Exploring the Benefits of Smart Healthcare Devices: Imagine a world where your smartwatch not only tracks your steps but also predicts potential health issues. That’s the promise of smart healthcare, a rapidly evolving field transforming how we monitor, diagnose, and treat illnesses. From wearable fitness trackers to implantable sensors, these devices are revolutionizing patient care, offering unprecedented levels of personalized medicine and proactive health management.
This isn’t just about convenience; it’s about empowering individuals to take control of their health. We’ll delve into the specifics, examining how smart devices improve diagnostic capabilities, enhance treatment adherence, and even contribute to cost-effective healthcare solutions. But we’ll also address the crucial aspects of data privacy and security, ensuring a balanced perspective on this transformative technology.
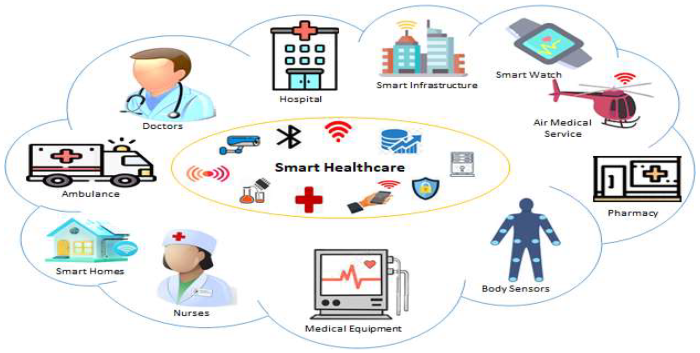
Introduction to Smart Healthcare Devices
Source: mdpi.com
Exploring the benefits of smart healthcare devices reveals a fascinating trend: personalized medicine is getting a serious upgrade. This is largely thanks to the advancements in AI, as detailed in this insightful article on The Future of AI-Powered Predictive Analytics , which shows how predictive analytics are transforming preventative care. Ultimately, this means smarter devices leading to healthier outcomes.
Smart healthcare devices are revolutionizing how we approach health and wellness. These aren’t your grandma’s medical equipment; they’re sophisticated tools integrating technology to monitor, manage, and improve various aspects of our health, often seamlessly integrating into our daily lives. Key characteristics include connectivity (allowing data transmission), data analysis capabilities (providing insights into health trends), and user-friendliness (making them accessible and easy to use).
The evolution of smart healthcare devices has been rapid, fueled by advancements in miniaturization, sensor technology, and wireless communication. From bulky, hospital-bound machines, we’ve progressed to sleek, wearable devices that track our steps, sleep, and heart rate. This increasing prevalence is driven by a growing awareness of personal health, the affordability of technology, and the potential for proactive healthcare management. The global market is booming, with projections indicating substantial growth in the coming years, reflecting a significant shift towards personalized and preventative healthcare.
Categories of Smart Healthcare Devices
Smart healthcare devices encompass a broad spectrum of technologies, each serving a distinct purpose. These can be broadly categorized into wearables, implantables, and remote monitoring systems. Understanding these categories helps illustrate the diverse applications of this technology.
Wearable Smart Healthcare Devices
Wearable devices are perhaps the most recognizable category. These are portable devices worn on the body, often unobtrusively, to collect health data. Examples include smartwatches that track heart rate and activity levels, fitness trackers that monitor sleep patterns and calories burned, and continuous glucose monitors for individuals with diabetes. The convenience and accessibility of wearables have made them incredibly popular, empowering individuals to take a more active role in managing their health. For instance, the Apple Watch’s ability to detect irregular heart rhythms has been credited with saving lives by providing early warnings of potential cardiac issues.
Implantable Smart Healthcare Devices
Implantable devices represent a more advanced segment, involving devices surgically placed within the body. These devices offer continuous monitoring and even therapeutic interventions. Pacemakers, which regulate heart rhythm, are a classic example. More recently, advancements have led to implantable glucose sensors for diabetes management and neurostimulators for managing chronic pain or neurological disorders. While requiring surgical intervention, these devices offer continuous, real-time data and the potential for life-altering improvements in health outcomes. Consider the impact of an implantable defibrillator preventing a sudden cardiac arrest – a clear demonstration of the life-saving potential of these technologies.
