The Future of Blockchain in Securing Internet of Things (IoT) Networks: Imagine a world where your smart fridge orders groceries autonomously, your car drives itself, and your home adjusts its temperature based on your preferences – all seamlessly and securely. This is the promise of the IoT, but its explosive growth has unveiled a critical vulnerability: security. Existing security measures struggle to keep pace with the sheer volume and complexity of connected devices. Enter blockchain, a technology poised to revolutionize IoT security, offering a decentralized, transparent, and tamper-proof solution to the escalating threats facing our increasingly interconnected world. This exploration dives deep into how blockchain can safeguard the future of IoT.
From the inherent vulnerabilities of current IoT security protocols to the potential of blockchain’s decentralized architecture, we’ll unpack the challenges and opportunities presented by this rapidly evolving landscape. We’ll examine how blockchain’s cryptographic foundations, smart contracts, and various consensus mechanisms can bolster IoT security, addressing issues like data breaches, unauthorized access, and supply chain vulnerabilities. We’ll also delve into the practical applications of blockchain in various IoT sectors and discuss the hurdles that need to be overcome for widespread adoption, including scalability, energy consumption, and regulatory considerations.
Current State of IoT Security
The Internet of Things (IoT) is rapidly expanding, connecting billions of devices across various sectors. However, this explosive growth has outpaced the development of robust security measures, leaving a vast attack surface vulnerable to exploitation. The current state of IoT security is characterized by significant vulnerabilities, inadequate protocols, and immense challenges in managing large-scale deployments. This creates a landscape ripe for breaches, with potentially severe consequences.
Prevalent Security Vulnerabilities in Current IoT Networks
Many IoT devices suffer from inherent security weaknesses. These include weak or default passwords, lack of encryption, outdated software with known vulnerabilities, and insufficient authentication mechanisms. The sheer number of devices, coupled with their often limited processing power and memory, makes implementing strong security measures difficult and expensive. Many devices are designed with a primary focus on functionality and cost-effectiveness, often at the expense of security. This creates a situation where even a single vulnerable device can serve as an entry point for attackers to compromise an entire network.
Limitations of Existing Security Protocols in IoT
Traditional security protocols, designed for larger, more powerful systems, often prove inadequate for the resource-constrained nature of many IoT devices. For example, implementing robust public-key cryptography can be computationally expensive for smaller devices, hindering their performance. Furthermore, the heterogeneity of IoT devices – encompassing a wide range of operating systems, communication protocols, and hardware – makes it challenging to establish a uniform security standard. The lack of standardization leads to fragmentation and interoperability issues, making it difficult to manage security across a diverse IoT ecosystem.
Challenges of Managing and Securing Large-Scale IoT Deployments
Managing and securing large-scale IoT deployments presents unique challenges. The sheer volume of devices, their diverse locations, and the complexity of their interactions make it difficult to monitor and manage security effectively. Centralized security management systems often struggle to cope with the scale and complexity of these deployments. Furthermore, the distributed nature of IoT networks makes it challenging to detect and respond to security incidents promptly. The lack of standardized security protocols and the difficulty in updating software on a massive scale exacerbate these challenges.
Examples of Real-World IoT Security Breaches and Their Consequences
Several high-profile IoT security breaches have highlighted the real-world consequences of inadequate security. For instance, the Mirai botnet, which leveraged compromised IoT devices to launch massive distributed denial-of-service (DDoS) attacks, demonstrated the devastating potential of unsecured IoT devices. Similarly, breaches involving smart home devices have resulted in unauthorized access to personal data and even physical control of devices. The consequences of these breaches range from financial losses and reputational damage to potential threats to physical safety and national security.
Comparison of Traditional and Blockchain-Based Security Methods for IoT
| Feature | Traditional Security Methods | Blockchain-Based Approaches |
|---|---|---|
| Authentication | Username/password, certificates | Cryptographic keys, smart contracts |
| Authorization | Access control lists (ACLs) | Decentralized access control, smart contracts |
| Data Integrity | Digital signatures, hashing | Immutable blockchain ledger |
| Data Privacy | Encryption, anonymization | Homomorphic encryption, zero-knowledge proofs |
Blockchain Technology Fundamentals in IoT
Blockchain technology offers a revolutionary approach to securing the Internet of Things (IoT), addressing many of the current vulnerabilities plaguing this rapidly expanding network. Its decentralized, transparent, and immutable nature provides a robust foundation for trust and security in a landscape increasingly threatened by cyberattacks and data breaches. Let’s dive into the specifics of how this works.
