How Blockchain is Facilitating Cross-Border Payments and Financial Inclusion? Forget slow, expensive international transfers! Blockchain is shaking up the global finance game, offering a faster, cheaper, and more inclusive way to send money across borders. This revolutionary technology is using its transparent, secure nature to connect billions to the global financial system, bypassing traditional banking hurdles and empowering underserved communities. Get ready to dive into the world of decentralized finance and discover how blockchain is leveling the playing field.
Imagine a world where sending money overseas is as easy as sending a text. That’s the promise of blockchain technology in cross-border payments. By utilizing distributed ledger technology and smart contracts, blockchain streamlines the entire process, reducing fees, increasing speed, and enhancing security. This not only benefits businesses but also opens doors for millions previously excluded from the formal financial system, particularly in developing countries. We’ll explore the mechanics, the challenges, and the exciting future potential of this game-changing technology.
Introduction to Cross-Border Payments and Financial Inclusion
Cross-border payments, simply put, are financial transactions that cross international borders. They’re crucial for global trade, remittances, and international investments, but they face significant hurdles. These challenges often result in high costs, slow processing times, and a lack of transparency, disproportionately impacting individuals and businesses in developing countries. Financial inclusion, on the other hand, aims to provide access to affordable and convenient financial services for everyone, regardless of their location, income, or social status. It’s a global imperative, recognizing that access to finance is a fundamental driver of economic growth and poverty reduction. The two concepts are deeply intertwined, as the limitations of existing cross-border payment systems directly hinder financial inclusion on a global scale.
Challenges in Traditional Cross-Border Payment Systems
Traditional cross-border payment systems rely heavily on correspondent banking networks, a complex web of intermediaries that handle the transfer of funds. This structure creates several bottlenecks. High transaction fees, often hidden within the exchange rates, eat into the amount sent. Processing times can stretch for days, even weeks, delaying crucial payments for businesses and individuals alike. Furthermore, the lack of real-time tracking and transparency makes it difficult to monitor the progress of a transaction, increasing the risk of fraud and disputes. These complexities and associated costs are particularly burdensome for low-value transactions, significantly limiting access to financial services for many in developing economies. For instance, a migrant worker sending a small amount of money home might lose a significant portion to fees, rendering the process economically unviable. The opacity of the system also creates opportunities for exploitation and manipulation.
Financial Inclusion and its Global Significance
Financial inclusion is not just about having a bank account; it’s about accessing a full range of financial services, including payments, savings, credit, and insurance. Globally, billions of people remain unbanked or underbanked, lacking access to these essential services. This exclusion limits their ability to participate fully in the economy, hindering economic growth and perpetuating cycles of poverty. Financial inclusion has been identified by numerous international organizations, including the UN and the World Bank, as a key element in achieving the Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs), particularly those related to poverty reduction, economic growth, and gender equality. Providing access to financial services empowers individuals, allowing them to save for the future, invest in their businesses, and manage risk more effectively. It fosters economic stability and contributes to a more equitable and inclusive society. For example, access to microfinance loans can empower women entrepreneurs in developing countries, enabling them to start and grow their businesses, contributing to their own financial independence and the broader economy.
Blockchain Technology’s Role in Cross-Border Payments: How Blockchain Is Facilitating Cross-Border Payments And Financial Inclusion
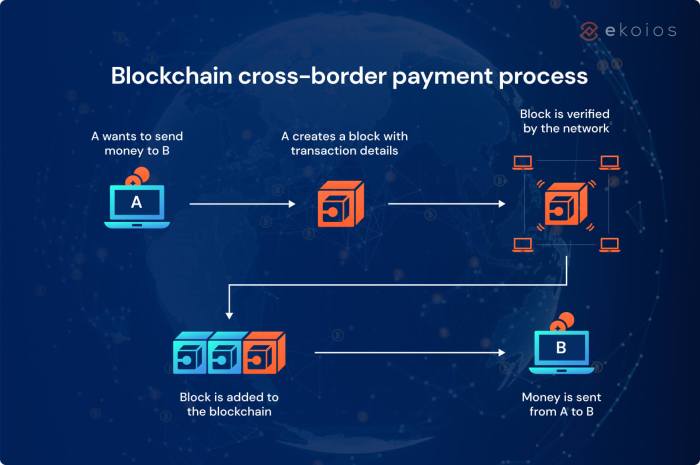
Source: ekoios.vn
Blockchain’s transparent and secure nature is revolutionizing cross-border payments, making them faster and cheaper. This efficiency opens doors for financial inclusion globally, especially in underserved communities. Understanding these transactional patterns is crucial, and that’s where the insights from The Future of Data-Driven Marketing with AI and Big Data become invaluable. Analyzing this data helps financial institutions tailor services and reach more people, further accelerating the positive impact of blockchain on global finance.
