How Blockchain is Changing the Concept of Digital Currency? It’s a game-changer, folks. Forget clunky, centralized systems – blockchain introduces a revolutionary approach to digital money, prioritizing decentralization, security, and transparency. This isn’t just about Bitcoin; it’s about reimagining how we handle value in the digital age, from cryptocurrencies to stablecoins and even central bank digital currencies (CBDCs). We’re diving deep into how this technology is shaking up the financial world and what it means for the future of money.
From its cryptographic underpinnings to the rise of smart contracts, we’ll explore the implications of this disruptive technology. We’ll compare traditional payment systems with blockchain-based ones, highlighting the enhanced security and transparency offered by the latter. We’ll also unpack the challenges – scalability, regulation, environmental concerns – and examine potential solutions, all while keeping it real and relatable.
Blockchain’s Impact on Digital Currency
Before blockchain, the world of digital currency was a Wild West. While offering the potential for faster and cheaper transactions than traditional banking systems, digital currencies lacked the robust security and trust mechanisms needed for widespread adoption. Centralized systems controlled most digital currencies, making them vulnerable to hacking, fraud, and single points of failure. The introduction of blockchain technology fundamentally changed this landscape.
Blockchain is a decentralized, distributed ledger technology that records and verifies transactions across a network of computers. Its core principles include immutability (once a transaction is recorded, it cannot be altered), transparency (all transactions are visible on the blockchain), and consensus (all participants must agree on the validity of a transaction). This differs drastically from traditional centralized databases, which are vulnerable to manipulation by a single entity.
Blockchain’s Enhancement of Security and Trust in Digital Currencies
The inherent security and transparency of blockchain directly address the limitations of previous digital currency systems. The decentralized nature eliminates single points of failure. Instead of relying on a central authority to validate transactions, blockchain uses cryptographic hashing and consensus mechanisms like Proof-of-Work or Proof-of-Stake to ensure the integrity of the ledger. This makes it incredibly difficult for malicious actors to alter transaction records or create fraudulent currencies. Furthermore, the public and transparent nature of the blockchain allows anyone to verify the authenticity of transactions, fostering trust among users. This increased security and transparency are crucial for building a reliable and widely accepted digital currency ecosystem. For example, Bitcoin, the first and most well-known cryptocurrency, utilizes blockchain technology to secure its transactions, making it significantly more resistant to fraud than earlier attempts at digital cash. The immutability of the blockchain ensures that once a Bitcoin transaction is confirmed, it cannot be reversed or altered, unlike traditional banking systems which are susceptible to chargebacks or fraudulent reversals.
Decentralization and Digital Currency
Decentralization is the beating heart of blockchain technology, and its impact on digital currencies is nothing short of revolutionary. Unlike traditional currencies controlled by central banks, blockchain-based digital currencies distribute control across a network of participants, creating a system that’s inherently more resistant to censorship and single points of failure. This shift has profound implications for how we think about money, access to finance, and the very nature of trust in the digital age.
The core principle of decentralization in blockchain is the distribution of ledger maintenance and transaction validation across numerous nodes within the network. This means no single entity, government, or institution holds absolute control over the currency’s supply or transactions. This inherent transparency and distributed governance form the bedrock of many blockchain-based digital currencies’ security and resilience.
Centralized versus Decentralized Digital Currency Systems
Centralized digital currencies, like those issued by central banks or large tech companies, operate under the control of a single authority. This authority dictates the currency’s supply, transaction rules, and overall management. Think of it like a traditional banking system, but in a digital format. In contrast, decentralized digital currencies, like Bitcoin or Ethereum, utilize blockchain technology to distribute control among a network of participants. This distributed ledger ensures transparency and prevents any single entity from manipulating the system. The key difference lies in the power dynamic: centralized systems are top-down, while decentralized systems are bottom-up, empowering users and fostering a more inclusive financial landscape.
Implications of Decentralization for Financial Inclusion and Accessibility
Decentralization significantly impacts financial inclusion by lowering the barriers to entry for individuals and businesses previously excluded from traditional financial systems. In many developing countries, access to traditional banking services is limited due to geographical constraints, high transaction costs, or stringent KYC/AML regulations. Blockchain-based digital currencies, however, offer a pathway to financial participation for the unbanked and underbanked populations. They can send and receive money globally with minimal fees, fostering economic empowerment and driving financial innovation in underserved communities. For example, the use of cryptocurrencies in countries with hyperinflation or unstable political climates provides an alternative to traditional fiat currencies, allowing individuals to preserve their savings and participate in the global economy. This shift towards decentralized finance (DeFi) is progressively democratizing access to financial services, leading to a more equitable and inclusive global financial system.
