The Role of AI in Enhancing Traffic Flow and Urban Mobility is no longer a futuristic fantasy; it’s rapidly becoming our reality. Imagine a city where traffic jams are a thing of the past, public transport runs like clockwork, and finding a parking spot is less stressful than a root canal. Sounds utopian? Not with the power of artificial intelligence. From smart traffic lights that adapt to real-time conditions to self-driving cars navigating our streets, AI is poised to revolutionize how we move around our urban landscapes. This deep dive explores the exciting potential—and the challenges—of this technological transformation.
We’ll unpack how AI is optimizing everything from traffic signal control and public transport scheduling to autonomous vehicle integration and even parking solutions. But it’s not all smooth sailing. We’ll also tackle the ethical considerations, data privacy concerns, and the need for responsible AI development in this crucial area. Get ready for a ride into the future of urban mobility!
AI-Powered Traffic Management Systems
The rise of smart cities necessitates intelligent solutions to the age-old problem of urban congestion. AI is stepping up to the plate, offering sophisticated tools to manage traffic flow and improve urban mobility. These systems move beyond simple traffic light coordination, utilizing advanced algorithms and data analysis to optimize traffic movement in real-time and even predict future congestion patterns.
Types of AI-Powered Traffic Management Systems
Several different AI-powered traffic management systems are currently in use, each leveraging different aspects of artificial intelligence. These systems vary in their complexity and the data they utilize, but share the common goal of improving traffic flow efficiency. Some examples include adaptive traffic signal control systems, which dynamically adjust signal timings based on real-time traffic conditions, and predictive modeling systems, which forecast traffic patterns to proactively manage congestion. Furthermore, some systems integrate data from various sources, including GPS data from vehicles, social media feeds reporting incidents, and weather forecasts to provide a holistic view of the traffic situation.
Adaptive Traffic Signal Control vs. Predictive Modeling
Adaptive traffic signal control systems (ATSC) react to current traffic conditions, optimizing signal timings to minimize delays at intersections. Think of it as a constantly adjusting conductor of the urban traffic orchestra. These systems excel at immediate responses to unexpected events, like accidents or sudden influxes of vehicles. Predictive modeling, on the other hand, takes a more proactive approach. By analyzing historical traffic data, weather forecasts, and even social media trends, it anticipates potential congestion hotspots and adjusts traffic management strategies accordingly. While ATSC focuses on reactive optimization, predictive modeling aims for preventative measures. The effectiveness of each depends on the specific context; ATSC is better suited for handling immediate disruptions, while predictive modeling excels at long-term planning and mitigating predictable congestion. A truly effective system would likely integrate both approaches.
Hypothetical AI-Driven Traffic Management System for Dense Urban Areas, The Role of AI in Enhancing Traffic Flow and Urban Mobility
Imagine a city grappling with chronic congestion. Our hypothetical AI-driven system, dubbed “UrbanFlow,” would address this using a multi-pronged approach. It would begin by integrating data from various sources: real-time traffic cameras, GPS data from vehicles, public transport schedules, and weather forecasts. This data would be fed into a sophisticated AI engine employing machine learning algorithms to analyze traffic patterns, identify congestion hotspots, and predict future traffic flow. The system would then dynamically adjust traffic signals, reroute traffic based on real-time conditions, and even communicate with connected vehicles to suggest optimal routes. Furthermore, UrbanFlow would incorporate predictive maintenance capabilities for traffic infrastructure, identifying potential problems before they disrupt traffic flow.
