How Blockchain Can Increase Transparency in Government Operations? Forget shadowy backroom deals and opaque processes. Imagine a government where every transaction, every decision, is auditable and readily available to the public. That’s the promise of blockchain technology, a revolutionary system that could reshape how governments operate and interact with their citizens. This isn’t just about tech; it’s about rebuilding trust and accountability.
Blockchain’s decentralized, immutable ledger ensures data integrity, making it virtually impossible to alter records after they’re added. This level of security and transparency could dramatically reduce corruption, streamline bureaucratic processes, and empower citizens with unprecedented access to information. From tracking public funds to securing voting systems, blockchain’s potential applications in government are vast and transformative. But, as with any disruptive technology, challenges exist – scalability, interoperability, and the need for robust legal frameworks all need careful consideration.
Introduction
Government transparency – the idea that public information should be readily available to the public – is a cornerstone of a healthy democracy. However, in reality, accessing this information often proves to be a frustrating, opaque, and time-consuming process. This lack of transparency erodes public trust, hinders accountability, and fuels cynicism towards government institutions. Blockchain technology, with its inherent security and immutability, offers a potential solution to these persistent problems.
Government transparency, in its purest form, means that all government actions, decisions, and financial transactions are open to public scrutiny. It involves clear and accessible communication about how public funds are allocated, how laws are made, and how government services are delivered. This isn’t just about releasing data; it’s about making that data understandable and usable for citizens.
Blockchain technology can significantly enhance government transparency by creating a secure, auditable, and tamper-proof record of government activities. Its decentralized nature prevents single points of failure or manipulation, ensuring that information remains accurate and accessible. This inherent security fosters trust and accountability, addressing many of the challenges associated with traditional, centralized systems.
Challenges to Government Transparency
Several factors contribute to the lack of transparency in many government operations. These include complex bureaucratic processes, a lack of standardized data formats, inadequate technology infrastructure, and a reluctance to share information, often citing concerns about security or privacy. Furthermore, the sheer volume of data generated by government agencies can be overwhelming, making it difficult to analyze and interpret. The absence of a unified, easily accessible platform further exacerbates the issue. Existing systems often rely on outdated technology, making data retrieval and analysis challenging.
Examples of Government Processes Lacking Transparency
Consider the process of public procurement. Often, the details of contracts awarded, the selection criteria used, and the bidding process itself are shrouded in secrecy. This lack of transparency opens the door to corruption and favoritism. Similarly, land registration processes in many countries are opaque, leading to disputes and uncertainty over land ownership. The allocation of public funds, particularly in large infrastructure projects, often lacks sufficient detail and accountability, making it difficult to track how money is spent and whether it is being used effectively. Finally, the internal workings of many government agencies, including decision-making processes and internal communications, are not readily available to the public.
How Blockchain Can Address These Challenges
Blockchain’s decentralized and immutable ledger can provide a solution to these problems. For instance, all procurement contracts could be recorded on a blockchain, making the entire process – from bidding to award – transparent and auditable. Similarly, land registries could be digitized and secured on a blockchain, providing irrefutable proof of ownership and preventing fraudulent transactions. Public expenditure could be tracked on a blockchain, allowing citizens to easily monitor how public funds are used. Furthermore, the use of smart contracts could automate certain government processes, reducing the potential for human error and bias. This increased transparency leads to greater accountability, improved efficiency, and increased public trust.
How Blockchain Enhances Data Integrity and Security
Blockchain technology offers a revolutionary approach to data management, promising unprecedented levels of transparency and security, particularly beneficial for government operations. Unlike traditional databases, blockchain’s inherent design features significantly improve data integrity and security, fostering trust and accountability within public institutions. This section will delve into the specifics of how blockchain achieves this.