Security and Transparency in Blockchain-Based Digital Currencies
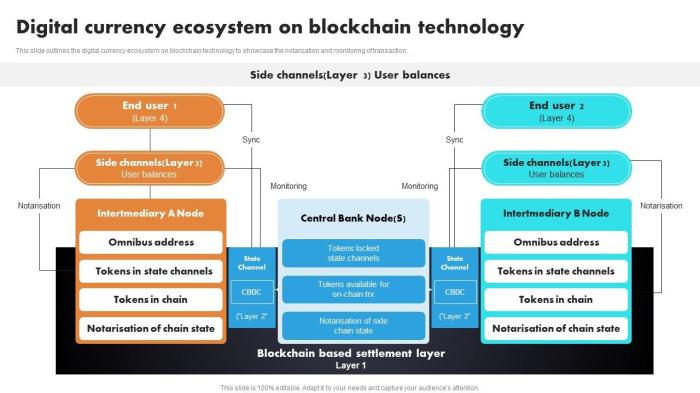
Source: slideteam.net
Blockchain technology fundamentally reshapes the landscape of digital currency security and transparency, offering significant improvements over traditional payment systems. Its inherent design features, primarily cryptography and distributed ledger technology, create a robust and auditable system, fostering trust and minimizing vulnerabilities.
Blockchain’s cryptographic features significantly enhance the security of digital currencies. This isn’t just about making transactions harder to crack; it’s about building a system where tampering is practically impossible without detection.
Cryptographic Security Mechanisms
Blockchain utilizes sophisticated cryptographic techniques to secure transactions and maintain data integrity. Each block in the chain contains a cryptographic hash – a unique digital fingerprint – of the previous block. Altering even a single bit of data within a block would drastically change its hash, creating an immediate inconsistency and making the fraudulent transaction easily detectable. This chain-like structure, combined with the use of public and private keys for digital signatures, ensures that transactions are authentic and tamper-proof. The distributed nature of the blockchain further strengthens security; no single point of failure exists, making it highly resistant to attacks. For example, Bitcoin’s use of elliptic curve cryptography (ECC) for its digital signatures provides a robust security layer against forgery and unauthorized spending.
Transaction Verification and Validation
Transaction verification and validation in a blockchain-based system is a multi-step process that leverages the collective power of the network. When a transaction is initiated, it’s broadcast to the network of nodes. These nodes then verify the transaction’s validity by checking the digital signatures, ensuring the sender possesses the necessary funds and that the transaction hasn’t already been processed. Once a sufficient number of nodes (a consensus mechanism, such as Proof-of-Work or Proof-of-Stake) confirm the transaction’s legitimacy, it’s added to a new block and appended to the existing blockchain. This distributed consensus mechanism eliminates the need for a central authority and enhances security against fraud and manipulation. For instance, in Ethereum, transactions are validated through a consensus mechanism involving miners who compete to solve complex cryptographic puzzles.
Transparency and Accountability
The transparent nature of blockchain enhances accountability in digital currency transactions. All transactions are recorded on a publicly accessible ledger, allowing anyone to view the history of transactions. While user identities might be pseudonymous (represented by public keys), the transaction details are visible, creating a verifiable audit trail. This transparency discourages fraudulent activities as all actions are permanently recorded and easily traceable. For example, if a merchant processes a payment using a blockchain-based system, the customer can easily verify that the payment has been successfully recorded on the blockchain. This transparency helps to resolve disputes and builds trust between parties.
Comparison of Security Features
| Feature | Traditional Payment System (e.g., Credit Card) | Blockchain-Based System (e.g., Bitcoin) | Comparison |
|---|---|---|---|
| Transaction Verification | Centralized authority (e.g., bank) | Distributed network of nodes | Blockchain offers decentralized verification, enhancing security and resilience against single points of failure. |
| Data Security | Vulnerable to hacking and data breaches | Cryptographic hashing and distributed ledger | Blockchain provides significantly higher security due to cryptographic techniques and data redundancy. |
| Transparency | Limited transparency; only parties involved have access to transaction details | Publicly accessible ledger | Blockchain’s transparency improves accountability and enables independent verification of transactions. |
| Reversibility | Transactions can be reversed (chargebacks) | Transactions are generally irreversible | Irreversibility in blockchain enhances security but also requires careful transaction management. |
Smart Contracts and Digital Currency
Smart contracts are revolutionizing the way we think about digital currency transactions. They’re essentially self-executing contracts with the terms of the agreement between buyer and seller directly written into lines of code. This code resides on a blockchain, ensuring transparency, security, and automation that traditional contracts simply can’t match. Think of them as automated, trustless intermediaries, eliminating the need for lawyers, notaries, or other third parties to oversee the agreement.
