How Blockchain is Improving Transparency in Government Operations: Forget shadowy backroom deals. Blockchain’s arrival is shaking up the status quo, promising a future where government actions are crystal clear. This revolutionary technology, with its inherent security and immutability, is poised to redefine how we interact with public services, from tax collection to elections. Prepare for a deep dive into how this game-changing tech is making government more accountable and, dare we say, *actually* transparent.
We’ll explore specific applications, like streamlining public procurement and securing land registries, while also addressing potential challenges like data privacy and implementation costs. Think of it as your cheat sheet to understanding how blockchain is transforming the relationship between citizens and their government – for the better.
Introduction
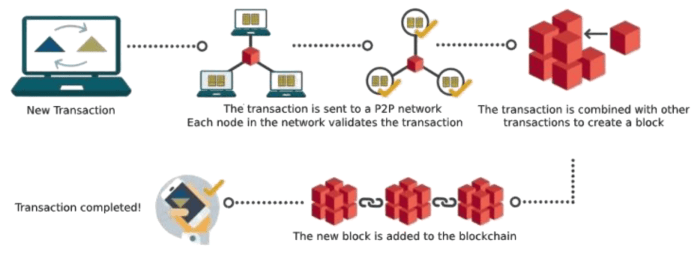
Source: mdpi.com
Blockchain’s impact on government transparency is undeniable, creating auditable records for everything from budgets to permits. This increased accountability mirrors the efficiency gains seen in customer service, as highlighted in this insightful piece on How AI is Reshaping the Customer Service Industry. Ultimately, both technologies promise a future where trust and efficiency are the new norms, particularly within public sector operations.
Transparency in government is the bedrock of a functioning democracy. It ensures accountability, fosters public trust, and allows citizens to understand how their tax dollars are being spent and how decisions affecting their lives are being made. However, traditional government operations often struggle with opacity. Complex bureaucratic processes, siloed data systems, and a lack of standardized record-keeping create significant hurdles to achieving genuine transparency. Citizens frequently face difficulty accessing information, and verifying the accuracy of what is provided. This lack of transparency breeds cynicism and erodes public faith in institutions.
Blockchain technology, with its decentralized and immutable ledger, offers a powerful solution to these challenges. Its inherent features—decentralization, immutability, and cryptographic security—directly address the core issues hindering transparency in government. By recording transactions and data on a distributed network, blockchain creates a permanent, verifiable record that is resistant to tampering and manipulation. This fosters trust and allows for greater public scrutiny.
Challenges of Ensuring Transparency in Traditional Government Operations
Traditional government systems often rely on centralized databases and paper-based record-keeping. This makes it difficult to track information across different departments and agencies. Data silos prevent a holistic view of government operations, hindering oversight and accountability. Furthermore, manual processes are prone to errors and inconsistencies, making it challenging to verify the accuracy and completeness of information. The lack of standardized data formats further complicates the process of data analysis and cross-referencing. For example, discrepancies in land registry records across different municipalities can lead to disputes and inefficiencies. Similarly, inconsistencies in public procurement data can obscure potential corruption or favoritism.
Blockchain’s Contribution to Increased Transparency
Blockchain’s decentralized nature eliminates single points of failure and reduces the risk of manipulation or censorship. The immutability of the blockchain ensures that once data is recorded, it cannot be altered or deleted without detection. This provides a high level of assurance regarding the integrity and authenticity of government records. Cryptographic hashing further enhances security by ensuring the integrity of each transaction or record. Public access to the blockchain (depending on the specific implementation) allows citizens to independently verify information and track government activities. This enhanced transparency promotes accountability and builds public trust.
Sectors Where Lack of Transparency is Problematic
Several government sectors are particularly vulnerable to a lack of transparency, leading to significant consequences. Public procurement, where contracts and spending are awarded, is a prime example. Lack of transparency in this area can lead to corruption, favoritism, and inefficient use of public funds. Similarly, land registries, managing property ownership and transactions, are susceptible to fraud and disputes if records are not accurately maintained and publicly accessible. Finally, the management of social welfare programs and aid distribution requires transparency to ensure equitable and efficient allocation of resources, preventing fraud and misuse of funds.
