The Future of Autonomous Vehicles in Shaping Traffic Management: Imagine a world without gridlock, where self-driving cars glide seamlessly through city streets, orchestrated by a symphony of smart technology. This isn’t science fiction; it’s the rapidly approaching reality of autonomous vehicles (AVs), poised to revolutionize how we manage traffic. From sophisticated sensor systems to AI-powered navigation, the advancements are breathtaking, promising a future of safer, smoother, and more efficient commutes.
This transformation, however, isn’t without its hurdles. We’ll delve into the technological leaps needed, the infrastructural changes required, and the societal impacts – both positive and negative – that this seismic shift will bring. Get ready to explore the exciting (and sometimes bumpy) road ahead as we navigate the future of autonomous driving and its influence on our daily lives.
Technological Advancements in Autonomous Vehicle Systems
The race towards fully autonomous vehicles is accelerating, driven by leaps in sensor technology, artificial intelligence, and communication protocols. These advancements are not merely about self-driving cars; they’re fundamentally reshaping how we manage traffic, promising safer, smoother, and more efficient roadways. The integration of these technologies is poised to revolutionize urban planning and transportation infrastructure.
The evolution of autonomous vehicle systems is a testament to rapid technological progress. Improvements in sensor fusion, AI algorithms, and communication networks are crucial for enabling autonomous vehicles to navigate complex environments and interact safely with other road users, including human-driven vehicles and pedestrians.
Sensor Technology Evolution and its Impact on Traffic Management
Autonomous vehicles rely on a sophisticated suite of sensors to perceive their surroundings. LiDAR (Light Detection and Ranging), radar, and cameras are the key players, each offering unique capabilities. LiDAR, using lasers to create a 3D point cloud map of the environment, excels at detecting objects at longer ranges and with high precision, even in low-light conditions. Radar, using radio waves, is less susceptible to weather conditions like fog and rain, providing robust distance and velocity measurements. Cameras, while offering high-resolution visual data, are vulnerable to poor lighting and challenging weather. The synergistic combination of these sensors, known as sensor fusion, allows autonomous vehicles to build a comprehensive and robust understanding of their surroundings, far surpassing the capabilities of a human driver. This improved perception directly translates to better traffic management, as autonomous vehicles can anticipate potential hazards and react more effectively than humans, leading to fewer accidents and smoother traffic flow. For instance, a system combining LiDAR’s precise object detection with radar’s weather resilience could significantly reduce accidents caused by adverse weather conditions.
Advancements in AI and Machine Learning for Autonomous Navigation
The brain of an autonomous vehicle is its AI system, specifically machine learning algorithms. These algorithms enable the vehicle to learn from vast amounts of data, improving its ability to navigate complex scenarios. Deep learning models, for example, are trained on massive datasets of driving situations, allowing the vehicle to recognize patterns, predict the behavior of other road users, and make optimal driving decisions. Advancements in reinforcement learning are enabling autonomous vehicles to learn optimal driving strategies in simulated environments before deployment in the real world, thereby minimizing the risk of accidents during the initial stages of operation. This ability to learn and adapt in real-time is critical for navigating unpredictable traffic conditions, such as sudden lane changes or unexpected pedestrian movements. Imagine a scenario where an autonomous vehicle anticipates a potential collision based on its analysis of a driver’s erratic behavior and proactively adjusts its speed or trajectory to avoid an accident – a feat impossible for a human driver to consistently replicate.
Autonomous Vehicle Architectures and Traffic Flow Optimization
Autonomous vehicle architectures can be broadly categorized as centralized or distributed. In a centralized architecture, a single powerful computer processes all sensor data and makes all driving decisions. This approach simplifies software development but can become a bottleneck in processing speed and create a single point of failure. Distributed architectures, on the other hand, distribute processing tasks across multiple smaller computers, improving robustness and potentially enabling faster reaction times. The choice of architecture has significant implications for traffic flow optimization. A distributed architecture, for example, could allow for faster responses to changing traffic conditions, leading to smoother and more efficient traffic flow. Consider a highway scenario where multiple autonomous vehicles, each equipped with a distributed system, communicate with each other to collectively optimize their speeds and trajectories, minimizing congestion and maximizing throughput.
