How Blockchain is Enabling Decentralized Finance Solutions? It’s the question buzzing through the fintech world, a revolution quietly reshaping how we interact with money. Forget stuffy banks and complicated processes; DeFi, powered by blockchain’s transparent and secure ledger, is democratizing finance. This isn’t just about crypto; it’s about creating a fairer, more accessible, and efficient financial system for everyone.
We’ll dive deep into the mechanics of DeFi, exploring everything from smart contracts and decentralized exchanges (DEXs) to the exciting possibilities – and potential pitfalls – of this rapidly evolving landscape. Think of it as your no-nonsense guide to understanding the future of money, explained in a way that even your grandma (maybe) could grasp.
Introduction to Decentralized Finance (DeFi)
Source: mdpi-res.com
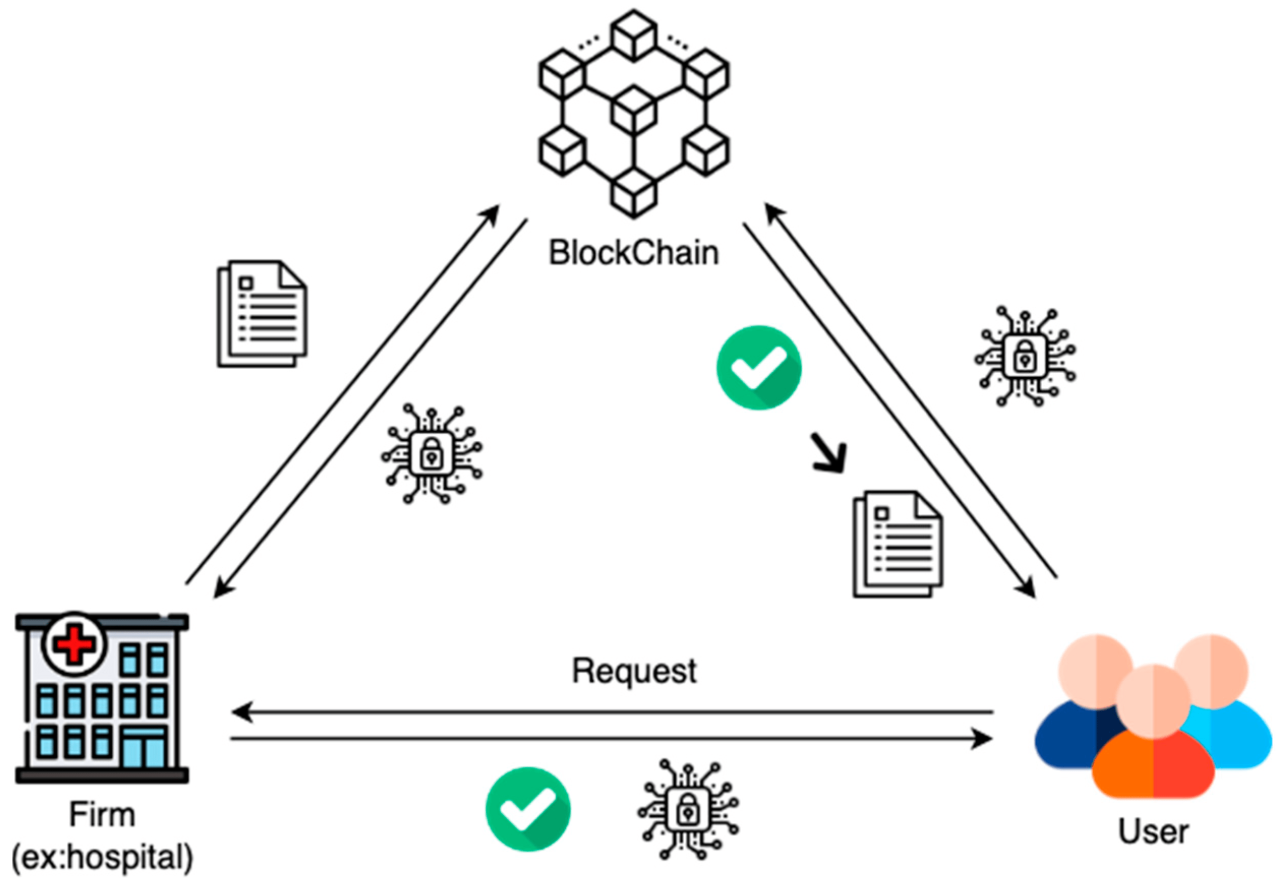
Decentralized Finance, or DeFi, is revolutionizing the financial world by leveraging blockchain technology to create open, transparent, and permissionless financial systems. It aims to recreate traditional financial services in a way that cuts out intermediaries, increases efficiency, and empowers users with greater control over their assets. This shift promises a more inclusive and accessible financial landscape.