Data Immutability Mechanisms
Blockchain’s core strength lies in its immutability – the inability to alter or delete existing data once it’s recorded. This is achieved through a sophisticated system of interconnected blocks, each containing a timestamped record of transactions. Each new block is cryptographically linked to the previous one, creating a chronologically ordered and tamper-evident chain. Any attempt to modify data in a previous block would require altering all subsequent blocks, a computationally infeasible task given the decentralized and distributed nature of the blockchain. This chain of cryptographic hashes ensures that any tampering would be immediately detectable. Furthermore, the distributed nature of the ledger means that multiple copies exist across a network, making it extremely difficult to compromise the integrity of the entire system.
Cryptographic Security Features
Blockchain leverages robust cryptographic techniques to secure data and transactions. Public-key cryptography is central to this, using unique key pairs for each participant. Private keys are kept secret and used to authorize transactions, while public keys are publicly available for verification. Every transaction is digitally signed using the sender’s private key, ensuring authenticity and preventing unauthorized modifications. The cryptographic hashing algorithm used to link blocks together further enhances security, as even a minor change in data results in a completely different hash value, immediately revealing any tampering. This makes blockchain significantly more secure than traditional databases that rely on centralized access controls which are vulnerable to hacking and single points of failure.
Comparison of Traditional Databases and Blockchain
Traditional databases, while useful, are susceptible to data breaches, manipulation, and single points of failure. A central server holds all data, making it a prime target for hackers. Data integrity depends entirely on the security measures implemented around this central server, which can be compromised. Blockchain, in contrast, distributes the data across a network, eliminating the single point of failure vulnerability. Its cryptographic security and immutability make it significantly more resistant to unauthorized access and data manipulation. The distributed nature of the blockchain means that even if some nodes are compromised, the integrity of the data remains intact due to the existence of multiple copies.
Hypothetical Scenario: A Blockchain-Secured Government Database
Imagine a government database storing land registry information. Traditionally, this data would be stored on a central server, vulnerable to corruption or manipulation. With blockchain, each land transaction (sale, transfer, etc.) would be recorded as a block on a distributed ledger. This would provide an immutable record of ownership, accessible to all authorized parties. The cryptographic security would prevent fraudulent transactions, and the transparency of the ledger would make it easy to audit and verify the accuracy of the data. This would significantly reduce the risk of land fraud and disputes, increasing public trust and efficiency in government operations. The public could verify land ownership information directly through the blockchain, eliminating the need for intermediaries and reducing bureaucracy.
Tracking Public Funds and Reducing Corruption
Blockchain technology, with its inherent transparency and immutability, offers a powerful solution to the age-old problem of government corruption and inefficient public fund management. By creating a shared, verifiable ledger of all financial transactions, blockchain can significantly improve accountability and reduce opportunities for embezzlement and misappropriation of funds. This enhanced transparency empowers citizens to monitor government spending and hold officials responsible for their actions.
Blockchain’s impact on tracking public funds stems from its decentralized and secure nature. Every transaction is recorded on the blockchain, creating an auditable trail that is resistant to tampering. This eliminates the possibility of altering records after the fact, a common tactic used in traditional systems prone to corruption.
Blockchain’s Role in Enhancing Public Procurement Transparency
Public procurement, the process by which governments purchase goods and services, is often a fertile ground for corruption. Traditional methods rely on centralized databases and paper-based systems, making them vulnerable to manipulation and lack of oversight. Blockchain can revolutionize this process by creating a transparent and secure platform for all stages of procurement, from tendering to contract award and payment. For instance, a blockchain-based system could record all bids, ensuring fairness and preventing favoritism. The entire process, from the initial request for proposals to the final payment, would be visible to all authorized parties, making it significantly harder to engage in corrupt practices. Imagine a scenario where every step of a road construction project, from awarding the contract to the payment of subcontractors, is publicly and verifiably recorded on a blockchain. This would drastically reduce the potential for kickbacks and inflated invoices.