Remote Monitoring Systems
Remote monitoring systems utilize technology to track vital signs and other health metrics from a distance. This often involves wearable or implantable devices transmitting data wirelessly to healthcare providers or a central monitoring system. This allows for proactive intervention and reduces the need for frequent hospital visits. Examples include remote patient monitoring systems for individuals with chronic conditions like heart failure or COPD, enabling early detection of worsening symptoms and timely medical intervention. For example, a patient with congestive heart failure might have a device that monitors their weight and heart rate daily, alerting their doctor to any concerning changes, preventing hospital readmissions and improving quality of life.
Enhanced Patient Monitoring and Management: Exploring The Benefits Of Smart Healthcare Devices
Smart healthcare devices are revolutionizing how we monitor and manage patient health, moving beyond the limitations of traditional methods. These devices offer a more accurate, timely, and convenient approach, empowering both patients and healthcare providers. The result? Better health outcomes and a more efficient healthcare system.
Smart devices significantly improve the accuracy and timeliness of patient data collection through continuous monitoring and automated data transmission. This contrasts sharply with traditional methods, which often rely on infrequent, manual checks that can lead to delays in identifying critical changes in a patient’s condition.
Remote Patient Monitoring for Chronic Disease Management
Remote patient monitoring (RPM) using smart devices is particularly transformative for managing chronic conditions like diabetes, heart failure, and hypertension. Wearable sensors continuously track vital signs such as heart rate, blood pressure, and blood glucose levels, transmitting this data directly to healthcare providers. This allows for early detection of potential problems, proactive interventions, and personalized treatment adjustments, ultimately leading to improved patient outcomes and reduced hospital readmissions. For example, a diabetic patient using a continuous glucose monitor (CGM) can receive real-time alerts if their blood sugar levels fall outside a safe range, allowing them to take corrective action immediately. Similarly, a patient with heart failure can be monitored remotely for signs of worsening fluid retention, enabling timely intervention to prevent hospitalization.
Patient Empowerment Through Smart Devices
Smart devices empower patients to take a more active role in managing their own health. Wearable fitness trackers encourage healthier lifestyles by tracking activity levels, sleep patterns, and other health metrics. Mobile health apps provide patients with access to educational resources, medication reminders, and communication tools to connect with their healthcare providers. For instance, a patient using a hypertension tracking app can monitor their blood pressure regularly, log their readings, and share the data with their doctor. This increased transparency and engagement fosters a stronger patient-provider relationship and promotes better adherence to treatment plans.
Comparison of Traditional and Smart Device Monitoring
The following table compares traditional healthcare monitoring methods with smart device-based monitoring across key factors:
| Method | Cost | Accuracy | Convenience |
|---|---|---|---|
| Traditional in-person visits | High (doctor visits, lab tests) | Moderate (relies on infrequent measurements) | Low (requires travel, scheduling) |
| Smart devices (wearables, apps) | Variable (device cost, subscription fees) | High (continuous monitoring, automated data) | High (convenient data collection, remote monitoring) |
Improved Diagnostic Capabilities and Early Disease Detection
Smart healthcare devices are revolutionizing how we approach diagnosis, moving beyond reactive treatment to proactive prevention. These devices offer the potential for earlier and more accurate detection of various health conditions, leading to improved patient outcomes and reduced healthcare costs. By leveraging advanced sensors and sophisticated algorithms, they provide insights previously unattainable through traditional methods.
Smart devices contribute to early disease detection through continuous monitoring of vital signs and subtle physiological changes. This constant data stream allows for the identification of anomalies that might otherwise go unnoticed until the disease progresses to a more advanced and difficult-to-treat stage. This proactive approach allows for timely intervention, improving treatment efficacy and potentially saving lives.
Smart Device Applications in Diagnostics, Exploring the Benefits of Smart Healthcare Devices
Several smart devices are making significant contributions to diagnostic capabilities. For example, wearable fitness trackers continuously monitor heart rate, sleep patterns, and activity levels. Deviations from established baselines can flag potential issues like atrial fibrillation or sleep apnea, prompting further investigation. Smart scales can track weight changes and body composition, providing early warnings of conditions like obesity or muscle loss. Furthermore, smart inhalers can monitor medication usage, helping doctors assess the effectiveness of asthma or COPD treatment and identify potential compliance issues. Non-invasive blood glucose monitors allow for continuous glucose monitoring, enabling better management of diabetes and reducing the risk of complications.