Improved Communication Protocols for Safer and More Efficient Traffic Movement
Imagine a highway scenario: a sudden lane closure due to an accident. In today’s traffic, this often leads to cascading braking and potential pile-ups. However, with improved Vehicle-to-Everything (V2X) communication protocols, autonomous vehicles could instantly communicate this information to each other and to traffic management systems. This would allow vehicles to proactively adjust their speed and trajectory, avoiding sudden braking and preventing congestion. Furthermore, V2X communication could enable autonomous vehicles to coordinate their movements at intersections, optimizing traffic flow and reducing wait times. For example, autonomous vehicles could coordinate their movements to avoid unnecessary stops, leading to a smoother and more efficient flow of traffic, particularly during peak hours. This proactive communication and coordination are key to achieving significant improvements in traffic safety and efficiency.
Impact on Traffic Flow and Congestion
The rise of autonomous vehicles (AVs) promises a radical reshaping of our urban landscapes, and perhaps nowhere is this more evident than in their potential impact on traffic flow and congestion. Current traffic management systems struggle to cope with the unpredictable nature of human drivers, leading to bottlenecks, delays, and significant environmental impact. AVs, with their sophisticated sensors and AI-powered decision-making, offer a pathway to a more efficient and less congested future.
Autonomous vehicles, unlike human drivers, can react instantaneously to changing traffic conditions, communicate seamlessly with other vehicles and infrastructure, and optimize their speed and route in real-time. This coordinated behavior stands in stark contrast to the stop-and-go patterns often seen in human-driven traffic, which are exacerbated by individual driver decisions and unpredictable actions.
Traffic Flow Patterns: A Comparative Analysis
Cities with widespread AV adoption are projected to experience significantly improved traffic flow compared to those relying solely on human-driven vehicles. Simulation studies and early real-world deployments suggest a substantial reduction in average travel times and a more consistent flow of traffic. In cities without widespread AV adoption, traffic flow is often characterized by unpredictable stop-and-go patterns, congestion at intersections, and significant delays during peak hours. In contrast, simulations of cities with high AV penetration indicate smoother, more continuous traffic flow, even during peak periods. This is due to AVs’ ability to maintain consistent speeds and spacing, minimizing braking and acceleration events that contribute to congestion. For example, studies in simulated environments have shown that the introduction of a significant percentage of AVs can reduce average travel times by 15-20% during peak hours in congested urban areas.
Optimizing Traffic Signal Timing and Coordination
Autonomous vehicles can dramatically enhance traffic signal timing and coordination. By communicating directly with traffic management systems, AVs can provide real-time data on their location, speed, and intended route. This allows traffic signals to adapt dynamically to current conditions, prioritizing traffic flow and minimizing delays. Imagine a scenario where an intersection is approaching congestion. AVs, communicating with the traffic management system, could subtly adjust their speeds to prevent a complete standstill, or even temporarily adjust the signal timing to allow a smoother flow of traffic. This level of real-time coordination is impossible with human drivers, leading to significant improvements in overall traffic efficiency. Moreover, AVs can contribute to the development of more sophisticated adaptive traffic control systems that optimize signal timing across entire road networks.
Accident Reduction and Improved Road Safety
Human error is the leading cause of road accidents. Autonomous vehicles, programmed to adhere strictly to traffic laws and equipped with advanced sensor systems, have the potential to significantly reduce the number of accidents. Features such as automatic emergency braking, lane keeping assist, and adaptive cruise control are already contributing to improved road safety in existing vehicles. The widespread adoption of fully autonomous vehicles could drastically reduce accidents caused by speeding, distracted driving, drunk driving, and other human errors. This leads to smoother traffic flow by minimizing the disruption caused by accidents and emergency services responding to incidents. For instance, some projections estimate that fully autonomous vehicles could reduce accident rates by up to 90%, although this figure is highly dependent on the level of AV penetration and the robustness of the underlying technology.
