How Blockchain is Empowering the Future of Digital Rights Management? Forget dusty copyright laws and frustrating licensing deals. Blockchain’s decentralized, transparent nature is shaking up the digital world, offering a revolutionary approach to managing digital assets. Imagine a world where creators directly control their work, fans easily access content, and copyright infringement becomes a thing of the past – that’s the promise of blockchain in DRM.
This technology, built on a secure, immutable ledger, offers unparalleled security and transparency. Smart contracts automate royalty payments, cryptographic hashing verifies authenticity, and immutable records prove ownership. It’s not just about security; it’s about empowering creators, streamlining transactions, and fostering a fairer digital ecosystem. We’ll delve into how this game-changing technology is reshaping the future of digital rights.
Blockchain’s Role in Digital Asset Management
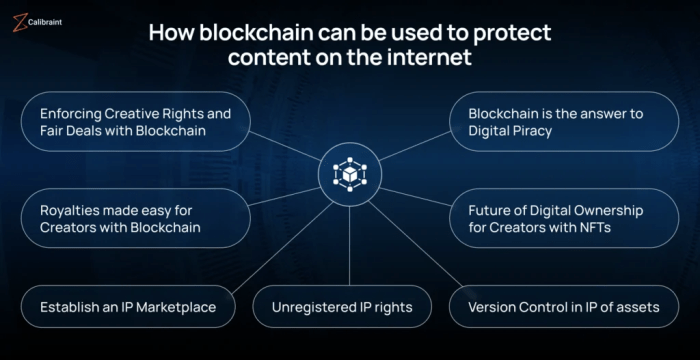
Source: calibraint.com
Blockchain’s immutable ledger is game-changing for digital rights, ensuring provenance and authenticity. This same secure, transparent system is revolutionizing data handling in other sectors too, like healthcare; check out this insightful piece on How Blockchain is Revolutionizing Healthcare Data Security to see how it’s improving patient privacy. Ultimately, this tech empowers individuals to control their digital assets, whether it’s creative works or sensitive medical information.
Imagine a world where digital ownership is as clear-cut as owning a physical asset. Blockchain technology, with its immutable ledger and decentralized nature, is making this a reality, revolutionizing how we manage digital rights and assets. This innovative approach offers a significant upgrade to traditional digital rights management (DRM) systems, offering enhanced security, transparency, and efficiency.
Blockchain’s core strength lies in its decentralized, distributed ledger technology. Unlike traditional centralized databases, which are vulnerable to single points of failure and manipulation, blockchain distributes information across a network of computers. This makes it incredibly secure and resistant to tampering. Each transaction is recorded as a “block,” cryptographically linked to the previous block, creating an immutable chain of records. This inherent transparency and security are precisely what makes blockchain so relevant to DRM. Traditional DRM systems often rely on centralized servers, making them susceptible to hacking, data breaches, and unauthorized access. Blockchain eliminates these vulnerabilities, offering a robust and secure platform for managing digital rights.
Blockchain’s Enhanced Security and Transparency
Blockchain’s decentralized nature significantly enhances the security of digital assets. Because the data isn’t stored in a single location, there’s no central point of attack. Any attempt to alter the information on the blockchain would require compromising a significant portion of the network, a practically impossible feat. This heightened security ensures that the ownership and usage rights of digital assets are accurately recorded and verifiable. Furthermore, the transparent nature of the blockchain allows for easy tracking of asset ownership and transactions. This transparency promotes accountability and reduces the risk of fraud or unauthorized access. For example, imagine a musician using blockchain to manage the distribution of their music. Every sale, license, or stream could be recorded on the blockchain, providing a clear and auditable trail of revenue and usage. This eliminates the need for intermediaries and provides the musician with complete control over their work. Similarly, a photographer could use blockchain to prove ownership of their images, preventing unauthorized use and ensuring they receive proper compensation for their work. This level of transparency and control is simply not possible with traditional DRM systems.