Comparison of Auditing Methods
The following table compares traditional auditing methods with blockchain-based auditing, highlighting the key differences in cost, efficiency, transparency, and security.
| Method | Cost | Time Efficiency | Transparency Level | Security Level |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Traditional Auditing | High (manual processes, extensive labor) | Low (time-consuming, often delayed) | Low (access limited to auditors) | Moderate (vulnerable to data manipulation) |
| Blockchain-Based Auditing | Initially high (implementation costs), but lower long-term (automation) | High (automated processes, real-time data) | High (publicly accessible, verifiable data) | High (cryptographically secure, tamper-proof) |
Benefits of Blockchain for Public Fund Management
The benefits of utilizing blockchain for public fund management are substantial and far-reaching. Implementing blockchain can lead to increased efficiency, improved accountability, and ultimately, a more trustworthy government.
- Enhanced Transparency: All transactions are publicly auditable, increasing public trust and accountability.
- Reduced Corruption: The immutability of the blockchain makes it extremely difficult to manipulate financial records.
- Improved Efficiency: Automated processes reduce administrative overhead and streamline workflows.
- Increased Security: Cryptographic security protects funds from unauthorized access and theft.
- Better Data Management: Centralized and easily accessible data improves reporting and analysis.
- Faster Audits: Real-time data availability significantly reduces the time required for audits.
Improving Citizen Engagement and Participation
Blockchain technology, with its inherent transparency and security features, offers a compelling pathway to revolutionize citizen engagement in government. By providing a verifiable and auditable record of interactions, it fosters trust and encourages greater participation in the democratic process. This increased transparency can lead to more informed decision-making and a stronger sense of civic responsibility.
Blockchain’s decentralized nature ensures that no single entity controls the data, reducing the risk of manipulation and enhancing the integrity of citizen interactions with the government. This shift towards a more participatory and accountable governance model holds immense potential for strengthening democracy.
Secure and Verifiable Voting Systems
Blockchain’s cryptographic security and immutability make it ideally suited for creating secure and verifiable voting systems. Each vote is recorded on the blockchain as a unique cryptographic hash, ensuring its authenticity and preventing tampering. This eliminates the need for centralized vote counting servers, reducing the risk of fraud and manipulation. Furthermore, citizens can verify the integrity of their votes through blockchain explorers, providing transparency and building confidence in the electoral process. Estonia, for example, has explored the use of blockchain technology for secure digital identity management, a crucial component of secure online voting systems. While full blockchain-based voting systems are still under development, pilot projects are showing promising results in terms of security and transparency.
Blockchain-Based Citizen Feedback Mechanisms
Blockchain can power transparent and secure feedback mechanisms, allowing citizens to submit comments, suggestions, and complaints directly to government agencies. These submissions are recorded immutably on the blockchain, creating a verifiable record of citizen engagement. This ensures that feedback is not lost or ignored, and it promotes accountability by allowing citizens to track the status of their submissions. A municipality could, for example, use a blockchain-based platform to manage citizen feedback on proposed infrastructure projects, ensuring all comments are recorded and considered in the decision-making process. This increased transparency and accountability would foster greater trust between citizens and their government.
Challenges in Implementing Blockchain-Based Citizen Engagement Tools
While the potential benefits are significant, several challenges need to be addressed before widespread adoption of blockchain-based citizen engagement tools. Scalability remains a concern, particularly for large populations. The technical complexity of blockchain technology can also pose a barrier to adoption, requiring significant investment in infrastructure and training. Furthermore, ensuring data privacy and complying with existing data protection regulations are crucial considerations. The need for widespread public understanding and acceptance of blockchain technology is also paramount for successful implementation. Addressing these challenges through careful planning and collaboration is crucial for the successful integration of blockchain into citizen engagement processes.
Improving Access to Government Information
Blockchain can enhance access to government information by creating a decentralized, tamper-proof repository of public records. Citizens can easily access this information through blockchain explorers, ensuring transparency and accountability. This improved access to information empowers citizens to make informed decisions and participate more effectively in the democratic process. Imagine a scenario where all government contracts and procurement data are stored on a public blockchain. Citizens could then easily verify the fairness and transparency of these processes, potentially uncovering instances of corruption or inefficiency. This increased access to information would contribute to a more informed and engaged citizenry.
