How Blockchain is Changing the Future of Online Privacy? Forget Big Brother – imagine a world where *you* control your digital identity. Blockchain, that revolutionary tech behind crypto, is quietly rewriting the rules of online privacy. It’s not just about Bitcoin anymore; it’s about reclaiming your data, securing your information, and building a more transparent, user-centric internet. This isn’t science fiction; it’s the dawn of a new era of digital freedom.
This deep dive explores how blockchain’s decentralized nature is disrupting traditional data management. We’ll unpack how it empowers users with self-sovereign identity, strengthens encryption, and even helps mitigate the damage from data breaches. Get ready to rethink everything you know about online privacy – because the future is decentralized, secure, and it’s powered by blockchain.
Decentralized Identity and Blockchain
Imagine a world where you’re in complete control of your digital identity, a world free from the prying eyes of massive corporations and data breaches. That’s the promise of decentralized identity powered by blockchain technology. It’s a shift from the current system where your personal information is scattered across countless platforms, often vulnerable to misuse. Blockchain offers a radical new approach, putting you back in the driver’s seat.
Decentralized identity uses blockchain’s inherent security and transparency to give individuals more control over their personal data. Instead of relying on centralized authorities like Facebook or Google to verify your identity, you become the custodian of your own digital credentials. This means you decide who gets access to what information and under what conditions. This level of control is not only empowering but also crucial in safeguarding your online privacy.
Self-Sovereign Identity and its Advantages
Self-sovereign identity (SSI) is the core concept behind this revolution. It signifies the ability of individuals to control and manage their digital identities independently. Unlike centralized systems where companies hold your data and dictate how it’s used, SSI allows you to selectively share specific attributes with different entities, only when necessary. This fine-grained control minimizes the risk of large-scale data breaches and significantly enhances privacy. For example, instead of providing your entire driver’s license information to rent a car, you could only share your age and driving status, thereby reducing the amount of personal information exposed. The benefits of this are clear: increased privacy, reduced risk of identity theft, and greater transparency in data usage.
Blockchain’s Role in Ensuring Data Immutability and Security
Blockchain’s decentralized and immutable nature is what makes it ideal for managing digital identities. Once data is recorded on a blockchain, it cannot be altered or deleted without detection. This immutability is critical because it guarantees the integrity and authenticity of your digital identity. Furthermore, cryptographic techniques secure the blockchain, making unauthorized access extremely difficult. Each transaction, which could be a verification of your identity or a sharing of a specific attribute, is cryptographically signed and linked to the previous transaction, forming an unbroken chain of trust. This makes tampering with the data nearly impossible. Imagine a digital ledger where every transaction related to your identity is permanently recorded and verified by multiple parties, making it highly secure and transparent.
Comparison of Blockchain-Based Identity Solutions
Several blockchain-based identity solutions are emerging, each with its strengths and weaknesses. Some systems utilize public blockchains like Ethereum, offering transparency and decentralization but potentially sacrificing speed and scalability. Others opt for private or permissioned blockchains, prioritizing performance and control but potentially compromising on complete decentralization. For instance, some systems focus on verifiable credentials, allowing users to prove specific attributes without revealing unnecessary information. Others focus on decentralized identifiers (DIDs), offering a more comprehensive approach to managing all aspects of a digital identity. The optimal solution often depends on the specific use case and the desired balance between privacy, security, and efficiency. The ongoing development and refinement of these solutions promise even greater advancements in the future, constantly improving user privacy and control.
Data Encryption and Blockchain
Blockchain technology, with its inherent security features, offers a powerful foundation for enhancing data privacy. By combining blockchain’s immutable ledger with robust encryption techniques, we can create systems that significantly improve the protection of sensitive user information online. This synergy protects data both in transit and at rest, making it significantly more resistant to unauthorized access and manipulation.
Blockchain’s integration with encryption isn’t simply about adding another layer of security; it’s about fundamentally changing how we approach data management and privacy. Instead of relying on centralized servers vulnerable to hacking and data breaches, we can distribute data across a network, making it exponentially harder for malicious actors to compromise the entire system. This distributed nature, combined with encryption, offers a new paradigm for data security.
