How Blockchain is Improving the Future of Cross-Border Financial Transactions? Let’s ditch the snail-paced, expensive international money transfers of the past. Blockchain technology is shaking things up, offering a faster, cheaper, and more transparent way to send money across borders. Imagine a world where sending funds overseas is as easy as tapping a button – that’s the promise of blockchain, and it’s closer than you think.
For too long, businesses and individuals have wrestled with the complexities and high costs of traditional cross-border payments. Banks, intermediaries, and fluctuating exchange rates all contribute to delays and hefty fees. Blockchain’s decentralized, secure, and transparent nature offers a compelling alternative, streamlining transactions and slashing costs. This innovative technology is poised to transform international finance, empowering businesses and individuals alike.
Introduction to Cross-Border Payments and their Challenges
Navigating the world of international finance can feel like traversing a dense jungle, especially when it comes to sending or receiving money across borders. Traditional methods, while established, are often plagued by inefficiencies and hidden costs that significantly impact both businesses and individuals. Let’s delve into the complexities and limitations of these systems.
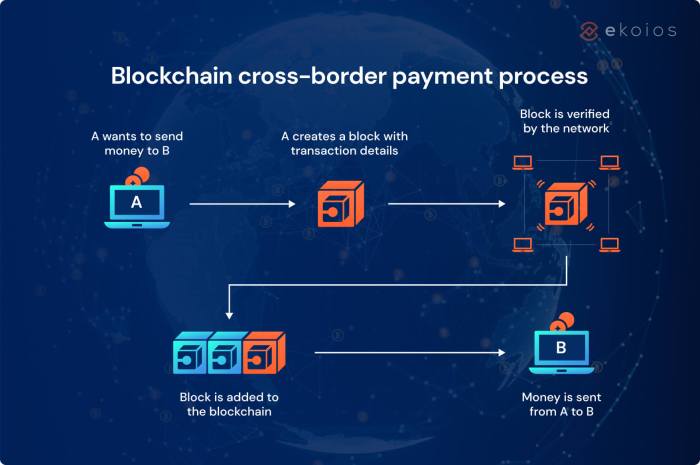
Cross-border payments traditionally rely on a network of intermediaries, including correspondent banks, payment processors, and sometimes even SWIFT (Society for Worldwide Interbank Financial Telecommunication). This multi-layered approach, while seemingly robust, introduces numerous bottlenecks and increases the overall transaction time. The process involves multiple conversions between currencies, each incurring fees and potentially unfavorable exchange rates. Furthermore, tracking the progress of a transaction can be opaque, leaving senders and recipients in the dark about its status until it finally arrives – or doesn’t.
High Costs Associated with Traditional Cross-Border Transactions
The cost of sending money internationally can be surprisingly high. These costs are not always transparent, often buried within seemingly innocuous fees charged by various intermediaries. These fees can include transfer fees, processing fees, and correspondent banking fees, all of which accumulate and inflate the total cost. Additionally, unfavorable exchange rates further exacerbate the expense. A seemingly small percentage difference in the exchange rate can translate to a substantial amount of money, especially for larger transactions. For instance, sending $10,000 might incur fees totaling hundreds of dollars, significantly reducing the actual amount received by the recipient. This impacts businesses’ profit margins and individuals’ budgets alike.
Slow Processing Times and Lack of Transparency
Speed is of the essence in today’s fast-paced global economy. However, traditional cross-border payments are notoriously slow. A simple transfer can take several days, or even weeks, to complete, depending on the complexity of the transaction and the number of intermediaries involved. This delay can have serious consequences for businesses, particularly those involved in time-sensitive transactions like international trade. Imagine a small business relying on timely payments for crucial supplies; a delay of several days can disrupt their operations and even threaten their survival. Moreover, the lack of transparency in the process adds to the frustration. Tracking the transaction’s progress can be difficult, leaving senders and recipients uncertain about its status and potential delays.
Impact on Businesses and Individuals
The limitations of traditional cross-border payment systems have far-reaching consequences. For businesses, high costs and slow processing times erode profit margins, hinder growth, and increase operational complexity. The inability to easily and efficiently manage international payments can severely limit their ability to expand into new markets or collaborate with international partners. For individuals, these limitations translate to higher costs for remittances, making it more expensive to support family members in other countries. The delays and lack of transparency can also cause significant stress and uncertainty, especially for those relying on timely payments for essential needs. Consider a migrant worker sending money home to support their family; every delay and extra fee chips away at their already limited resources.