Streamlining Government Processes and Reducing Bureaucracy: How Blockchain Can Increase Transparency In Government Operations
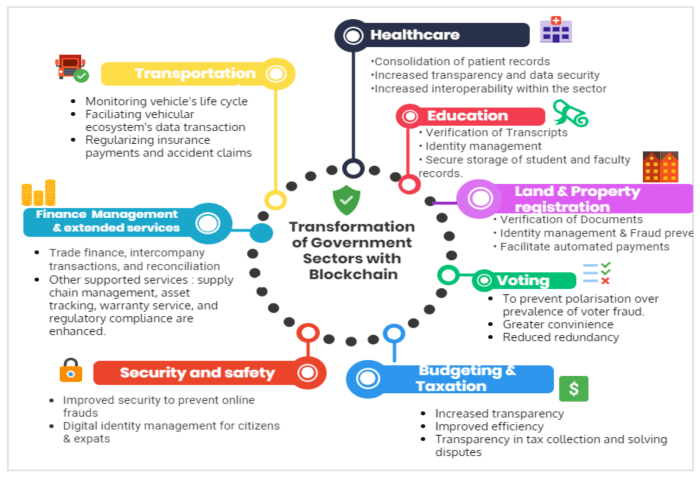
Source: mdpi.com
Imagine a government where every transaction is publicly verifiable, boosting accountability. This level of transparency, achievable through blockchain technology, isn’t just about fiscal responsibility; it extends to areas like healthcare data management, mirroring the secure, transparent systems needed in fields like genomics, as explored in The Intersection of Biotechnology and Technology in Medicine. Ultimately, blockchain’s potential for secure data handling offers a blueprint for more trustworthy governance across the board.
Blockchain technology, with its inherent transparency and immutability, offers a powerful solution to the age-old problem of bureaucratic inefficiencies in government. By creating a shared, verifiable ledger of transactions and data, blockchain can significantly streamline processes, reduce delays, and ultimately improve the delivery of public services. This translates to better outcomes for citizens and a more efficient use of taxpayer money.
Implementing blockchain can drastically reduce the time and resources spent on verifying information, reducing paperwork, and eliminating the need for multiple intermediaries. This is achieved through the automation of processes and the establishment of trust between different government departments and citizens.
Examples of Streamlined Government Processes
Several government processes can benefit significantly from blockchain integration. Consider land registries: currently, transferring land ownership often involves lengthy paperwork, multiple approvals, and potential for fraud. A blockchain-based land registry would provide a secure, transparent, and easily auditable record of ownership, eliminating delays and reducing the risk of disputes. Similarly, the issuance and verification of licenses and permits, currently a slow and often opaque process, could be dramatically accelerated through blockchain. Imagine instantly verifiable driver’s licenses or building permits accessible to all relevant authorities. The process of managing government procurement, often plagued by corruption and inefficiency, could also be revolutionized by using blockchain to track contracts, payments, and deliverables in a transparent and immutable manner. Finally, the management of social welfare programs, often complex and prone to errors, could benefit from blockchain’s secure and efficient data management capabilities.
Reducing Bureaucratic Delays Through Blockchain Implementation
Traditional government processes often rely on paper-based systems and manual verification, leading to significant delays. Requests can get lost, approvals can be delayed, and information can be easily manipulated. Blockchain’s decentralized and immutable nature eliminates many of these bottlenecks. Automated workflows, triggered by events recorded on the blockchain, can significantly speed up processing times. For instance, a citizen applying for a passport might see the entire application process, from submission to issuance, tracked and updated on the blockchain in real-time, eliminating the need for constant follow-up calls or visits. This increased transparency and efficiency reduces frustration for citizens and improves government responsiveness.
