How Blockchain is Creating a New Era of Digital Transactions – that’s the headline grabbing everyone’s attention. Forget slow, clunky payment systems; blockchain’s shaking things up with its decentralized, secure, and super-fast transactions. This isn’t just about Bitcoin anymore; it’s a total game-changer impacting everything from finance to supply chains. Get ready to dive into the future of money, because it’s here, and it’s blockchain-powered.
We’re talking cryptographic security so tight, fraud practically becomes a myth. Transparency? It’s baked right in. Think instant cross-border payments, automated contracts that eliminate red tape, and a level of trust that’s almost unheard of in the digital world. This isn’t just tech talk; it’s a revolution reshaping how we handle digital value.
Introduction
For decades, digital transactions relied on centralized systems controlled by intermediaries like banks and payment processors. This created bottlenecks, vulnerabilities, and high transaction fees. Imagine trying to send money across the globe – the process is often slow, expensive, and fraught with paperwork. This reliance on trusted third parties also introduced single points of failure, making the system susceptible to fraud, censorship, and data breaches. The need for a more efficient, secure, and transparent system was clear.
Blockchain technology emerged as a revolutionary solution, fundamentally altering the landscape of digital transactions. It’s a decentralized, distributed ledger that records and verifies transactions across a network of computers. This eliminates the need for intermediaries, enhancing speed, security, and transparency.
Core Principles of Blockchain Technology
Blockchain’s impact on digital transactions stems from its core principles: decentralization, immutability, and transparency. Decentralization means no single entity controls the network; instead, it’s distributed across many participants. Immutability ensures that once a transaction is recorded, it cannot be altered or deleted, providing a high level of security. Transparency allows all participants to view the transaction history, fostering trust and accountability. These three pillars combine to create a robust and reliable system for digital transactions.
Blockchain: A Definition and its Impact
A blockchain is essentially a continuously growing list of records, called blocks, which are linked and secured using cryptography. Each block contains a batch of validated transactions, and once added to the chain, it’s virtually impossible to tamper with. This cryptographic linking and the distributed nature of the network make blockchain exceptionally secure. Its impact on digital transactions is profound, enabling faster, cheaper, and more secure transfers of value, information, and assets. The potential extends far beyond simple money transfers, encompassing supply chain management, digital identity verification, and voting systems, among other applications.
Enhanced Security and Transparency
Blockchain technology is revolutionizing digital transactions by offering unprecedented levels of security and transparency. Unlike traditional systems, which often rely on centralized authorities and intermediaries, blockchain leverages cryptography and a distributed ledger to create a secure and auditable record of all transactions. This fundamentally changes how we think about trust and verification in the digital world.
Cryptography plays a crucial role in securing blockchain transactions. Each transaction is cryptographically signed using private keys, ensuring only the authorized party can initiate the transfer. These digital signatures are verified by the network using public keys, preventing unauthorized access and manipulation. The cryptographic hashing of blocks also ensures the integrity of the entire chain, making it incredibly difficult to alter past transactions. Any attempt to modify a single block would trigger a cascade of inconsistencies, immediately alerting the network to the fraudulent activity.
Cryptographic Security of Blockchain Transactions
The foundation of blockchain security rests on robust cryptographic techniques. Public-key cryptography, a cornerstone of blockchain technology, enables secure communication and transaction verification without requiring a trusted third party. Each participant has a unique pair of keys: a private key, kept secret, and a public key, shared openly. The private key is used to digitally sign transactions, proving authenticity, while the public key verifies the signature. This ensures only the owner of the private key can authorize a transaction, providing a high level of security against unauthorized access and fraud. Furthermore, the use of hashing algorithms creates a unique digital fingerprint for each block, linking it securely to the previous block in the chain. This chaining mechanism makes it computationally infeasible to alter any transaction without detection.