Cryptographic Methods Used with Blockchain
Several cryptographic methods are crucial for securing data within a blockchain-based system. These methods work in concert to provide a multi-layered defense against attacks. For example, Elliptic Curve Cryptography (ECC) is often used for generating digital signatures, verifying transactions, and managing cryptographic keys. ECC provides strong security with relatively smaller key sizes compared to other methods like RSA, making it suitable for resource-constrained environments. Additionally, symmetric encryption algorithms, such as AES (Advanced Encryption Standard), are employed to encrypt the actual data stored on the blockchain or associated with it. This ensures that even if an attacker gains access to the data, they cannot easily decipher it without the correct decryption key. Hashing algorithms, like SHA-256, play a critical role in creating unique identifiers for data blocks, ensuring data integrity and preventing tampering. These algorithms produce a fixed-size output, regardless of the input size, making them ideal for creating secure fingerprints of data.
Challenges of End-to-End Encryption in Blockchain Systems
Implementing end-to-end encryption within a blockchain-based system presents unique challenges. The decentralized nature of blockchain, while beneficial for security, complicates the management and distribution of encryption keys. If not carefully managed, the process of sharing keys between users could introduce vulnerabilities. Furthermore, ensuring that encrypted data remains searchable and usable while maintaining its confidentiality requires sophisticated techniques. One significant hurdle is balancing the need for transparency (a core tenet of blockchain) with the need for privacy. Publicly available data on the blockchain needs to be carefully handled to avoid compromising sensitive information.
Solutions for End-to-End Encryption Challenges
Several solutions are emerging to address the challenges of end-to-end encryption in blockchain systems. Homomorphic encryption allows computations to be performed on encrypted data without decryption, enabling searches and other operations on sensitive information without revealing its contents. Zero-knowledge proofs allow users to prove the validity of their claims without revealing the underlying data. For example, a user could prove they own a certain digital asset without revealing the private key associated with it. Secure multi-party computation (MPC) enables multiple parties to jointly compute a function over their private inputs without revealing anything beyond the output. These advanced cryptographic techniques are crucial for building truly private and secure blockchain-based applications.
Hypothetical System Architecture for Secure User Data
Imagine an online healthcare application using blockchain and encryption. User medical records are encrypted using AES-256 before being stored on a distributed ledger. Each record is uniquely identified using a SHA-256 hash. Access to the records is controlled using digital signatures based on ECC. Only authorized healthcare providers, with their verified digital identities on the blockchain, can access and decrypt the records using their private keys. The blockchain itself acts as an immutable audit trail, recording all access attempts and modifications to the records. This system ensures data integrity, confidentiality, and accountability. The use of homomorphic encryption could allow for analysis of aggregated medical data without compromising individual patient privacy. The entire system relies on a robust key management system to ensure the secure generation, storage, and distribution of cryptographic keys.
Data Ownership and Control with Blockchain
Blockchain technology is revolutionizing how we think about data ownership and control. For too long, our personal information has been scattered across various platforms, with little say over how it’s used and shared. Blockchain offers a potential solution, empowering individuals to reclaim their digital sovereignty. By leveraging its decentralized and immutable nature, blockchain allows for greater transparency, security, and control over personal data.
Imagine a world where you, and only you, hold the keys to your digital identity and data. This isn’t science fiction; blockchain is making this a reality. It does this by enabling users to create and manage their own data, decide who can access it, and even track its usage. This shift from centralized control to individual empowerment is a game-changer in the fight for online privacy.
Blockchain’s decentralized nature promises a future where our online data is more secure and private, shifting power away from centralized entities. This drive for enhanced control extends beyond personal data; consider the implications for property transactions, where transparency is key. Check out this article on The Role of Augmented Reality in Revolutionizing Real Estate to see how tech is transforming the industry, a sector ripe for blockchain’s secure and transparent capabilities.
Ultimately, both technologies aim to empower users with greater control over their digital lives and assets.
Blockchain Empowers Users with Greater Control Over Their Data
Blockchain empowers users with greater control over their data by establishing a system of verifiable and transparent data management. Instead of relying on centralized entities to store and manage personal data, individuals can use blockchain to store their information in a secure, decentralized ledger. This allows them to selectively share specific data points with chosen parties, maintaining complete control over their privacy. For instance, a user could store their medical records on a blockchain and grant access only to their chosen doctors, while keeping other data private. Similarly, a user might store their employment history on a blockchain, sharing only relevant portions with prospective employers. This fine-grained control is a significant improvement over the all-or-nothing approach often seen in traditional systems. Unauthorized access or sharing is significantly hindered due to the cryptographic security and decentralized nature of the blockchain.
