The Role of Robotics in Modernizing the Automotive Industry – Robotics: Modernizing the Automotive Industry. That’s the game-changer we’re diving into. Forget clunky assembly lines of yesteryear; today’s automotive world is a whirlwind of automated precision. From welding robots wielding laser beams to AI-powered quality control, the automotive industry’s transformation is a high-octane spectacle of technological prowess. This isn’t just about faster production; it’s about creating safer, more efficient, and ultimately, better cars.
We’ll explore how robots are revolutionizing every stage, from initial design to the final inspection, uncovering the surprising ways AI and collaborative robots (cobots) are reshaping the industry landscape. Get ready for a deep dive into the future of driving – and the tech that’s building it.
Introduction to Robotics in Automotive Manufacturing

Source: alamy.com
The automotive industry has always been at the forefront of technological innovation, and the integration of robotics has played a pivotal role in shaping its modern landscape. From humble beginnings, robotic systems have revolutionized manufacturing processes, leading to increased efficiency, improved product quality, and enhanced worker safety. This journey reflects a broader trend across numerous industries, showcasing the transformative power of automation.
The increasing adoption of robotics in automotive manufacturing is driven by several key factors. Firstly, the relentless demand for higher production volumes and faster turnaround times necessitates automation to maintain competitiveness in a global market. Secondly, the pursuit of consistent product quality, minimizing human error, is a significant motivator. Finally, the need to address labor shortages and improve workplace safety through the automation of dangerous or repetitive tasks has pushed the industry towards increased robotic integration.
Types of Robots and Their Applications in Automotive Manufacturing
Currently, a diverse range of robots are employed across various stages of automotive production. These robots are categorized based on their functionalities and applications. For example, industrial robots, often articulated robotic arms, are prevalent in tasks like welding, painting, and assembly. These robots excel at performing repetitive tasks with high precision and speed, significantly boosting productivity. Collaborative robots, or “cobots,” are designed to work alongside human workers, assisting with more complex or delicate operations that require a degree of human-robot interaction. These cobots are particularly useful in tasks requiring adaptability and problem-solving capabilities, enhancing human-machine collaboration. Furthermore, Automated Guided Vehicles (AGVs) and Autonomous Mobile Robots (AMRs) are increasingly used for material handling, transporting parts and components across the factory floor, optimizing logistics and minimizing downtime. The use of vision systems and advanced sensors enables these robots to navigate complex environments autonomously and efficiently. Specific examples include the use of robotic arms in welding car bodies, cobots assisting in the intricate assembly of dashboards, and AGVs transporting engine blocks between assembly stations. These diverse applications highlight the versatility and transformative impact of robotics in the modern automotive factory.
Historical Evolution of Robotics in the Automotive Sector
The integration of robotics in automotive manufacturing wasn’t an overnight revolution; it was a gradual process spanning several decades. Early adoption focused on simple, repetitive tasks like spot welding, where robots offered a clear advantage in speed and consistency over human workers. This initial phase, starting in the late 1960s and early 1970s, laid the groundwork for future advancements. Subsequent decades witnessed a steady increase in the sophistication of robotic systems, driven by advancements in computing power, sensor technology, and control algorithms. The development of more dexterous robots, capable of handling complex assembly tasks, marked a significant leap forward. The integration of vision systems allowed robots to adapt to variations in part positioning and orientation, improving flexibility and reducing the need for highly structured work environments. More recently, the rise of collaborative robots and autonomous mobile robots has further broadened the scope of robotic applications, paving the way for more flexible and human-centric manufacturing processes. The evolution of robotics in the automotive sector reflects a continuous drive towards greater efficiency, precision, and adaptability in manufacturing. For example, the shift from simple, fixed-path welding robots to flexible, sensor-guided systems exemplifies this ongoing evolution.
Robotics in Assembly and Production Lines
The automotive industry, always chasing efficiency and quality, has found a powerful ally in robotics. From the early days of simple automated tasks to the sophisticated, collaborative robots of today, robots have revolutionized vehicle assembly and production lines, significantly impacting speed, precision, and overall cost. This section delves into the specifics of robotic integration in automotive manufacturing, exploring the benefits, challenges, and various types of robots employed.
Robotic Roles in Vehicle Assembly Stages
Robots perform a wide array of tasks throughout the vehicle assembly process. In the body shop, robots handle tasks like welding, spot welding, and adhesive bonding with unparalleled precision and speed. They are crucial in the painting process, applying paint evenly and consistently, reducing waste and ensuring a high-quality finish. In the final assembly stage, robots install parts like dashboards, seats, and doors, often working in collaboration with human workers. They also perform quality control checks, identifying defects and ensuring that vehicles meet stringent quality standards. The use of robots allows for 24/7 operation, maximizing production capacity and minimizing downtime.