Immutability and Fraud Prevention
A key feature of blockchain is the immutability of its data. Once a transaction is recorded and added to a block, it becomes virtually impossible to alter or delete. This immutability is a powerful tool for fraud prevention. Traditional systems, often centralized and susceptible to manipulation, lack this inherent security. Consider a bank statement: it’s relatively easy to alter a single entry in a centralized database. However, altering a blockchain transaction would require compromising a significant portion of the distributed network, a task that is practically impossible given the decentralized nature of the system. This inherent immutability makes blockchain an ideal platform for applications requiring high levels of data integrity and security, such as supply chain management and digital identity verification. For example, tracking a product’s journey from origin to consumer is far more secure and transparent on a blockchain, making it significantly harder to counterfeit or misrepresent its provenance.
Transparency of Blockchain vs. Traditional Systems
Blockchain transactions offer a level of transparency unmatched by traditional systems. While traditional systems often obscure transaction details, requiring trust in intermediaries, blockchain makes transaction data publicly accessible (depending on the specific blockchain’s design; some are permissioned and not fully public). This transparency fosters accountability and builds trust among participants. This doesn’t necessarily mean every single detail is available to everyone, as some blockchains utilize privacy-enhancing techniques, but the overall process is auditable.
| Feature | Blockchain | Traditional Systems |
|---|---|---|
| Security | High, due to cryptography and distributed ledger | Variable, often reliant on centralized security measures |
| Transparency | High, depending on the blockchain’s design. Public blockchains offer high transparency | Low, often opaque and requiring trust in intermediaries |
| Speed | Variable, depending on the specific blockchain and its consensus mechanism. Can be slower than some traditional systems, but is improving. | Generally faster for individual transactions, but can be slower for complex processes. |
Increased Efficiency and Speed
Blockchain technology is revolutionizing the way we conduct digital transactions, offering significant improvements in efficiency and speed compared to traditional methods. This enhanced speed and efficiency stem from the inherent design of blockchain, particularly its use of smart contracts and the elimination of intermediaries. The result? Faster transaction processing and reduced costs.
Smart contracts automate transaction processes by eliminating the need for human intervention in many stages. This automation drastically reduces processing time and minimizes the potential for errors associated with manual processes. Imagine a scenario where you’re buying a property: traditionally, this involves multiple parties, lawyers, escrow services, and significant paperwork. With smart contracts, the agreement’s terms are encoded on the blockchain, automatically executing the transfer of ownership and funds once predefined conditions are met. This streamlined approach ensures faster and more reliable transactions.
Smart Contract Automation
Smart contracts are self-executing contracts with the terms of the agreement between buyer and seller directly written into lines of code. These contracts reside on the blockchain and automatically execute when predetermined conditions are met. This eliminates the need for intermediaries like lawyers or escrow agents to verify and process transactions, leading to faster settlement times and lower costs. For example, supply chain management can benefit greatly; once a shipment reaches a certain location, verified by GPS tracking integrated with the smart contract, payment is automatically released to the supplier. This automation removes delays caused by manual verification and reconciliation.
Reduced Intermediaries and Transaction Speed
Traditional transaction systems often involve multiple intermediaries, such as banks, payment processors, and clearing houses. Each intermediary adds time and cost to the process. Blockchain technology, however, allows for peer-to-peer transactions, minimizing or eliminating the need for these intermediaries. This directly translates to faster transaction speeds. For instance, international money transfers that typically take days or even weeks using traditional banking systems can be completed within minutes on a blockchain network. The reduction in intermediaries also reduces the risk of fraud and errors, further enhancing the overall efficiency.
Comparison of Transaction Processes
A flowchart can effectively illustrate the difference between a blockchain transaction and a traditional one.
Traditional Transaction Flowchart:
Imagine a box labeled “Customer”. An arrow points from this box to a box labeled “Bank A”. Another arrow goes from “Bank A” to “Payment Processor”. Then an arrow goes from “Payment Processor” to “Bank B”. Finally, an arrow goes from “Bank B” to “Merchant”. Each arrow represents a stage with potential delays.
Blockchain Transaction Flowchart:
Here, an arrow goes directly from “Customer” to “Merchant”. The transaction is recorded on the blockchain, and the transfer of funds is automated and almost instantaneous, eliminating the multiple intermediary steps. This streamlined process is significantly faster and more efficient.