Data Portability and Blockchain
Data portability refers to the ability to easily move your personal data from one platform to another. Blockchain facilitates seamless data transfer by creating a standardized format for data representation. Imagine switching from one social media platform to another. With blockchain, you could easily transfer your profile information, posts, and connections without relying on the cooperation of the platforms themselves. This portability reduces vendor lock-in and gives users more freedom in choosing the services they utilize. A practical example would be a user moving their contact list from one email provider to another using a blockchain-based solution. The process would be automated and secure, ensuring a smooth transition without data loss or privacy breaches.
Potential Risks and Mitigation Strategies
While blockchain offers significant advantages in data ownership and control, potential risks exist. One major concern is the complexity of managing personal data on a blockchain for users lacking technical expertise. Another risk is the potential for data loss if a user loses access to their private keys. Moreover, ensuring the security and integrity of the blockchain itself is crucial.
To mitigate these risks, user-friendly interfaces and educational resources are necessary. Multi-signature wallets and key recovery mechanisms can help prevent data loss. Robust security protocols and regular audits are vital for maintaining blockchain integrity. Furthermore, regulatory frameworks are needed to establish clear guidelines and standards for data management on blockchain platforms.
Comparison of Traditional and Blockchain-Based Data Management
| Feature | Traditional Data Management | Blockchain-Based Data Management |
|---|---|---|
| Data Ownership | Centralized (companies/platforms) | Decentralized (users) |
| Data Control | Limited user control | Enhanced user control & transparency |
| Data Portability | Difficult and often impossible | Seamless and efficient |
| Data Security | Vulnerable to breaches and hacks | Improved security through cryptography and decentralization |
Blockchain and Anonymous Transactions

Source: smartsight.in
Blockchain technology, while lauded for its transparency, also offers avenues for anonymous transactions, raising complex questions about privacy and security. The inherent nature of distributed ledgers, where transactions are recorded publicly, seems at odds with the desire for anonymity. However, clever cryptographic techniques and architectural designs allow for a level of obfuscation, creating a fascinating duality at the heart of blockchain’s potential.
Cryptocurrencies like Monero and Zcash, built on blockchain, exemplify this pursuit of anonymity. These systems employ techniques that obscure the sender, receiver, and transaction amounts, creating a layer of privacy not found in more transparent cryptocurrencies like Bitcoin. This inherent anonymity, however, comes with its own set of challenges and ethical considerations.
Privacy Implications of Anonymous Cryptocurrencies
The privacy implications of anonymous blockchain transactions are significant. While proponents argue that such anonymity protects individual freedom and shields users from surveillance, the potential for misuse is undeniable. The lack of readily available transaction details makes it difficult for law enforcement to track illicit activities such as money laundering, terrorist financing, and the trade of illegal goods. The balance between protecting individual privacy and preventing criminal activity is a delicate one, constantly evolving with technological advancements and regulatory efforts. The anonymity provided by these systems could also be used to circumvent sanctions and tax regulations, creating further complexities.
Comparison of Anonymity Approaches on Blockchain Networks
Different approaches to achieving anonymity on blockchain networks exist, each with its own strengths and weaknesses. Monero, for instance, utilizes ring signatures and stealth addresses to mask transaction details. Zcash employs zero-knowledge proofs, allowing for verification of transactions without revealing the identities involved. These methods, while effective to varying degrees, introduce complexities in terms of computational overhead and scalability. A trade-off always exists between the level of anonymity achieved and the security and efficiency of the blockchain network. Simpler, more transparent blockchains, while sacrificing anonymity, often enjoy better performance and easier auditing.
Potential Misuse of Anonymous Blockchain Transactions
The potential for misuse of anonymous blockchain transactions for illicit activities is a significant concern. The inherent difficulty in tracing transactions makes it an attractive tool for those seeking to operate outside the regulatory framework. Darknet marketplaces, for example, often rely on cryptocurrencies offering enhanced anonymity to facilitate illegal transactions. Law enforcement agencies face significant challenges in investigating crimes involving these systems, requiring specialized expertise and sophisticated forensic techniques. The decentralized and borderless nature of blockchain further complicates regulatory efforts.