Blockchain technology is revolutionizing cross-border payments by offering a secure, transparent, and efficient alternative to traditional methods. Its decentralized nature and cryptographic security features address many of the long-standing challenges associated with international transactions, paving the way for faster, cheaper, and more inclusive financial systems.
Enhanced Transparency and Security
Blockchain’s inherent transparency significantly improves the security and traceability of cross-border payments. Every transaction is recorded on a distributed ledger, accessible to all participants with the appropriate permissions. This shared, immutable record makes it incredibly difficult to alter or manipulate transactions, reducing the risk of fraud and errors. Furthermore, the use of cryptography ensures the confidentiality and integrity of the data, protecting sensitive financial information from unauthorized access. Imagine a system where every step of a payment, from initiation to final settlement, is visible and verifiable by all parties involved – this is the power of blockchain’s transparency. This enhanced visibility minimizes disputes and increases trust among participants, a crucial element in facilitating smoother cross-border transactions.
Smart Contracts for Automation and Streamlining
Smart contracts, self-executing contracts with the terms of the agreement directly written into code, are a game-changer for international payments. These automated agreements eliminate the need for intermediaries, significantly reducing processing time and costs. When specific pre-defined conditions are met, the smart contract automatically executes the payment, ensuring timely and accurate settlement. For example, a smart contract could be programmed to release payment to a supplier upon verification of goods delivery, eliminating delays caused by manual checks and paperwork. This automation not only streamlines the payment process but also reduces the risk of human error and potential delays.
Comparison of Blockchain-Based Solutions and Traditional Methods
Traditional cross-border payment methods often involve multiple intermediaries (banks, payment processors), leading to increased processing times and higher fees. Blockchain-based solutions, however, offer a more streamlined approach, reducing both time and cost.
| Method | Processing Time | Fees | Security Level |
|---|---|---|---|
| Traditional Banking System | 3-5 business days or more | High (often includes correspondent bank fees and exchange rate markups) | Moderate (vulnerable to fraud and errors) |
| Blockchain-based Payment System | Minutes to hours | Lower (reduced intermediary fees) | High (cryptographic security and distributed ledger) |
Note: Processing times and fees can vary depending on the specific blockchain solution and transaction details. The security level reflects the relative resilience to fraud and errors, not absolute invulnerability.
Blockchain’s Impact on Financial Inclusion
Blockchain technology offers a revolutionary approach to financial inclusion, particularly for underserved populations in developing countries who lack access to traditional banking systems. Its decentralized and transparent nature allows for secure and efficient transactions, bypassing the need for intermediaries that often create barriers to entry for these communities. This unlocks opportunities for economic empowerment and improves overall financial well-being.
Blockchain facilitates access to financial services by creating a secure and transparent system for managing transactions and identities. This is particularly beneficial in regions with weak regulatory frameworks or limited infrastructure where traditional financial institutions struggle to operate effectively. The inherent security features of blockchain technology minimize the risks associated with fraud and theft, encouraging greater participation in the financial system.
Blockchain’s Role in Microfinance
Blockchain’s impact on microfinance is significant. Traditional microfinance institutions often face challenges in reaching remote populations and managing loan disbursements and repayments efficiently. Blockchain-based platforms streamline these processes, reducing operational costs and increasing transparency. They provide a secure and auditable record of transactions, improving trust between lenders and borrowers. This enhanced trust fosters greater financial inclusion by making it easier for individuals with limited credit history to access small loans and build their creditworthiness. For example, imagine a farmer in a remote village who needs a loan to buy seeds. With a blockchain-based microfinance platform, they can easily apply for a loan, provide necessary information, and receive funds directly, without relying on intermediaries who may charge high fees or demand bribes. The entire process is recorded on the blockchain, ensuring transparency and accountability.