Improved Trust and Interoperability: How Blockchain Is Creating A New Era Of Digital Transactions
Blockchain technology is revolutionizing trust and collaboration in the digital world. By eliminating the need for a central authority, it creates a system where multiple parties can interact securely and transparently, fostering a new level of confidence in digital transactions. This inherent trust, combined with the potential for seamless cross-border transactions, opens up exciting new possibilities for businesses and individuals alike.
Blockchain’s decentralized nature is the key to its trust-building capabilities. Instead of relying on a single entity to validate transactions, blockchain uses a distributed ledger that’s replicated across numerous nodes. This means that every transaction is verified and recorded by multiple participants, making it virtually tamper-proof. This inherent transparency and immutability create a high level of trust, even among parties who may not know each other.
Blockchain Fosters Trust Without Central Authority
The lack of a central authority is both a strength and a challenge. Consider the example of international supply chains. Traditionally, tracking goods across borders involves multiple intermediaries, each adding a layer of complexity and potential for fraud. Blockchain can streamline this process by providing a shared, immutable record of the goods’ journey. Every participant—from the manufacturer to the importer—can access the same information, fostering trust and accountability. Another example is in the realm of digital identity verification. Blockchain-based systems can securely store and manage individuals’ digital identities, reducing the risk of identity theft and fraud while offering greater control to the individual over their own data. This eliminates the need for a central authority to manage and control these identities, thereby fostering trust amongst users.
Cross-Border Transactions Facilitated by Blockchain, How Blockchain is Creating a New Era of Digital Transactions
The potential for blockchain to facilitate seamless cross-border transactions is enormous. Traditional international payments can be slow, expensive, and prone to delays. Blockchain can significantly reduce these friction points by offering faster, cheaper, and more transparent cross-border payments. Ripple, for example, is a blockchain-based payment network that enables near-instantaneous international transfers. This speed and efficiency are particularly beneficial for businesses operating in global markets. Furthermore, the transparency provided by blockchain can reduce the risk of fraud and disputes, as all parties have access to a shared record of the transaction. This enhanced transparency is especially important in regions with less developed financial infrastructure. Imagine the impact on small businesses in developing countries, who can now access global markets with ease and reduced transaction costs.
Challenges to Interoperability Between Different Blockchain Networks
Despite its potential, the widespread adoption of blockchain is hampered by the lack of interoperability between different blockchain networks. Each blockchain operates independently, using its own protocols and standards. This fragmentation creates significant challenges for businesses and users who need to interact with multiple blockchains. For instance, a company may use one blockchain for supply chain management and another for payment processing. The inability to seamlessly transfer data or assets between these networks creates inefficiencies and limits the overall utility of blockchain technology. Efforts are underway to develop solutions such as cross-chain communication protocols and interoperability standards, but overcoming these technological hurdles is crucial for the widespread adoption of blockchain. The challenge lies not only in technological standardization but also in establishing consensus and cooperation amongst diverse stakeholders in the blockchain ecosystem.
Real-World Applications of Blockchain in Transactions
Blockchain technology, once a niche concept, is rapidly transforming how we conduct transactions across various sectors. Its decentralized, transparent, and secure nature is proving invaluable in streamlining processes and building trust in a digital world increasingly prone to fraud and inefficiency. This section explores some compelling real-world examples showcasing blockchain’s transformative power.
Supply Chain Management
Blockchain’s ability to create immutable records makes it ideal for tracking goods throughout their journey from origin to consumer. This enhanced transparency combats counterfeiting and improves traceability. Imagine a shipment of pharmaceuticals: each step—from manufacturing to distribution—is recorded on the blockchain, providing verifiable proof of authenticity and preventing the introduction of counterfeit drugs into the supply chain. This not only protects consumers but also safeguards the reputation and financial stability of legitimate businesses. Similarly, in the food industry, blockchain can track the origin of produce, ensuring consumers know exactly where their food comes from and how it was handled, bolstering consumer confidence and enabling quicker responses to contamination outbreaks.