This automation is key to the efficiency and security of digital currency ecosystems. By codifying the conditions for a transaction, smart contracts automatically execute the transfer of funds when those conditions are met. This eliminates delays, reduces costs associated with intermediaries, and minimizes the risk of fraud or disputes. The immutability of the blockchain further reinforces the reliability of these agreements.
Smart Contract Functionality in Digital Currency Transactions
Smart contracts facilitate secure and transparent transactions by automating the process from beginning to end. For example, imagine a scenario where a company needs to pay its freelance developers upon completion of a project. A smart contract could be programmed to release payment automatically once the developer uploads the completed code to a specified location and it passes pre-defined quality checks, all verifiable on the blockchain. This removes the need for manual invoice processing, payment approvals, and potential disputes over the completion of work. The entire process is transparent, verifiable, and automated, significantly streamlining the payment process and building trust between the company and its developers.
Examples of Smart Contracts in Action
Several real-world examples illustrate the power of smart contracts in digital currency transactions. Decentralized finance (DeFi) platforms extensively utilize smart contracts for lending, borrowing, and trading cryptocurrencies. For instance, a user could lend their cryptocurrency to a DeFi platform through a smart contract, earning interest automatically based on pre-defined terms. Similarly, stablecoins, which aim to maintain a stable value pegged to a fiat currency, often use smart contracts to manage their reserves and ensure price stability. These contracts automatically adjust the supply of the stablecoin to maintain its peg. Furthermore, supply chain management is being transformed by smart contracts. Imagine tracking the movement of goods across borders – smart contracts can automatically trigger payments to suppliers upon verification of delivery at each stage of the process, improving efficiency and transparency.
Security and Transparency Enhancements through Smart Contracts
The inherent security and transparency of blockchain technology are amplified by smart contracts. The code of the smart contract is publicly auditable, allowing anyone to inspect its functionality and ensure it operates as intended. This significantly reduces the risk of manipulation or hidden clauses. Moreover, the immutability of the blockchain ensures that once a transaction is recorded, it cannot be altered or reversed, enhancing the security and integrity of the transaction. The transparent nature of these contracts promotes trust among participants, as all actions and conditions are publicly visible on the blockchain. This level of transparency fosters accountability and reduces the potential for disputes.
The Evolution of Digital Currency Models

Source: exactdn.com
Blockchain’s decentralized nature is revolutionizing digital currency, offering transparency and security previously unimaginable. But as crypto adoption explodes, so do the threats. That’s where AI steps in; read more about how it’s bolstering defenses in this insightful piece on The Future of AI in Enhancing the Security of Digital Transactions , which ultimately strengthens the overall blockchain ecosystem and its impact on digital finance.
Ultimately, the future of digital currency hinges on a robust security framework, blending the innovation of blockchain with the power of AI.
The world of digital currency is constantly evolving, branching out from its cryptocurrency roots into a diverse landscape of models, each with its own strengths and weaknesses. Understanding these different models is crucial to grasping the full potential and challenges of blockchain technology in finance. This section will explore the key differences between cryptocurrencies, stablecoins, and central bank digital currencies (CBDCs), highlighting their underlying technologies, practical applications, and regulatory hurdles.
The rise of blockchain has fueled innovation in digital currency, leading to the development of various models designed to address specific needs and challenges. These models differ significantly in their design, functionality, and the level of regulatory oversight they face.
Types of Blockchain-Based Digital Currencies
The blockchain revolution has given rise to a variety of digital currency models, each with its unique characteristics. These can be broadly categorized into cryptocurrencies, stablecoins, and central bank digital currencies (CBDCs). Understanding their distinctions is essential for navigating this rapidly evolving financial landscape.
Comparison of Digital Currency Models
The differences between these models are substantial, impacting their suitability for various use cases and their interaction with existing regulatory frameworks. While cryptocurrencies prioritize decentralization and often experience significant price volatility, stablecoins aim to maintain price stability by pegging their value to a fiat currency or other assets. CBDCs, on the other hand, are issued and regulated by central banks, offering a potential bridge between traditional and digital financial systems.