Blockchain’s Decentralized Nature and Enhanced IoT Security
Unlike traditional centralized systems where a single point of failure exists, blockchain distributes data across a network of nodes. This means there’s no single entity controlling the data, making it significantly harder for hackers to compromise the entire system. If one node is attacked, the others continue to operate, ensuring the integrity and availability of the data. This resilience is crucial for IoT, where devices are often geographically dispersed and vulnerable to various attacks. Imagine a smart city network: if a hacker compromises a single traffic light controller, the decentralized nature of a blockchain-based system would prevent the entire traffic management system from collapsing.
Cryptographic Hashing and Consensus Mechanisms in Securing IoT Data
Blockchain’s security relies heavily on cryptographic hashing and consensus mechanisms. Cryptographic hashing transforms data into unique, fixed-size strings (hashes). Any alteration to the data results in a completely different hash, instantly revealing tampering. This ensures data integrity. Consensus mechanisms, on the other hand, are algorithms that ensure all nodes agree on the validity of new blocks added to the blockchain. Proof-of-Work (PoW) and Proof-of-Stake (PoS) are common examples. These mechanisms prevent malicious actors from altering the blockchain’s history, guaranteeing data immutability. For example, imagine tracking the temperature and humidity levels in a smart greenhouse; cryptographic hashing would ensure the integrity of these readings, and consensus mechanisms would guarantee that all nodes agree on the recorded data.
Blockchain Architectures for IoT Applications
Different blockchain architectures cater to specific IoT needs. Permissioned blockchains, like Hyperledger Fabric, allow only authorized participants to join the network, making them ideal for private IoT networks within organizations. This controlled access enhances security and allows for stricter governance. Permissionless blockchains, like Bitcoin and Ethereum, are open to anyone, offering greater transparency but potentially sacrificing some security in the context of sensitive IoT data. Choosing the right architecture depends on the application’s security requirements and the level of transparency needed. A large corporation might prefer a permissioned blockchain for managing its internal sensor network, while a public environmental monitoring project might opt for a permissionless blockchain for greater data accessibility.
Smart Contracts for Managing IoT Devices and Data
Smart contracts are self-executing contracts with the terms of the agreement directly written into code. In IoT, smart contracts automate device management, data sharing, and payment processing. For instance, a smart contract could automatically trigger a payment to a farmer when a sensor in their field detects a specific level of moisture, ensuring timely irrigation and optimized resource management. They improve efficiency, reduce reliance on intermediaries, and enhance security by automating processes and eliminating the risk of human error.
Comparison of Consensus Mechanisms in Blockchain for IoT
The choice of consensus mechanism significantly impacts the performance and security of an IoT blockchain. Here’s a comparison:
| Consensus Mechanism | Description | Pros | Cons |
|---|---|---|---|
| Proof-of-Work (PoW) | Nodes compete to solve complex cryptographic puzzles to validate transactions. | Highly secure, resistant to attacks. | High energy consumption, slow transaction speeds. |
| Proof-of-Stake (PoS) | Nodes are selected to validate transactions based on the amount of cryptocurrency they stake. | Energy efficient, faster transaction speeds. | Potential for centralization, vulnerability to attacks from large stakeholders. |
| Practical Byzantine Fault Tolerance (PBFT) | Requires a designated set of nodes to reach consensus. | High throughput, low latency. | Limited scalability, susceptible to single points of failure. |
| Delegated Proof-of-Stake (DPoS) | Users vote for delegates who validate transactions. | Faster and more energy-efficient than PoW. | Potential for centralization, susceptible to attacks on delegates. |
Applications of Blockchain in Securing IoT Networks
Blockchain technology, with its inherent security features, offers a compelling solution to the vulnerabilities plaguing the Internet of Things (IoT). Its decentralized and immutable nature provides a robust framework for securing various aspects of IoT networks, from data storage to device authentication and communication. Let’s delve into the practical applications of this transformative technology.