DeFi operates on core principles of decentralization, transparency, and programmability. Decentralization means no single entity controls the system; instead, it’s governed by code and the community. Transparency stems from the public and immutable nature of blockchain transactions, allowing anyone to audit the system’s activity. Programmability refers to the ability to create and deploy sophisticated financial applications using smart contracts, automated self-executing contracts with the terms of the agreement between buyer and seller being directly written into lines of code. This enables the creation of innovative financial products and services previously unimaginable.
Traditional finance relies heavily on centralized intermediaries like banks, brokers, and clearinghouses. These intermediaries control access to financial services, often imposing high fees, lengthy processing times, and limited accessibility, particularly for those in underserved communities. Furthermore, these centralized systems are susceptible to single points of failure, censorship, and fraud. DeFi aims to address these limitations by providing a more efficient, transparent, and inclusive alternative.
DeFi Applications
DeFi offers a range of applications that are reshaping the financial landscape. These applications leverage smart contracts to automate processes and create new opportunities for users. Some prominent examples include decentralized exchanges (DEXs), lending and borrowing platforms, stablecoins, and yield farming. DEXs allow users to trade cryptocurrencies without relying on centralized exchanges, offering greater control and potentially lower fees. Lending and borrowing platforms enable users to lend or borrow cryptocurrencies without intermediaries, earning interest on their assets or accessing capital at potentially more favorable rates than traditional institutions. Stablecoins provide price stability in the volatile cryptocurrency market, acting as a bridge between fiat currencies and cryptocurrencies. Yield farming involves lending and borrowing cryptocurrencies to earn interest or rewards, allowing users to generate passive income. For instance, Aave and Compound are prominent examples of DeFi lending and borrowing platforms, facilitating millions of dollars in lending and borrowing transactions daily. Uniswap is a popular DEX that has processed billions of dollars in trading volume. These examples illustrate the scale and impact of DeFi applications.
Blockchain Technology’s Role in DeFi
Decentralized finance (DeFi) wouldn’t exist without blockchain technology. It’s the bedrock upon which this revolutionary financial system is built, providing the essential infrastructure for trust, transparency, and automation. Think of it as the secure, shared ledger that makes all the magic happen.
Blockchain technology facilitates trust and transparency in DeFi by creating a publicly auditable and immutable record of all transactions. This eliminates the need for intermediaries like banks, reducing costs and increasing efficiency. Every transaction is cryptographically secured and verifiable by anyone on the network, making manipulation incredibly difficult. This inherent transparency fosters trust among participants, a crucial element in a system operating without central authorities.
Smart Contracts and Their Function in DeFi Applications
Smart contracts are self-executing contracts with the terms of the agreement directly written into code. These contracts reside on the blockchain and automatically execute when predetermined conditions are met. In DeFi, smart contracts are the engine driving various applications, such as lending platforms, decentralized exchanges (DEXs), and stablecoins. For instance, a smart contract on a lending platform automatically transfers funds to a borrower upon fulfillment of loan terms and returns the funds plus interest to the lender. This automation removes the need for human intervention, reducing delays and risks associated with traditional financial systems. The code itself, publicly viewable on the blockchain, ensures that the agreement is executed fairly and transparently.