Accuracy of Smart Device Diagnostics
The accuracy of smart device diagnostics varies depending on the device, the condition being detected, and the algorithm used for data analysis. While they cannot entirely replace traditional diagnostic methods like blood tests or imaging scans, they provide valuable supplementary information. For instance, a smart watch detecting an irregular heartbeat might prompt a visit to a cardiologist for an electrocardiogram (ECG) to confirm the diagnosis. The accuracy of these devices is constantly improving with advancements in sensor technology and machine learning algorithms. It’s crucial to remember that these devices are tools to assist healthcare professionals, not to replace them. The interpretation of data obtained from smart devices requires professional medical expertise.
Smart Devices and Disease Detection
| Device | Disease | Detection Method | Accuracy |
|---|---|---|---|
| Smartwatch with ECG | Atrial Fibrillation | Continuous heart rate monitoring, rhythm analysis | High sensitivity, requires confirmation with ECG |
| Smart Scale | Obesity, Muscle Loss | Weight, BMI, body fat percentage measurement | High accuracy for weight and BMI; body fat percentage accuracy varies |
| Continuous Glucose Monitor (CGM) | Diabetes | Continuous glucose level monitoring | High accuracy, provides real-time data for better management |
| Smart Inhaler | Asthma, COPD | Medication usage tracking | High accuracy for medication usage; effectiveness assessment requires clinical evaluation |
Enhanced Treatment and Medication Adherence
Smart healthcare devices are revolutionizing how we approach treatment and medication adherence, moving beyond simple reminders to personalized, data-driven interventions that significantly improve patient outcomes. These devices offer a powerful combination of convenience, monitoring, and personalized support, ultimately leading to better health management.
Smart devices enhance treatment efficacy by providing continuous data on a patient’s condition, medication intake, and lifestyle factors. This real-time information empowers both patients and healthcare providers to make more informed decisions, leading to adjustments in treatment plans that optimize results and minimize adverse effects. This personalized approach is crucial in managing chronic conditions, where consistent medication adherence is vital.
Medication Reminders and Dosage Tracking
Smart devices offer a variety of methods for medication reminders and dosage tracking. Many smartphone apps, for instance, allow users to input their medication schedule, receiving timely alerts throughout the day. More sophisticated devices, like smart pill dispensers, can physically dispense medication at the prescribed times, providing an extra layer of assurance for patients who might struggle with remembering their doses. Wearable devices, such as smartwatches, can also send reminders and track medication intake through user input or integration with other health apps. These diverse approaches cater to different patient needs and preferences, ensuring accessibility and effectiveness.
Personalized Medicine and Treatment Plans
The data collected by smart healthcare devices plays a pivotal role in personalized medicine. By tracking vital signs, activity levels, and medication adherence, these devices create a comprehensive picture of a patient’s health status. This detailed information allows healthcare providers to tailor treatment plans to individual needs, optimizing medication dosages and treatment strategies for maximum effectiveness. For example, a patient with diabetes might use a continuous glucose monitor (CGM) integrated with an insulin pump. The CGM continuously monitors blood sugar levels, and the insulin pump automatically adjusts insulin delivery based on the real-time data, significantly improving blood sugar control. This level of personalization minimizes trial-and-error and improves the quality of life for patients.
Case Studies Illustrating Impact on Treatment Outcomes
A study published in the Journal of the American Medical Informatics Association demonstrated that patients using a medication adherence app showed a significant improvement in medication adherence rates compared to a control group. The app provided reminders, progress tracking, and educational materials, leading to better treatment outcomes. In another study, published in the journal Diabetes Care, researchers found that patients using a CGM integrated with an insulin pump experienced a significant reduction in HbA1c levels (a marker of long-term blood sugar control) compared to patients using traditional methods of insulin management. These studies highlight the tangible benefits of smart devices in improving medication adherence and ultimately, patient health.
Cost-Effectiveness and Efficiency in Healthcare
Smart healthcare devices hold the potential to revolutionize healthcare delivery, not just by improving patient outcomes, but also by significantly impacting the cost and efficiency of the system. By streamlining processes, reducing hospital readmissions, and enabling proactive care, these devices offer a compelling case for long-term cost savings and improved resource allocation.
The integration of smart devices can lead to substantial cost reductions across various aspects of healthcare. Early disease detection, for instance, prevents the need for more expensive interventions later on. Remote patient monitoring minimizes the need for frequent and costly hospital visits, while improved medication adherence reduces the burden of managing chronic conditions and their associated complications. This overall shift towards preventative and proactive care translates into significant financial benefits for both individuals and the healthcare system as a whole.