Comparison of Traditional and Blockchain-Based Processes
Let’s compare the issuance of a business license. Traditionally, this involves submitting numerous forms to different departments, waiting for approvals at each stage, and potentially facing delays due to lost paperwork or bureaucratic hurdles. This process can take weeks, or even months. A blockchain-based system, however, could automate much of this. The application, once submitted and verified, is recorded on the blockchain. Different departments can access and verify the information in real-time, eliminating the need for repeated submissions and manual checks. The entire process could be completed in a matter of days, if not hours, significantly improving efficiency. The transparency offered by the blockchain also reduces the potential for corruption and delays caused by intentional or unintentional bottlenecks.
Streamlined Government Process Flowchart: Business License Issuance, How Blockchain Can Increase Transparency in Government Operations
Imagine a flowchart depicting the process. It begins with the applicant submitting their application digitally. This application, along with all supporting documents, is then digitally signed and added to the blockchain. The blockchain automatically triggers notifications to the relevant departments (e.g., tax, licensing, zoning). Each department verifies their specific requirements and updates the application status on the blockchain. Once all verifications are complete, the system automatically issues the license, which is then recorded on the blockchain and accessible to the applicant and relevant authorities. The entire process is transparent, secure, and auditable, eliminating delays and improving efficiency. This visual representation clearly demonstrates the reduced number of steps and the elimination of manual intervention compared to traditional methods.
Addressing Scalability and Interoperability Challenges
Source: blockchainlion.com
Implementing blockchain technology in large-scale government systems presents unique hurdles. While blockchain offers numerous benefits, its inherent limitations in processing speed and data capacity, coupled with the need for seamless communication between different government agencies and potentially even international bodies, require careful consideration and innovative solutions. Successfully navigating these challenges is crucial for realizing the full potential of blockchain in government.
The sheer volume of transactions a large government handles daily poses a significant scalability challenge. Current blockchain technologies, especially those relying on proof-of-work consensus mechanisms, can struggle to process the high throughput required for managing citizen records, financial transactions, and supply chain information simultaneously. Furthermore, the need for different government departments to share information securely and efficiently necessitates seamless interoperability between disparate blockchain networks. This lack of standardization hinders the development of a unified, comprehensive system.
Scalability Solutions for Government Blockchains
Addressing scalability involves exploring various technical approaches. Sharding, for example, divides the blockchain into smaller, more manageable parts, allowing parallel processing of transactions. This significantly increases throughput. Another approach is to utilize layer-2 scaling solutions, such as state channels or sidechains, which handle transactions off the main blockchain, reducing the load on the primary network. These solutions can be tailored to the specific needs of different government applications, optimizing performance and efficiency. For instance, a city might use sharding to manage property records, while a national government could leverage sidechains for secure cross-border data exchange. The choice of solution depends on factors like the volume of transactions, the complexity of the data, and the required level of security.
Interoperability Between Blockchain Networks
Interoperability is crucial for effective data sharing across different government agencies and systems. A lack of standardization can lead to data silos and hinder the development of a holistic, integrated government platform. Solutions such as cross-chain communication protocols, which allow different blockchains to communicate and exchange information securely, are vital. These protocols often involve the use of atomic swaps or other mechanisms to ensure that transactions are completed seamlessly across different networks. Furthermore, the development of common data standards and formats can significantly improve interoperability, allowing for smoother data exchange between disparate systems. The adoption of open standards and collaborative efforts between government agencies and technology providers are key to achieving this goal. A successful implementation could resemble a federated network, where multiple blockchain networks operate independently but can communicate and share information through agreed-upon protocols.
Technical Considerations for Large-Scale Implementation
Implementing a large-scale blockchain system in government requires careful planning and consideration of several technical factors. This includes choosing the appropriate consensus mechanism (proof-of-stake, delegated proof-of-stake, or other alternatives) to balance security and efficiency. Security audits and penetration testing are crucial to identify and mitigate potential vulnerabilities. The system should also be designed with robust data governance and privacy controls to ensure compliance with relevant regulations and protect sensitive information. Finally, the implementation should involve a phased approach, starting with pilot projects to test and refine the system before full-scale deployment. This iterative approach minimizes risks and allows for adjustments based on real-world experience. For example, a pilot project could focus on a specific department or function before expanding to other areas of government.