Consensus Mechanisms in Blockchain and Their Impact on DeFi
Different blockchain networks employ various consensus mechanisms to validate transactions and add new blocks to the chain. The choice of consensus mechanism significantly impacts the speed, security, and scalability of a DeFi application. Proof-of-Work (PoW), like that used by Bitcoin, prioritizes security through computationally intensive mining but can be slow and energy-intensive. Proof-of-Stake (PoS), utilized by Ethereum 2.0 and Solana, offers faster transaction speeds and lower energy consumption by allowing validators to stake their cryptocurrency to participate in consensus. Other mechanisms like Delegated Proof-of-Stake (DPoS) and Practical Byzantine Fault Tolerance (PBFT) offer alternative approaches with varying trade-offs. The choice of consensus mechanism directly impacts a DeFi application’s performance and user experience, influencing factors like transaction fees and speed. For example, a high-throughput DeFi application might prefer a PoS or DPoS mechanism for faster transactions, while a security-critical application might opt for a more robust PoW system.
Comparison of Blockchain Platforms Used in DeFi
The following table compares several popular blockchain platforms used in DeFi, highlighting key differences in their consensus mechanisms, transaction speeds, and fees. Note that transaction speeds and fees can fluctuate significantly depending on network congestion.
| Platform | Consensus Mechanism | Transaction Speed | Fees |
|---|---|---|---|
| Ethereum | Proof-of-Stake (PoS) | Varies, but generally slower than Solana or Polygon | Varies widely depending on network congestion; can be high |
| Solana | Proof-of-History (PoH) and Proof-of-Stake (PoS) hybrid | Very high, among the fastest | Generally low |
| Polygon | Proof-of-Stake (PoS) | High, significantly faster than Ethereum | Generally low |
| Binance Smart Chain (BSC) | Proof-of-Staked Authority (PoSA) | High | Generally low, but can fluctuate |
Key DeFi Applications Enabled by Blockchain
Decentralized finance (DeFi) wouldn’t exist without blockchain technology. Blockchain’s inherent security, transparency, and automation are the bedrock upon which various DeFi applications are built, offering innovative alternatives to traditional financial services. Let’s delve into some of the most impactful.
Decentralized Exchanges (DEXs), How Blockchain is Enabling Decentralized Finance Solutions
DEXs are peer-to-peer marketplaces for trading cryptocurrencies without intermediaries like centralized exchanges. Instead of relying on a central authority to manage assets and orders, DEXs utilize smart contracts deployed on a blockchain to automate the trading process. This eliminates single points of failure and reduces the risk of censorship or manipulation. The most common type of DEX uses automated market makers (AMMs), which employ algorithms and liquidity pools to determine asset prices and facilitate trades. For example, Uniswap, a prominent DEX, uses a constant product formula x * y = k, where ‘x’ and ‘y’ represent the quantities of two tokens in a liquidity pool, and ‘k’ is a constant. This formula ensures that trades are executed automatically based on the existing liquidity in the pool. Other DEXs utilize order books similar to centralized exchanges, but with the decentralized aspect ensured by blockchain technology.
Decentralized Lending and Borrowing Platforms
These platforms allow users to lend and borrow cryptocurrencies without needing a traditional bank or financial institution. Smart contracts manage the lending and borrowing process, ensuring transparency and automation. Users can earn interest by lending their crypto assets, while borrowers can access funds without undergoing stringent credit checks. The interest rates are often determined algorithmically based on supply and demand. A prime example is Aave, which allows users to deposit various cryptocurrencies into lending pools and earn interest, while borrowers can take out loans using their deposited assets as collateral. The platform employs a risk assessment mechanism to manage the potential risks associated with lending and borrowing. This system helps to maintain the stability of the platform by ensuring that borrowers are able to repay their loans.
