the blockchain, automatically enforcing access rules and preventing unauthorized access. For example, a general practitioner might have access to a patient’s basic medical history, while a specialist would have access to more detailed information relevant to their expertise. This granular control is a significant improvement over traditional systems where access is often based on broad roles, leading to potential overexposure of sensitive information.
Comparison of Blockchain and Traditional DHR Security
Traditional DHR systems typically rely on firewalls, intrusion detection systems, and access control lists to secure patient data. However, these measures can be circumvented by sophisticated attacks. A single point of failure, like a compromised database server, can expose the entire system. Blockchain, on the other hand, eliminates this single point of failure through its decentralized architecture. The cryptographic hashing and immutability features provide an additional layer of security, making data manipulation incredibly difficult. Furthermore, the transparent and auditable nature of blockchain allows for easy tracking of data access and modifications, enhancing accountability and reducing the risk of unauthorized access or data breaches. The inherent security improvements offered by blockchain represent a significant advancement in protecting patient privacy and data integrity within the digital healthcare landscape.
Improved Data Interoperability and Data Sharing
Source: octaldigital.com
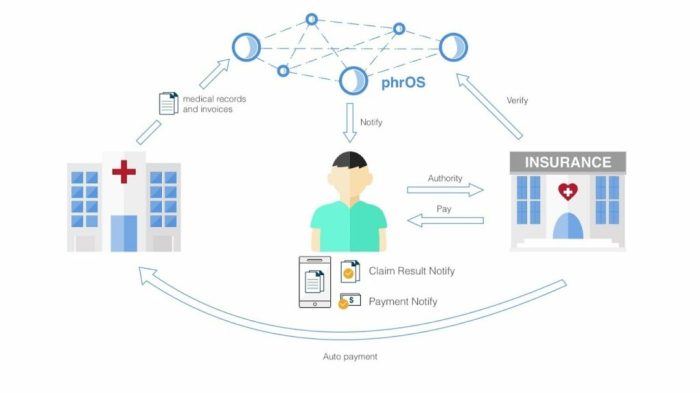
The current healthcare system often feels like a game of telephone, where patient information gets whispered from doctor to doctor, hospital to hospital, with crucial details getting lost or distorted along the way. This lack of interoperability – the ability of different systems to seamlessly share data – is a major hurdle to providing efficient and effective care. Blockchain technology offers a potential solution, promising to revolutionize how patient data is shared and accessed.
Blockchain facilitates seamless data sharing by creating a secure, shared, and immutable ledger of patient information. Unlike traditional systems that rely on centralized databases vulnerable to breaches and inconsistencies, blockchain distributes the data across a network of computers, making it virtually impossible to alter or delete records without detection. This enhanced security fosters trust and transparency among healthcare providers, encouraging a more collaborative approach to patient care.
Blockchain’s Role in Streamlining Patient Information Exchange
Blockchain streamlines the exchange of patient information by creating a standardized, verifiable system. Imagine a scenario where a patient’s allergy information is recorded on a blockchain. Every doctor, hospital, or clinic accessing this information receives a verified and up-to-date record, eliminating the risk of conflicting or outdated data. This eliminates the need for multiple data entry points and reduces the chance of human error. Furthermore, patient consent mechanisms can be built directly into the blockchain, giving individuals more control over their data. This transparent and secure exchange of information allows for more informed decision-making, leading to better patient outcomes.
Hypothetical Scenario: Multi-Hospital Network Using Blockchain
Let’s picture a multi-hospital network in a large metropolitan area. A patient, let’s call her Sarah, is involved in a serious car accident and is initially treated at Hospital A. Her medical records, including scans, lab results, and treatment details, are immediately and securely uploaded to a shared blockchain network accessible to all hospitals in the network. When Sarah needs specialized care and is transferred to Hospital B, her complete medical history is instantly available to the specialists there. There’s no need for paperwork, faxes, or time-consuming data transfers. Subsequently, if Sarah requires follow-up care at Hospital C, her comprehensive record, updated with the latest information from Hospitals A and B, is readily accessible. This seamless flow of information ensures consistent and coordinated care, preventing potentially harmful delays and redundancies. The blockchain’s immutable nature ensures data integrity, providing a single source of truth for all healthcare providers involved in Sarah’s care. This scenario demonstrates how blockchain can improve patient safety and efficiency by significantly reducing data transfer delays and improving coordination among different healthcare providers.