Efficiency and Cost-Effectiveness of Robotic Assembly Lines, The Role of Robotics in Modernizing the Automotive Industry
Robotic assembly lines significantly boost efficiency compared to traditional methods. Robots work tirelessly, consistently performing tasks at a much faster rate than human workers, leading to increased production volume. Their precision reduces errors and waste, resulting in fewer rejects and rework. While the initial investment in robotic systems can be substantial, the long-term cost-effectiveness is undeniable. The reduction in labor costs, material waste, and improved quality often outweighs the upfront investment, leading to a positive return on investment (ROI) over time. For example, Tesla’s Gigafactory utilizes extensive automation, demonstrating the potential for increased production efficiency and lower per-unit costs.
Challenges of Integrating Robots into Existing Production Lines
Integrating robots into existing automotive production lines presents several challenges. Retrofitting existing facilities to accommodate robotic systems can be expensive and disruptive to ongoing operations. Existing infrastructure may not be suitable for the weight, power requirements, or safety protocols of advanced robotic systems. Moreover, re-training existing workers to operate and maintain these new systems is crucial for successful integration. This necessitates significant investment in training programs and the development of new skills within the workforce. Finally, the programming and maintenance of complex robotic systems require specialized expertise, leading to a need for skilled technicians and engineers.
Types of Robots Used in Automotive Assembly
The following table compares different types of robots commonly used in automotive assembly, highlighting their advantages and disadvantages:
| Robot Type | Advantages | Disadvantages | Typical Applications |
|---|---|---|---|
| Articulated Robots | High degree of freedom, versatility, large reach | Complex programming, higher cost, potential for safety hazards | Welding, painting, material handling |
| SCARA Robots | High speed and precision, cost-effective, suitable for repetitive tasks | Limited reach and payload capacity, less versatile than articulated robots | Assembly of small parts, pick-and-place operations |
| Collaborative Robots (Cobots) | Safe to work alongside humans, easy to program, flexible deployment | Lower payload capacity compared to industrial robots, limited speed | Assembly tasks requiring human-robot collaboration, quality inspection |
Robotics in Welding and Painting Processes
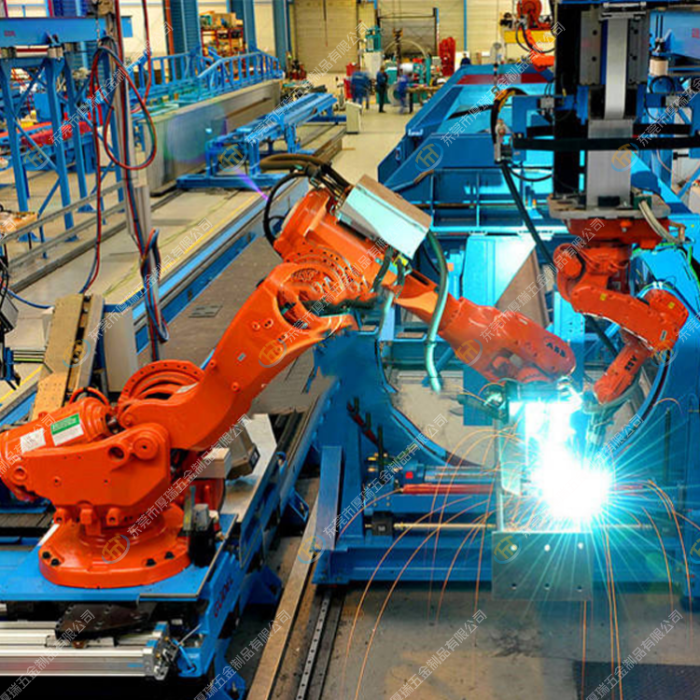
Source: group-ttm.com
The automotive industry’s relentless pursuit of higher quality, faster production, and improved safety has propelled the integration of robotics into welding and painting processes. These robots offer unparalleled precision and consistency, surpassing human capabilities in repetitive, high-precision tasks, leading to significant improvements in efficiency and product quality.
Robots have revolutionized these traditionally labor-intensive and potentially hazardous operations. Their consistent performance minimizes defects, reduces material waste, and creates a safer working environment for human employees. The increased speed and efficiency contribute directly to lower production costs and faster delivery times.