Stablecoins and Price Stability in DeFi
Stablecoins are cryptocurrencies designed to maintain a stable value relative to a fiat currency (like the US dollar) or a commodity (like gold). They play a crucial role in DeFi by mitigating the volatility inherent in other cryptocurrencies. This stability is essential for various DeFi applications, including lending and borrowing, where price fluctuations could significantly impact the value of collateral and loan repayments. Several mechanisms are used to maintain stability, including collateralization (backing the stablecoin with a reserve of fiat currency or other assets) and algorithmic mechanisms (using algorithms to adjust the supply of the stablecoin based on market demand). Tether (USDT) is a widely used stablecoin, although its collateralization practices have been subject to scrutiny. Other examples include USD Coin (USDC) and Dai (DAI), which employ different approaches to maintain price stability.
Decentralized Insurance Protocols
These protocols offer risk mitigation solutions within the DeFi ecosystem. They provide coverage for various events, such as smart contract failures, hacks, or oracle manipulation. Users can purchase insurance policies to protect their assets from unforeseen circumstances. The insurance payouts are often automated through smart contracts, ensuring transparency and efficiency. These protocols utilize various risk assessment models and risk pooling mechanisms to distribute risk among participants. Nexus Mutual is an example of a decentralized insurance protocol that allows users to purchase coverage for smart contract risks. The protocol uses a community-governed risk assessment model to determine the premiums and payouts.
Benefits and Challenges of Blockchain-Enabled DeFi

Source: wixstatic.com
Decentralized finance (DeFi) is revolutionizing financial services, offering transparency and accessibility like never before. This disruptive technology mirrors the impact of innovations in other sectors, such as urban planning, where advancements like How Machine Learning Algorithms Are Improving Traffic Management in Cities are optimizing efficiency. Just as machine learning streamlines traffic flow, blockchain streamlines financial transactions, creating a more efficient and equitable system for everyone.
Decentralized finance (DeFi) promises a revolution in how we interact with financial systems, leveraging blockchain technology to create a more accessible, transparent, and efficient landscape. However, this brave new world isn’t without its hurdles. Let’s delve into the exciting possibilities and the potential pitfalls of this rapidly evolving sector.
DeFi offers a compelling alternative to traditional finance, boasting several key advantages. The inherent nature of blockchain technology underpins these benefits, creating a system that is fundamentally different from the centralized models we’re used to.
Accessibility and Inclusivity
Traditional financial systems often exclude individuals lacking access to banks or credit. DeFi, however, lowers the barriers to entry. Anyone with an internet connection and a digital wallet can participate, regardless of their geographical location or socioeconomic status. This democratizing effect is a significant advantage, potentially bringing financial services to billions previously underserved. For example, individuals in developing countries with limited access to traditional banking infrastructure can leverage DeFi platforms for microloans and other financial services.
Transparency and Immutability
All transactions on a blockchain are publicly recorded and cryptographically secured, ensuring transparency and immutability. This contrasts sharply with traditional finance, where transactions often lack the same level of visibility. This enhanced transparency fosters trust and accountability, making it harder for fraudulent activities to go unnoticed. Smart contracts, self-executing agreements written in code, further enhance transparency by automating processes and reducing the potential for human error or manipulation.
Efficiency and Speed
DeFi processes often operate significantly faster and more efficiently than traditional financial systems. Automated processes, reduced reliance on intermediaries, and 24/7 availability contribute to this efficiency. For instance, cross-border payments can be executed much faster and cheaper through DeFi platforms than through traditional banking channels, which often involve multiple intermediaries and lengthy processing times.
Security Vulnerabilities and Risks
While blockchain technology offers inherent security benefits, DeFi platforms are not immune to vulnerabilities. Smart contract bugs, exploits, and hacks are a constant threat. The decentralized nature of DeFi also makes it challenging to recover funds lost due to security breaches, unlike centralized systems where regulatory bodies and institutions can intervene. The infamous Poly Network hack, where millions of dollars worth of cryptocurrency were stolen, serves as a stark reminder of these risks.