Examples of Blockchain-Based Microfinance Platforms
Several organizations are leveraging blockchain technology to create innovative microfinance solutions. One notable example is a platform that uses smart contracts to automate loan disbursement and repayment processes. These smart contracts automatically release funds to borrowers upon meeting pre-defined conditions and trigger automatic repayments based on agreed-upon schedules. This reduces the administrative burden on both lenders and borrowers, making microfinance more accessible and efficient. Another example involves a platform that uses blockchain to create a decentralized credit scoring system. This system leverages data from various sources, including mobile money transactions and social networks, to assess the creditworthiness of individuals who may lack traditional credit history. This allows lenders to make more informed lending decisions and expand access to credit for a wider range of individuals. These platforms not only facilitate access to credit but also foster financial literacy by providing borrowers with clear and accessible information about their loans and repayment schedules. The transparency provided by the blockchain also enhances accountability and reduces the potential for exploitation.
Specific Blockchain Applications for Cross-Border Payments
Blockchain technology isn’t just a buzzword; it’s actively reshaping the landscape of international finance. Several platforms leverage its decentralized and transparent nature to streamline cross-border payments, offering faster, cheaper, and more secure transactions compared to traditional methods. This section dives into specific examples and illustrates how these systems work in practice.
Several blockchain platforms are specifically designed to facilitate cross-border payments. Each offers unique features and functionalities, catering to different needs and priorities within the financial ecosystem. Understanding their strengths and weaknesses is crucial for choosing the most appropriate solution for a particular use case.
RippleNet’s Functionality in Cross-Border Payments
RippleNet, Ripple’s payment network, utilizes the XRP cryptocurrency alongside its blockchain technology to enable near real-time, low-cost international transfers. It acts as a bridge between different financial institutions, allowing them to send and receive payments quickly and efficiently. Unlike some other blockchain solutions, RippleNet focuses on interoperability with existing banking infrastructure, making it attractive to established players in the financial industry. Its system employs a unique consensus mechanism, allowing for faster transaction speeds compared to some other public blockchains. For example, a bank in the US could send funds to a bank in Japan through RippleNet, bypassing the complexities and delays of the correspondent banking system. This process typically involves multiple intermediaries, increasing transaction time and costs. RippleNet aims to reduce these inefficiencies by streamlining the process and utilizing XRP for faster settlement.
Hypothetical Cross-Border Payment Using a Blockchain-Based System
Let’s imagine Maria, a freelance graphic designer in Argentina, needs to receive payment from a client, David, in Germany. David hired Maria to design his company’s logo, and the agreed-upon payment is €500. Instead of using traditional banking methods that can take days and incur hefty fees, they decide to use a blockchain-based payment system like Stellar.
- David initiates the payment through a Stellar-integrated platform, specifying the amount (€500) and Maria’s Stellar address.
- The platform converts the Euros to Stellar Lumens (XLM), Stellar’s native cryptocurrency, at the current exchange rate.
- The transaction is broadcast to the Stellar network and validated by its decentralized network of nodes.
- The transaction is recorded on the Stellar blockchain, providing a transparent and immutable record of the payment.
- Maria receives the XLM in her Stellar wallet. She can then convert the XLM back to Argentinian Pesos (ARS) through a Stellar exchange if needed.
This entire process could take only a few minutes, significantly faster than traditional methods which might take several days due to intermediary banks and international regulations. The transparency of the blockchain also ensures both parties have a verifiable record of the transaction.
Scalability and Interoperability Challenges of Blockchain Solutions for International Payments
While blockchain offers numerous advantages, scaling to handle the volume of global transactions and ensuring interoperability between different systems remain significant challenges. Public blockchains like Bitcoin, while secure, often suffer from scalability issues due to slow transaction speeds and high fees during periods of network congestion. Private blockchains offer better scalability but may compromise on decentralization and transparency. Interoperability is another hurdle; different blockchain platforms often lack the ability to communicate seamlessly with each other, hindering the smooth flow of cross-border payments. Solutions like RippleNet aim to address these challenges through strategic partnerships and the use of intermediary tokens, but widespread adoption and standardization are still needed to fully realize the potential of blockchain in global finance.
Regulatory and Security Considerations
Source: medium.com
The exciting potential of blockchain for cross-border payments and financial inclusion doesn’t exist in a vacuum. A robust regulatory framework and strong security measures are crucial for widespread adoption and to ensure trust in the system. Navigating the complexities of international regulations and mitigating inherent security risks are key challenges that need addressing.