Enhanced Security and Provenance Tracking
Blockchain technology is revolutionizing digital rights management by offering unprecedented levels of security and transparency. Its inherent features, like cryptographic hashing and immutable ledgers, create a system where the authenticity and ownership of digital assets are verifiable and tamper-proof. This not only protects creators but also fosters trust and efficiency within the digital marketplace.
The core of this enhanced security lies in blockchain’s ability to create a permanent and verifiable record of a digital asset’s journey, from creation to distribution. This “provenance” is crucial for establishing authenticity and resolving disputes.
Cryptographic Hashing and Content Integrity
Blockchain uses cryptographic hashing to ensure the integrity and authenticity of digital content. Each file is assigned a unique cryptographic hash – a fingerprint, if you will – generated through a one-way function. Any alteration to the file, no matter how small, results in a completely different hash. This hash is then recorded on the blockchain, creating an immutable record of the file’s state at a specific point in time. If someone tries to tamper with the file, the mismatch between the stored hash and the newly generated hash immediately reveals the tampering. This provides irrefutable proof of the file’s authenticity and integrity. Think of it like a digital seal of approval that’s impossible to forge or break.
Smart Contracts for Automated Licensing and Royalties
Smart contracts, self-executing contracts with the terms of the agreement directly written into code, automate the licensing and royalty payment processes. These contracts are stored on the blockchain, ensuring transparency and eliminating the need for intermediaries. When a licensed digital asset is used, the smart contract automatically triggers the payment of royalties to the rights holder. This eliminates delays, disputes, and the need to trust third-party intermediaries to manage payments fairly. For example, a musician could upload their music to a platform, set royalty rates within a smart contract, and automatically receive payments every time their song is streamed or downloaded. The entire process is transparent and verifiable on the blockchain.
Examples of Blockchain-Based Solutions for Immutable Ownership Records
Several blockchain-based solutions are already providing immutable records of ownership and usage. For example, platforms like Verisart use blockchain technology to verify the authenticity and provenance of digital art, providing collectors with a certificate of authenticity that is verifiable on the blockchain. Similarly, some music platforms are exploring blockchain-based solutions to manage licensing and royalty payments, ensuring artists receive fair compensation for their work. These platforms offer a transparent and secure way to track ownership and usage, improving the overall experience for both creators and consumers.
Provenance Tracking for Digital Art: A Hypothetical Scenario
Imagine Anya, a digital artist, creates a unique piece of artwork. She uploads it to a blockchain-based platform, which generates a unique cryptographic hash and records it on the blockchain along with metadata such as the creation date and copyright information. Every time the artwork is sold or transferred, the transaction is recorded on the blockchain, creating a complete and verifiable history of its ownership. If a dispute arises regarding ownership or authenticity, the blockchain provides an immutable record of the artwork’s journey, easily resolving the conflict. This contrasts sharply with traditional methods, where proving ownership of a digital asset can be extremely difficult. This transparent and verifiable history significantly increases the value and trust associated with the artwork.
Improved Copyright Protection and Enforcement
The digital world, while offering unprecedented opportunities for creators, has also presented a monumental challenge: protecting copyright. The ease of copying and distributing digital content online has made infringement rampant, leaving artists and businesses struggling to safeguard their intellectual property. Blockchain technology, with its immutable ledger and decentralized nature, offers a compelling solution to these longstanding problems.
Traditional copyright protection relies heavily on centralized authorities like copyright offices and legal action. This system is often slow, expensive, and prone to fraud. Establishing proof of ownership can be a lengthy and complex process, particularly in cases involving online infringement. Blockchain, however, offers a different approach, recording copyright information directly onto a distributed, tamper-proof ledger. This creates a verifiable and auditable record of ownership, simplifying the process of proving ownership and deterring infringement.