Key Characteristics of Digital Currency Types
The following table summarizes the key characteristics of each type of digital currency, offering a clear comparison based on their underlying technology, use cases, and regulatory status. Note that the regulatory status is constantly evolving and varies significantly across jurisdictions.
| Currency Type | Underlying Technology | Use Cases | Regulatory Status |
|---|---|---|---|
| Cryptocurrency (e.g., Bitcoin, Ethereum) | Decentralized blockchain networks, cryptographic principles | Payments, investments, decentralized applications (dApps) | Highly variable across jurisdictions; often subject to evolving regulations regarding anti-money laundering (AML) and know-your-customer (KYC) compliance. |
| Stablecoin (e.g., Tether, USDC) | Blockchain technology, often backed by reserves (fiat currency, other assets) | Stable value transactions, facilitating smoother crypto trading | Increasing regulatory scrutiny; regulations are developing rapidly to address risks related to reserve management and transparency. |
| Central Bank Digital Currency (CBDC) (e.g., potential future digital dollar, digital euro) | Central bank-controlled digital ledger, potentially utilizing blockchain or distributed ledger technology (DLT) | Retail payments, wholesale interbank settlements, potential for enhanced monetary policy tools | Subject to significant central bank oversight and regulation; design and implementation vary considerably depending on the central bank. |
Challenges and Future Trends
Source: tastycrypto.com
The rapid rise of blockchain-based digital currencies hasn’t been without its hurdles. While offering exciting possibilities, scalability issues, regulatory uncertainty, and environmental concerns are significant challenges that need addressing for widespread adoption. Overcoming these obstacles will pave the way for a more inclusive and sustainable future for digital finance.
Scalability Limitations
Blockchain technology, in its current form, faces limitations in processing a high volume of transactions efficiently. Many blockchains, especially those using Proof-of-Work consensus mechanisms like Bitcoin, struggle to handle the transaction throughput required for mass adoption. This results in slower transaction speeds and higher fees, hindering their usability for everyday payments. For example, during peak times, Bitcoin transaction fees can skyrocket, making it impractical for small-value transactions. This limitation is actively being addressed through various scaling solutions like layer-2 protocols (e.g., Lightning Network), sharding, and improved consensus mechanisms (e.g., Proof-of-Stake). These solutions aim to increase transaction speed and reduce costs without compromising security.
Regulatory Uncertainty
The decentralized nature of blockchain-based digital currencies presents a challenge for regulators worldwide. Governments are grappling with how to classify these assets, implement taxation policies, and prevent illicit activities like money laundering and terrorist financing. The lack of a universally accepted regulatory framework creates uncertainty for businesses and investors, hindering innovation and adoption. Different jurisdictions have adopted varying approaches, leading to a fragmented regulatory landscape. For instance, some countries have embraced cryptocurrencies, while others have imposed strict bans. The development of clear and consistent regulatory frameworks is crucial for fostering responsible innovation and protecting consumers.
Environmental Impact
Some blockchain networks, particularly those employing Proof-of-Work consensus mechanisms, have drawn criticism for their high energy consumption. The computational power required to validate transactions can lead to significant carbon emissions. Bitcoin mining, for example, has been estimated to consume substantial amounts of electricity, raising environmental concerns. This issue is being tackled through the adoption of more energy-efficient consensus mechanisms like Proof-of-Stake, which require significantly less energy to validate transactions. Furthermore, the increasing use of renewable energy sources for mining operations is contributing to a reduction in the environmental footprint of some cryptocurrencies.
Emerging Trends Shaping the Future, How Blockchain is Changing the Concept of Digital Currency
Several emerging trends are poised to reshape the future of digital currencies. Central Bank Digital Currencies (CBDCs) are gaining traction globally, with many central banks exploring the possibility of issuing digital versions of their fiat currencies. These CBDCs could offer benefits such as improved payment efficiency and financial inclusion. Another significant trend is the increasing integration of blockchain technology with other emerging technologies like the Internet of Things (IoT) and Artificial Intelligence (AI). This convergence could lead to innovative applications in various sectors, from supply chain management to healthcare. Moreover, the development of decentralized finance (DeFi) protocols is expanding access to financial services, particularly in underserved communities. DeFi platforms offer a range of services, including lending, borrowing, and trading, without the need for intermediaries. These developments are driving innovation and shaping the future of digital finance.
Case Studies
Real-world applications of blockchain-based digital currencies are rapidly expanding, demonstrating their potential to revolutionize various sectors. These case studies highlight the practical benefits and challenges associated with implementing this innovative technology. Let’s dive into some compelling examples.