Secure Data Storage and Management in IoT, The Future of Blockchain in Securing Internet of Things (IoT) Networks
Blockchain’s decentralized ledger system ensures data integrity and prevents unauthorized modifications. Each transaction, representing a data update or access event, is cryptographically secured and added to the chain, creating an auditable trail. This is particularly crucial for sensitive IoT data like medical records from wearable devices or industrial sensor readings from manufacturing plants. For instance, a smart agriculture system could use blockchain to record soil conditions, irrigation data, and crop yields, guaranteeing the authenticity and reliability of this information for farmers and supply chain partners. The transparency provided by blockchain also enhances trust and accountability across the network.
Device Authentication and Authorization in IoT Networks
Blockchain can establish a secure and verifiable identity for each IoT device. This eliminates the risk of unauthorized access and manipulation. Each device receives a unique cryptographic key, registered on the blockchain, acting as its digital identity. Access control mechanisms can be implemented based on these keys, allowing only authorized devices to communicate and share data. Imagine a smart city scenario where only verified streetlights can access the city’s energy grid, preventing unauthorized usage and potential power outages. This robust authentication system dramatically reduces the vulnerability of IoT networks to hacking and malicious attacks.
Securing IoT Communication Channels
Blockchain enhances the security of communication channels between IoT devices and the cloud or other network components. By encrypting data using cryptographic keys stored on the blockchain, communication becomes resistant to eavesdropping and tampering. Furthermore, blockchain’s consensus mechanisms can be leveraged to ensure the authenticity and integrity of messages exchanged between devices. For example, a system monitoring critical infrastructure like power grids can utilize blockchain to secure communication between sensors and control centers, ensuring reliable data transmission and preventing disruptions caused by malicious interference.
Supply Chain Management and Tracking in IoT-Enabled Industries
Blockchain’s transparency and immutability are invaluable for tracking goods and materials throughout the supply chain. Each stage of the supply chain, from origin to delivery, can be recorded on the blockchain, creating a verifiable and tamper-proof record. This allows for real-time tracking of products, improved inventory management, and enhanced traceability, enabling businesses to quickly identify and address any issues or irregularities. For instance, in the food industry, blockchain can track the journey of a product from farm to table, ensuring food safety and combating counterfeit goods. This increased transparency benefits both consumers and producers.
Hypothetical Scenario: Securing a Smart Home IoT Network with Blockchain
Consider a smart home equipped with various IoT devices: smart locks, lighting systems, security cameras, and appliances. A blockchain-based system could manage access control for each device. Each device would have a unique cryptographic key stored on the blockchain. Only authorized users with the corresponding keys can control these devices. For instance, the smart lock would only unlock for users with authorized keys registered on the blockchain. The system would also record all access attempts, creating an auditable log. If a security breach is suspected, the blockchain provides a detailed record of all activities, facilitating investigation and mitigation. Furthermore, data from security cameras could be encrypted and stored on the blockchain, ensuring data integrity and privacy. This integrated approach offers a comprehensive security solution for the entire smart home network.
Addressing Challenges and Limitations
Blockchain’s integration into IoT presents exciting possibilities, but significant hurdles remain before widespread adoption. The inherent characteristics of blockchain, while beneficial for security, introduce complexities when applied to the resource-constrained and often decentralized nature of IoT networks. Overcoming these challenges is crucial for realizing the full potential of this technology.
Scalability Challenges in Large-Scale IoT Deployments
Implementing blockchain across vast IoT networks, potentially involving millions of devices, poses a considerable scalability challenge. Traditional blockchain architectures, like Bitcoin or Ethereum, struggle with the transaction throughput required for real-time data processing from numerous connected devices. The computational overhead of consensus mechanisms, like Proof-of-Work, becomes prohibitive, leading to slow transaction speeds and high latency. This is exacerbated by the limited processing power and bandwidth available in many IoT devices. For example, imagine a smart city network using blockchain to manage traffic flow; the sheer volume of data from sensors would quickly overwhelm a standard blockchain implementation. Solutions like sharding, which partitions the blockchain into smaller, more manageable parts, or using more efficient consensus mechanisms like Proof-of-Stake, are being explored to address this.