Estimated Reduction in Congestion and Accidents
| City | Estimated Congestion Reduction (%) | Estimated Accident Reduction (%) | Notes |
|---|---|---|---|
| Singapore (Simulated) | 25-30 | 40-50 | Based on simulations incorporating various AV penetration rates. |
| Los Angeles (Projected) | 15-20 | 30-40 | Based on projected AV adoption rates and accident statistics. |
| London (Estimated) | 10-15 | 25-35 | Estimates based on current traffic patterns and projected AV deployment. |
| Tokyo (Predicted) | 20-25 | 35-45 | Predictions based on city’s dense urban environment and potential for AV integration. |
Infrastructure Requirements and Adaptations: The Future Of Autonomous Vehicles In Shaping Traffic Management
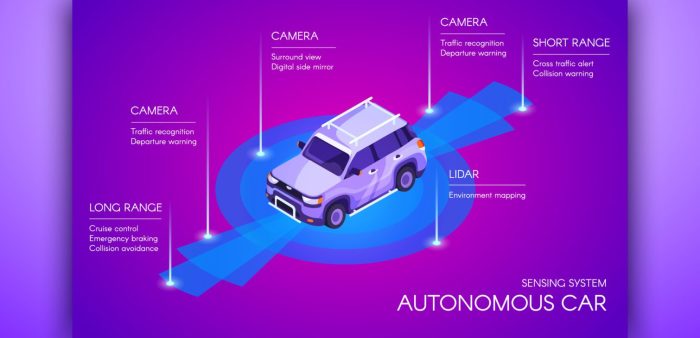
Source: zuken.com
The rise of autonomous vehicles (AVs) isn’t just about the cars themselves; it’s a complete overhaul of how we manage our roads and cities. To truly unleash the potential of self-driving technology, we need a significant upgrade to our existing infrastructure. This isn’t just about adding a few new traffic lights; it’s about creating a smart, interconnected system that can handle the complexities of a world shared by human-driven and autonomous vehicles.
The successful integration of AVs requires a multi-faceted approach to infrastructure development, encompassing technological advancements, policy changes, and public acceptance. Ignoring these aspects could lead to a chaotic and inefficient transportation system, negating the potential benefits of AV technology.
Necessary Infrastructure Upgrades for Autonomous Vehicles
Supporting widespread autonomous vehicle deployment demands significant investments in upgrading existing infrastructure. This includes installing and improving various technological components and adjusting road layouts to accommodate the unique needs of AVs. For example, smart traffic lights capable of communicating with AVs in real-time are crucial for optimizing traffic flow and preventing congestion. Dedicated lanes, especially in high-traffic areas, can help separate AVs from human-driven vehicles, improving safety and efficiency. Furthermore, high-definition mapping and precise positioning systems are essential for AVs to navigate accurately and safely. The absence of these elements would severely hinder the effective deployment of autonomous vehicles and potentially cause safety issues.
Examples of Successful Autonomous Vehicle Integration
Several cities are actively working on integrating autonomous vehicle technology into their existing infrastructure, with varying degrees of success. For instance, some cities are using AVs in controlled environments like university campuses or industrial parks, gradually expanding their deployment to public roads as the technology matures and infrastructure improvements are made. These controlled environments allow for data collection and system refinement before wider implementation. Other cities are focusing on upgrading their traffic management systems with sensors and communication networks that facilitate communication between AVs and infrastructure, leading to more efficient traffic flow. These pilot programs provide valuable real-world data that informs future infrastructure development. One example of a city actively pursuing this is Pittsburgh, Pennsylvania, which has served as a testing ground for numerous autonomous vehicle companies.
Cybersecurity Challenges and Solutions for Autonomous Vehicle Infrastructure
The interconnected nature of AV infrastructure presents significant cybersecurity challenges. Hackers could potentially disrupt traffic flow, compromise vehicle control, or even cause accidents. Robust cybersecurity measures are therefore crucial, including secure communication protocols, encryption, and intrusion detection systems. Regular security audits and updates are also essential to address emerging threats. Furthermore, collaboration between AV manufacturers, infrastructure providers, and cybersecurity experts is crucial to develop and implement effective security measures. This collaborative approach ensures a comprehensive security framework, safeguarding against potential vulnerabilities and threats.
Roadblocks and Mitigation Strategies for Integrating Autonomous Vehicles into Existing Road Networks
Several roadblocks hinder the seamless integration of autonomous vehicles into existing road networks.
- High initial investment costs for infrastructure upgrades: This can be mitigated through public-private partnerships and phased implementation plans.
- Lack of standardized communication protocols between AVs and infrastructure: The development of universal standards and open communication protocols is necessary to address this.
- Concerns about data privacy and security: Strict data privacy regulations and transparent data handling practices can alleviate these concerns.
- Resistance from the public and lack of public awareness: Public education campaigns and demonstrations of the safety and benefits of AVs can build trust and acceptance.
- Legal and regulatory uncertainties: Clear and consistent regulations are crucial to ensure the safe and responsible deployment of AVs.