Comparison of Traditional and Blockchain-Based Record-Keeping
| Feature | Traditional Record-Keeping | Blockchain-Based System |
|---|---|---|
| Data Storage | Centralized databases, paper records | Decentralized, distributed ledger |
| Data Security | Vulnerable to hacking, manipulation, loss | High security due to cryptography and decentralization |
| Transparency | Limited, often requiring requests and approvals | Potentially high, depending on access controls; verifiable records |
| Auditability | Difficult and time-consuming | Easy and efficient due to immutable ledger |
Specific Applications of Blockchain in Government Transparency
Blockchain technology, with its inherent security and immutability, offers a powerful tool for enhancing transparency in various government operations. By creating a shared, verifiable ledger, it fosters trust and accountability, making it harder to manipulate or conceal information. This, in turn, strengthens public confidence in government processes and promotes good governance. Let’s delve into some specific applications.
Blockchain’s Role in Public Procurement
Public procurement, often a breeding ground for corruption, can benefit significantly from blockchain’s transparency. Imagine a system where every stage of the procurement process – from tendering to contract award – is recorded on a blockchain. This would create an auditable trail, visible to all stakeholders, including citizens. Any attempt to manipulate the process would be immediately apparent, deterring fraudulent activities and ensuring fairness. This increased visibility promotes competition and reduces the potential for bias or favoritism. For example, a city government could use a blockchain-based system to manage its bids for road construction projects, making the entire process, from bid submission to contract award, publicly viewable and tamper-proof.
Secure and Transparent Land Registry Systems Using Blockchain
Land registry systems are often plagued by issues of fraud, double-selling, and inefficient record-keeping. Blockchain can revolutionize these systems by providing a secure and transparent platform for recording land ownership. Each transaction, including the transfer of ownership, is recorded on the blockchain, creating an immutable record that is easily accessible to all authorized parties. This eliminates the risk of fraudulent transactions and reduces disputes over land ownership. A country like Sweden, for example, has explored the use of blockchain technology to improve its land registry system, aiming for a more efficient and secure process. The blockchain’s decentralized nature also makes it resilient to single points of failure, unlike traditional centralized systems.
Blockchain in Election Management and Verification
The integrity of elections is paramount for a functioning democracy. Blockchain can enhance election transparency by providing a secure and auditable record of votes cast. A blockchain-based voting system could allow voters to verify their votes, reducing concerns about fraud or manipulation. While full-scale implementation faces challenges, pilot projects are underway in several countries exploring different aspects of using blockchain in elections, focusing on aspects like voter registration and vote counting verification rather than direct voting on the blockchain itself. The focus is on ensuring the integrity of the process, not necessarily replacing existing voting mechanisms entirely.
Successful Blockchain Implementations in Government Transparency
Several governments worldwide are exploring and implementing blockchain solutions to improve transparency. Estonia, known for its digital government initiatives, has been a pioneer in using blockchain for various government services, including secure digital identity and data sharing. Other countries are exploring blockchain applications in areas like supply chain management for government procurement, ensuring the authenticity of goods and services purchased by public bodies. These initiatives demonstrate the growing recognition of blockchain’s potential to transform government operations and improve public trust.
Hypothetical Scenario: Enhancing Social Welfare Payments with Blockchain
Consider a social welfare system where benefit payments are managed using a blockchain. Each payment transaction, from the government’s disbursement to the recipient’s account, is recorded on the blockchain, creating a transparent and auditable trail. This eliminates the possibility of funds being diverted or lost, ensuring that beneficiaries receive their entitlements accurately and efficiently. Furthermore, the system can be designed to provide recipients with real-time access to their payment history, empowering them to monitor their benefits and identify any discrepancies. This level of transparency and accountability can significantly reduce fraud and improve the efficiency of the social welfare system.
Addressing Challenges and Limitations of Blockchain Implementation
The promise of blockchain for increased government transparency is undeniable, but the path to widespread adoption isn’t paved with gold. Several significant hurdles stand in the way, ranging from technical complexities to deeply ingrained societal concerns. Understanding these challenges is crucial for developing effective strategies to unlock blockchain’s full potential in the public sector.
Technical Challenges in Blockchain Implementation and Maintenance
Implementing and maintaining blockchain systems within a government context presents unique technical difficulties. Scalability remains a major issue; many existing blockchain platforms struggle to handle the high transaction volumes expected from large-scale government applications. Interoperability—the ability for different blockchain systems to communicate seamlessly—is another critical challenge. Governments often use diverse systems, and ensuring they can integrate with a blockchain network requires careful planning and potentially significant modifications to existing infrastructure. Furthermore, the technical expertise required to build, deploy, and maintain these systems is often scarce, leading to high costs and potential delays. The need for ongoing maintenance and updates to ensure security and efficiency adds to the long-term cost considerations. For instance, the complexity of integrating a blockchain system with existing voter registration databases would require extensive technical expertise and coordination between different government departments.
