How Blockchain is Enhancing Transparency in Government: Forget shadowy backroom deals and opaque processes. Blockchain, that revolutionary tech everyone’s buzzing about, is poised to shake up government operations, bringing a level of transparency that was once unthinkable. Imagine a world where every government transaction, from procurement contracts to land registrations, is permanently recorded on a secure, immutable ledger – open for all to see. That’s the promise of blockchain, and it’s already starting to deliver.
This transformative technology, built on a foundation of decentralization and cryptographic security, tackles head-on the age-old issues of corruption, inefficiency, and lack of accountability that plague many governmental systems. By leveraging blockchain’s inherent transparency and immutability, we can build more trustworthy, responsive, and accountable governments. This article dives deep into how blockchain is reshaping various aspects of governance, exploring its applications in public procurement, land registry, voting systems, and public records management, while also acknowledging the challenges and limitations that need to be addressed.
Blockchain’s Potential in Government
Imagine a government where every transaction, every decision, every piece of data is transparent and verifiable. That’s the promise of blockchain technology, a revolutionary system that could reshape how governments operate and interact with their citizens. Its decentralized, secure, and immutable nature offers a powerful antidote to many of the transparency challenges plaguing governments worldwide.
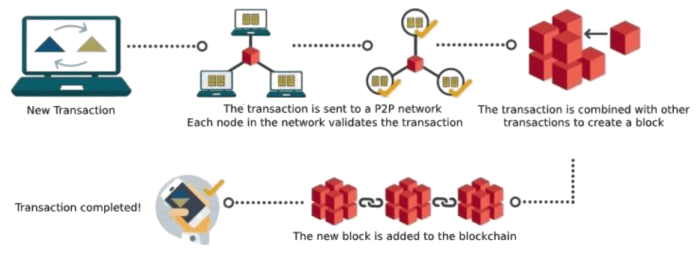
Blockchain’s core principle lies in its distributed ledger system. Instead of a single, centralized database, information is replicated across numerous computers, creating a tamper-proof record. This immutability – the inability to alter past records – is key to building trust and accountability. Furthermore, the transparent nature of the blockchain allows anyone with access to view the transaction history, fostering public scrutiny and reducing the potential for corruption or manipulation. This contrasts sharply with traditional systems often characterized by opaque processes and limited public access to information.
Blockchain Applications in Government Sectors, How Blockchain is Enhancing Transparency in Government
Blockchain’s transformative potential extends across various government sectors. Its inherent transparency and security can significantly improve efficiency, accountability, and public trust. Below, we highlight some key areas where blockchain can make a substantial impact:
| Sector | Current Transparency Issue | Potential Blockchain Solution | Expected Improvement |
|---|---|---|---|
| Land Registry | Fraudulent land transactions, opaque record-keeping, lengthy processing times. | A blockchain-based land registry storing secure and immutable records of land ownership. All transactions are recorded transparently and can be verified by anyone. | Reduced fraud, faster transaction processing, increased public trust in land ownership records. For example, the Swedish Land Registry is exploring blockchain solutions to streamline its processes. |
| Supply Chain Management (Public Procurement) | Lack of traceability in the procurement process, potential for corruption and favoritism. | Tracking the entire procurement process on a blockchain, from tendering to payment, providing complete transparency to all stakeholders. | Increased accountability, reduced corruption, improved efficiency in public procurement. Imagine a system where every step of a public works project, from bidding to material sourcing, is visible to the public. |
| Voting Systems | Concerns about election fraud, lack of verifiable audit trails. | Secure and transparent voting systems using blockchain technology to record votes immutably and prevent manipulation. | Increased voter confidence, reduced concerns about election integrity, faster and more accurate vote counting. While widespread adoption is still under development, several pilot projects are demonstrating the potential. |
| Healthcare Data Management | Data breaches, difficulties in data sharing between healthcare providers, lack of patient control over their data. | Secure and permissioned blockchain networks allowing patients to control access to their medical records while enabling authorized sharing between healthcare providers. | Improved data security, better patient control over their health information, enhanced interoperability between healthcare systems. This can lead to better coordinated care and potentially reduced medical errors. |
Enhancing Transparency in Public Procurement
Public procurement, the process by which governments buy goods and services, is often shrouded in secrecy and susceptible to corruption. Billions of dollars are spent annually globally on public contracts, making it a prime target for unethical practices. However, the immutable and transparent nature of blockchain technology offers a powerful solution to increase accountability and reduce the risk of fraud in this crucial area.