Cost Savings Through Smart Healthcare Devices
Smart devices contribute to cost savings in several key areas. Remote patient monitoring, for example, allows for early detection of potential problems, preventing costly hospitalizations. Consider a scenario where a patient with congestive heart failure is monitored remotely via a smart wearable. Early detection of irregular heart rhythms allows for timely intervention, preventing a potentially life-threatening emergency room visit. Similarly, smart inhalers for asthma patients can track medication usage, ensuring adherence and reducing the need for costly emergency room visits related to asthma attacks. These examples highlight how proactive monitoring can drastically reduce healthcare expenses associated with acute events.
Improved Efficiency of Healthcare Delivery
Smart devices enhance efficiency by optimizing workflows and resource allocation. Automated data collection and analysis streamline administrative tasks, freeing up healthcare professionals to focus on direct patient care. For example, remote diagnostics and consultations using telehealth platforms powered by smart devices can reduce the need for in-person appointments, saving both time and travel costs for patients. Moreover, improved data management allows for more informed decision-making, leading to more efficient allocation of resources such as hospital beds and medical staff. The integration of AI-powered diagnostic tools also speeds up the diagnostic process, reducing delays and improving overall efficiency.
Challenges and Limitations in Implementing Smart Healthcare Devices
Despite the numerous advantages, widespread adoption of smart healthcare devices faces certain challenges. High initial investment costs for devices and infrastructure can be a significant barrier, particularly for smaller healthcare providers. Data privacy and security concerns also need careful consideration, as the collection and transmission of sensitive patient data necessitate robust security measures. Furthermore, the integration of these devices into existing healthcare systems can be complex and require significant changes to workflows and training for healthcare professionals. The digital divide, where access to technology and internet connectivity varies across populations, can also limit the equitable distribution of benefits. Finally, the lack of standardized data formats and interoperability between different devices can hinder the seamless sharing and analysis of patient data.
Comparison of Healthcare Costs
Let’s compare healthcare costs with and without the widespread adoption of smart healthcare devices:
- Without Smart Devices: Higher frequency of hospital visits and emergency room visits, increased costs associated with managing chronic conditions due to poor adherence, higher administrative costs due to manual data entry and processing, delays in diagnosis leading to more expensive interventions.
- With Smart Devices: Reduced hospitalizations and emergency room visits through proactive monitoring and early detection, improved medication adherence leading to better management of chronic conditions, streamlined administrative processes through automated data collection and analysis, faster diagnostics and improved treatment outcomes leading to cost savings.
For instance, a study by [insert credible source and specific data here, e.g., a reputable journal article or government report] showed a [percentage]% reduction in hospital readmissions for patients with heart failure using remote monitoring technology. Another study [insert credible source and specific data here] demonstrated a [percentage]% decrease in healthcare costs associated with managing diabetes through improved medication adherence using smart inhalers. These examples underscore the significant potential of smart healthcare devices to deliver both improved patient outcomes and substantial cost savings.
Privacy and Security Concerns of Smart Healthcare Data
The rise of smart healthcare devices, while offering incredible potential for improving health outcomes, introduces significant privacy and security challenges. The sheer volume of sensitive personal data collected – from biometric readings to diagnoses and treatment plans – makes these devices prime targets for cyberattacks and data breaches. Understanding these risks and implementing robust safeguards is crucial for ensuring the ethical and responsible use of this technology.
The sensitive nature of health data demands stringent security measures. A single breach could expose individuals to identity theft, financial fraud, and discrimination. Moreover, compromised medical information could lead to incorrect diagnoses, inappropriate treatments, and potentially life-threatening consequences. This underscores the critical need for robust security protocols and a comprehensive understanding of the potential vulnerabilities.
Data Encryption and Secure Data Storage
Protecting patient data requires a multi-layered approach, starting with robust encryption techniques. Data encryption transforms sensitive information into an unreadable format, rendering it useless to unauthorized individuals. This is crucial both during data transmission (e.g., from a wearable device to a server) and during storage. Secure data storage, often involving cloud-based solutions, needs to comply with industry best practices, including access controls, regular security audits, and intrusion detection systems. For instance, a hospital utilizing a cloud-based system to store patient ECG data should ensure the platform employs end-to-end encryption and multi-factor authentication to prevent unauthorized access.