Legal and Regulatory Frameworks for Blockchain in Government
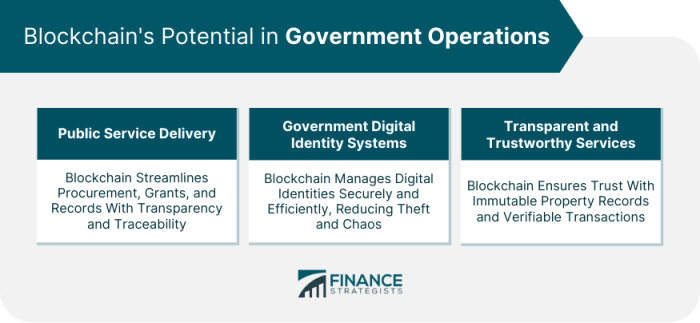
Source: financestrategists.com
Implementing blockchain technology in government requires navigating a complex legal and regulatory landscape. The decentralized, immutable nature of blockchain presents both opportunities and challenges for existing legal frameworks designed for centralized systems. Ensuring public trust and responsible innovation necessitates careful consideration of legal implications at every stage of implementation.
Legal and Regulatory Challenges of Blockchain Adoption
The decentralized nature of blockchain technology clashes with traditional governmental structures and regulations. Data privacy laws, particularly concerning personally identifiable information (PII), need careful consideration. Existing laws around data ownership, access, and control may not fully address the unique characteristics of blockchain data. Furthermore, the lack of established legal precedents regarding blockchain’s use in evidence and legal proceedings poses a significant hurdle. Contract law also needs adaptation to accommodate smart contracts, automated agreements executed on the blockchain. Finally, the potential for misuse, such as for illicit activities, requires robust regulatory mechanisms. For example, the anonymity features of some blockchains could be exploited, necessitating measures to balance privacy with accountability.
The Need for Clear Legal Frameworks
Clear legal frameworks are crucial for establishing trust and fostering the responsible adoption of blockchain technology in the public sector. These frameworks should define the legal status of blockchain data, the rights and responsibilities of different stakeholders, and the processes for resolving disputes related to blockchain transactions. Without clear legal guidance, uncertainty can stifle innovation and discourage public sector organizations from adopting this potentially transformative technology. Furthermore, a robust legal framework can help ensure accountability and transparency, preventing misuse and fostering public confidence in blockchain-based government services. A well-defined legal environment reduces risks for both government entities and citizens, encouraging broader adoption.
Examples of Existing or Proposed Legal Frameworks
While a universally accepted legal framework for blockchain in government is still developing, several jurisdictions are leading the way. The Estonian e-Residency program, for example, leverages blockchain technology for secure digital identity management. Other countries, including Singapore and Australia, are actively exploring the use of blockchain for various government services, accompanied by regulatory initiatives that address data privacy, security, and interoperability. The EU’s focus on data protection through the GDPR also indirectly impacts the use of blockchain, necessitating careful consideration of data handling practices. These initiatives demonstrate a growing recognition of the need for adaptable and forward-looking legal frameworks. These frameworks often involve a combination of existing laws adapted to the blockchain context and new regulations tailored to the technology’s unique aspects.
Key Legal Considerations for Blockchain Adoption in Government
Before implementing blockchain in government operations, several crucial legal considerations must be addressed:
- Data Privacy and Protection: Compliance with existing data protection regulations (e.g., GDPR, CCPA) is paramount. Mechanisms for anonymization or pseudonymization of data must be carefully considered.
- Data Security and Integrity: Legal frameworks should address the security and integrity of blockchain systems, including measures to prevent unauthorized access, modification, or deletion of data.
- Smart Contract Legality and Enforceability: The legal status and enforceability of smart contracts need to be clearly defined, addressing potential disputes and liabilities.
- Interoperability and Standardization: Legal frameworks should encourage interoperability between different blockchain systems used by various government agencies.