Energy Consumption in Resource-Constrained IoT Devices
Blockchain’s energy consumption is a significant concern, particularly for battery-powered IoT devices. The computational intensity of creating and verifying blocks, especially in Proof-of-Work systems, drains battery life rapidly. Consider a network of environmental sensors in a remote location; the energy required for blockchain operations could severely limit their lifespan and necessitate frequent battery replacements, adding to the cost and complexity of deployment. Lightweight blockchains, optimized for low-power devices, and the exploration of alternative consensus mechanisms that require less energy are actively being researched.
Challenges in Integrating Blockchain with Existing IoT Infrastructure
Integrating blockchain into pre-existing IoT infrastructure can be complex and costly. Many IoT systems rely on proprietary protocols and architectures, making seamless integration with blockchain a significant challenge. Retrofitting existing systems to incorporate blockchain functionality requires substantial effort, potentially necessitating significant changes to the underlying hardware and software. For instance, a company with a large, established network of industrial sensors may find it difficult and expensive to migrate to a blockchain-based security system without disrupting ongoing operations. Developing standardized interfaces and protocols that bridge the gap between blockchain and existing IoT technologies is crucial for smoother integration.
Improving Interoperability of Blockchain-Based IoT Systems
Currently, many blockchain platforms operate in silos, hindering interoperability between different IoT systems. Lack of standardization across blockchain implementations makes it difficult for devices from different manufacturers or using different blockchain networks to communicate and share data securely. This limits the scalability and overall utility of blockchain in IoT. The development of common standards and protocols, along with the use of interoperability layers, are key to enabling seamless communication between disparate blockchain-based IoT systems. This might involve creating standardized data formats and APIs that allow different blockchain networks to interact effectively.
Regulatory and Legal Considerations
The use of blockchain in IoT raises various regulatory and legal challenges. Data privacy, security, and compliance with existing regulations, such as GDPR, are paramount. The decentralized and often anonymous nature of blockchain can complicate data governance and accountability. Establishing clear legal frameworks and regulatory guidelines for the use of blockchain in IoT is crucial for fostering trust and encouraging wider adoption. This includes defining liability in cases of data breaches or security incidents involving blockchain-based IoT systems and ensuring compliance with data privacy laws across jurisdictions.
Future Trends and Developments: The Future Of Blockchain In Securing Internet Of Things (IoT) Networks
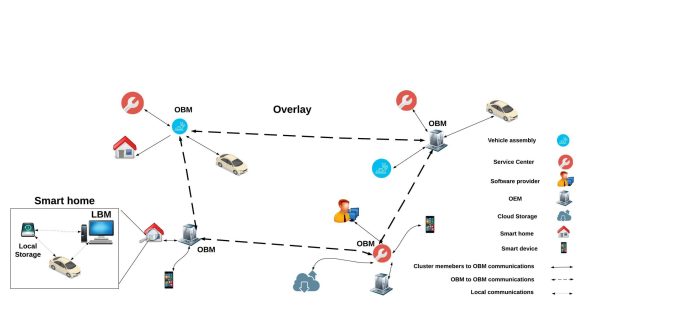
Source: edu.au
The convergence of blockchain and IoT is still in its nascent stages, but the potential for revolutionizing security is undeniable. The next decade will see significant advancements, driven by the integration of emerging technologies and a growing awareness of the vulnerabilities inherent in expanding IoT networks. This section explores the exciting future of blockchain in securing IoT, highlighting key trends and potential breakthroughs.
The synergy between blockchain’s inherent security and the expanding capabilities of other technologies promises to create a more robust and resilient IoT ecosystem. This evolution won’t be linear; rather, it will be a dynamic interplay of innovation and adaptation, shaping the landscape of secure connected devices for years to come.
The Role of Edge Computing and AI in Enhancing Blockchain-Based IoT Security
Edge computing, by processing data closer to the source (the IoT device), reduces latency and bandwidth requirements, significantly improving the efficiency of blockchain-based security solutions. Integrating AI enhances this further by enabling real-time threat detection and response. For example, AI algorithms can analyze data streams from IoT devices, identifying anomalies that indicate potential attacks, and triggering automated responses, such as isolating compromised devices or adjusting security protocols on the blockchain. This proactive approach minimizes the impact of breaches and strengthens the overall security posture. The combination of edge computing’s speed and AI’s intelligence creates a powerful defense against sophisticated attacks.