The regulatory landscape surrounding blockchain-based cross-border payments is still evolving, varying significantly across jurisdictions. Different countries have different approaches, ranging from outright bans to cautious experimentation with regulatory sandboxes. This lack of harmonization presents a significant hurdle for businesses looking to operate internationally. Furthermore, existing regulations designed for traditional financial systems may not be entirely suitable for the decentralized nature of blockchain technology. This creates uncertainty and necessitates a collaborative approach between regulators and blockchain developers to establish clear, consistent guidelines.
Regulatory Landscape for Blockchain-Based Cross-Border Payments
The global regulatory landscape for blockchain-based cross-border payments is fragmented. Some countries, like Singapore and Switzerland, have adopted a more progressive approach, establishing regulatory frameworks specifically designed to encourage blockchain innovation. Others maintain a more cautious stance, prioritizing risk mitigation and consumer protection. The European Union, for example, is working on comprehensive regulations like the Markets in Crypto-Assets (MiCA) regulation, which aims to provide a unified regulatory framework for crypto assets within the EU. However, the lack of global harmonization continues to hinder the seamless adoption of blockchain technology for cross-border payments. This necessitates a collaborative effort among international regulatory bodies to establish common standards and guidelines. A key area of focus is establishing clear guidelines on anti-money laundering (AML) and know-your-customer (KYC) compliance within blockchain-based systems.
Security Mechanisms in Blockchain Technology
Blockchain’s inherent security features, such as cryptography and decentralization, offer significant advantages over traditional systems. Cryptography secures transactions by encrypting data, making it virtually impossible for unauthorized individuals to access or alter information. The decentralized nature of blockchain means that there’s no single point of failure; data is distributed across multiple nodes, making the system highly resilient to attacks. Furthermore, the immutable nature of the blockchain ensures that once a transaction is recorded, it cannot be altered or deleted, enhancing data integrity and auditability. Smart contracts, self-executing contracts with the terms of the agreement between buyer and seller being directly written into lines of code, automate and streamline transactions, reducing the risk of human error and fraud.
Potential Risks and Vulnerabilities
Despite the inherent security of blockchain, certain risks and vulnerabilities remain. Smart contract vulnerabilities, for example, can be exploited by malicious actors to gain unauthorized access to funds or manipulate transactions. 51% attacks, where a malicious actor controls more than half of the network’s computing power, can compromise the integrity of the blockchain. While unlikely in established, large-scale blockchains, it remains a theoretical risk. Furthermore, the anonymity associated with some cryptocurrencies can be exploited for illicit activities, such as money laundering and terrorist financing. Robust KYC/AML procedures and ongoing security audits are crucial to mitigate these risks. Another potential vulnerability lies in the reliance on third-party custodians for private keys. If these custodians are compromised, it could lead to significant financial losses. Therefore, robust security protocols and regular audits are essential to maintain the integrity and security of blockchain-based cross-border payment systems.
Future Trends and Potential
The future of cross-border payments and financial inclusion is inextricably linked to the continued evolution and adoption of blockchain technology. We’re poised for a significant shift, driven by advancements in scalability, interoperability, and regulatory clarity, leading to a more efficient, transparent, and inclusive global financial system. This section explores the key trends shaping this exciting landscape.
Blockchain’s potential to revolutionize cross-border payments extends far beyond its current applications. The technology’s inherent ability to streamline processes, reduce costs, and enhance security will continue to attract both businesses and individuals seeking faster and more reliable international transactions. This is particularly true in regions currently underserved by traditional financial infrastructure.
Increased Scalability and Interoperability
Improvements in blockchain scalability are crucial for widespread adoption. Solutions like sharding and layer-2 scaling protocols are addressing the limitations of older blockchain networks, allowing for faster transaction processing and lower fees. Simultaneously, efforts towards greater interoperability between different blockchain networks are paving the way for a more seamless and unified global payment system. Imagine a future where payments can flow effortlessly across various blockchain platforms, without the need for complex conversions or intermediaries. This interconnectedness will be a game-changer, facilitating frictionless cross-border transactions. For example, the development of cross-chain communication protocols is already making this vision a reality.
Enhanced Privacy and Security, How Blockchain is Facilitating Cross-Border Payments and Financial Inclusion
Blockchain’s inherent security features, such as cryptographic hashing and distributed ledger technology, will continue to be a major draw for cross-border payments. However, future advancements will focus on enhancing user privacy. Techniques like zero-knowledge proofs and homomorphic encryption will allow for secure transactions without revealing sensitive personal information. This is vital for building trust and encouraging wider adoption, especially in jurisdictions with stringent data protection regulations. This increased focus on privacy will be crucial for maintaining the confidence of users and regulators alike.