Blockchain’s decentralized and cryptographically secure ledger can revolutionize public procurement by providing an auditable trail of every transaction and decision. This enhanced transparency empowers citizens to monitor the process, fostering trust in government institutions and promoting efficient resource allocation. Imagine a system where every bid, negotiation, and contract award is publicly verifiable, leaving no room for hidden deals or backroom negotiations.
Blockchain’s Role in Tracking Procurement Stages
Blockchain can meticulously track every stage of the public procurement process, from the initial tendering phase to the final contract award. This comprehensive tracking ensures complete visibility and accountability throughout the entire lifecycle.
A blockchain-based system would record all relevant information, including the tender specifications, the identities of bidders, the submitted bids themselves (encrypted if necessary to protect sensitive commercial information), the evaluation criteria, the evaluation scores, and the final contract award. Each transaction is time-stamped and cryptographically linked to the previous one, creating an immutable and tamper-proof record.
Blockchain’s impact on government transparency is undeniable, creating immutable records of transactions and decisions. This same drive for visual clarity extends to other fields, like design, where visualizing projects before construction is key; check out how Augmented Reality is Shaping the Future of Design and Architecture for a glimpse into the future. Ultimately, both technologies share a common goal: making complex information readily accessible and understandable, fostering trust and accountability.
Reducing Corruption and Increasing Accountability
The use of blockchain in public procurement directly addresses several key vulnerabilities that contribute to corruption. By making the entire process transparent and auditable, it significantly reduces the opportunities for bribery, collusion, and favoritism. Furthermore, the decentralized nature of blockchain makes it extremely difficult for any single entity to manipulate the system.
For instance, imagine a scenario where a government official attempts to favor a specific bidder. With a blockchain system in place, any attempt to alter bid scores or manipulate the evaluation process would be immediately detectable, as it would break the chain of cryptographic hashes. This level of transparency not only deters corruption but also facilitates swift investigation and prosecution of any wrongdoing.
Simplified Blockchain-Based Procurement System Flowchart
The following flowchart illustrates a simplified version of how a blockchain-based procurement system could operate:
- Tender Publication: The government publishes tender specifications on the blockchain, ensuring all potential bidders have access to the same information.
- Bid Submission: Bidders submit their bids, which are recorded as transactions on the blockchain. Hashing techniques can be used to ensure the integrity and confidentiality of bid details while maintaining verification.
- Bid Evaluation: A panel of evaluators assesses the bids according to predefined criteria. Their evaluations are also recorded as blockchain transactions.
- Contract Award: The winning bid is selected and the contract award is recorded on the blockchain. This includes details of the awarded contract and its value.
- Contract Execution and Payment: Progress updates and payment releases are recorded on the blockchain, providing real-time transparency into the contract fulfillment.
Improving Transparency in Land Registry
Land ownership is a fundamental right, yet globally, opaque land registration systems fuel corruption, disputes, and hinder economic development. Blockchain technology, with its inherent immutability and transparency, offers a powerful solution to modernize and secure land records, benefiting both governments and citizens. By creating a shared, verifiable ledger of land ownership, blockchain can dramatically improve the efficiency and transparency of land administration.
Blockchain’s potential to streamline land registration stems from its decentralized and tamper-proof nature. Traditional land registries often rely on centralized databases vulnerable to fraud, errors, and manipulation. Paper-based systems are particularly susceptible to loss, damage, and inefficient retrieval processes. In contrast, a blockchain-based system records land transactions in a distributed ledger, making the data accessible to authorized parties while maintaining its integrity. This enhanced transparency reduces the potential for corruption and simplifies the verification of ownership claims.