Societal and Economic Implications
The rise of autonomous vehicles (AVs) promises a radical reshaping of our societies and economies, extending far beyond simply changing how we travel. The implications are multifaceted, impacting employment, costs, ethical frameworks, and the very structure of our public transportation systems. Understanding these implications is crucial for navigating the transition to a future dominated by self-driving technology.
Impact on Transportation Employment
The automation of driving will undoubtedly disrupt the transportation sector’s employment landscape. Millions of jobs – truck drivers, taxi drivers, delivery drivers, and even bus drivers – are at risk of displacement. This isn’t simply a matter of job losses; it represents a significant societal shift requiring proactive measures. Retraining initiatives focusing on emerging technologies within the AV industry, such as maintenance, software development, and data analysis, will be crucial to mitigating the negative effects of this disruption. Furthermore, the creation of entirely new roles related to AV fleet management and oversight will help to balance the equation, although the net impact on employment numbers remains a complex and evolving question. For example, the transition could lead to a net decrease in driving-related jobs, but an increase in jobs related to the development, maintenance, and management of autonomous vehicle systems.
Cost Savings from Autonomous Vehicles, The Future of Autonomous Vehicles in Shaping Traffic Management
The potential for cost savings through widespread AV adoption is substantial. Reduced accidents, a major contributor to economic losses, are a primary factor. Autonomous vehicles, programmed to adhere strictly to traffic laws and equipped with advanced sensor systems, are expected to drastically reduce the number of accidents caused by human error. Furthermore, optimized driving patterns, minimizing braking and acceleration, lead to significant fuel efficiency gains. This translates directly into lower fuel costs for individuals and businesses alike. Finally, the smoother flow of traffic facilitated by AVs promises to alleviate congestion, reducing wasted time and fuel consumption. Consider a scenario where a city experiences a 20% reduction in accidents, a 15% improvement in fuel efficiency, and a 10% decrease in congestion-related delays. The cumulative cost savings would be immense, impacting both individual budgets and the broader economy.
Ethical Considerations in Autonomous Vehicle Decision-Making
The programming of ethical decision-making in AVs presents a complex ethical dilemma. In unavoidable accident scenarios, the vehicle’s programming must decide which course of action to take, potentially resulting in harm to either the occupants of the vehicle or to pedestrians or other road users. Defining the algorithms that govern these life-or-death choices is a challenge that requires input from ethicists, legal experts, and engineers. Transparency in the decision-making processes of AVs is crucial to build public trust and ensure accountability. The debate involves questions of utilitarian ethics (minimizing overall harm) versus deontological ethics (adhering to strict rules regardless of consequences). Finding a balance between these competing ethical frameworks is a key challenge in the development and deployment of autonomous vehicles.
Societal and Economic Benefits in Public Transportation
Imagine a future where public transportation systems are fully integrated with autonomous vehicles. Buses and trains operate with increased efficiency and precision, reducing wait times and improving punctuality. On-demand autonomous shuttles could provide convenient and affordable transportation to underserved areas, improving accessibility for all citizens. This system could significantly reduce the need for private car ownership, leading to less traffic congestion, reduced parking demands, and a smaller carbon footprint. The economic benefits would be substantial, including decreased healthcare costs associated with traffic accidents, reduced infrastructure spending on roads and parking facilities, and increased productivity due to reduced commuting times. For example, a city could see a decrease in traffic-related hospitalizations by 30%, a 15% reduction in parking infrastructure costs, and a 10% increase in worker productivity due to shorter commutes. The combined effect would represent a significant boost to the city’s overall economic health and quality of life.
Integration with Existing Transportation Systems

Source: bitperfect.pe
Self-driving cars promise to revolutionize traffic flow, but managing this complex system needs smart solutions. Think about it: optimizing routes and preventing congestion requires sophisticated algorithms, much like the advanced AI powering customer service. Check out this article on The Evolution of Chatbots and Virtual Assistants in Customer Service to see how similar challenges are being tackled.
The parallels are striking, suggesting that the future of autonomous vehicle management might borrow heavily from these advancements in AI-driven communication.
The seamless integration of autonomous vehicles (AVs) into our existing transportation infrastructure is crucial for realizing their full potential. This involves not only technological compatibility but also careful consideration of how AVs will interact with existing public transit systems and reshape logistics networks. Success hinges on a coordinated approach that optimizes efficiency and minimizes disruption.