Streamlined Patient Data Management and Access
Managing patient data in traditional healthcare systems is a monumental task. Think mountains of paper charts, disparate electronic systems that don’t talk to each other, and the constant risk of lost or misplaced information. This fragmented approach leads to inefficiencies, delays in care, and increased administrative costs, ultimately impacting both healthcare providers and patients. The sheer volume of data, coupled with the need for strict security and privacy protocols, makes it a complex and often frustrating process.
Blockchain technology offers a potential solution by streamlining patient data management and access. Its decentralized and immutable nature allows for a more efficient and secure way to store, manage, and share sensitive health information. By creating a single, unified record, blockchain eliminates the need for multiple copies spread across various systems, significantly reducing administrative overhead and the potential for errors.
Improved Patient Data Access
Imagine a world where accessing your medical records is as simple as checking your bank balance online. With blockchain-based systems, patients can gain secure and immediate access to their complete health history, including lab results, prescriptions, and doctor’s notes, anytime, anywhere. This empowers patients to actively participate in their healthcare decisions and fosters a more collaborative relationship with their providers. For example, a patient could easily download their vaccination records to share with a new doctor or quickly access allergy information in an emergency situation. The transparency and accessibility offered by blockchain puts patients firmly in control of their own health data.
Comparison of Data Access Time and Efficiency
The following table illustrates the stark contrast between traditional and blockchain-based systems regarding patient data access:
| Feature | Traditional System | Blockchain-Based System |
|---|---|---|
| Data Access Time | Hours to days, often requiring multiple requests and follow-ups. | Near real-time access, often within seconds. |
| Efficiency | Highly inefficient, involving manual processes and potential for errors. | Highly efficient, automated processes with minimal human intervention. |
| Cost | High administrative costs associated with manual data handling and retrieval. | Lower administrative costs due to automation and reduced manual effort. |
| Security | Vulnerable to data breaches and unauthorized access. | Enhanced security through cryptographic hashing and decentralized storage. |
Blockchain’s Role in Clinical Trials and Research
Clinical trials, the backbone of medical advancements, face significant hurdles in data management. The sheer volume of data generated, coupled with the need for rigorous verification and secure sharing across multiple research sites and organizations, creates a complex and often inefficient process. Blockchain technology offers a potential solution to these challenges, revolutionizing how clinical trials are conducted and data is handled.
The integrity and transparency of clinical trial data are paramount for ensuring the reliability of research findings and the safety of participants. Traditional methods often rely on centralized databases, susceptible to manipulation, hacking, and data breaches. Blockchain’s decentralized and immutable ledger offers a robust alternative, providing a secure and auditable record of all trial activities.
Enhanced Data Integrity and Transparency in Clinical Trials
Blockchain’s decentralized nature eliminates single points of failure, making data manipulation significantly more difficult. Each data entry is cryptographically secured and linked to the previous entry, creating an unbroken chain of records. This ensures that any attempt to alter data is immediately detectable. Furthermore, the transparent nature of the blockchain allows all authorized participants – researchers, sponsors, regulatory bodies – to access and verify the data, fostering trust and accountability throughout the trial process. This increased transparency could lead to faster regulatory approvals and increased confidence in research outcomes. For example, imagine a scenario where a pharmaceutical company uses blockchain to record all patient data and trial results. Any attempt to alter data would be instantly flagged, enhancing the credibility of the trial findings and speeding up the drug approval process.
Secure Data Sharing Among Researchers
Sharing data securely and efficiently across research institutions is crucial for collaborative research. Blockchain facilitates this by enabling controlled access to data while maintaining its confidentiality and integrity. Researchers can be granted specific permissions to access relevant data without compromising the overall security of the system. This streamlined approach accelerates data analysis and fosters greater collaboration among researchers globally. This is particularly important in large-scale international trials where data needs to be shared across various geographical locations and regulatory environments. Consider a global study on a rare disease: blockchain could allow researchers in different countries to access relevant patient data while adhering to strict data privacy regulations, accelerating the pace of discovery.