Comparison of Traditional and Blockchain-Based Copyright Mechanisms
Traditional methods often involve registering copyrights with government agencies, which can be time-consuming and costly. Enforcement relies primarily on lawsuits, which are expensive and can be difficult to win, especially against individuals or entities operating outside of a country’s jurisdiction. Blockchain-based systems, conversely, offer a more streamlined and transparent process. By recording copyright information on a blockchain, creators can establish a verifiable record of ownership that is readily accessible to anyone. Smart contracts can also be used to automate royalty payments and licensing agreements, further enhancing efficiency and security. This approach offers a potentially faster, cheaper, and more effective way to protect and enforce copyright.
Legal and Regulatory Hurdles in Blockchain Copyright Adoption
Despite its potential, the adoption of blockchain for copyright management faces significant legal and regulatory challenges. The lack of clear legal frameworks around blockchain technology in many jurisdictions creates uncertainty for creators and businesses. Questions around the admissibility of blockchain evidence in court, the legal enforceability of smart contracts, and the potential for jurisdictional conflicts need to be addressed. Furthermore, the decentralized nature of blockchain can make it difficult to regulate and control, raising concerns about potential misuse and the need for robust mechanisms to prevent fraudulent claims. Harmonizing international copyright laws with the unique characteristics of blockchain technology will be crucial for widespread adoption.
Blockchain-Based Copyright Platforms
The following table compares the features of different blockchain-based copyright platforms. Note that the features and functionalities of these platforms are constantly evolving.
| Platform | Key Features | Strengths | Weaknesses |
|---|---|---|---|
| CopyrightChain | Timestamping, provenance tracking, automated royalty payments | User-friendly interface, robust security | Limited platform adoption |
| BitLicense | Secure digital rights management, licensing and royalty management | Strong emphasis on security and compliance | Higher development costs |
| Arweave | Permanent storage of digital assets, immutable record of ownership | Cost-effective, decentralized storage | Limited functionality for copyright enforcement |
| Chainpoint | Timestamping and proof of existence for digital assets | High level of security and immutability | Requires technical expertise to use effectively |
Empowering Creators and Content Owners
Blockchain technology is revolutionizing the relationship between creators and their audiences, offering a powerful tool to regain control over their digital assets and build more sustainable careers. By cutting out intermediaries and enabling direct transactions, blockchain empowers creators to connect directly with their fans and receive fair compensation for their work. This shift towards a more decentralized and transparent system is fostering a new era of creative independence.
Blockchain facilitates direct transactions between creators and consumers by acting as a secure and transparent ledger of all transactions. Instead of relying on platforms that take a significant cut of profits, creators can use blockchain-based platforms to sell their work directly to consumers, receiving a larger share of the revenue. Smart contracts automate the process, ensuring that payments are released automatically upon completion of the transaction, building trust and streamlining the process. This direct connection also allows for stronger relationships between creators and their audiences, fostering loyalty and community building.
Direct Transactions and Micropayments
Blockchain’s ability to handle microtransactions makes it particularly beneficial for creators of digital content. Imagine a scenario where fans can pay a small fee for access to exclusive content, or even reward creators for individual pieces of work, like a single song or blog post. This model allows for a more granular approach to monetization, enabling creators to generate income from various smaller transactions, rather than relying on larger, infrequent sales. Platforms utilizing blockchain can handle the complex logistics of these numerous micropayments efficiently and securely, ensuring creators receive fair compensation for their efforts. The transparency of the blockchain also allows creators to easily track all income generated.
Fractional Ownership and NFTs
The concept of fractional ownership, enabled by blockchain, allows creators to offer portions of their work for sale. This opens up access to larger audiences, as fans can invest in a piece of something they love without having to purchase the entire asset. Non-Fungible Tokens (NFTs) are a prime example of this, enabling creators to sell unique digital assets with verifiable ownership and provenance. This can be applied to everything from digital artwork and music to virtual real estate in metaverse environments. Fractional ownership increases the potential market size and creates additional revenue streams for creators.
Examples of Blockchain-Based Creator Platforms
Several platforms are already leveraging blockchain technology to empower creators. For example, platforms like Audius utilize blockchain to distribute music directly to listeners, allowing artists to retain a larger share of royalties. Other platforms are using NFTs to create marketplaces for digital art, enabling artists to sell their work directly to collectors and receive payments directly, without relying on intermediaries like galleries or auction houses. These platforms demonstrate the practical applications of blockchain technology in empowering creators and fostering a more equitable digital ecosystem.