- Cybersecurity and Risk Management: Robust cybersecurity measures and risk management strategies are essential to mitigate potential threats and vulnerabilities.
- Accessibility and Inclusivity: Legal frameworks should ensure that blockchain-based government services are accessible and inclusive to all citizens, regardless of their technical skills or digital literacy.
- Accountability and Transparency: Mechanisms for accountability and transparency in the use of blockchain technology within government operations must be established.
Case Studies of Blockchain Implementation in Government
Real-world applications of blockchain in government are emerging, offering valuable insights into its potential and limitations. Examining these case studies reveals both successes and challenges, shaping future implementations. Understanding these experiences is crucial for effective adoption.
Estonia’s e-Governance System
Estonia has long been a pioneer in digital governance. While not solely reliant on blockchain, its X-Road data exchange system leverages distributed ledger technology principles for secure data sharing between government agencies and citizens. This allows for efficient interoperability and enhanced data security, reducing reliance on centralized databases vulnerable to breaches. The system’s success highlights the value of integrating blockchain-like principles into existing infrastructure rather than a complete overhaul. Challenges included integrating the system with legacy systems and ensuring consistent data quality across various agencies.
Dubai’s Blockchain Strategy
Dubai’s ambitious goal is to become a fully blockchain-powered government by 2021. While not completely achieved, significant progress has been made in various sectors. The implementation of blockchain for land registry has streamlined property transactions, improving transparency and reducing processing times. Similarly, blockchain-based digital identity solutions aim to simplify citizen interactions with government services. Challenges encountered include the need for robust regulatory frameworks and overcoming technological hurdles related to scalability and interoperability across different systems. The Dubai experience underscores the importance of a comprehensive, phased approach to blockchain adoption.
Sweden’s Blockchain-Based Voting Pilot Project
Sweden has experimented with blockchain for secure and transparent voting in pilot projects. These initiatives aim to enhance the integrity of the electoral process by providing an immutable record of votes. While still in the testing phase, these pilots demonstrate the potential of blockchain to increase trust and confidence in elections. However, challenges include ensuring accessibility for all citizens, addressing potential vulnerabilities to cyberattacks, and navigating legal and regulatory complexities surrounding electronic voting. The lessons learned from these projects emphasize the need for rigorous security audits and public education to ensure widespread acceptance.
The Andhra Pradesh, India Land Records Management System
Andhra Pradesh, a state in India, implemented a blockchain-based land records management system. This system aimed to address issues of land fraud and disputes by creating a transparent and tamper-proof record of land ownership. The system improved the efficiency of land registration and reduced the time and cost associated with land transactions. However, challenges included ensuring data accuracy and integrating the system with existing land records databases. The successful implementation in Andhra Pradesh showcases the potential of blockchain technology to improve governance in developing countries.
Comparison of Approaches
These case studies showcase diverse approaches to blockchain adoption in government. Some, like Estonia, integrate blockchain principles into existing systems, while others, like Dubai, aim for more comprehensive transformation. Each approach presents unique benefits and challenges depending on the existing infrastructure, technological capabilities, and regulatory environment. Successful implementation often involves a phased approach, starting with pilot projects in specific areas before broader deployment.
Lessons Learned
The successful implementation of blockchain in government requires careful planning, robust security measures, and a phased approach. Collaboration between government agencies, technology providers, and citizens is crucial for building trust and ensuring widespread adoption. Addressing scalability and interoperability challenges is also essential for achieving the full potential of blockchain technology in the public sector. Furthermore, establishing clear legal and regulatory frameworks is vital for fostering innovation and mitigating risks.
Conclusion
The integration of blockchain technology into government operations isn’t just a technological upgrade; it’s a fundamental shift towards a more open, accountable, and efficient public sector. While challenges remain, the potential benefits – reduced corruption, increased citizen engagement, and streamlined processes – are too significant to ignore. The journey towards a blockchain-powered, transparent government is underway, and its success hinges on collaboration between technologists, policymakers, and the citizens it serves. The future of governance might just be more transparent than we ever imagined.