Cross-Border Payments in the Financial Sector
International money transfers are often slow, expensive, and opaque. Blockchain technology offers a solution. Platforms leveraging blockchain can significantly reduce transaction times and fees associated with cross-border payments. For example, Ripple’s network uses blockchain to facilitate near-instantaneous transfers between banks, bypassing the traditional correspondent banking system and significantly reducing costs. This allows for faster and more efficient movement of funds across geographical boundaries, benefiting both businesses and individuals engaging in international trade and remittances. The increased transparency also helps in mitigating risks associated with fraud and regulatory compliance.
Digital Identity Management
Blockchain can revolutionize digital identity management by creating secure and verifiable digital identities. Instead of relying on centralized databases vulnerable to hacking, individuals can control their own data, granting access selectively to various services. This eliminates the need for multiple usernames and passwords, reducing the risk of identity theft. A decentralized identity system built on blockchain could empower individuals with greater control over their personal information, fostering greater trust and privacy in online interactions. For instance, a person could use their blockchain-based digital identity to prove their age for accessing age-restricted content or verify their credentials for accessing specific services without revealing unnecessary personal information.
Scalability and Future Developments
Blockchain technology, while revolutionary, faces significant hurdles in its quest for mainstream adoption. The inherent limitations in processing speed and transaction capacity, particularly on public blockchains, present a major challenge. Addressing these scalability issues is crucial for blockchain to fulfill its potential and become a truly transformative force in various sectors. This section explores the challenges, potential solutions, and emerging trends shaping the future of blockchain scalability.
The current architecture of many blockchain networks, particularly those using Proof-of-Work (PoW) consensus mechanisms, struggles to handle a large volume of transactions efficiently. This leads to slower transaction processing times, increased network congestion, and higher transaction fees. The limited throughput directly impacts user experience and makes the technology less attractive for large-scale applications requiring high transaction volumes, such as financial settlements or supply chain management. Furthermore, the energy consumption associated with some consensus mechanisms is a growing concern, both environmentally and economically.
Solutions for Improved Transaction Throughput and Cost Reduction
Several innovative solutions are being explored to enhance the scalability of blockchain networks. Layer-2 scaling solutions, such as state channels and rollups, are gaining traction. These techniques process transactions off-chain, significantly reducing the load on the main blockchain while maintaining security and integrity. Sharding, another promising approach, divides the blockchain into smaller, more manageable fragments, allowing parallel processing of transactions. Each shard handles a subset of the data and transactions, thereby improving throughput. Furthermore, advancements in consensus mechanisms, such as Proof-of-Stake (PoS), offer a more energy-efficient alternative to PoW, contributing to both improved scalability and reduced environmental impact. The transition to more efficient consensus mechanisms and the adoption of layer-2 scaling solutions are key to unlocking the full potential of blockchain technology.
Emerging Trends Shaping the Future of Blockchain Transactions
The landscape of blockchain technology is constantly evolving, with several emerging trends poised to revolutionize how we conduct digital transactions. These advancements are not only improving scalability but also enhancing security, privacy, and interoperability.
- Cross-chain interoperability: Enabling seamless transfer of assets and data between different blockchain networks, fostering collaboration and reducing fragmentation.
- Decentralized Identity (DID): Providing users with greater control over their digital identities, enhancing privacy and security in online transactions.
- Zero-knowledge proofs (ZKPs): Allowing for verification of information without revealing the underlying data, enhancing privacy and security in various applications.
- Quantum-resistant cryptography: Developing cryptographic algorithms resistant to attacks from quantum computers, ensuring the long-term security of blockchain networks.
- Blockchain-as-a-Service (BaaS): Making blockchain technology more accessible to businesses and developers through cloud-based platforms, simplifying development and deployment.
For instance, the increasing adoption of decentralized finance (DeFi) protocols, which often utilize layer-2 scaling solutions, demonstrates the growing need for and successful implementation of improved scalability. The rise of cross-chain bridges, like those connecting Ethereum and other blockchains, showcases the progress towards interoperability. These real-world examples highlight the rapid evolution of the blockchain ecosystem and its potential to transform various aspects of our digital lives.