Financial Inclusion through Mobile Money
Many developing countries lack robust financial infrastructure, leaving a significant portion of the population unbanked. Blockchain-based digital currencies offer a solution by enabling mobile money transfers without relying on traditional banking systems. For instance, some organizations are leveraging blockchain to create peer-to-peer payment systems that allow individuals to send and receive money using only their mobile phones. This bypasses the need for bank accounts or credit cards, dramatically increasing financial access. The benefits include reduced transaction costs, faster transfer speeds, and increased financial inclusion for underserved populations. Challenges include ensuring network scalability to handle large transaction volumes and educating users on the technology’s functionality and security measures.
Supply Chain Transparency with Provenance Tracking
Blockchain’s immutable ledger provides unparalleled transparency in supply chains. Imagine tracking a product’s journey from origin to consumer, recording every step along the way. This is precisely what blockchain enables. Companies can record information about the product’s origin, manufacturing processes, transportation, and handling. This data is cryptographically secured and readily accessible to all authorized parties. Benefits include increased product traceability, reduced counterfeiting, improved consumer trust, and enhanced supply chain efficiency. Challenges include integrating blockchain technology with existing supply chain management systems and ensuring data privacy and security across different stakeholders.
Healthcare Data Management and Interoperability
The healthcare industry struggles with data silos and interoperability issues. Patient records are often scattered across different systems, making it difficult for healthcare providers to access a complete picture of a patient’s health history. Blockchain can address this challenge by creating a secure and shared platform for storing and managing patient data. This allows authorized healthcare professionals to access relevant information seamlessly, improving the quality of care and reducing medical errors. Benefits include improved data security, enhanced patient privacy, and greater interoperability between healthcare systems. Challenges include regulatory compliance, data governance, and the need for robust data encryption and access control mechanisms.
Illustrative Example: How Blockchain Is Changing The Concept Of Digital Currency
Let’s imagine a scenario involving Sarah, a freelance graphic designer in New York, and David, a small business owner in London needing her design services. This example showcases how blockchain technology can revolutionize their financial transaction, making it faster, more secure, and transparent than traditional methods.
This hypothetical scenario details a cross-border payment using a blockchain-based digital currency, highlighting the efficiency and security advantages over traditional banking systems. We’ll track the transaction from initiation to completion, emphasizing the role of blockchain in each step.
Transaction Process Using Blockchain
Sarah and David agree on a price of $1000 for Sarah’s design work. Instead of using a traditional bank transfer, which involves intermediaries and high fees, they opt for a blockchain-based digital currency transaction. David sends Sarah the equivalent of $1000 in this digital currency using a cryptocurrency wallet. The transaction is broadcast to the blockchain network. Multiple nodes verify the transaction, ensuring its legitimacy and preventing double-spending. Once validated, the transaction is added to a block, permanently recorded on the blockchain. Sarah receives the funds in her cryptocurrency wallet, and the entire process is transparent and auditable. Both parties can view the transaction details on the public blockchain.
Benefits of Blockchain in This Transaction
The use of blockchain offers several significant advantages:
* Reduced Transaction Fees: Blockchain eliminates the need for intermediaries like banks, significantly reducing transaction fees compared to traditional methods.
* Increased Security: Blockchain’s cryptographic security measures protect the transaction from fraud and unauthorized access. The decentralized nature of the blockchain makes it highly resistant to hacking attempts.
* Enhanced Transparency: Both Sarah and David can track the transaction’s progress and status on the public blockchain, ensuring transparency and accountability.
* Faster Processing: Blockchain transactions are typically processed much faster than traditional bank transfers, eliminating delays.
* Improved Efficiency: The automation of the transaction process reduces administrative overhead and streamlines the payment process.
Comparison with Traditional Banking
In a traditional banking system, this transaction would involve multiple intermediaries (Sarah’s bank, David’s bank, potentially international payment processors), resulting in delays, higher fees, and less transparency. The transaction could take several days to complete, and the security risks are higher due to the involvement of multiple parties. In contrast, the blockchain-based transaction is faster, cheaper, and more secure.
Concluding Remarks
The blockchain revolution isn’t just hype; it’s reshaping the very fabric of digital currency. By prioritizing decentralization, security, and transparency, blockchain technology is paving the way for a more inclusive and efficient financial system. While challenges remain, the potential benefits are undeniable. From transforming financial transactions to revolutionizing supply chains and healthcare, the impact of blockchain on digital currency is profound and only set to grow exponentially. So buckle up, because the future of finance is here, and it’s decentralized.