Comparison of Traditional and Blockchain-Based Land Registration Systems
The key difference lies in the accessibility and security of land records. Traditional systems often involve multiple intermediaries, leading to delays and increased costs. Information may be scattered across different departments, making it difficult to obtain a complete and accurate picture of land ownership. Blockchain, on the other hand, provides a single, immutable record accessible to all authorized users, significantly reducing processing time and eliminating the need for multiple verifications. This enhanced transparency also empowers citizens, enabling them to easily verify the authenticity of land titles and reducing the risk of fraudulent transactions.
| Country | System Name | Key Features | Impact on Transparency |
|---|---|---|---|
| Georgia | National Agency of Public Registry (NAPR) | Digitalization of land registry, integration with blockchain for secure record-keeping. | Reduced land disputes, increased efficiency in land registration processes, improved access to land information for citizens. |
| Sweden | Various pilot projects | Exploration of blockchain for secure land title transfer and improved data management. | Improved data security and reduced risk of fraud in land transactions. Early stage, but promising results in increased data integrity. |
| Honduras | National Institute of Agrarian Reform (INA) | Pilot program using blockchain to record land titles, particularly for rural communities. | Increased transparency and security in land ownership for marginalized communities, reducing disputes over land rights. |
| Rwanda | Land Registry initiative | Utilizing blockchain technology to create a secure and transparent land registry system. | Improved efficiency in land registration and reduced potential for corruption. Aims to enhance access to land information for citizens. |
Strengthening Transparency in Voting Systems
Source: mdpi.com
Blockchain technology, with its inherent immutability and transparency, offers a compelling solution to enhance the security and trustworthiness of elections. Its decentralized nature makes it resistant to manipulation, potentially revolutionizing how we conduct and perceive voting processes. By recording votes on a distributed ledger, blockchain can provide a verifiable audit trail, fostering greater public confidence in election outcomes.
Blockchain’s ability to create a secure and transparent voting system stems from its fundamental characteristics. Each vote is recorded as a block, cryptographically linked to previous blocks, forming an immutable chain. This prevents unauthorized alteration or deletion of votes after they are cast. Furthermore, the decentralized nature of the blockchain means no single entity controls the voting data, mitigating the risk of centralized manipulation.
Blockchain’s Role in Preventing Voter Fraud
The decentralized and immutable nature of blockchain significantly reduces the opportunities for voter fraud. Traditional voting systems, often reliant on centralized servers and potentially vulnerable to hacking or manipulation, are susceptible to various forms of fraud, including ballot stuffing, double voting, and vote rigging. A blockchain-based system, however, makes these activities extremely difficult, if not impossible, to execute undetected. The cryptographic hashing and distributed ledger ensure that any attempt to alter votes would be immediately detectable by the network. This increased security leads to higher public trust in the integrity of the election process. For example, a hypothetical scenario in a small town election could illustrate this. Imagine 100 votes cast. If even one vote is tampered with, the entire chain would be flagged as compromised, alerting election officials and observers. This immediate detection significantly reduces the potential impact of fraudulent activities.
Conceptual Illustration of a Blockchain-Based Voting System
Imagine a system where each voter receives a unique digital identity, verified through secure methods like biometric authentication. When a voter casts their ballot, the choice is encrypted and added as a block to the blockchain. This block contains the encrypted vote, the voter’s unique identifier (but not their personal details), and a timestamp. The encryption ensures vote secrecy while the blockchain guarantees immutability. After the voting period closes, authorized election officials can decrypt the votes using a secure, multi-party computation method, ensuring that no single entity has access to individual votes while still allowing the aggregate results to be tallied accurately. The entire process is recorded on the blockchain, creating a publicly auditable record that can be independently verified. The system includes mechanisms for detecting and handling potential discrepancies or irregularities, further enhancing its integrity. The transparency of the blockchain allows for independent verification of the process by external auditors and citizens alike, fostering public trust and accountability.
Boosting Transparency in Public Records Management
Public records – birth certificates, property deeds, marriage licenses, and countless other documents – are the bedrock of a functioning society. Easy access to accurate and verifiable public records is crucial for citizens to exercise their rights, businesses to operate legally, and researchers to understand societal trends. However, traditional methods of managing these records often fall short, creating significant hurdles for transparency and efficiency.