Regulatory Uncertainty
The decentralized and borderless nature of DeFi presents a significant regulatory challenge. Governments worldwide are still grappling with how to effectively regulate this rapidly evolving sector. This uncertainty can deter institutional investors and create legal ambiguity for DeFi projects and users. Lack of clear regulatory frameworks can lead to inconsistent enforcement and potentially stifle innovation.
Scalability Issues
Many blockchain networks face scalability challenges, limiting the number of transactions they can process per second. This can lead to network congestion, increased transaction fees, and slower processing times, particularly during periods of high demand. This is a critical issue for DeFi platforms aiming to handle a large volume of transactions. Solutions like layer-2 scaling solutions are being developed to address this challenge.
Security: Centralized vs. Decentralized Finance
Centralized finance relies on trusted intermediaries like banks and financial institutions to secure assets and transactions. While these institutions have established security protocols, they are also susceptible to single points of failure and internal fraud. Decentralized finance, on the other hand, distributes trust across a network of participants, making it theoretically more resistant to single points of failure. However, smart contract vulnerabilities and the lack of centralized oversight can expose DeFi to different types of risks.
Hypothetical Scenario: A Successful DeFi Application
Imagine a decentralized lending platform built on a highly scalable blockchain. This platform connects borrowers in developing countries directly with lenders worldwide, bypassing traditional financial intermediaries. Using smart contracts, the platform automatically assesses creditworthiness, disburses loans, and manages repayments. The transparency of the blockchain ensures fair pricing and prevents manipulation, while the platform’s scalability allows for rapid processing of a large number of loan applications. This scenario demonstrates how DeFi can provide access to financial services to underserved populations, driving economic growth and financial inclusion on a global scale. The platform’s success is built on a robust smart contract, strong community governance, and a user-friendly interface. It leverages the efficiency and transparency of blockchain technology to create a truly impactful financial service.
The Future of Blockchain in DeFi
The decentralized finance (DeFi) revolution, powered by blockchain technology, is still in its early stages. However, the rapid pace of innovation suggests a future brimming with transformative potential, impacting not just finance but numerous other sectors. We’re on the cusp of a significant shift in how we interact with financial systems, and understanding the emerging trends is crucial to navigating this exciting new landscape.
DeFi’s future hinges on addressing current limitations while capitalizing on its inherent strengths. Scalability, regulatory clarity, and user experience remain key challenges. However, ongoing developments in areas like layer-2 scaling solutions and improved user interfaces promise to overcome these hurdles, paving the way for mainstream adoption. The integration of artificial intelligence and machine learning also holds immense promise for enhancing DeFi’s efficiency and security.
Emerging Trends and Innovations in DeFi
Several key innovations are shaping the future of DeFi. These include the increasing sophistication of decentralized exchanges (DEXs), the rise of decentralized autonomous organizations (DAOs) managing DeFi protocols, and the exploration of novel blockchain architectures designed for enhanced scalability and interoperability. Furthermore, the development of privacy-enhancing technologies, like zero-knowledge proofs, is crucial for addressing concerns about data security and user anonymity within DeFi applications. For example, the growth of DEXs like Uniswap and SushiSwap, coupled with the increasing use of automated market makers (AMMs), has fundamentally altered how trading occurs, moving away from centralized exchanges and their associated vulnerabilities. The rise of DAOs, such as MakerDAO, demonstrates the potential for community-governed financial systems, fostering transparency and democratic decision-making.
Potential Impact of DeFi on Various Sectors
DeFi’s impact extends far beyond traditional finance. In payments, DeFi could offer faster, cheaper, and more transparent cross-border transactions, potentially disrupting existing payment networks. Imagine sending money internationally instantly and without hefty fees, a reality DeFi is actively working towards. In supply chain finance, DeFi can streamline processes by providing transparent and secure financing options, improving efficiency and reducing fraud. For instance, blockchain-based tracking of goods could provide real-time visibility into the supply chain, reducing delays and improving accountability. Investment management is another area poised for disruption. DeFi platforms are enabling the creation of novel investment products and strategies, offering increased accessibility and potentially higher returns for investors. The emergence of decentralized investment funds and automated investment strategies highlights the potential for democratizing access to sophisticated investment opportunities.