Blockchain Security in the Metaverse and Web3
The Metaverse and Web3, with their emphasis on decentralized identities and data ownership, create a fertile ground for blockchain-based IoT security. Imagine a scenario where every connected device in a virtual world has a unique, verifiable digital identity secured on a blockchain. This ensures authenticity and prevents unauthorized access. Moreover, blockchain can facilitate secure data exchange between users and devices within the Metaverse, enabling secure transactions and interactions. The decentralized nature of blockchain aligns perfectly with the decentralized ethos of Web3, creating a trustless environment for IoT devices and applications. This is crucial for applications like virtual real estate, digital assets, and interactive experiences within the Metaverse, where security and trust are paramount.
Innovative Blockchain-Based Solutions for Future IoT Security Challenges
Several innovative solutions are emerging to address the evolving challenges in IoT security. One promising approach is the development of decentralized identity management systems based on blockchain. These systems can provide secure and verifiable identities for IoT devices, enabling better authentication and authorization. Another area of innovation involves the use of blockchain for secure data sharing and collaboration among multiple IoT devices and platforms. This allows for the creation of secure data ecosystems where data can be shared securely and transparently without compromising privacy. Furthermore, blockchain-based consensus mechanisms can be used to improve the reliability and integrity of data transmitted between IoT devices. This reduces the risk of data manipulation or unauthorized access.
Predictions for the Evolution of Blockchain in IoT Security (Next 5-10 Years)
Over the next 5-10 years, we can expect to see widespread adoption of blockchain technology in securing various IoT applications. For instance, the automotive industry is likely to leverage blockchain for secure vehicle-to-everything (V2X) communication, ensuring the safety and integrity of data exchanged between vehicles and infrastructure. Similarly, the healthcare industry might use blockchain to secure patient data and medical devices, enhancing data privacy and security. The increasing complexity of IoT networks will drive the demand for more sophisticated and scalable blockchain-based security solutions. We predict that the integration of AI and machine learning into blockchain-based security systems will become increasingly prevalent, leading to more proactive and adaptive security measures. This will lead to a significant reduction in security breaches and enhance the overall trustworthiness of IoT networks.
Potential Research Directions in Blockchain and IoT Security
The intersection of blockchain and IoT security presents a wealth of opportunities for future research. Further advancements are needed to address the scalability and performance limitations of current blockchain technologies, especially in resource-constrained IoT environments.
The following research areas warrant further investigation:
- Developing lightweight blockchain protocols optimized for IoT devices with limited processing power and bandwidth.
- Exploring the use of homomorphic encryption techniques to enable secure data processing on encrypted data stored on the blockchain.
- Investigating the application of federated learning to enhance the security and privacy of AI models used in blockchain-based IoT security systems.
- Developing robust mechanisms for handling denial-of-service attacks and other types of malicious activities targeting blockchain-based IoT networks.
- Creating standardized frameworks and protocols for secure interoperability between different blockchain platforms and IoT devices.
Final Review
The integration of blockchain technology with the Internet of Things represents a pivotal step towards a more secure and reliable digital future. While challenges remain – particularly in scalability and energy efficiency – the potential benefits are undeniable. From enhanced data security and device authentication to robust supply chain management and innovative solutions for emerging technologies like the Metaverse, blockchain offers a powerful framework for mitigating the inherent risks of IoT. As we move forward, continued research, development, and collaboration will be crucial in unlocking the full potential of this transformative technology, paving the way for a truly secure and interconnected world.
Securing the exploding IoT network is a huge challenge, demanding robust solutions like blockchain. But even the most secure network needs compelling user experiences to thrive. Think about how the rise of personalized shopping, fueled by advancements like those detailed in this article on How Augmented Reality is Enhancing Online Shopping Experiences , shows the power of user engagement.
Ultimately, blockchain’s future in IoT hinges on building a user-friendly ecosystem that people actually *want* to use.