Advanced Robotic Welding Techniques
Modern automotive plants employ a variety of advanced robotic welding techniques to ensure superior weld quality and speed. These include laser welding, which offers high precision and deep penetration for joining different materials; arc welding, a widely used method offering versatility and speed; and resistance spot welding, ideal for joining sheet metal components quickly and efficiently. For example, laser welding is often preferred for joining high-strength steel components in car bodies, ensuring robust structural integrity. The precision of these robotic systems minimizes the need for rework and enhances the overall quality of the welded joints.
Robotic Painting Processes and Improvements
Robotic painting systems in automotive manufacturing boast significant advantages over traditional methods. Robots can apply paint with consistent thickness and coverage, eliminating runs, drips, and uneven finishes. They can access complex geometries and hard-to-reach areas with ease, ensuring complete paint coverage even on intricate car body parts. Advanced robotic painting systems use vision systems to identify and correct for imperfections in the surface, leading to a flawless finish. For instance, some systems employ electrostatic painting, where charged paint particles are attracted to the grounded car body, minimizing paint waste and ensuring even coating.
Robotic Welding Process Workflow Diagram for a Car Body Component
Imagine the robotic welding process for a car door frame. The workflow could be visualized as follows:
1. Part Loading: The robotic arm picks up a pre-fabricated car door frame component from a conveyor system.
2. Positioning: Using sensors and vision systems, the robot precisely positions the component in its welding fixture.
3. Welding Parameter Setting: The robot’s control system selects the appropriate welding parameters (e.g., current, voltage, speed) based on the material and weld type.
4. Welding Process: The robot performs the weld using a specified welding technique (e.g., arc welding, laser welding). The precise movements of the robot ensure consistent weld penetration and bead formation.
5. Weld Inspection: Post-weld inspection may involve vision systems to verify the quality of the weld, checking for defects or inconsistencies.
6. Part Unloading: The completed welded component is unloaded from the fixture and transferred to the next stage of the assembly process.
Robotics in Quality Control and Inspection
Source: whataftercollege.com
Robotics are revolutionizing car manufacturing, boosting efficiency and precision. This tech-driven leap mirrors advancements in other sectors; for example, the innovative use of technology in agriculture is crucial, as highlighted in this insightful article on The Role of Technology in Improving Global Food Security , addressing critical food production challenges. Similarly, automotive robotics are key to meeting the demands of a rapidly evolving industry, promising a future of smarter, faster, and more sustainable car production.
The automotive industry’s relentless pursuit of perfection necessitates rigorous quality control. Traditional methods, while effective, often fall short in terms of speed, consistency, and the ability to detect subtle defects. This is where robotics steps in, offering a powerful solution to enhance the accuracy and efficiency of quality inspection processes across the entire manufacturing pipeline. Robots, equipped with advanced sensors and sophisticated software, can perform inspections with unparalleled precision, leading to improved product quality and reduced waste.
Robots are increasingly employed for quality control and inspection in automotive manufacturing, significantly improving efficiency and accuracy. These robotic systems are typically integrated into the production line, performing various tasks ranging from visual inspections to dimensional measurements. They leverage advanced technologies like computer vision and machine learning to identify defects that might be missed by the human eye, ensuring a higher level of product consistency. The data collected by these robotic systems also provides valuable insights into manufacturing processes, helping to identify areas for improvement and prevent future defects.
Robotic Vision Systems and Defect Detection
Robotic vision systems are the eyes of the automated quality control process. These systems utilize high-resolution cameras, advanced lighting techniques, and sophisticated algorithms to capture and analyze images of automotive parts. The images are processed using computer vision techniques to identify deviations from pre-programmed specifications. For example, a robotic vision system might be programmed to identify scratches, dents, or inconsistencies in paint finish on a car body. Another application might involve checking for minute imperfections in the assembly of intricate components, such as engine parts or electronic systems. The system can then flag the defective parts for further investigation or rejection, ensuring only high-quality components are used in the final assembly. Some systems even employ 3D scanning technology for more comprehensive inspections, allowing for the detection of flaws not easily visible in 2D images. This allows for complete surface analysis, providing a highly detailed assessment of the part’s quality.
Benefits of Robotic Quality Control
The implementation of robots in quality control offers a multitude of advantages over traditional methods. The improvements translate directly into enhanced product quality, reduced costs, and increased production efficiency.
- Increased Speed: Robots can inspect parts significantly faster than human inspectors, leading to a quicker turnaround time and increased throughput.
- Improved Accuracy: Robotic vision systems possess a higher degree of accuracy than human inspectors, capable of detecting even minute defects that might be overlooked by the human eye.