Advantages and Disadvantages for Creators Using Blockchain for DRM
Let’s weigh the pros and cons of using blockchain for digital rights management from a creator’s perspective.
- Advantages: Increased control over their work, direct access to fans, reduced reliance on intermediaries, potential for new revenue streams through micropayments and fractional ownership, enhanced security and provenance tracking, improved copyright protection.
- Disadvantages: Technical complexity, potential for high transaction fees (depending on the blockchain used), scalability challenges for extremely high-volume transactions, the need for digital literacy, potential for misunderstanding of the technology among audiences.
Interoperability and Data Privacy
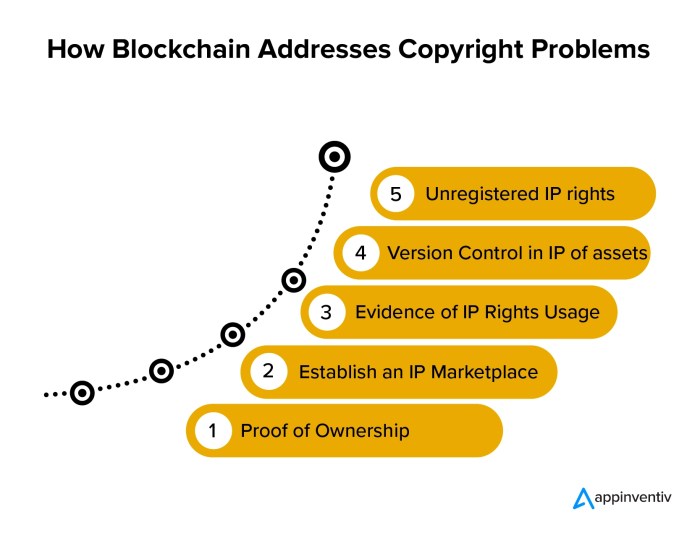
Source: appinventiv.com
The future of digital rights management (DRM) hinges on seamless collaboration between different systems and a robust commitment to user privacy. Blockchain technology, with its inherent decentralized nature, offers a compelling pathway towards achieving both, but careful consideration of interoperability and privacy-preserving mechanisms is crucial for widespread adoption. This section delves into the complexities of ensuring a secure and user-friendly blockchain-based DRM ecosystem.
Blockchain’s decentralized structure presents both opportunities and challenges regarding interoperability. While this decentralization empowers creators and prevents single points of failure, it also means different blockchain platforms might not communicate easily with each other. This lack of interoperability could create silos of digital assets, hindering the seamless exchange and management of rights across various platforms and services. Solutions involving cross-chain communication protocols and standardized data formats are vital to overcome this obstacle and foster a truly interconnected digital ecosystem.
Interoperability Challenges and Solutions in Blockchain-Based DRM
Achieving true interoperability in blockchain-based DRM requires a multifaceted approach. One key strategy involves the development of standardized data formats and protocols that allow different blockchain platforms to understand and interact with each other’s data. This could involve the creation of a universal data schema for representing digital assets and their associated rights, allowing seamless transfer and management across platforms. Another promising avenue is the exploration of cross-chain communication protocols, which enable the secure transfer of information and assets between different blockchains without compromising security. These protocols could facilitate the seamless exchange of digital rights information between different platforms, ensuring that creators and content owners can manage their assets effectively regardless of the underlying blockchain technology. The successful implementation of these solutions will be crucial for the widespread adoption of blockchain-based DRM.