Examples of DeFi Evolution in the Coming Years
We can expect DeFi to become increasingly user-friendly, with intuitive interfaces and simplified onboarding processes. This will be crucial for wider adoption. Moreover, the integration of DeFi with existing financial systems will likely accelerate, creating hybrid models that leverage the benefits of both centralized and decentralized finance. Imagine a future where your traditional bank account seamlessly interacts with a DeFi lending platform, offering you the best of both worlds. Furthermore, we’ll see the emergence of more sophisticated DeFi products, such as decentralized insurance protocols and advanced derivatives markets, catering to a wider range of financial needs. The development of robust regulatory frameworks will also play a vital role in shaping DeFi’s future, ensuring responsible innovation and protecting consumers. The increasing use of stablecoins pegged to real-world assets will also improve the stability and usability of DeFi systems.
Potential Future Developments in DeFi
The future of DeFi is dynamic and unpredictable, but several key developments are likely to shape its trajectory:
- Increased Interoperability: Different blockchain networks will become more interconnected, allowing for seamless transfer of assets and data between platforms. This will foster innovation and competition.
- Improved Scalability: Solutions like layer-2 scaling and sharding will address the limitations of current blockchain technology, enabling faster transaction speeds and lower fees.
- Enhanced Security: Advanced cryptographic techniques and security audits will strengthen the security of DeFi protocols, mitigating the risks of hacks and exploits. This includes the wider adoption of formal verification techniques for smart contracts.
- Regulatory Clarity: Governments will develop clearer regulatory frameworks for DeFi, balancing innovation with consumer protection. This is crucial for building trust and encouraging mainstream adoption.
- Greater Institutional Adoption: Large financial institutions will increasingly explore and integrate DeFi solutions into their operations, driving further growth and maturity of the ecosystem.
While these developments offer significant benefits, such as increased efficiency, transparency, and accessibility, they also pose potential drawbacks. For example, increased interoperability could create new security vulnerabilities if not carefully managed. Similarly, regulatory uncertainty could stifle innovation, while rapid institutional adoption might lead to a centralization of power, undermining some of DeFi’s core principles.
Case Studies of Successful Blockchain-Based DeFi Projects
The decentralized finance (DeFi) landscape is brimming with innovative projects, each vying for a piece of the pie. While many projects emerge and fade, a few stand out due to their robust functionality, significant impact, and clever use of blockchain technology. Let’s examine two such projects to understand their strategies and contributions to the DeFi ecosystem.
MakerDAO and its DAI Stablecoin
MakerDAO is a pioneering decentralized autonomous organization (DAO) that created DAI, a stablecoin pegged to the US dollar. This project addresses the volatility inherent in cryptocurrencies by offering a stable alternative for transactions and DeFi applications. MakerDAO achieves this stability through a complex system of collateralized debt positions (CDPs). Users lock up collateral (primarily ETH) in CDPs to mint DAI. The system uses algorithms and governance mechanisms to maintain the DAI peg, adjusting collateralization ratios and interest rates as needed. The impact of MakerDAO is substantial: it provides a reliable, decentralized stablecoin used across numerous DeFi platforms, fostering increased liquidity and stability within the ecosystem. Its reliance on blockchain technology ensures transparency and immutability in all transactions, fostering trust and accountability. The decentralized governance model allows for community participation in decision-making, strengthening its resilience and adaptability.