Cost-Benefit Analysis of Blockchain Solutions versus Traditional Methods
The decision to adopt blockchain technology in government requires a thorough cost-benefit analysis. While the potential benefits, such as increased transparency and reduced fraud, are significant, the initial investment can be substantial. This includes not only the costs of developing and implementing the blockchain system itself but also the costs of training personnel, integrating the system with existing infrastructure, and ongoing maintenance. Traditional methods, while potentially less secure and transparent, often have lower upfront costs and require less specialized expertise. A realistic cost-benefit analysis should consider the long-term implications, weighing the potential savings from reduced fraud and increased efficiency against the ongoing maintenance and operational costs of the blockchain system. For example, a city might compare the cost of implementing a blockchain-based land registry system with the costs associated with maintaining its current paper-based system, including the costs of manual record-keeping, potential errors, and the risk of fraud.
Data Privacy and Security Concerns in Blockchain-Based Government Systems
While blockchain’s inherent transparency is a significant advantage, it also raises concerns about data privacy. The immutability of blockchain data means that once information is recorded, it is extremely difficult, if not impossible, to remove or alter it. This can pose challenges in situations where sensitive personal information needs to be protected or where errors need to be corrected. Furthermore, the security of the blockchain system itself is crucial. A breach of security could lead to the exposure of sensitive government data or even manipulation of records. Robust security measures, including encryption and access control mechanisms, are essential to mitigate these risks. The potential for misuse of data, such as unauthorized access or manipulation, needs to be carefully addressed through stringent security protocols and regulatory frameworks.
Strategies for Mitigating Risks Associated with Blockchain Implementation
Several strategies can help mitigate the risks associated with blockchain implementation in government. Prioritizing thorough planning and feasibility studies is paramount. This includes a comprehensive assessment of the technical requirements, potential costs, and potential impact on existing systems. Investing in training and education for government personnel is also critical to ensure the successful adoption and maintenance of blockchain systems. Establishing clear governance structures and regulatory frameworks can help address concerns about data privacy and security. Furthermore, adopting a phased approach, starting with smaller pilot projects before scaling up to larger implementations, can help reduce risks and allow for iterative improvements. Collaboration and knowledge sharing between different government agencies and external experts can also facilitate the successful implementation of blockchain technology. For example, a phased approach might involve first implementing a blockchain-based system for tracking government contracts in a single department before expanding its use across multiple departments.
The Future of Blockchain and Government Transparency: How Blockchain Is Improving Transparency In Government Operations
The integration of blockchain technology into government operations is still in its nascent stages, but its potential to revolutionize transparency and accountability is undeniable. Looking ahead, we can anticipate a significant shift in how governments interact with citizens and manage resources, driven by the inherent security and immutability of blockchain. This will lead to a more efficient, trustworthy, and participatory governance model.
Blockchain’s Impact on Government Accountability
In the coming years, blockchain’s impact on government accountability will be profound. Increased transparency in public spending, facilitated by blockchain’s auditable record-keeping, will deter corruption and mismanagement. For example, tracking the allocation of funds for infrastructure projects on a public blockchain will allow citizens to verify that money is being used as intended, reducing the potential for embezzlement. This increased scrutiny will incentivize government officials to operate with greater integrity, fostering a culture of accountability. We can envision a future where real-time data on government spending is readily available to the public, enabling independent verification and analysis. This level of transparency will be transformative for holding governments responsible for their actions.
The Synergistic Role of Emerging Technologies
The convergence of blockchain with other emerging technologies, particularly Artificial Intelligence (AI) and the Internet of Things (IoT), will exponentially enhance its impact on government transparency. AI can be utilized to analyze vast amounts of blockchain data, identifying patterns and anomalies that might indicate fraudulent activity or inefficiencies. IoT devices, connected to a blockchain network, can provide real-time data on infrastructure performance, environmental conditions, or resource utilization, further enhancing transparency and enabling proactive governance. For instance, smart city initiatives can leverage IoT sensors to monitor traffic flow, air quality, and waste management, with data securely recorded and transparently shared on a blockchain, allowing citizens to see the impact of government policies in real time.
Enhancing Citizen Engagement and Trust
Blockchain technology has the potential to dramatically improve citizen engagement and trust in government. By providing citizens with direct access to verifiable information about government operations, blockchain empowers them to participate more meaningfully in the decision-making process. For example, a blockchain-based voting system could ensure the integrity of elections, eliminating concerns about fraud and manipulation. Furthermore, secure digital identity systems built on blockchain can streamline government services, making them more accessible and efficient for citizens. This increased accessibility and transparency will foster greater trust in government institutions and promote a more participatory democracy. Consider a scenario where citizens can easily track the progress of their requests for government services, such as passport renewals or benefit applications, through a transparent blockchain-based system. This direct visibility builds confidence and reduces frustration.
