How AI is Revolutionizing Predictive Analytics for Business? Forget crystal balls; the future of business is here, and it’s powered by algorithms. Predictive analytics, once a realm of statistical guesswork, is undergoing a radical transformation thanks to artificial intelligence. From crunching massive datasets to uncovering hidden patterns, AI is boosting prediction accuracy like never before, impacting everything from financial forecasting to personalized marketing. Get ready to dive into the AI-powered revolution that’s reshaping how businesses anticipate and adapt to the ever-changing market landscape.
This shift isn’t just about slightly better predictions; it’s about unlocking entirely new levels of insight. AI’s ability to process vast amounts of data – both structured and unstructured – allows businesses to identify trends and make decisions with a level of precision previously unimaginable. This means smarter investments, more efficient operations, and a competitive edge in a world that demands constant adaptation.
The Rise of AI in Predictive Analytics
Predictive analytics, the art of forecasting future outcomes based on historical data, has been a cornerstone of business decision-making for decades. Think back to simpler times – maybe using spreadsheets to extrapolate sales trends or relying on gut feeling informed by past experience. While effective in its own way, this traditional approach had significant limitations.
Traditional methods often relied on simpler statistical models and lacked the capacity to handle the massive, complex datasets that modern businesses generate. These limitations resulted in less accurate predictions, missed opportunities, and inefficient resource allocation. Imagine trying to predict customer churn with only basic regression analysis when you have access to petabytes of data on customer behavior, social media interactions, and economic indicators. The sheer volume and complexity would overwhelm traditional methods.
The integration of Artificial Intelligence (AI) into predictive analytics has fundamentally changed the game. Advancements in machine learning, particularly deep learning algorithms, have unlocked the potential to analyze far larger and more intricate datasets than ever before. AI algorithms can identify subtle patterns and correlations that would be invisible to human analysts or simpler statistical models, leading to significantly more accurate and nuanced predictions. Furthermore, AI systems can adapt and improve their predictive accuracy over time through continuous learning and refinement.
AI’s Impact Across Industries
The transformative power of AI-driven predictive analytics is felt across numerous sectors. For example, in finance, AI algorithms are used to detect fraudulent transactions in real-time, assess credit risk more accurately, and optimize investment portfolios. The healthcare industry leverages AI to predict patient readmissions, personalize treatment plans, and accelerate drug discovery. Retail giants use AI to forecast demand, optimize inventory management, and personalize customer recommendations, leading to increased sales and customer satisfaction. Even the manufacturing sector benefits, using AI for predictive maintenance to minimize downtime and optimize production processes. These examples showcase the broad applicability and significant impact of AI in enhancing predictive capabilities across diverse business landscapes.
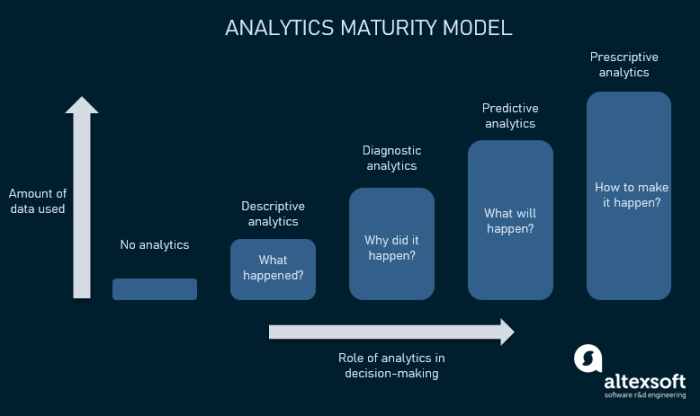
Core AI Techniques in Predictive Analytics: How AI Is Revolutionizing Predictive Analytics For Business
Source: squarespace-cdn.com
AI’s predictive power is transforming business, offering insights previously unimaginable. This data-driven revolution extends beyond analytics; consider how AI is streamlining workflows, as seen in the rise of AI-powered virtual assistants, check out this insightful piece on How AI-Powered Virtual Assistants Are Changing the Way We Work to see how this impacts efficiency. Ultimately, these advancements feed back into more accurate and insightful predictive analytics, creating a powerful feedback loop for business growth.