Illustrative Example
Let’s imagine a scenario involving a simple blockchain transaction to understand how it works in practice. We’ll follow the journey of a digital payment from Alice to Bob, illustrating the key elements and security features.
This example will walk you through the process, showing how a transaction is verified, added to the blockchain, and becomes immutable. We’ll visualize the data structure on the blockchain itself, revealing its inherent security and transparency.
A Hypothetical Transaction: Alice Pays Bob
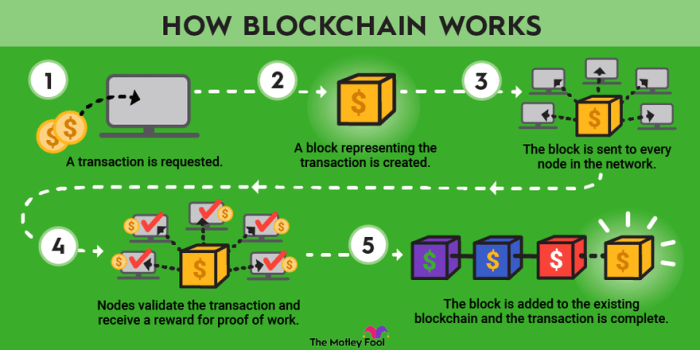
Alice wants to send Bob 5 digital tokens. First, Alice initiates the transaction using a digital wallet application. This application creates a transaction request, including details like the sender’s address (Alice’s public key), the recipient’s address (Bob’s public key), the amount (5 tokens), and a timestamp. Alice then signs this transaction request using her private key, proving her ownership and authorization. This signed transaction is then broadcast to the network of nodes participating in the blockchain.
Transaction Verification and Block Addition
Multiple nodes on the network receive Alice’s transaction. These nodes independently verify the transaction’s validity. They check if Alice possesses sufficient funds, if the recipient’s address is valid, and if the digital signature is authentic. Once a sufficient number of nodes confirm the transaction’s legitimacy (reaching a consensus), it’s bundled with other verified transactions into a block. This block contains a cryptographic hash of the previous block, creating an immutable chain. The new block, including Alice’s transaction, is added to the blockchain.
Visual Representation on the Blockchain
Imagine the blockchain as a chain of interconnected blocks. Each block contains multiple transactions. Let’s visualize Alice’s transaction within a block. The block itself would contain:
- Block Header: This includes a timestamp, a hash of the previous block, a hash of the block’s contents, and other metadata.
- Transaction Data: This section holds details of Alice’s transaction. It’s structured as follows:
- Sender’s Public Key: Alice’s public key, uniquely identifying her.
- Recipient’s Public Key: Bob’s public key, identifying the recipient.
- Amount: 5 digital tokens.
- Timestamp: The exact time of the transaction.
- Digital Signature: Alice’s digital signature, verifying the transaction’s authenticity.
This block is then linked to the previous block via its cryptographic hash. This hash is a unique fingerprint of the block’s contents, ensuring that any alteration to the block will result in a different hash, instantly revealing tampering. The chain of blocks, each linked to the previous one, creates an immutable record of all transactions, publicly accessible and auditable. Alice’s transaction, once added to the block and the block added to the chain, becomes permanently recorded on the blockchain, visible to anyone with access to the network.
Ending Remarks
Source: foolcdn.com
Blockchain isn’t just a buzzword; it’s the engine driving a new era of digital transactions. From revolutionizing finance to streamlining supply chains, its impact is undeniable. While scalability challenges remain, the innovative solutions emerging promise an even brighter future. The decentralized, secure, and efficient world of blockchain transactions is here to stay, fundamentally changing how we interact with digital value. Get ready for a smoother, safer, and faster digital economy.
Blockchain’s revolutionizing digital transactions isn’t just about faster payments; it’s about fundamentally altering ownership. This shift is all about verifiable provenance and secure transfer of assets, which is precisely what’s explored in this insightful piece: How Blockchain is Changing the Way We Approach Digital Ownership. Ultimately, this new paradigm of digital ownership is paving the way for a more transparent and efficient era of digital transactions, building trust in a previously murky landscape.