Enhancing Data Privacy and User Control
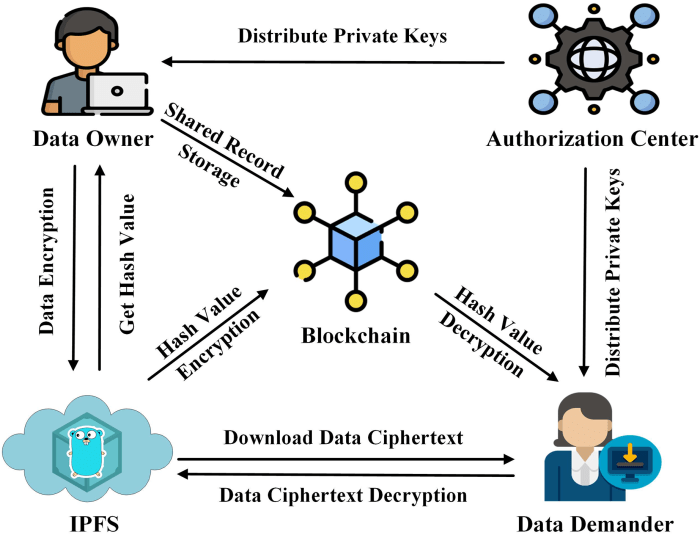
Blockchain’s inherent transparency can be a double-edged sword when it comes to data privacy. While the immutability of the blockchain ensures the integrity of digital rights information, it also means that anyone with access to the blockchain can potentially view the transaction history. To mitigate this risk, several privacy-enhancing techniques can be employed. Zero-knowledge proofs, for example, allow users to prove ownership of a digital asset without revealing any sensitive information about the asset itself. Homomorphic encryption enables computations to be performed on encrypted data without decryption, preserving confidentiality. Furthermore, the use of decentralized identifiers (DIDs) and verifiable credentials allows users to control and share their digital identity and ownership information selectively, ensuring greater user control over their data.
Data Privacy Approaches in Blockchain-Based DRM Systems
Different approaches to ensuring data privacy in blockchain-based DRM systems exist. One approach is to leverage zero-knowledge proofs (ZKPs) to verify ownership of digital assets without revealing the asset’s identity or other sensitive information. Another approach is to use confidential transactions, which encrypt the transaction details on the blockchain, preventing unauthorized access to sensitive information. Finally, the use of private blockchains or permissioned networks can limit access to the blockchain to authorized users only, thereby enhancing data privacy. The choice of the most suitable approach depends on the specific requirements of the DRM system and the level of privacy required. A hybrid approach, combining multiple techniques, may be the most effective strategy.
User Interface Design for Privacy-Focused Blockchain-Based DRM, How Blockchain is Empowering the Future of Digital Rights Management
A user-friendly interface is paramount for the success of any blockchain-based DRM system. A privacy-focused design should prioritize user control over data sharing and access. The interface should clearly display the user’s digital assets and associated rights, allowing them to manage their assets effectively. It should also provide clear and concise information about data privacy policies and practices. Crucially, it should enable users to selectively share their data with specific parties, only granting access to the necessary information while maintaining control over their sensitive data. For instance, the user interface could allow users to grant temporary access to their assets for specific purposes, revoking access when no longer needed. Furthermore, the system should allow users to easily audit their data usage and access history, providing transparency and accountability. Visual cues, such as color-coding access levels and clear indicators of data sharing, can further enhance the user experience and ensure that users understand the privacy implications of their actions. This intuitive design fosters trust and encourages wider adoption of blockchain-based DRM.
Future Trends and Challenges: How Blockchain Is Empowering The Future Of Digital Rights Management
The application of blockchain to digital rights management (DRM) is still nascent, but its potential is undeniable. While early adopters are already experiencing the benefits, several trends are shaping the future of this technology, alongside significant challenges that need to be addressed for widespread adoption. Understanding these trends and challenges is crucial for stakeholders to navigate the evolving landscape of digital asset protection.
The intersection of blockchain and DRM is poised for significant evolution. Several key trends and challenges will define its trajectory in the coming years. Scalability, interoperability, and the ongoing evolution of blockchain technology itself will all play critical roles in determining the success of blockchain-based DRM solutions.