Regulatory Frameworks and Ethical Considerations
Navigating the legal and ethical landscape of smart healthcare data is complex. Regulations like HIPAA in the US and GDPR in Europe provide frameworks for protecting patient privacy and data security, outlining requirements for data handling, consent, and breach notification. However, the rapid evolution of technology often outpaces regulatory frameworks, creating a need for ongoing adaptation and interpretation. Ethical considerations extend beyond legal compliance, encompassing issues like informed consent, data minimization, and the potential for algorithmic bias in data analysis. For example, the use of AI in diagnostic tools requires careful consideration of potential biases embedded in the algorithms, ensuring fair and equitable access to healthcare for all populations.
Mitigating Privacy and Security Risks
Several strategies can mitigate the privacy and security risks associated with smart healthcare data. These include implementing strong authentication mechanisms (e.g., multi-factor authentication), regularly updating device software and security patches, educating users about best practices for data security, and conducting thorough risk assessments to identify and address vulnerabilities. Furthermore, adopting a privacy-by-design approach, which integrates privacy considerations into the design and development phases of smart healthcare devices, is essential. This proactive approach ensures that privacy and security are not merely add-ons but integral components of the technology itself. For example, designing a smart insulin pump with built-in encryption and tamper-detection mechanisms is a key aspect of privacy-by-design. Regular security audits and penetration testing can further strengthen the security posture, proactively identifying and remediating potential weaknesses before they can be exploited.
The Future of Smart Healthcare Devices
The world of smart healthcare is poised for explosive growth, driven by relentless technological advancements and a growing demand for personalized, efficient, and accessible healthcare. We’re moving beyond simple monitoring to a future where preventative care, personalized medicine, and proactive interventions are the norm, all powered by increasingly sophisticated smart devices.
The integration of artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning (ML) is the key driver of this transformation. These technologies are not merely enhancing existing devices; they are enabling entirely new possibilities in diagnosis, treatment, and overall patient management. The future isn’t just about smarter devices; it’s about smarter healthcare systems, interconnected and responsive to individual needs.
Artificial Intelligence and Machine Learning in Smart Healthcare
AI and ML are revolutionizing how smart healthcare devices function. AI algorithms are being trained on massive datasets of patient information to identify patterns and predict health risks with unprecedented accuracy. This allows for earlier disease detection, personalized treatment plans, and more effective preventative measures. For example, AI-powered devices can analyze ECG data to detect subtle irregularities indicative of heart conditions long before they manifest as noticeable symptoms. ML algorithms, meanwhile, are constantly learning and improving their accuracy, leading to increasingly refined diagnostic tools and personalized therapies. This continuous learning process ensures that these devices remain at the cutting edge of medical innovation.
Predictions for the Transformation of Healthcare Delivery
Smart healthcare devices are predicted to dramatically alter healthcare delivery in the coming years. We can anticipate a significant shift towards preventative and personalized care, with remote monitoring and virtual consultations becoming increasingly commonplace. This will lead to a reduction in hospital readmissions, improved patient outcomes, and a more efficient use of healthcare resources. Imagine a future where chronic conditions are managed proactively through smart devices, alerting healthcare professionals to potential problems before they escalate into crises. This proactive approach will transform the healthcare experience, moving from reactive treatment to preventative wellness. Companies like Apple with its HealthKit and Google with its FitBit integration are already paving the way for this interconnected ecosystem.
A Futuristic Healthcare Scenario
Imagine a world where a personalized health dashboard, accessible via a sleek, wearable device, constantly monitors your vital signs, sleep patterns, and activity levels. This dashboard uses AI to analyze this data, providing personalized insights and recommendations tailored to your individual needs. If an anomaly is detected, the device immediately alerts your physician, allowing for early intervention. Simultaneously, advanced diagnostic tools, integrated into your home environment, perform non-invasive screenings, detecting potential health issues before they become serious. Your medication is dispensed automatically, with dosages adjusted based on your real-time health data. This seamless integration of smart devices and AI transforms healthcare from a reactive system to a proactive, personalized, and efficient one, enhancing both quality of life and longevity.
Final Summary
The integration of smart devices into healthcare isn’t just a trend; it’s a fundamental shift in how we approach wellness. While challenges remain, particularly concerning data security and equitable access, the potential benefits are undeniable. From early disease detection to improved treatment outcomes, smart healthcare devices are paving the way for a more proactive, personalized, and ultimately healthier future. The journey towards a smarter healthcare system is underway, and the possibilities are truly exciting.