How Blockchain Technology Addresses These Challenges
Source: coinpayments.net
Blockchain’s transparent ledger is revolutionizing cross-border payments, boosting efficiency and security. This tech-driven shift mirrors the advancements in other sectors, like environmental protection, where How Robotics is Changing the Future of Environmental Monitoring is leading to more precise data collection. Ultimately, both innovations point towards a future of streamlined, data-driven processes, making international finance faster and more reliable.
Cross-border payments have long been plagued by slow processing times, high fees, and a lack of transparency. But blockchain technology offers a potential game-changer, leveraging its unique properties to overcome these persistent hurdles and revolutionize international finance. This section explores how blockchain’s decentralized architecture, smart contracts, and cryptocurrencies are reshaping the landscape of cross-border transactions.
Blockchain’s Decentralized Nature Enhances Security and Trust
Blockchain’s decentralized nature is its superpower when it comes to cross-border payments. Unlike traditional systems that rely on centralized intermediaries (banks, payment processors), blockchain distributes the transaction record across a network of computers. This eliminates single points of failure and reduces the risk of fraud or manipulation. Each transaction is cryptographically secured and verified by multiple nodes, creating an immutable and transparent ledger. This inherent transparency builds trust among participants, as all parties can view the transaction history, fostering greater accountability and reducing the need for intermediaries to vouch for the legitimacy of transactions. For instance, imagine tracking a shipment of goods internationally; with blockchain, all parties – shipper, receiver, and customs – can view the goods’ journey and status in real-time, minimizing disputes and delays.
Smart Contracts Automate and Streamline the Payment Process
Smart contracts are self-executing contracts with the terms of the agreement directly written into code. On a blockchain, these contracts automate various stages of the cross-border payment process, significantly reducing manual intervention and associated delays. For example, a smart contract can automatically release payment to a supplier upon confirmation of goods receipt, eliminating the need for lengthy verification processes. This automation also minimizes human error and speeds up the overall transaction time. The use of smart contracts in international trade finance, for example, is already showing promising results in reducing processing times and costs for letters of credit.
Cryptocurrencies Facilitate Faster and Cheaper International Transfers
Cryptocurrencies, operating on blockchain networks, provide a faster and more cost-effective alternative to traditional international transfer methods. They bypass traditional banking infrastructure, reducing reliance on correspondent banks and their associated fees. Transactions are processed directly between parties, often at a fraction of the cost of traditional wire transfers. Furthermore, cryptocurrencies can operate 24/7, irrespective of banking hours or holidays, enabling faster settlement times. While volatility remains a concern, stablecoins – cryptocurrencies pegged to fiat currencies – are mitigating this risk, providing a more stable alternative for cross-border payments. For example, using stablecoins for international remittances can significantly reduce transfer fees compared to traditional money transfer operators.
Comparison of Blockchain-Based and Traditional Cross-Border Transactions
The following table compares the speed, cost, security, and transparency of blockchain-based transactions with traditional methods:
| Feature | Blockchain-Based Transactions | Traditional Transactions |
|---|---|---|
| Transaction Speed | Minutes to hours | Days to weeks |
| Cost | Significantly lower | Relatively high (including intermediary fees) |
| Security | High (cryptographic security and decentralized ledger) | Moderate to high (dependent on intermediary security measures) |
| Transparency | High (all transactions visible on the blockchain) | Low (limited visibility for parties outside the transaction) |
Specific Applications of Blockchain in Cross-Border Finance
Blockchain technology is rapidly transforming the landscape of cross-border financial transactions, offering solutions to long-standing challenges related to speed, cost, and transparency. Its decentralized and secure nature is proving particularly beneficial in several key areas, revolutionizing how money and assets move across international borders. Let’s delve into some specific applications.
Blockchain in International Remittances
International remittances, the transfer of money across borders, are a vital lifeline for millions of migrant workers sending funds back to their families. Traditional methods often involve high fees, slow processing times, and a lack of transparency. Blockchain offers a compelling alternative. By leveraging its decentralized architecture, blockchain platforms can significantly reduce transaction costs and processing times. Furthermore, the immutable ledger provides a transparent record of the transaction, increasing trust and accountability for both senders and recipients. This enhanced transparency can empower migrant workers by giving them greater control and visibility over their hard-earned money. The reduced costs also mean more money reaches the intended recipients, contributing significantly to their well-being and economic development in their home countries.