Traditional systems for managing public records frequently suffer from a lack of standardization, scattered storage locations, and cumbersome access procedures. This often leads to delays, inconsistencies, and even outright corruption. Imagine trying to track down a property deed from decades ago, navigating dusty archives and potentially encountering incomplete or illegible records. This is the reality for many individuals and organizations interacting with government agencies worldwide. The sheer volume of paper documents, coupled with inefficient indexing and retrieval systems, makes the process both time-consuming and frustrating. Security concerns are also significant, with the risk of physical damage, theft, or even intentional alteration of vital documents.
Challenges in Accessing and Managing Public Records Using Traditional Methods
The challenges inherent in traditional public records management systems are multifaceted. Data is often siloed across different government agencies and departments, making it difficult to obtain a complete picture. The lack of a centralized, easily searchable database necessitates laborious manual searches, often involving multiple agencies and significant time investment. Furthermore, the reliance on paper-based systems increases the risk of document loss, damage, and alteration. The lack of standardized data formats also hinders interoperability and data analysis, limiting the potential for leveraging this information for broader societal benefit. Finally, security vulnerabilities are prevalent, with physical documents susceptible to theft, damage, and unauthorized access.
How a Blockchain-Based System Can Improve Access to and Management of Public Records
A blockchain-based system offers a compelling solution to many of these challenges. The immutable nature of blockchain technology ensures the integrity and authenticity of records, preventing unauthorized alterations or deletions. By storing records on a distributed ledger, accessibility is greatly enhanced, as authorized users can access the information securely from anywhere with an internet connection. A well-designed system can also incorporate smart contracts to automate processes, such as record verification or the release of information based on pre-defined criteria. Moreover, blockchain can facilitate interoperability between different government agencies, allowing for seamless data sharing and a more comprehensive view of public records. The enhanced security and transparency fostered by blockchain can significantly reduce instances of fraud and corruption.
Security and Accessibility Comparison of Traditional and Blockchain-Based Public Records Systems
Traditional public records systems, often reliant on physical storage and centralized databases, are vulnerable to various security threats, including physical theft, data breaches, and human error. Accessibility is often limited by geographical location, operating hours, and bureaucratic procedures. In contrast, a blockchain-based system offers significantly enhanced security through cryptography and distributed storage. The decentralized nature of blockchain minimizes the risk of a single point of failure, while cryptographic hashing ensures the integrity of each record. Accessibility is dramatically improved, with authorized users gaining access anytime, anywhere, subject to appropriate authorization protocols. The inherent transparency of blockchain also provides an audit trail, enhancing accountability and trust in the system. For example, a land registry system built on blockchain would make it virtually impossible to forge land titles or create duplicate ownership claims, thereby protecting property rights and fostering economic stability. Similarly, a blockchain-based system for managing birth certificates would provide tamper-proof records, accessible to citizens and government agencies alike.
Addressing Challenges and Limitations: How Blockchain Is Enhancing Transparency In Government
Implementing blockchain technology in government isn’t a simple case of flipping a switch. It requires careful consideration of various technical, security, and legal hurdles. While the potential benefits are significant, a realistic assessment of the challenges is crucial for successful adoption. Ignoring these limitations could lead to costly failures and erode public trust.
The integration of blockchain into existing governmental systems presents a complex array of interconnected obstacles. These range from the technical intricacies of data migration and system compatibility to the need for robust security protocols and a clear legal framework to govern its use. Successfully navigating these challenges requires a phased approach, prioritizing projects with clear objectives and measurable outcomes.
Technical Challenges in Blockchain Government Implementation
The technical hurdles to blockchain adoption in government are substantial. Existing government systems are often legacy systems, built on outdated technologies and lacking the interoperability needed for seamless blockchain integration. Data migration, ensuring data integrity during the transition, and the need for specialized skills to manage and maintain blockchain networks are all significant challenges. Furthermore, scalability remains a concern, particularly for large-scale government applications handling massive datasets. For example, a national land registry system using blockchain would require a network capable of handling millions of transactions efficiently and securely. The complexity of integrating blockchain with existing systems, requiring significant investment in infrastructure and expertise, also poses a significant challenge. The need for specialized hardware and software, along with ongoing maintenance and updates, adds to the overall cost and complexity.