Benefits and Drawbacks of Enhanced Anonymity in Online Interactions
The enhanced anonymity offered by blockchain technology presents a double-edged sword.
- Benefits: Increased user privacy and protection from surveillance, enhanced freedom of speech and expression in regions with restrictive governments, facilitation of secure and private transactions in contexts where traditional financial systems are unreliable or unavailable.
- Drawbacks: Increased risk of illicit activities, challenges in tracking criminal behavior, potential for abuse in circumventing regulations, reduced transparency and accountability, and the possibility of fostering a climate of distrust and uncertainty.
The future of anonymous blockchain transactions hinges on finding a balance between privacy and security, a challenge that will require ongoing technological innovation and robust regulatory frameworks.
Blockchain’s Impact on Data Breaches and Security
Data breaches are a terrifying reality in our increasingly digital world. The theft of sensitive personal information, financial records, and intellectual property can have devastating consequences for individuals and organizations alike. However, blockchain technology offers a potential game-changer in the fight against data breaches, providing a robust and secure framework for data management and incident response.
Blockchain’s immutable ledger, a chronologically ordered and cryptographically secured record of transactions, plays a crucial role in enhancing data security and mitigating the impact of breaches. This inherent immutability means that once data is recorded on the blockchain, it cannot be altered or deleted without detection, creating an auditable trail of all data activity. This significantly improves transparency and accountability, making it easier to identify the source and extent of a breach.
Tracing and Mitigating Data Breaches with Blockchain’s Immutable Ledger
The immutable nature of the blockchain allows for precise tracking of data movement. Imagine a scenario where a data breach occurs. By analyzing the blockchain’s transaction history, investigators can trace the compromised data’s path, identifying the point of entry, the affected data points, and potentially even the perpetrator. This detailed audit trail enables a faster and more effective response, minimizing the damage and reducing the time it takes to contain the breach. This is a significant improvement over traditional methods, which often struggle to pinpoint the source and scope of a breach quickly. For instance, if a company uses blockchain to track access to sensitive customer data, any unauthorized access would be immediately flagged and investigated.
Automating Data Breach Response with Smart Contracts
Smart contracts, self-executing contracts with the terms of the agreement directly written into code, can automate many aspects of data breach response. These contracts can be programmed to automatically initiate actions such as notifying affected users, freezing compromised accounts, and triggering forensic investigations upon detection of a breach. This automation reduces the time it takes to respond to a breach, limiting the window of vulnerability and minimizing potential damage. A smart contract, for example, could automatically initiate a credit monitoring service for affected customers following a breach, streamlining the process and improving customer experience.
Verifying Data Integrity and Authenticity Post-Breach, How Blockchain is Changing the Future of Online Privacy
After a data breach, verifying the integrity and authenticity of the remaining data is paramount. Blockchain technology can help by providing a tamper-evident record of data. By hashing data and storing the hashes on the blockchain, any unauthorized alteration to the data will be immediately apparent, as the hash will no longer match the data. This allows organizations to confirm the authenticity of their data and rebuild trust with their users. This is particularly useful in situations involving sensitive information like medical records or financial transactions, where data integrity is crucial. For example, a hospital could use blockchain to record patient medical data, ensuring its authenticity and integrity even after a cyberattack.
Blockchain-Based Data Breach Response Flowchart
A flowchart illustrating a blockchain-based data breach response would show a series of steps:
1. Breach Detection: Security systems detect unauthorized access or data exfiltration.
2. Alert Trigger: An alert is automatically sent via smart contract to relevant stakeholders (IT security, legal, compliance).
3. Blockchain Analysis: The blockchain is analyzed to trace the compromised data, identifying the source and extent of the breach.
4. Containment: Smart contracts automatically initiate actions to contain the breach, such as freezing accounts or blocking access.
5. Notification: Affected users are notified of the breach via automated messaging systems.
6. Forensic Investigation: A forensic investigation is launched to determine the root cause of the breach and identify the perpetrator.
7. Data Integrity Verification: The integrity of remaining data is verified using blockchain-stored hashes.
8. Remediation: Steps are taken to remediate the vulnerability and prevent future breaches.
9. Reporting: The breach is reported to relevant authorities and stakeholders.
10. Recovery: Data recovery and system restoration are undertaken.
This flowchart highlights the collaborative effort required and how blockchain facilitates efficient communication and coordinated action amongst various stakeholders. The speed and efficiency gained through automation and transparency drastically reduce the impact of a data breach.