A Visual Representation of the Future Landscape
Imagine an infographic depicting a city skyline, with buildings representing various government departments interconnected by glowing lines representing blockchain networks. Each building has a transparent window displaying real-time data on its operations, such as budget allocation, project progress, and citizen feedback. Smaller, interconnected nodes represent IoT devices feeding data into the network, while AI algorithms are depicted as intelligent agents analyzing the data and identifying potential issues. The overall image conveys a sense of interconnectedness, transparency, and efficiency, highlighting the synergistic relationship between blockchain, AI, and IoT in creating a more accountable and responsive government.
Future Applications of Blockchain in Government Transparency
Beyond the applications already discussed, blockchain can be leveraged for enhanced transparency in areas such as land registry, supply chain management for public procurement, and healthcare data management. A blockchain-based land registry could prevent land fraud and ensure secure property ownership, while a transparent supply chain for public procurement would improve accountability and reduce the risk of corruption. Similarly, secure and private management of citizen health records on a blockchain could enhance patient control over their data and improve the efficiency of healthcare systems. These are just a few examples of how blockchain can continue to reshape the future of government transparency, creating a more efficient, trustworthy, and citizen-centric governance model.
Case Studies
Real-world applications of blockchain in government are emerging, demonstrating its potential to revolutionize transparency and accountability. These case studies showcase diverse implementations, highlighting both successes and challenges in leveraging this technology for public good. The examples below illustrate how different countries have tailored blockchain solutions to their specific needs and contexts.
Estonia’s e-Governance System, How Blockchain is Improving Transparency in Government Operations
Estonia has long been a pioneer in digital governance. Their existing robust digital infrastructure provided a fertile ground for integrating blockchain technology to enhance transparency and security within their e-governance system. Specifically, they focused on improving the security and verifiability of digital identities and land registries. The blockchain-based system provides citizens with secure access to their digital identities, allowing for streamlined interactions with government services. This system also enhances the security and transparency of land ownership records, reducing the risk of fraud and disputes.
- Problem Addressed: Security and verifiability of digital identities and land registries; potential for fraud and data manipulation.
- Blockchain Solution: Integration of blockchain technology into existing e-governance infrastructure for secure digital identity management and land registry.
- Positive Outcomes: Enhanced security and transparency of digital identities and land records; reduced instances of fraud and disputes; streamlined government services.
Georgia’s Land Registry
Georgia’s implementation of a blockchain-based land registry aimed to tackle widespread land ownership disputes and corruption. The traditional system was plagued by inefficiencies and lack of transparency, making it difficult to verify land ownership and resolve disputes effectively. By leveraging blockchain technology, Georgia created a secure and transparent system that provides a verifiable record of land ownership, making it readily accessible to citizens and reducing the potential for fraud and corruption.
- Problem Addressed: Widespread land ownership disputes, corruption, and inefficiencies in the traditional land registry system.
- Blockchain Solution: Development of a blockchain-based land registry system to provide a secure and transparent record of land ownership.
- Positive Outcomes: Reduced land ownership disputes; increased transparency and accountability in land administration; minimized corruption.
Sweden’s Vote Verification
While not a full-scale implementation across all government operations, Sweden has explored the use of blockchain for vote verification in local elections. This pilot program aimed to increase public trust and confidence in the electoral process by providing a secure and auditable record of votes. The blockchain solution ensured the integrity of the vote count by creating a tamper-proof record that could be independently verified. This approach represents a more limited but significant application of blockchain for enhancing government transparency in a specific area.
- Problem Addressed: Maintaining public trust and confidence in the electoral process; ensuring the integrity of vote counts.
- Blockchain Solution: Pilot program using blockchain technology for vote verification in local elections.
- Positive Outcomes: Increased transparency and verifiability of election results; enhanced public trust and confidence in the electoral process.
Last Word

Source: coredevsltd.com
Ultimately, the integration of blockchain in government operations signifies a monumental shift towards greater accountability and public trust. While challenges remain, the potential benefits – increased transparency, reduced corruption, and enhanced citizen engagement – are too significant to ignore. The future of government might just be written on the blockchain, one secure, verifiable transaction at a time. And that’s a future worth getting excited about.