- Enhanced Consistency: Robots perform inspections consistently, eliminating the variability associated with human fatigue or subjective judgment. This ensures a uniform level of quality across all produced parts.
- Reduced Costs: While the initial investment in robotic systems can be significant, the long-term cost savings from reduced waste, improved efficiency, and minimized rework often outweigh the initial expense.
- Improved Safety: Robots can handle tasks that may be dangerous or hazardous for human workers, such as inspecting parts in high-temperature environments or those involving sharp edges.
The Role of AI and Machine Learning in Robotic Automotive Applications
The automotive industry’s relentless pursuit of efficiency, quality, and innovation has led to a significant embrace of artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning (ML) in its robotic systems. No longer are robots simply programmed automatons; they’re evolving into intelligent, adaptable agents capable of learning, optimizing, and even anticipating needs within the manufacturing process. This integration isn’t just about incremental improvements; it’s a fundamental shift towards a more flexible, responsive, and ultimately, smarter automotive production landscape.
AI and ML algorithms are profoundly impacting the capabilities of robots used in automotive manufacturing. This integration allows for enhanced decision-making, increased adaptability to changing conditions, and the development of continuous learning capabilities within the robotic systems themselves. This means robots can handle more complex tasks, adapt to variations in materials or processes, and even improve their performance over time without human intervention.
AI-Enhanced Robotic Decision-Making in Automotive Manufacturing
The integration of AI allows robots to move beyond pre-programmed routines. Instead of rigidly following a set of instructions, AI-powered robots can analyze real-time data from sensors and cameras to make informed decisions. For example, a robot tasked with welding might use AI to adjust its welding parameters based on the specific material thickness or joint geometry it encounters, ensuring a consistently high-quality weld even with variations in the input. This level of adaptability significantly reduces the need for human intervention and minimizes errors. AI algorithms can also optimize the robot’s path planning, minimizing travel time and improving overall efficiency. Consider a scenario where a robot needs to navigate a cluttered factory floor – AI algorithms enable it to dynamically avoid obstacles and choose the most efficient route.
Adaptability and Learning in Automotive Robots
One of the most significant impacts of AI is the ability to endow robots with adaptive capabilities. Traditional robots require reprogramming for even minor changes in the production process. However, AI-powered robots can learn and adapt to new situations. Machine learning algorithms enable robots to analyze large datasets of past performance, identify patterns, and adjust their behavior accordingly. For instance, a robot involved in painting car bodies can learn to adjust its spray pattern based on the specific color or texture of the paint, ensuring a consistent and high-quality finish. This continuous learning process leads to improved performance and reduces the need for constant human supervision.
Examples of AI-Powered Robots in Automotive Factories
Several automotive manufacturers are already leveraging AI-powered robots in their factories. Autonomous mobile robots (AMRs) are used for material handling, navigating complex factory layouts without the need for pre-defined paths. These AMRs utilize AI-powered navigation systems to avoid obstacles and optimize their routes. Another example is the use of AI for predictive maintenance. By analyzing sensor data from robots and other factory equipment, AI algorithms can predict potential failures before they occur, allowing for proactive maintenance and minimizing downtime. This reduces costly repairs and improves overall production efficiency. Furthermore, AI-powered vision systems are used for quality control, enabling robots to identify defects with greater accuracy and speed than human inspectors. This ensures that only high-quality vehicles leave the factory.
Collaborative Robots (Cobots) in Automotive Manufacturing: The Role Of Robotics In Modernizing The Automotive Industry
The automotive industry, always pushing the boundaries of efficiency and precision, is increasingly embracing collaborative robots, or cobots. Unlike their industrial robot predecessors, cobots are designed to work alongside humans, sharing workspace and tasks in a safe and productive manner. This shift reflects a move towards more flexible, adaptable, and human-centered manufacturing processes.
Cobots represent a significant departure from traditional industrial robots. While industrial robots are typically large, caged, and operate independently, performing repetitive tasks at high speed, cobots are smaller, more agile, and designed for direct interaction with human workers. This collaboration opens up new possibilities for automotive manufacturing, particularly in tasks requiring dexterity, adaptability, and human judgment.