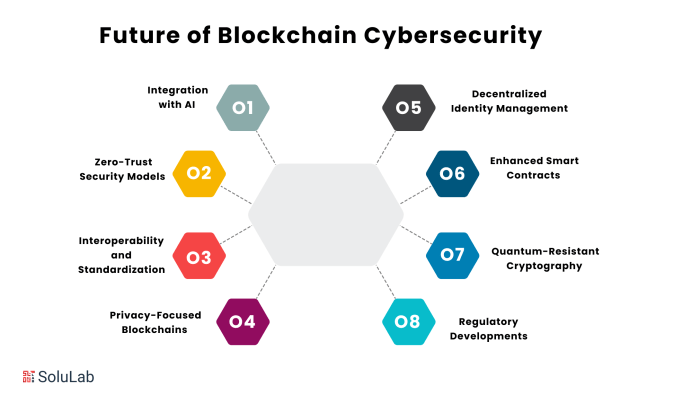
The Future of Online Privacy with Blockchain
The rise of big data and increasingly sophisticated surveillance techniques has left many feeling vulnerable online. Traditional methods of protecting privacy are struggling to keep pace with technological advancements. However, blockchain technology offers a potential game-changer, promising a more secure and user-controlled digital landscape. Its decentralized nature and cryptographic security features could revolutionize how we interact with the internet and manage our personal information.
Blockchain’s influence on future online privacy regulations and compliance will likely be profound. Its inherent transparency and immutability could make it easier to audit data handling practices, ensuring adherence to regulations like GDPR and CCPA. This increased accountability could incentivize companies to prioritize user privacy, fearing the repercussions of non-compliance exposed on a public, verifiable ledger. Furthermore, the development of standardized blockchain-based privacy protocols could simplify compliance efforts for businesses, reducing the administrative burden and cost.
Blockchain Fostering Trust and Transparency
Blockchain’s decentralized nature inherently fosters trust. Instead of relying on a single entity to control and manage data, information is distributed across a network of nodes. This eliminates single points of failure and reduces the risk of data manipulation or unauthorized access. Moreover, the immutability of the blockchain ensures that once data is recorded, it cannot be altered or deleted without detection. This transparency allows users to verify the legitimacy of data and track its usage, building trust in the organizations handling their information. Imagine a healthcare system using blockchain to store patient records: patients could access and verify their own data, while healthcare providers could share relevant information securely and transparently, all while maintaining patient confidentiality and complying with HIPAA regulations.
A Vision for a Blockchain-Powered Privacy-Centric Internet
Imagine a future internet where users have complete control over their data. Blockchain-based identity systems allow individuals to manage their digital identities without relying on centralized authorities like Facebook or Google. They can selectively share specific data points with different services, only when and how they choose. This granular control empowers individuals to protect their privacy while still benefiting from online services. Data breaches become less impactful as data is decentralized and encrypted, limiting the potential damage from a single point of compromise. The focus shifts from data protection to data empowerment, placing the individual firmly in control of their digital footprint.
Societal Implications of Widespread Blockchain Adoption
The widespread adoption of blockchain-based privacy solutions would have significant societal implications. It could lead to increased individual empowerment and a greater sense of digital sovereignty. Users would have more agency over their personal information, leading to greater trust in online services and a reduction in digital inequality. However, challenges remain. The technical complexity of blockchain technology could create a digital divide, excluding those without the necessary technical skills or access to technology. Furthermore, the decentralized nature of blockchain could make it more difficult to enforce regulations and address malicious actors. Therefore, careful consideration and proactive measures are crucial to ensure equitable access and responsible implementation of blockchain-based privacy solutions. The development of user-friendly interfaces and educational initiatives will be key to bridging this gap and maximizing the benefits of this transformative technology.
Summary: How Blockchain Is Changing The Future Of Online Privacy
Source: solulab.com
In short, blockchain isn’t just a technological advancement; it’s a paradigm shift in how we approach online privacy. By decentralizing data control, enhancing encryption, and fostering transparency, blockchain offers a powerful solution to the persistent challenges of data security and user autonomy. While challenges remain, the potential for a more private and secure digital future, fueled by blockchain, is undeniable. It’s time to embrace this revolution and take control of your digital life.