Potential Risks Associated with Blockchain Adoption in Government and Mitigation Strategies
Security breaches, data corruption, and the potential for malicious actors to exploit vulnerabilities are significant risks associated with blockchain implementation in government. However, these risks can be mitigated through robust security protocols, regular audits, and rigorous testing. For instance, implementing multi-signature authorization for critical transactions can significantly reduce the risk of unauthorized access. Furthermore, careful selection of consensus mechanisms and the use of encryption techniques can enhance the security and integrity of the blockchain network. Regular security audits by independent third parties can help identify and address potential vulnerabilities before they can be exploited. It’s also crucial to develop comprehensive incident response plans to effectively manage and mitigate any security breaches that may occur. A layered approach to security, combining technical safeguards with strong governance and risk management practices, is essential.
Regulatory and Legal Frameworks for Blockchain in Government
The absence of clear legal and regulatory frameworks poses a major obstacle to the widespread adoption of blockchain technology in government. Existing laws and regulations may not adequately address the unique characteristics of blockchain, creating uncertainty and hindering innovation. Clear guidelines are needed on data privacy, data ownership, and the legal enforceability of blockchain-based records. Furthermore, mechanisms for dispute resolution and liability in case of blockchain-related errors or malfunctions need to be established. The development of robust legal frameworks should consider international best practices and ensure compatibility with existing legal systems. Regulatory sandboxes, where blockchain solutions can be tested and evaluated in a controlled environment, can be valuable tools for promoting responsible innovation and informing the development of appropriate regulations. A collaborative approach, involving government agencies, technology providers, and legal experts, is essential for creating a regulatory environment that fosters innovation while mitigating risks.
Case Studies of Blockchain in Government Transparency
Blockchain technology’s potential to revolutionize government transparency is no longer theoretical; real-world applications are proving its effectiveness. Several governments and organizations have successfully implemented blockchain-based systems, resulting in increased citizen trust and more efficient public services. These case studies illustrate the tangible benefits and highlight crucial lessons learned during implementation.
Successful Blockchain Projects Enhancing Government Transparency
Examining successful blockchain implementations in government reveals valuable insights into its practical application and impact. Several projects globally have demonstrated the positive effects of leveraging this technology for greater transparency and accountability. The following examples showcase the diversity of applications and the positive outcomes achieved.
| Project Name | Location | Key Outcomes | Lessons Learned |
|---|---|---|---|
| Estonia’s e-Residency Program | Estonia | Increased efficiency in issuing digital identities and providing access to government services for citizens and businesses worldwide. Enhanced security and reduced fraud. Improved transparency in government processes. | Careful planning and strong collaboration between government agencies and technology providers are crucial for successful implementation. Robust cybersecurity measures are essential to protect sensitive data. |
| Dubai’s Blockchain Strategy | Dubai, UAE | Significant reduction in document processing time and costs across various government departments. Improved data security and integrity. Enhanced transparency in land registration and other public services. | The success depends on strong political will and commitment from leadership. Public awareness and education are vital for widespread adoption and acceptance. |
| Georgia’s Land Registry System | Georgia | Elimination of land fraud and disputes. Improved access to land information for citizens. Increased efficiency in land registration processes. Reduced corruption. | Effective integration with existing systems is crucial. A phased approach to implementation can minimize disruption and risks. Continuous monitoring and evaluation are essential for long-term success. |
| West Virginia’s Blockchain-Based Voting System (Pilot Program) | West Virginia, USA | Improved security and auditability of the voting process. Increased voter confidence in the integrity of election results (in the pilot program). While a full-scale implementation is still pending, the pilot provided valuable data. | Addressing scalability challenges for large-scale elections is paramount. Ensuring accessibility for all voters, regardless of technological literacy, is crucial. Robust security measures are paramount to prevent manipulation or cyberattacks. |
Concluding Remarks
The integration of blockchain technology into government operations isn’t just a futuristic dream; it’s a tangible reality with the potential to revolutionize how we interact with and perceive our governing bodies. While challenges remain, the benefits of increased transparency, accountability, and efficiency are too significant to ignore. As blockchain technology continues to mature and regulatory frameworks adapt, we can expect to see even more widespread adoption, leading to a more open, honest, and ultimately, more effective government – a win for citizens and policymakers alike. The future of governance is transparent, and it’s powered by blockchain.