Aave: A Decentralized Lending and Borrowing Platform
Aave is a leading decentralized lending and borrowing protocol. Unlike traditional finance, Aave operates on a permissionless basis, enabling users to lend and borrow crypto assets without intermediaries. Users deposit assets into liquidity pools, earning interest on their contributions. Borrowers can access these funds by providing collateral, paying interest on their loans. Aave’s utilization of blockchain technology is crucial; smart contracts automate the lending and borrowing processes, ensuring transparency and efficiency. The platform’s success stems from its innovative features, such as flash loans (allowing users to borrow and repay funds within a single transaction) and various lending options catering to different risk appetites. The impact of Aave is significant; it facilitates efficient capital allocation within the DeFi ecosystem, connecting lenders and borrowers directly and promoting liquidity in the cryptocurrency market. Its user-friendly interface and diverse range of supported assets contribute to its widespread adoption.
Comparison of MakerDAO and Aave
Both MakerDAO and Aave are significant players in the DeFi space, leveraging blockchain technology to offer innovative financial services. While MakerDAO focuses on providing a stablecoin to mitigate volatility, Aave concentrates on facilitating lending and borrowing. However, both projects rely heavily on smart contracts for automation and transparency, and both demonstrate the potential of decentralized finance to disrupt traditional financial systems. MakerDAO’s emphasis on stability contrasts with Aave’s focus on liquidity and accessibility, reflecting different approaches to addressing the challenges within the DeFi landscape. Both, however, share a common goal: to democratize finance and offer greater financial inclusion.
Illustrative Examples of DeFi Applications: How Blockchain Is Enabling Decentralized Finance Solutions
Decentralized finance (DeFi) offers a plethora of innovative applications built on blockchain technology. These applications are transforming traditional financial services, making them more accessible, transparent, and efficient. Let’s explore three key examples to visualize the power of DeFi in action.
Decentralized Exchange (DEX) Interface
Imagine a vibrant, user-friendly interface. This isn’t your typical centralized exchange. Instead, it’s a DEX, showcasing a dynamic list of cryptocurrency pairs. You can see real-time price charts, order books reflecting decentralized trading activity, and easily swap tokens without relying on a central authority. The interface itself is visually clean, with clear indicators of transaction fees and slippage, ensuring transparency in every trade. Think of it as a modern, self-regulating marketplace for digital assets, operating with the security and immutability of blockchain. The design emphasizes ease of use, making complex trading accessible to a broader audience.
Smart Contract Workflow for Lending
This image depicts a simplified flowchart representing a decentralized lending process. It begins with a user depositing crypto assets into a smart contract-controlled pool. The smart contract, acting as an autonomous intermediary, automatically verifies the user’s collateral and allocates funds to a borrower based on pre-defined parameters. The flowchart clearly Artikels the stages: deposit, loan disbursement, interest accrual, and repayment. Importantly, it highlights the automated nature of the process, eliminating the need for intermediaries and reducing friction. Each step is secured and verified on the blockchain, guaranteeing transparency and accountability. The final stage shows the return of the collateral to the lender upon successful repayment.
Decentralized Lending Platform Dashboard
The image showcases a dashboard displaying a user’s activity on a decentralized lending platform. It features a clear overview of their deposited assets, outstanding loans (both lent and borrowed), accrued interest, and available liquidity. The dashboard is designed to provide real-time information, enabling users to actively manage their portfolio. Key metrics such as Annual Percentage Yield (APY) for lending and borrowing are prominently displayed, allowing users to compare rates and optimize their strategies. The platform’s security features are subtly indicated, highlighting the safeguards in place to protect user funds. This visual representation emphasizes the user-friendly nature of DeFi, making complex financial operations accessible and straightforward.
Final Summary

Source: 101blockchains.com
Decentralized finance, powered by blockchain, is undeniably disrupting the traditional financial world. While challenges remain – security, regulation, scalability – the potential benefits are too significant to ignore. From increased accessibility and transparency to innovative applications across various sectors, DeFi is poised to redefine financial inclusion and efficiency. The journey is just beginning, and the future of finance is looking decidedly… decentralized.