Safety Features and Advantages of Cobots in Human-Robot Collaboration
The inherent safety of cobots is paramount. Unlike traditional industrial robots, which require safety cages and barriers to prevent accidents, cobots employ various safety features to ensure safe human-robot interaction. These include force limiting capabilities, meaning that if a cobot encounters unexpected resistance (like a human hand), it will automatically stop. Advanced sensor systems, such as vision systems and proximity sensors, constantly monitor the surrounding environment, detecting obstacles and adjusting the cobot’s movements accordingly. Furthermore, cobots often feature user-friendly interfaces, allowing for simple programming and operation, minimizing the risk of human error. The advantages of cobot integration extend beyond safety; they offer increased flexibility, improved efficiency, and reduced production costs by optimizing human-robot collaboration. This allows for a more efficient allocation of tasks, leveraging the strengths of both humans and robots.
Examples of Cobot Applications in Automotive Manufacturing
Cobots are finding numerous applications in automotive manufacturing where human-robot interaction is crucial. One example is in assembly tasks, where cobots can assist human workers by providing parts, guiding tools, or performing delicate assembly operations. Imagine a cobot assisting in the intricate assembly of a car dashboard, handling small components with precision while a human worker focuses on the more complex aspects of the assembly. Another area is quality control, where cobots can work alongside human inspectors, performing repetitive inspection tasks, such as checking for surface defects or verifying component alignment. The cobot could handle the repetitive scanning, freeing the human inspector to focus on more complex visual assessments. Furthermore, cobots are increasingly used in training and education programs within automotive plants, providing a safe and interactive environment for workers to learn new skills and techniques. This fosters a collaborative work environment that encourages continuous learning and improvement.
The Future of Robotics in the Automotive Industry
The automotive industry is on the cusp of a transformative era, driven by relentless technological advancements. Robotics, already a cornerstone of modern automotive manufacturing, is poised to play an even more significant role in shaping the future of vehicle production, impacting everything from design and manufacturing processes to the very nature of the automotive workforce. The coming years will witness a surge in sophistication and application, leading to unprecedented levels of efficiency, customization, and safety.
Emerging trends point towards a future where robots are not just automated arms on assembly lines, but highly adaptable, intelligent systems integrated seamlessly into every stage of the automotive lifecycle. This evolution will be fueled by breakthroughs in artificial intelligence, sensor technologies, and collaborative robotics, creating a dynamic and rapidly evolving landscape.
Emerging Trends in Automotive Robotics
The integration of exoskeletons, wearable robots designed to augment human capabilities, is gaining traction. These devices can assist workers in performing repetitive or physically demanding tasks, reducing the risk of injury and improving overall productivity. For example, Ford Motor Company has implemented exoskeletons to support workers assembling vehicle components, reducing strain on their backs and shoulders. Simultaneously, advancements in sensor technologies, including advanced vision systems, force sensors, and proximity sensors, enable robots to operate with greater precision, dexterity, and safety, allowing them to handle more complex tasks and interact more effectively with human colleagues. Imagine robots equipped with tactile sensors capable of discerning the subtle differences in materials, ensuring flawless assembly and quality control.
Future Applications of Robotics in Automotive Production
The future of automotive robotics extends far beyond the traditional assembly line. Autonomous vehicle production, for instance, will rely heavily on robotic systems capable of handling the complex processes involved in assembling self-driving cars, including the intricate integration of sensors, software, and other advanced technologies. Furthermore, personalized vehicle manufacturing, driven by increasing consumer demand for customized options, will require flexible and adaptable robotic systems capable of producing vehicles tailored to individual specifications. This could involve robots handling bespoke paint jobs, installing unique interior components, or even assembling custom-designed chassis. Companies like Tesla are already exploring advanced automation strategies in their manufacturing processes, reflecting this trend.
The Impact of Robotics on the Automotive Workforce
The increased adoption of robotics in the automotive industry will undoubtedly have a profound impact on the workforce. While some jobs may be automated, new opportunities will emerge in areas such as robotics programming, maintenance, and system integration. This necessitates a proactive approach to reskilling and upskilling initiatives to ensure that the workforce possesses the necessary skills to adapt to the changing landscape. Investing in training programs focused on robotics, AI, and related technologies is crucial for bridging the skills gap and preparing workers for the jobs of the future. Governments and industry stakeholders need to collaborate to implement effective reskilling and upskilling strategies to mitigate potential job displacement and ensure a smooth transition for the automotive workforce.
Epilogue
The automotive industry’s embrace of robotics isn’t just a trend; it’s a necessity. The future of car manufacturing is undeniably robotic, promising higher quality, increased efficiency, and safer working conditions. While challenges remain – integrating robots into existing infrastructure, reskilling the workforce – the potential rewards are immense. The journey towards fully automated car production is underway, and it’s a thrilling ride to witness.