Predictive analytics, once the realm of statistical guesswork, is now being supercharged by the power of artificial intelligence. AI algorithms are no longer just crunching numbers; they’re learning from data, identifying patterns invisible to the human eye, and making predictions with unprecedented accuracy. This section dives into the core AI techniques driving this revolution.
Machine Learning Algorithms and Prediction Accuracy
Machine learning (ML) forms the bedrock of many AI-powered predictive analytics solutions. Various algorithms, each with its strengths and weaknesses, contribute to improved prediction accuracy. Regression algorithms, for example, predict a continuous value (like future sales revenue). Linear regression models the relationship between variables with a straight line, while more complex models like polynomial regression can capture non-linear relationships. Classification algorithms, on the other hand, predict a categorical outcome (like customer churn – yes or no). Logistic regression is a common choice, offering probabilistic predictions. Support Vector Machines (SVMs) excel at finding optimal separating hyperplanes in high-dimensional data, making them useful for complex classification tasks. Clustering algorithms, such as K-means, group similar data points together, uncovering hidden segments within customer bases or product categories, informing targeted marketing or product development strategies. The choice of algorithm depends heavily on the specific prediction task and the nature of the data. For instance, predicting stock prices might use time-series analysis, a specialized type of regression.
Deep Learning Architectures for Complex Business Predictions
When dealing with extremely complex datasets and intricate relationships, deep learning steps in. Deep learning architectures, particularly neural networks, can handle massive amounts of data and learn highly non-linear patterns. For example, a feedforward neural network might be used to predict customer lifetime value based on a multitude of factors like demographics, purchase history, and website activity. Recurrent Neural Networks (RNNs), specifically designed for sequential data, are invaluable for forecasting time series data, such as predicting energy consumption based on historical usage patterns or anticipating fluctuations in supply chains. The power of deep learning lies in its ability to automatically learn hierarchical representations of data, extracting increasingly abstract features that improve prediction accuracy. For instance, in image recognition (applied to defect detection in manufacturing), a deep neural network might learn to identify edges, then shapes, then objects, finally classifying the image as containing a defect or not.
Supervised vs. Unsupervised Learning in Business Predictive Modeling
The two major paradigms of machine learning, supervised and unsupervised learning, offer distinct approaches to predictive modeling. Supervised learning utilizes labeled data – data where the outcome is already known. For example, a dataset of past loan applications, labeled with whether each applicant defaulted or not, can train a model to predict the likelihood of default for future applicants. Unsupervised learning, conversely, works with unlabeled data. Clustering algorithms, mentioned earlier, fall under this category. They can identify customer segments without pre-defined labels, allowing businesses to tailor marketing strategies to specific groups. The choice between supervised and unsupervised learning depends on the availability of labeled data and the nature of the prediction task. Often, a hybrid approach is employed, where unsupervised learning is used for exploratory data analysis, followed by supervised learning for predictive modeling. For instance, clustering might identify distinct customer groups, then supervised learning can predict the likelihood of each group purchasing a new product.
Natural Language Processing (NLP) and Unstructured Data, How AI is Revolutionizing Predictive Analytics for Business
A significant portion of business data exists in unstructured formats: emails, customer reviews, social media posts, and more. Natural Language Processing (NLP) bridges the gap, allowing AI to extract valuable insights from this textual data for prediction. Sentiment analysis, a key NLP technique, gauges the emotional tone of text, enabling businesses to understand customer opinions about their products or services. This sentiment can then be incorporated into predictive models to forecast sales or brand reputation. Topic modeling can identify recurring themes in large volumes of text, revealing emerging trends or potential risks. For example, analyzing customer reviews can help predict product failures or identify areas needing improvement. By integrating NLP with other AI techniques, businesses can unlock the predictive power hidden within their vast stores of unstructured data.
Applications of AI-Powered Predictive Analytics Across Industries
Source: website-files.com
AI-powered predictive analytics is no longer a futuristic concept; it’s rapidly transforming how businesses operate across diverse sectors. By leveraging vast datasets and sophisticated algorithms, companies are gaining unprecedented insights, optimizing processes, and achieving significant competitive advantages. This section explores the practical applications of AI in various industries, showcasing its transformative power.