Blockchain in Trade Finance, How Blockchain is Improving the Future of Cross-Border Financial Transactions
Trade finance, the financing of international trade transactions, is a complex and often slow process. Letters of credit, a key instrument in trade finance, often involve multiple intermediaries, leading to delays and increased costs. Blockchain can streamline this process by creating a shared, transparent ledger accessible to all parties involved. This eliminates the need for multiple intermediaries, reduces the risk of fraud, and speeds up the overall process. Supply chain finance, another critical aspect of trade finance, can also benefit from blockchain. By tracking goods and payments throughout the supply chain, blockchain enhances transparency and traceability, improving efficiency and reducing the risk of disputes.
Blockchain for Businesses of Varying Sizes
The benefits of blockchain extend to businesses of all sizes, offering tailored solutions to their specific needs in cross-border payments.
Here’s how different sized businesses can leverage blockchain:
- Small Enterprises: Blockchain can provide access to affordable and efficient cross-border payment solutions, previously out of reach due to high transaction fees and complex processes. This opens up new international markets and opportunities for growth.
- Medium Enterprises: Blockchain can streamline their supply chain finance, reducing costs and improving efficiency by providing real-time visibility into payments and inventory. This leads to better cash flow management and improved relationships with suppliers and customers.
- Large Enterprises: Blockchain can significantly reduce costs and risks associated with large-scale cross-border transactions. The improved transparency and traceability enhance compliance and reduce the risk of fraud, contributing to improved financial performance and a stronger corporate reputation.
Examples of Blockchain-Based Platforms for Cross-Border Payments
Several blockchain-based platforms are already facilitating cross-border payments, each with unique functionalities. RippleNet, for example, utilizes its own cryptocurrency, XRP, to enable fast and low-cost international transfers. Other platforms focus on specific industries or niches, offering tailored solutions to address specific challenges. These platforms often integrate with existing financial infrastructure, allowing for seamless integration into existing business processes. The continuous development and adoption of these platforms demonstrate the growing potential of blockchain in revolutionizing cross-border payments.
Security and Regulatory Aspects of Blockchain in Cross-Border Payments: How Blockchain Is Improving The Future Of Cross-Border Financial Transactions
Source: ekoios.vn
Blockchain technology, with its decentralized and cryptographic nature, offers a compelling solution to the challenges plaguing traditional cross-border payments. However, its implementation isn’t without its security and regulatory hurdles. Understanding these aspects is crucial for the widespread adoption of blockchain in this critical financial sector.
The inherent security features of blockchain significantly mitigate risks associated with traditional payment systems. This section delves into the strengths and weaknesses of blockchain’s security model, as well as the evolving regulatory landscape governing its use in cross-border transactions.
Blockchain’s Security Mechanisms Against Fraud and Double-Spending
Blockchain’s security rests on several pillars. Cryptographic hashing ensures the integrity of each transaction block, making it computationally infeasible to alter past transactions. The decentralized nature, with numerous nodes validating transactions, eliminates single points of failure and reduces the risk of fraud. Furthermore, the public and transparent nature of the ledger allows for easy auditing and detection of anomalies. While extremely robust, it’s important to note that smart contracts, often integral to blockchain-based payments, can contain vulnerabilities if not meticulously designed and audited. A poorly written smart contract could inadvertently expose funds to theft or misuse. Therefore, rigorous testing and auditing of smart contracts are essential to maintaining the security of the system.
Vulnerabilities and Challenges in the Regulatory Landscape
The decentralized and borderless nature of blockchain presents significant challenges for regulators. The anonymity afforded by some cryptocurrencies can be exploited for illicit activities like money laundering and terrorist financing. The lack of a unified global regulatory framework creates inconsistencies and jurisdictional conflicts, hindering cross-border payments. Furthermore, the volatility of cryptocurrencies poses a risk to users and businesses involved in cross-border transactions. Governments are grappling with how to regulate these new technologies without stifling innovation. The lack of clear legal definitions for cryptocurrencies and blockchain-based assets further complicates the regulatory landscape.
The Role of Regulatory Bodies in Overseeing Blockchain-Based Transactions
Regulatory bodies worldwide are actively working to establish frameworks for overseeing blockchain-based cross-border payments. Their primary goals are to prevent illicit activities, protect consumers, and ensure the stability of the financial system. This involves establishing clear guidelines for anti-money laundering (AML) and know-your-customer (KYC) compliance for blockchain platforms and businesses operating within this space. Collaboration between international regulatory bodies is essential to create a harmonized global framework, preventing regulatory arbitrage and ensuring a level playing field for all participants. This collaboration will also be crucial for facilitating the secure and efficient flow of cross-border payments.