Central Bank Digital Currencies (CBDCs) and Cross-Border Payments
The rise of CBDCs presents a significant opportunity to transform cross-border payment systems. CBDCs, being digital representations of fiat currencies issued by central banks, offer the potential for faster, cheaper, and more secure international transactions. A hypothetical example could be a scenario where a central bank in country A issues a CBDC, and a central bank in country B does the same. These two CBDCs could interact directly, facilitating near-instantaneous transfers between individuals and businesses in both countries, bypassing traditional correspondent banking networks. This direct interaction could drastically reduce transaction costs and processing times, fostering greater financial inclusion. Projects like the mBridge initiative, a cross-border CBDC pilot project involving several central banks, already demonstrate the feasibility of this approach. While challenges remain, the potential benefits are compelling.
Case Studies
Real-world examples showcase blockchain’s transformative power in cross-border payments. These case studies highlight how blockchain technology overcomes traditional hurdles, leading to faster, cheaper, and more transparent transactions, ultimately fostering financial inclusion. Let’s dive into some successful implementations.
RippleNet’s Impact on Cross-Border Payments
RippleNet, a real-time gross settlement system, leverages blockchain technology to facilitate faster and cheaper cross-border payments. Many financial institutions globally utilize RippleNet’s network for international money transfers.
- Challenge Addressed: Slow, expensive, and opaque traditional cross-border payment systems, often involving multiple intermediaries and lengthy processing times.
- Solution Implemented: RippleNet utilizes a distributed ledger to track transactions in real-time, reducing reliance on intermediaries and streamlining the process. Its XRP cryptocurrency can also be used for faster settlement.
- Results Achieved: Significant reduction in transaction processing time (from days to seconds in some cases), lower fees, and increased transparency. Improved efficiency has led to increased adoption by banks and payment providers worldwide.
The success of RippleNet is attributed to its scalability, adaptability to existing financial infrastructure, and focus on collaboration with financial institutions. Its ability to integrate with existing systems made adoption smoother, accelerating its widespread implementation.
Stellar’s Role in Enhancing Financial Inclusion
Stellar, an open-source, decentralized payment network, aims to connect banks, payment providers, and individuals globally. Its focus is on making financial services accessible to underserved populations.
- Challenge Addressed: Lack of access to financial services in developing countries, often due to high transaction costs and limited infrastructure.
- Solution Implemented: Stellar provides a low-cost, fast, and reliable platform for cross-border payments, enabling individuals and businesses in developing nations to access financial services more easily. Mobile money integration is a key feature.
- Results Achieved: Increased access to financial services for previously unbanked populations. Faster and cheaper remittances have improved the lives of many individuals, particularly migrant workers sending money home.
Stellar’s success stems from its open-source nature, promoting collaboration and innovation. Its focus on mobile money integration, tailored to the needs of developing economies, has proven crucial for its widespread adoption.
IBM’s Blockchain-Based Trade Finance Platform
IBM has developed blockchain-based platforms for trade finance, aiming to streamline and secure international trade transactions. These platforms offer improved transparency and efficiency in letter of credit processing and other trade finance operations.
- Challenge Addressed: Inefficient and paper-heavy processes in trade finance, leading to delays, increased costs, and fraud risks.
- Solution Implemented: IBM’s blockchain platforms digitize trade documents, creating a shared, secure, and transparent ledger accessible to all parties involved. This streamlines the process and reduces the need for manual verification.
- Results Achieved: Faster processing times for letters of credit and other trade finance instruments, reduced costs, and improved security through enhanced traceability and reduced fraud risks.
The success of IBM’s platform highlights the potential of blockchain to transform complex, multi-party processes like trade finance. Collaboration with key players in the industry and a focus on practical applications within existing workflows have been vital to its adoption.
Closing Summary

Source: ac.in
Blockchain’s impact on cross-border payments and financial inclusion is undeniable. While challenges remain – regulatory hurdles and scalability issues among them – the potential benefits are too significant to ignore. From faster and cheaper remittances to the expansion of microfinance opportunities, blockchain is paving the way for a more equitable and accessible global financial system. As the technology matures and regulations evolve, we can expect even more transformative changes in the years to come. The future of finance is decentralized, and it’s already here.