AI in the Financial Sector
The financial industry, with its massive data volumes and inherent risks, is a prime beneficiary of AI-driven predictive analytics. From fraud detection to personalized financial advice, AI is revolutionizing how financial institutions operate and manage risk. The following table highlights key applications, their advantages, and associated challenges.
| Application | Benefits | Challenges | Example |
|---|---|---|---|
| Fraud Detection | Reduced financial losses, improved customer trust, enhanced operational efficiency. | Data imbalance, evolving fraud techniques, model explainability. | AI algorithms analyze transaction patterns to identify anomalies indicative of fraudulent activity, flagging suspicious transactions for review. This allows for faster detection and prevention of fraud compared to traditional rule-based systems. |
| Risk Assessment | Improved credit scoring accuracy, better loan approval decisions, reduced default rates. | Data bias, model interpretability, regulatory compliance. | AI models analyze a wide range of data points – credit history, income, spending habits – to assess the creditworthiness of individuals and businesses, leading to more accurate and efficient lending decisions. |
| Algorithmic Trading | Increased profitability, faster execution speeds, improved portfolio diversification. | Market volatility, model overfitting, regulatory scrutiny. | AI algorithms analyze market data in real-time to identify profitable trading opportunities, executing trades at optimal prices and minimizing risk. |
| Customer Churn Prediction | Proactive customer retention strategies, improved customer loyalty, increased revenue. | Data quality, model accuracy, effective intervention strategies. | AI models analyze customer behavior patterns to identify individuals at high risk of churning, allowing for targeted interventions such as personalized offers or improved customer service. |
AI in Supply Chain Management
Predictive analytics powered by AI significantly enhances supply chain efficiency and resilience. By analyzing historical data, market trends, and external factors, businesses can optimize inventory management, improve logistics, and mitigate disruptions.
Predictive modeling in supply chain management employs several methods:
- Demand Forecasting: AI algorithms analyze sales data, seasonality, and external factors (e.g., weather patterns, economic indicators) to predict future demand, enabling optimal inventory levels and production planning.
- Inventory Optimization: AI helps determine optimal stock levels, minimizing storage costs while ensuring sufficient inventory to meet demand and avoid stockouts.
- Logistics Optimization: AI algorithms optimize transportation routes, warehouse locations, and delivery schedules, reducing costs and improving delivery times.
- Risk Management: AI identifies potential supply chain disruptions (e.g., natural disasters, geopolitical events) allowing businesses to develop contingency plans and mitigate potential losses.
AI in Marketing and Sales
AI is transforming marketing and sales by enabling hyper-personalization and data-driven decision-making. By analyzing customer data, AI algorithms can segment customers into distinct groups based on their characteristics and preferences, leading to more effective marketing campaigns and personalized recommendations.
For instance, AI facilitates:
- Customer Segmentation: AI algorithms analyze customer demographics, purchase history, and online behavior to group customers with similar characteristics, allowing for targeted marketing efforts.
- Personalized Recommendations: AI-powered recommendation engines analyze customer preferences to suggest products or services that are most likely to appeal to them, increasing sales and customer satisfaction.
- Predictive Lead Scoring: AI models predict the likelihood of a lead converting into a customer, allowing sales teams to prioritize their efforts on the most promising prospects.
- Marketing Campaign Optimization: AI analyzes the performance of marketing campaigns to identify what’s working and what’s not, enabling continuous improvement and optimization.
AI in Healthcare
In the healthcare industry, AI-powered predictive analytics is revolutionizing patient care and improving health outcomes. By analyzing patient data, AI can identify individuals at high risk of developing specific conditions, enabling early intervention and preventative measures.
AI applications in healthcare include:
- Patient Risk Stratification: AI algorithms analyze patient data (medical history, lifestyle factors, genetic information) to identify individuals at high risk of developing specific diseases, allowing for proactive interventions.
- Disease Prediction: AI models predict the likelihood of a patient developing a particular disease based on their risk factors, enabling early diagnosis and treatment.