| Component | Functionality | Data Sources | Benefits |
|---|---|---|---|
| Real-time Traffic Monitoring | Continuous monitoring of traffic flow using cameras and sensors. | Cameras, sensors, GPS data | Improved situational awareness, rapid response to incidents. |
| Predictive Modeling | Forecasting traffic patterns based on historical data and external factors. | Historical traffic data, weather forecasts, social media | Proactive congestion management, optimized resource allocation. |
| Adaptive Traffic Signal Control | Dynamic adjustment of signal timings based on real-time traffic conditions. | Real-time traffic data, sensor data | Reduced delays, improved intersection efficiency. |
| Connected Vehicle Integration | Communication with vehicles to provide optimal routes and warnings. | GPS data, vehicle-to-infrastructure communication | Reduced congestion, improved driver experience. |
AI and Public Transportation Optimization: The Role Of AI In Enhancing Traffic Flow And Urban Mobility
Public transportation, the backbone of many cities, often struggles with inefficiencies and unreliability. Overcrowding, unpredictable delays, and inconsistent service plague commuters daily. But what if we could leverage the power of artificial intelligence to smooth out these wrinkles and create a more efficient, reliable, and enjoyable public transit experience? AI offers a powerful toolkit for optimizing every aspect of public transportation, from route planning to predictive maintenance.
AI can significantly improve the efficiency and reliability of public transportation networks like buses, trains, and subways by analyzing massive datasets to identify patterns and predict future scenarios. This predictive capability allows for proactive adjustments to schedules, resource allocation, and maintenance, minimizing disruptions and maximizing passenger satisfaction. Think of it as having a super-smart traffic controller for your entire public transit system, constantly monitoring and adjusting to keep things running smoothly.
AI-Driven Bus Routing and Scheduling
Optimizing bus routes and schedules based on real-time data is a game-changer. AI algorithms can analyze passenger demand data from various sources – smart cards, mobile apps, and even social media – to predict ridership patterns at different times of day and across various routes. This information is then used to dynamically adjust routes and schedules, ensuring that buses are deployed where and when they’re needed most. For example, during rush hour, AI could reroute buses to areas experiencing higher-than-expected demand, or add extra buses to alleviate overcrowding. Conversely, during off-peak hours, it could optimize routes to minimize empty runs, improving fuel efficiency and operational costs. Imagine a system that automatically adjusts schedules based on real-time traffic conditions, avoiding congestion and ensuring punctual arrivals. This isn’t science fiction; it’s already happening in cities around the world.
AI-Powered Predictive Maintenance for Public Transportation