Streamlined Patient Recruitment and Data Collection, How Blockchain is Transforming Digital Healthcare Records
Patient recruitment is a time-consuming and often challenging aspect of clinical trials. Blockchain can streamline this process by creating a secure platform for patients to register their interest and provide consent. This reduces administrative overhead and ensures accurate tracking of participant data. Furthermore, blockchain can facilitate secure and automated data collection, reducing manual data entry errors and accelerating the overall trial timeline. For instance, wearable sensors connected to a blockchain network could automatically record patient data, eliminating the need for manual input and minimizing the risk of errors. This automated system would not only speed up data collection but also enhance data accuracy and reliability.
Impact on Medical Supply Chain Management: How Blockchain Is Transforming Digital Healthcare Records
The current medical supply chain faces significant challenges, impacting patient safety and healthcare costs. Inefficient tracking, lack of transparency, and the prevalence of counterfeit products create vulnerabilities throughout the system, from manufacturing to patient care. Blockchain technology offers a powerful solution to these persistent problems, promising increased security, traceability, and efficiency.
The global medical supply chain is a complex web, involving numerous manufacturers, distributors, wholesalers, and healthcare providers. Current methods for tracking medical products often rely on paper-based systems or disparate digital databases, making it difficult to maintain accurate and up-to-date information about product origin, movement, and authenticity. This lack of transparency creates opportunities for counterfeit products to enter the supply chain, posing serious risks to patient health and safety.
Challenges in Tracking and Managing Medical Supplies
Inefficient tracking and management of medical supplies result in significant losses, delays, and safety risks. These challenges include difficulties in verifying product authenticity, managing inventory effectively, and ensuring timely delivery of essential medical goods. Poor record-keeping and a lack of real-time data visibility hinder efforts to identify and address potential issues promptly. The absence of a standardized, secure system for tracking products throughout the supply chain contributes to the overall complexity and vulnerability. This often leads to increased costs associated with waste, recalls, and legal liabilities.
Blockchain Technology Improves Traceability and Authenticity of Medical Products
Blockchain technology’s decentralized and immutable nature makes it ideally suited for improving the traceability and authenticity of medical products. Each product’s journey is recorded as a series of tamper-proof blocks on the blockchain, creating a transparent and auditable record. This enhanced traceability allows for quick identification of the origin, handling, and distribution history of any given product. Furthermore, the use of cryptographic techniques ensures the integrity and authenticity of the data, making it virtually impossible to alter or forge records. This heightened security helps combat counterfeiting, a major concern in the pharmaceutical industry. For example, a pharmaceutical company could record the manufacturing date, batch number, and other relevant information on the blockchain, creating a unique digital identity for each product. This information can be accessed by authorized parties throughout the supply chain, providing complete transparency and accountability.
Reducing the Risk of Counterfeit Drugs and Medical Devices
Blockchain’s ability to provide verifiable provenance dramatically reduces the risk of counterfeit drugs and medical devices entering the supply chain. By tracking products from their origin to the point of use, blockchain allows healthcare providers and patients to verify the authenticity of the products they receive. This verification process involves comparing the product’s unique identifier on the blockchain with the physical product’s markings. Any discrepancy would immediately raise a red flag, indicating potential counterfeiting. Furthermore, blockchain can be integrated with other technologies, such as RFID tags and smart contracts, to enhance security and automate processes. Smart contracts, for example, can automatically trigger alerts or initiate recalls if a counterfeit product is detected. This proactive approach helps prevent counterfeit products from reaching patients, ensuring their safety and well-being.
Step-by-Step Process of Blockchain Enhancing Supply Chain Visibility
The integration of blockchain enhances supply chain visibility through a series of steps:
- Manufacturing: Each medical product receives a unique digital identifier (UDI) linked to its blockchain entry. This entry includes details such as manufacturing date, batch number, and raw materials used.