Autonomous vehicles offer a unique opportunity to enhance existing transportation networks, creating a more integrated and efficient system. Their integration requires a multi-faceted strategy addressing technological compatibility, operational coordination, and societal acceptance.
Autonomous Vehicles and Public Transportation
Integrating AVs with public transportation systems like buses, trains, and subways presents both challenges and opportunities. AVs could act as “feeder” services, transporting passengers from their homes to nearby transit hubs, thus improving access to public transit for those in areas with limited service. This could alleviate overcrowding on public transport and reduce reliance on private vehicles. Conversely, challenges include coordinating schedules and fares between AV services and existing public transport systems, as well as ensuring the safety and accessibility of shared spaces between AVs and pedestrians at transit stations. A well-defined interface between AV dispatch systems and public transit scheduling software is essential. For example, a system could predict passenger demand based on real-time transit data and dynamically adjust AV routes and schedules to optimize overall efficiency.
Improving Last-Mile Connectivity
The “last mile” – the journey from a public transit stop or parking area to a final destination – often proves a significant hurdle for commuters. Autonomous vehicles are ideally suited to address this challenge. On-demand AV services can provide flexible and efficient transportation for the final leg of a journey, improving accessibility for people with disabilities, the elderly, and those in underserved areas. Imagine a scenario where a commuter takes the subway to a central hub, then seamlessly transfers to an autonomous shuttle that takes them directly to their workplace or home. This reduces reliance on personal vehicles, easing congestion in city centers. Pilot programs in several cities are already demonstrating the potential of AVs to improve last-mile connectivity.
Autonomous Delivery Vehicles and Logistics
The impact of autonomous delivery vehicles on logistics and supply chains will be transformative. AVs can operate 24/7, reducing delivery times and improving efficiency. This can lead to significant cost savings for businesses and potentially lower prices for consumers. However, the integration of AV delivery vehicles into existing traffic patterns requires careful planning. Dedicated delivery lanes or designated parking areas might be needed to prevent congestion. Furthermore, efficient management of autonomous delivery fleets requires advanced routing algorithms and real-time traffic data integration to optimize delivery routes and minimize delays. For example, a large e-commerce company could use AVs to consolidate deliveries within a specific neighborhood, reducing the number of individual delivery vehicles on the road and thus reducing congestion.
System Architecture for Coordinating Autonomous Vehicles
Coordinating autonomous vehicles with existing traffic management systems requires a sophisticated system architecture. This architecture should include:
- Real-time data integration: AVs need access to real-time data from traffic sensors, cameras, and other sources to make informed decisions about routing and speed.
- Centralized traffic management system: A central system is needed to monitor and control the movement of AVs, coordinating their actions with human-driven vehicles and public transportation.
- Vehicle-to-everything (V2X) communication: V2X technology allows AVs to communicate with each other, infrastructure, and other vehicles, enabling coordinated movements and enhanced safety.
- Predictive modeling: Advanced algorithms can predict traffic patterns and optimize AV routing to minimize congestion and delays.
- Secure communication protocols: Robust cybersecurity measures are essential to protect against cyberattacks and ensure the safe operation of AVs.
This integrated system would dynamically adjust traffic flow based on real-time conditions, optimizing the movement of both autonomous and human-driven vehicles. For instance, the system could prioritize AVs in dedicated lanes during peak hours to improve overall traffic flow, while also ensuring the safety and smooth integration of all vehicles.
Regulatory and Policy Considerations
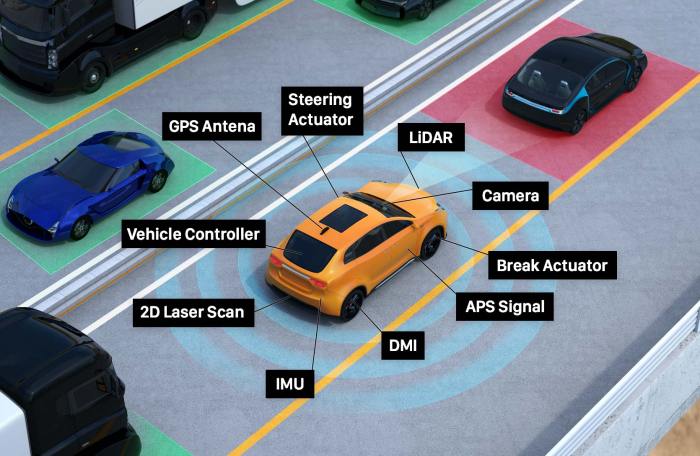
Source: labelyourdata.com
The widespread adoption of autonomous vehicles (AVs) presents a complex web of regulatory challenges, demanding a proactive and adaptable policy framework. Governments worldwide grapple with ensuring public safety, managing liability in accidents, and fostering innovation without stifling technological advancement. The lack of a unified global standard further complicates the matter, creating potential inconsistencies and barriers to international trade and deployment.