- Personalized Medicine: AI helps tailor treatment plans to individual patients based on their genetic makeup and other factors, improving treatment effectiveness and reducing side effects.
- Drug Discovery and Development: AI accelerates the drug discovery process by analyzing vast datasets to identify potential drug candidates and predict their efficacy.
Data Management and Ethical Considerations
Predictive analytics, fueled by AI, is only as good as the data it’s fed. Garbage in, garbage out, as the saying goes. This section dives into the crucial role of data management and the ethical tightrope walk inherent in using AI for business predictions. Getting this right isn’t just about accuracy; it’s about responsible innovation and building trust.
Data quality and preprocessing are paramount for accurate AI-driven predictions. Think of it like baking a cake – you wouldn’t use spoiled ingredients and expect a delicious result. Similarly, flawed data leads to flawed predictions, impacting everything from marketing campaigns to risk assessment. Cleaning, transforming, and validating data are essential steps, involving techniques like handling missing values, identifying and removing outliers, and ensuring data consistency across different sources. For example, inconsistencies in customer address data can significantly skew a marketing campaign’s effectiveness.
Data Quality and Preprocessing
High-quality data is the foundation of reliable predictive models. This involves several key steps: data cleaning (handling missing values, correcting errors), data transformation (scaling, encoding categorical variables), and feature engineering (creating new features from existing ones to improve model accuracy). For instance, a retailer might transform raw sales data into weekly sales averages to identify seasonal trends, thereby improving sales forecasting accuracy. Without these steps, the AI model may struggle to discern meaningful patterns and produce accurate predictions. Ignoring data quality can lead to costly errors and misinformed business decisions.
Challenges of Handling Large and Complex Datasets
The sheer volume and complexity of data in today’s business environment pose significant challenges. We’re talking petabytes of information from various sources – customer interactions, market trends, sensor data – all needing to be integrated and processed efficiently. Traditional data management techniques often struggle to cope with this scale and velocity. This necessitates the use of advanced technologies like distributed computing frameworks (like Hadoop and Spark) and cloud-based data warehouses to handle the processing and storage needs. Furthermore, the diverse formats and structures of data from different sources require robust data integration strategies to ensure consistency and compatibility. For example, a financial institution dealing with transaction data, customer profiles, and market data needs a sophisticated system to integrate and analyze this heterogeneous data for accurate risk assessment.
Data Privacy and Security in AI-Powered Predictive Analytics
Protecting sensitive customer data is non-negotiable. AI systems often process vast amounts of personal information, raising significant privacy concerns. Robust security measures, including encryption, access control, and anonymization techniques, are essential to prevent data breaches and unauthorized access. Compliance with regulations like GDPR and CCPA is also crucial. Furthermore, implementing privacy-preserving machine learning techniques, such as federated learning or differential privacy, allows for model training without directly accessing sensitive data, striking a balance between data utility and privacy. For instance, a healthcare provider using AI to predict patient outcomes must ensure that patient data is handled according to strict privacy regulations and security protocols.
Ethical Considerations in AI-Driven Predictive Analytics
Bias in algorithms is a significant ethical concern. AI models are trained on data, and if that data reflects existing societal biases (e.g., gender, racial), the model will likely perpetuate and even amplify those biases. This can lead to unfair or discriminatory outcomes. For example, a loan application algorithm trained on biased historical data might unfairly deny loans to applicants from certain demographic groups. Transparency and explainability in AI models are crucial for identifying and mitigating bias. Regular audits and monitoring are necessary to ensure fairness and accountability.
Key Ethical Principles for AI in Business:
- Fairness: Ensure AI systems do not discriminate against any group.
- Transparency: Make the decision-making process of AI systems understandable.
- Accountability: Establish clear lines of responsibility for AI-driven decisions.
- Privacy: Protect the confidentiality and security of personal data.
- Human Oversight: Maintain human control and oversight of AI systems.
Future Trends and Challenges

Source: techprofree.com
The rapid advancement of AI in predictive analytics isn’t without its hurdles. While the potential benefits are immense, understanding the emerging trends and anticipating the challenges is crucial for businesses aiming to leverage this technology effectively. This section delves into the exciting future of AI-powered predictive analytics, highlighting both the opportunities and the obstacles on the path ahead.