Emerging Trends in Blockchain-Based DRM
Several emerging trends are shaping the future of blockchain’s role in DRM. These include the increasing integration of blockchain with other technologies like AI and IoT, the development of more user-friendly interfaces, and a growing focus on decentralized and permissionless systems that empower creators and users alike. Specifically, we see a shift towards more sophisticated tokenization models for digital assets, allowing for fractional ownership and more complex licensing agreements. The rise of NFTs (Non-Fungible Tokens) has already demonstrated the potential of blockchain to represent unique digital ownership, and this is only expected to expand. Furthermore, advancements in zero-knowledge proofs and other cryptographic techniques are enhancing privacy while maintaining security and verifiability.
Challenges and Limitations of Blockchain-Based DRM Systems
Despite the potential, several challenges hinder the widespread adoption of blockchain for DRM. One significant hurdle is scalability. Current blockchain networks, especially public ones, can struggle to handle the volume of transactions required for managing the vast amount of digital content created and consumed daily. This leads to higher transaction fees and slower processing times, making it impractical for certain applications. Another challenge lies in the complexity of implementing and integrating blockchain technology into existing DRM systems. The technical expertise required for development and maintenance can be a barrier for many organizations. Furthermore, the regulatory landscape surrounding blockchain and digital assets is still evolving, creating uncertainty and potential legal challenges for businesses. Finally, user education and adoption are crucial; widespread adoption requires a user-friendly experience that isn’t overly technical.
Scalability and Efficiency Concerns
Scalability remains a critical concern for blockchain-based DRM. Public blockchains like Bitcoin and Ethereum, known for their security and decentralization, often suffer from slow transaction speeds and high fees due to their consensus mechanisms. This makes them unsuitable for real-time applications requiring rapid processing of numerous transactions, such as managing streaming content or large-scale digital asset marketplaces. To address this, several solutions are being explored, including the use of layer-2 scaling solutions (like Lightning Network for Bitcoin or Polygon for Ethereum), the development of more efficient consensus mechanisms, and the adoption of private or permissioned blockchains that offer faster transaction times and lower fees but compromise on decentralization. For example, a music streaming service might utilize a permissioned blockchain to track licensing agreements and royalty payments efficiently, while a decentralized NFT marketplace might leverage layer-2 scaling to handle a large volume of transactions.
Potential Future Landscape of Blockchain in DRM: A Visual Representation
Imagine a vibrant, interconnected network represented as a constellation of nodes. Each node represents a different stakeholder in the digital content ecosystem: creators, consumers, platforms, and rights management organizations. These nodes are connected by glowing lines representing secure, transparent transactions facilitated by blockchain technology. Within each node, smaller, brightly colored orbs represent individual digital assets – songs, videos, images, etc. – each uniquely identifiable and verifiable through its blockchain record. The overall network is dynamic, with new nodes and connections constantly forming, reflecting the ever-growing volume of digital content and the expanding reach of blockchain-based DRM. Some nodes are larger and brighter, representing established platforms with substantial digital asset portfolios, while others are smaller and dimmer, representing emerging creators building their digital presence. The network is overlaid with a subtle, protective shield representing the enhanced security and provenance tracking provided by the blockchain, safeguarding digital assets from unauthorized access and infringement. This visual represents the decentralized, secure, and efficient future of DRM powered by blockchain technology, enabling a more equitable and transparent ecosystem for creators and consumers alike. The size and brightness of the nodes represent the influence and market share of each stakeholder. The shield highlights the security features offered by blockchain, and the vibrant colors and dynamic connections represent the diverse and ever-evolving nature of the digital content ecosystem.
Conclusion
Source: cloudfront.net
Blockchain’s impact on digital rights management is undeniable. From enhancing security and streamlining transactions to empowering creators and fostering a more equitable digital landscape, the technology presents a compelling vision for the future. While challenges remain, the potential benefits are too significant to ignore. As blockchain matures and adoption increases, we can expect a more transparent, secure, and ultimately, fairer system for managing digital assets – one that truly puts the power back in the hands of creators and consumers.