Key Regulatory Challenges Associated with Widespread AV Adoption
The integration of AVs necessitates addressing several critical regulatory hurdles. One significant challenge is establishing clear liability frameworks. In the event of an accident involving an AV, determining responsibility—the manufacturer, the software developer, the owner, or even the passenger—can be complex and legally ambiguous. Further complicating this is the need to define safety standards and testing protocols for AVs, ensuring they meet or exceed the safety performance of human drivers. Data privacy and security are also paramount concerns, given the vast amounts of data collected by AVs during operation. Regulations must protect this sensitive information from unauthorized access and misuse. Finally, the integration of AVs into existing transportation systems requires careful planning and coordination to prevent disruption and ensure efficient traffic flow.
Government Agencies’ Role in Establishing Safety Standards and Regulations for Autonomous Vehicles
Government agencies play a crucial role in shaping the regulatory landscape for AVs. Organizations like the National Highway Traffic Safety Administration (NHTSA) in the United States and similar agencies in other countries are responsible for setting safety standards, conducting testing and evaluations, and overseeing the certification process for AVs. These agencies work in collaboration with industry stakeholders, researchers, and consumer advocacy groups to develop comprehensive and effective regulations. Their involvement is essential to build public trust and ensure the safe and responsible deployment of AVs. For example, NHTSA has issued guidelines for automated driving systems, focusing on performance requirements and testing procedures. These guidelines provide a framework for manufacturers to design and develop safe AVs while also offering a basis for enforcement and compliance monitoring.
Examples of Existing or Proposed Policies Aimed at Facilitating the Safe and Responsible Deployment of Autonomous Vehicles
Several jurisdictions have already implemented or proposed policies aimed at fostering the responsible deployment of AVs. California, for example, has a comprehensive regulatory framework governing the testing and deployment of AVs, including permitting requirements and safety standards. Other states and countries are following suit, developing their own policies based on their specific needs and priorities. Some policies focus on creating designated testing zones for AVs, allowing for controlled environments to evaluate their performance and identify potential safety issues. Other policies concentrate on establishing data-sharing protocols, allowing agencies to collect and analyze data from AVs to improve safety and traffic management. The development of these policies is an ongoing process, with constant revisions and updates to adapt to technological advancements and evolving safety concerns. For instance, the UK has established a Centre for Connected and Autonomous Vehicles to support the development and implementation of AV technologies.
Framework for a Comprehensive Regulatory System Governing the Operation and Deployment of Autonomous Vehicles
A comprehensive regulatory system for AVs should incorporate several key elements. First, it should establish clear definitions and classifications for different levels of automation, providing a consistent framework for regulation. Second, it should set rigorous safety standards and testing protocols for AVs, ensuring they meet or exceed the safety performance of human drivers. Third, it should establish a robust liability framework, clearly defining responsibility in the event of an accident. Fourth, it must address data privacy and security concerns, protecting sensitive information collected by AVs. Fifth, it should facilitate the integration of AVs into existing transportation systems, ensuring efficient traffic flow and minimizing disruption. Finally, the system should be flexible and adaptable, allowing for adjustments as technology evolves and new safety challenges emerge. A phased approach to deployment, starting with limited operational areas and gradually expanding, could mitigate risks and allow for continuous monitoring and refinement of regulations. This approach mirrors the strategies employed in the introduction of other disruptive technologies, such as aircraft and high-speed rail.
Epilogue
The integration of autonomous vehicles into our traffic systems is a complex undertaking, a fascinating blend of technological innovation, infrastructural adaptation, and policy considerations. While challenges remain – from cybersecurity concerns to ethical dilemmas – the potential benefits are undeniable: reduced congestion, fewer accidents, and a more efficient use of our roads. The future of traffic management is undeniably intertwined with the rise of the autonomous vehicle, promising a smoother, safer, and potentially more sustainable transportation landscape. Buckle up, the ride’s about to get interesting.