The future of AI in predictive analytics is a dynamic landscape shaped by both technological advancements and the evolving needs of businesses. Emerging trends like explainable AI (XAI) and reinforcement learning are poised to significantly impact how businesses utilize predictive models, while challenges related to data quality, ethical considerations, and the talent gap require careful attention.
Explainable AI (XAI) and Reinforcement Learning
Explainable AI focuses on making the decision-making processes of AI models more transparent and understandable. This is crucial for building trust and ensuring accountability, especially in high-stakes applications like loan approvals or medical diagnoses. Imagine a loan application being rejected; with XAI, the system could explain *why*, highlighting specific factors in the applicant’s profile that led to the decision. This contrasts with traditional “black box” models, where the reasoning behind a prediction remains opaque. Reinforcement learning, on the other hand, allows AI systems to learn through trial and error, improving their performance over time by interacting with their environment. This is particularly valuable in dynamic situations, such as optimizing supply chains or personalizing customer experiences in real-time. For example, an AI system managing a warehouse could learn the optimal path for robots to move goods based on real-time demand and stock levels, constantly refining its strategy for maximum efficiency.
Challenges in AI Adoption and Implementation
Several significant obstacles hinder the widespread adoption of AI-powered predictive analytics. Data quality remains a primary concern; inaccurate, incomplete, or biased data can lead to flawed predictions and unreliable insights. Furthermore, integrating AI systems into existing business processes can be complex and costly, requiring significant investment in infrastructure, training, and expertise. Concerns around data privacy and security are also paramount, particularly with the increasing reliance on sensitive customer data. Finally, regulatory frameworks are still evolving, creating uncertainty and potentially hindering innovation. Consider a retail company attempting to implement AI for personalized recommendations. If their customer data is not properly anonymized and secured, they risk violating privacy regulations and damaging their reputation.
The Need for Skilled Professionals
The successful development and deployment of AI-powered predictive analytics systems rely heavily on a skilled workforce. There is a growing demand for professionals with expertise in data science, machine learning, and AI ethics. These individuals are needed not only to build and maintain the systems but also to interpret the results, ensure responsible use, and address ethical concerns. The lack of adequately trained professionals poses a significant barrier to wider AI adoption. Companies need to invest in training and development programs to build internal expertise or collaborate with external consultants possessing the necessary skills. A team composed of data scientists, AI engineers, and ethicists is essential for developing and implementing trustworthy and effective AI solutions.
The Impact of AI on Future Business Decision-Making
Imagine a futuristic boardroom: Instead of relying solely on gut feelings and historical data, executives utilize AI-powered dashboards providing real-time insights and predictive analytics across all aspects of the business. AI anticipates market trends, optimizes resource allocation, identifies potential risks, and personalizes customer interactions with unprecedented accuracy. This leads to faster, more informed decisions, improved operational efficiency, and a significant competitive advantage. The illustration depicts a scenario where a manufacturing company uses AI to predict equipment failures, preventing costly downtime and optimizing maintenance schedules. The AI system analyzes sensor data from the machines, identifying patterns indicative of impending failure. This allows for proactive maintenance, minimizing disruptions to production and reducing overall operational costs. The AI system also helps the company optimize its supply chain, predicting fluctuations in demand and adjusting inventory levels accordingly. This prevents stockouts and reduces waste, leading to significant cost savings and improved customer satisfaction. The integration of AI into business decision-making transforms it from a largely reactive process to a proactive, data-driven approach, enabling companies to adapt swiftly to changing market conditions and stay ahead of the competition.
Final Review
The integration of AI into predictive analytics isn’t just a technological advancement; it’s a fundamental shift in how businesses operate. By harnessing the power of machine learning, deep learning, and NLP, companies can move beyond reactive strategies and embrace a proactive, data-driven approach. While challenges remain – data quality, ethical considerations, and the need for skilled professionals – the potential benefits are undeniable. The future of business is intelligent, and it’s being shaped by AI’s ability to predict, anticipate, and ultimately, succeed.