- Distribution: As the product moves through the distribution network, each transaction – shipment, storage, and transfer of ownership – is recorded on the blockchain, updating the product’s history.
- Wholesale and Retail: Wholesalers and retailers can access the product’s blockchain record to verify its authenticity and track its journey.
- Healthcare Provider: Hospitals and clinics can scan the product’s UDI to verify its authenticity and access its complete history before administering it to a patient.
- Patient Care: The patient receives a product with a verifiable history, ensuring safety and reducing the risk of receiving counterfeit goods.
This transparent and secure process significantly improves traceability, reduces fraud, and strengthens the overall integrity of the medical supply chain. The immutable nature of the blockchain ensures that any attempt to tamper with the data is immediately detectable.
The Role of Smart Contracts in Healthcare
Smart contracts, self-executing contracts with the terms of the agreement between buyer and seller being directly written into lines of code, are poised to revolutionize healthcare. By automating processes and ensuring transparency, they offer a significant leap forward in efficiency and security within a traditionally complex and paper-heavy industry. Their potential to streamline operations, reduce costs, and improve patient care is immense.
Smart contracts can automate various healthcare processes, significantly improving efficiency and reducing the need for manual intervention. This automation extends to numerous areas, from insurance claims processing to secure data sharing and even medication dispensing. The inherent security and transparency provided by blockchain technology underpinning these smart contracts builds trust and accountability across the healthcare ecosystem.
Automating Healthcare Processes with Smart Contracts
Smart contracts can automate a wide range of healthcare processes, leading to significant cost savings and increased efficiency. For instance, they can automate appointment scheduling, eliminating the back-and-forth communication between patients and providers. Imagine a system where a patient books an appointment directly through a secure portal; the smart contract automatically updates the provider’s schedule, sends reminders, and even handles payment processing. This eliminates administrative overhead and reduces the risk of human error. Similarly, the management of medical supplies can be automated. When inventory levels drop below a certain threshold, a smart contract automatically places an order with a supplier, ensuring that hospitals and clinics always have the necessary supplies on hand.
Secure and Transparent Transactions in Patient Care
The inherent security and transparency of smart contracts offer significant advantages in managing sensitive patient data and facilitating secure transactions. Every transaction is recorded on a tamper-proof blockchain, providing an auditable trail that ensures accountability and prevents fraud. For example, a smart contract could govern the release of patient data to authorized researchers, ensuring that only the necessary data is shared and that the patient’s privacy is protected. The conditions for data release—such as patient consent and research approval—are encoded within the contract, guaranteeing compliance with regulations. This eliminates the need for manual verification and reduces the risk of data breaches.
Automating Insurance Claims Processing and Medication Dispensing
Smart contracts can significantly streamline insurance claims processing. Once a claim is submitted, a smart contract automatically verifies the patient’s coverage, the provider’s credentials, and the medical services rendered. If everything is in order, the payment is automatically released to the provider, significantly reducing processing time and eliminating the need for manual review. In medication dispensing, smart contracts can ensure that patients receive the correct medication at the right time. A smart contract could be programmed to automatically dispense medication from a smart pill dispenser based on a doctor’s prescription, ensuring adherence to the treatment plan and preventing medication errors.
Smart Contract for Automated Release of Patient Data
Consider a smart contract designed to manage the release of a patient’s genetic data for research purposes. The contract would include the following conditions:
* Patient Consent: The patient must explicitly consent to the release of their data. This consent could be digitally signed and recorded on the blockchain.
* Research Approval: The research project must receive ethical approval from an Institutional Review Board (IRB). Proof of IRB approval would be a condition for the smart contract to execute.
* Data Anonymization: The patient’s identifying information would be removed from the data before release, ensuring their privacy is protected. This anonymization process could be verified by an independent auditor.
* Data Usage Restrictions: The contract would specify how the data can be used, ensuring it is only used for the approved research purposes.
* Payment Release: Upon fulfilling all the conditions, the smart contract would automatically release the agreed-upon payment to the patient for participation in the research.