A Hypothetical Regulatory Framework for Blockchain-Based Cross-Border Payments
A robust regulatory framework for blockchain-based cross-border payments should incorporate several key principles. Firstly, it should prioritize consumer protection by mandating transparency and accountability from blockchain platforms. Secondly, it should implement strict AML/KYC measures to prevent the misuse of the technology for illicit activities. Thirdly, it needs to establish clear licensing requirements for businesses operating blockchain-based payment systems. Finally, the framework should encourage innovation while ensuring the stability and security of the financial system. This could involve a tiered approach to regulation, with stricter rules applied to platforms handling larger volumes of transactions or those dealing with higher-risk assets. Such a framework would need to balance the need for innovation with the need for consumer protection and financial stability. For example, a licensing system could categorize blockchain platforms based on transaction volume and risk level, applying more stringent requirements to high-volume or high-risk platforms. This would allow for a flexible approach that adapts to the evolving nature of the technology and its applications.
The Future of Blockchain in Cross-Border Financial Transactions

Source: medium.com
The integration of blockchain technology into cross-border financial transactions is still in its nascent stages, yet its potential to revolutionize international finance is undeniable. We’re on the cusp of a significant shift, moving away from the slow, expensive, and often opaque systems of the past towards a more transparent, efficient, and secure future. This section explores the likely trajectory of this technological evolution, examining both the promising advancements and potential hurdles ahead.
Potential Impact of Blockchain on International Finance
Blockchain’s impact on international finance promises to be transformative. We can expect a significant reduction in transaction costs, processing times, and the need for intermediaries. This will empower smaller businesses and individuals with access to global markets previously out of reach. Imagine a world where a small artisan in Kenya can easily and affordably receive payment from a customer in Canada, without relying on expensive and time-consuming banking systems. This increased efficiency and accessibility will foster economic growth and financial inclusion on a global scale, potentially boosting cross-border trade exponentially. Examples like Ripple and Stellar already demonstrate the potential for faster and cheaper international transfers, although widespread adoption is still pending.
Technological Advancements Enhancing Blockchain-Based Payments
Several technological advancements are poised to further refine blockchain’s role in cross-border payments. Improved scalability solutions, such as sharding and layer-2 scaling, will be crucial in handling the high transaction volumes expected as adoption increases. The development of more robust and interoperable blockchain networks will facilitate seamless communication and data exchange between different systems. Furthermore, advancements in privacy-enhancing technologies, like zero-knowledge proofs, will address concerns about data security and regulatory compliance. For instance, the integration of decentralized identity solutions could streamline KYC/AML processes, significantly reducing friction in cross-border transactions.
Obstacles and Challenges to Widespread Adoption
Despite the immense potential, several obstacles hinder the widespread adoption of blockchain in cross-border finance. Regulatory uncertainty and a lack of standardized protocols remain significant hurdles. Different jurisdictions have varying approaches to regulating cryptocurrencies and blockchain technology, creating fragmentation and complexity for businesses operating internationally. Furthermore, the technological complexity of blockchain can be a barrier to entry for smaller businesses and individuals lacking the technical expertise to navigate the system effectively. The need for robust security measures to prevent fraud and cyberattacks is also paramount. Addressing these challenges requires collaboration between governments, regulatory bodies, and the blockchain industry to establish clear guidelines and foster innovation.
Vision for a Seamless Global Financial System
A future where blockchain seamlessly facilitates global financial transactions offers several key advantages:
- Instantaneous Cross-Border Transfers: Money moves across borders as quickly as an email, eliminating delays and uncertainty.
- Reduced Transaction Costs: The elimination of intermediaries and streamlined processes dramatically lower the cost of international payments.
- Enhanced Transparency and Traceability: Every transaction is recorded on a transparent, immutable ledger, increasing accountability and reducing fraud.
- Improved Financial Inclusion: Individuals and businesses previously excluded from the global financial system gain access to affordable and efficient cross-border payment solutions.
- Increased Security and Reduced Risk: Blockchain’s inherent security features minimize the risk of fraud and data breaches, enhancing trust and confidence in the system.
This vision is not just a utopian dream; it’s a realistic goal within reach, provided we overcome the current challenges and foster collaborative innovation within the industry and across regulatory bodies. The potential benefits for global economic growth and financial inclusion are simply too significant to ignore.
Final Wrap-Up
The future of cross-border financial transactions is undeniably intertwined with blockchain technology. While regulatory hurdles and technological advancements remain, the potential benefits are too significant to ignore. From faster remittances to streamlined trade finance, blockchain promises a more efficient, secure, and inclusive global financial system. It’s not just about faster payments; it’s about building a more equitable and accessible financial landscape for everyone.