This smart contract ensures that the release of patient data is secure, transparent, and compliant with all relevant regulations. The entire process is automated, reducing administrative overhead and increasing efficiency. The blockchain’s immutability ensures that all transactions are recorded permanently and cannot be altered.
Addressing Ethical and Legal Considerations
Source: nevinainfotech.com
The integration of blockchain technology into healthcare, while promising, necessitates a careful consideration of the ethical and legal ramifications. The inherent transparency and immutability of blockchain, while beneficial for data integrity, also raise concerns about patient privacy, data security, and the potential for misuse. Navigating this complex landscape requires a robust framework that balances innovation with ethical responsibility and legal compliance.
Implementing blockchain in healthcare requires a proactive approach to addressing potential ethical and legal challenges. Failing to do so could lead to significant risks, including breaches of patient confidentiality, legal disputes, and erosion of public trust in the healthcare system. A comprehensive understanding of these issues is crucial for the successful and responsible adoption of this transformative technology.
Potential Ethical Challenges Associated with Blockchain in Healthcare
The decentralized nature of blockchain introduces unique ethical considerations. For example, ensuring data accuracy and preventing malicious actors from manipulating records requires sophisticated mechanisms. Furthermore, the potential for algorithmic bias embedded within blockchain applications needs careful scrutiny. The question of data ownership and control also needs thorough examination, as does the potential for unequal access to blockchain-based healthcare services. Balancing the benefits of transparency with the need for patient confidentiality presents a continuous challenge. A critical element is the establishment of clear guidelines and protocols for data access and usage, ensuring responsible and ethical application of the technology.
Legal Implications of Using Blockchain for Storing and Sharing Sensitive Patient Data
The use of blockchain to store and share sensitive patient data brings forth significant legal implications. Compliance with regulations such as HIPAA in the United States, GDPR in Europe, and other national and regional data privacy laws is paramount. Legal frameworks surrounding data ownership, consent, and liability must be carefully considered and adapted to the unique characteristics of blockchain technology. The immutability of blockchain data raises questions about data correction and deletion, necessitating clear legal processes for handling errors or disputes. Furthermore, the cross-border nature of blockchain transactions necessitates international legal harmonization to ensure consistent data protection standards.
Data Governance Frameworks for Responsible Use of Blockchain in Healthcare
Robust data governance frameworks are essential to ensure the responsible use of blockchain in healthcare. These frameworks must encompass clear policies on data access, sharing, and usage, along with mechanisms for data security and auditing. Transparency and accountability are key principles, requiring the establishment of independent oversight bodies to monitor compliance and address potential breaches. These frameworks should also incorporate mechanisms for addressing ethical dilemmas and resolving disputes, ensuring fairness and equity in the application of blockchain technology. The establishment of industry-wide standards and best practices is crucial to foster trust and promote the responsible adoption of blockchain within the healthcare sector. Examples include establishing clear guidelines for data anonymization and pseudonymization techniques to minimize the risk of re-identification.
Patient Data Ownership and Consent in a Blockchain-Based Healthcare System
Patient data ownership and consent are central to the ethical and legal use of blockchain in healthcare. Clear and unambiguous consent mechanisms are needed to ensure patients have control over their data and understand how it will be used. Blockchain’s transparent nature allows patients to track the usage of their data, promoting accountability and enhancing trust. However, the complexities of managing consent across multiple stakeholders and jurisdictions require careful consideration. This includes developing mechanisms for revoking consent and ensuring data portability, allowing patients to easily transfer their data between different healthcare providers. The development of user-friendly interfaces that enable patients to easily understand and manage their data consent preferences is also crucial for successful implementation. Examples of such mechanisms include utilizing blockchain-based digital wallets that allow patients to directly manage their data access permissions and control data sharing across various platforms.
Ending Remarks
The integration of blockchain technology into healthcare isn’t just a futuristic concept; it’s a rapidly evolving reality. By addressing key vulnerabilities in traditional systems, blockchain offers a powerful solution for improved security, interoperability, and patient empowerment. While challenges remain in terms of regulation and adoption, the potential benefits are undeniable. The future of healthcare is secure, transparent, and patient-centric – and it’s powered by blockchain.