Predictive maintenance, powered by AI, is a critical tool for reducing delays and disruptions. By analyzing sensor data from vehicles (e.g., engine temperature, brake wear, vibration levels), AI algorithms can identify potential mechanical failures before they occur. This allows maintenance crews to proactively address issues, preventing breakdowns and minimizing costly repairs. For instance, an AI system might predict that a train’s braking system is nearing failure based on subtle changes in sensor readings, prompting a scheduled maintenance check before a potentially dangerous situation arises. This proactive approach reduces unexpected delays, improves safety, and significantly extends the lifespan of public transportation assets. Think of it as giving your transit system a regular health check-up, preventing minor issues from escalating into major headaches. This not only saves money but also improves the overall reliability and safety of the system.
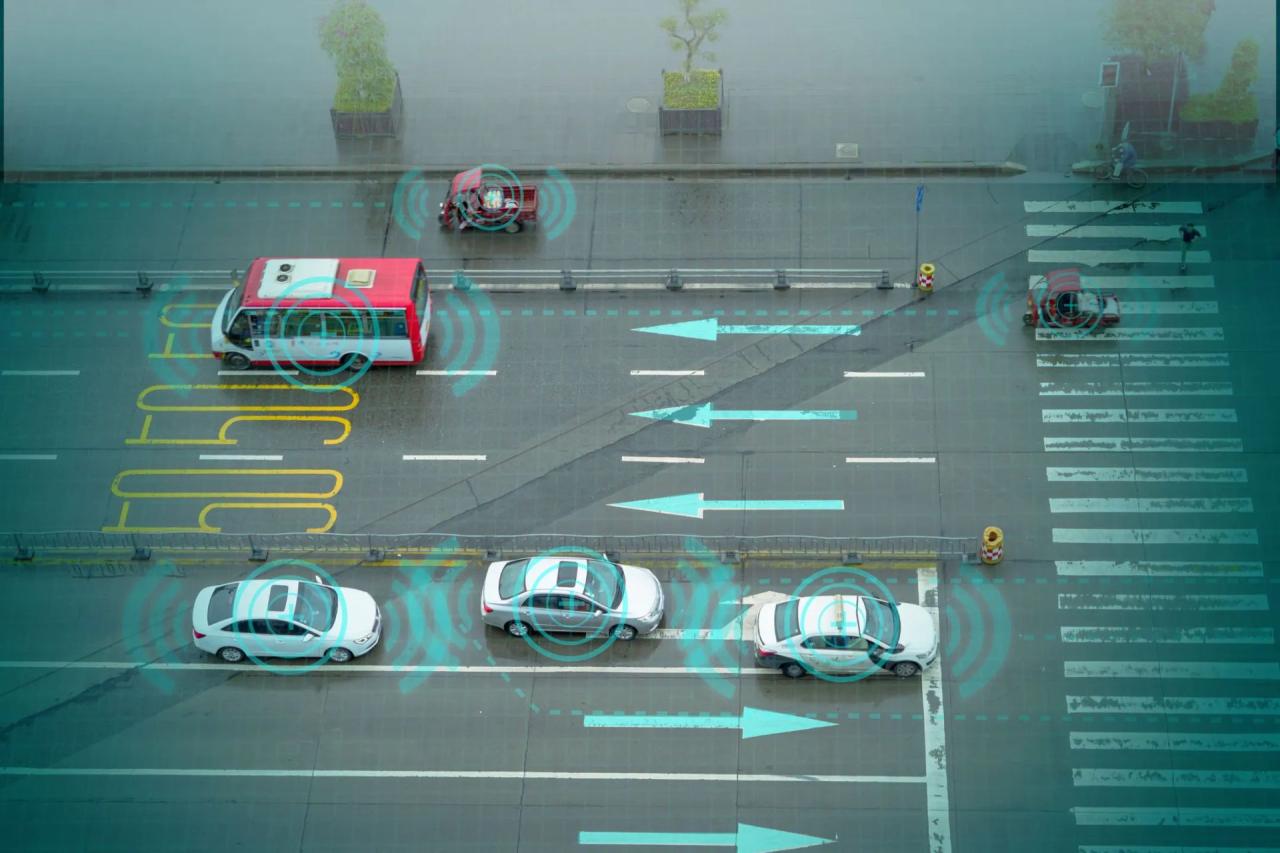
AI for Autonomous Vehicles and Urban Mobility
The rise of autonomous vehicles (AVs) promises a radical transformation of urban landscapes, impacting everything from traffic congestion to urban planning. While still in its early stages, the potential benefits of self-driving cars are significant, offering a glimpse into a future with smoother commutes and more efficient use of urban space. However, realizing this potential requires careful consideration of the challenges and safety implications involved in integrating AVs into our existing systems.
Autonomous vehicles have the potential to significantly reduce traffic congestion. By eliminating human error – such as erratic braking and inefficient lane changes – AVs can optimize traffic flow, leading to smoother movement and reduced stop-and-go driving. Imagine a city where vehicles seamlessly coordinate their movements, minimizing delays and maximizing throughput. This could lead to reduced commute times, lower fuel consumption, and a decrease in greenhouse gas emissions. Furthermore, the improved efficiency could allow for more efficient use of existing road infrastructure, potentially reducing the need for costly expansions. Real-world examples, although still limited, are emerging, with pilot programs in several cities demonstrating improved traffic flow in controlled environments.
Impact of Autonomous Vehicles on Traffic Congestion and Urban Mobility
The integration of autonomous vehicles could dramatically alter urban mobility. Improved traffic flow, as mentioned earlier, is a key benefit. But beyond that, AVs could also enable new transportation models. For instance, ride-sharing services utilizing fleets of autonomous vehicles could provide more efficient and affordable public transportation alternatives. Imagine on-demand, self-driving shuttles operating throughout a city, dynamically adjusting routes and schedules based on real-time demand. This could reduce the need for personal car ownership, freeing up valuable urban space currently dedicated to parking. Furthermore, the potential for autonomous delivery vehicles could revolutionize logistics and last-mile delivery, improving efficiency and reducing congestion caused by delivery trucks. The overall impact is a potential shift from individual car ownership towards shared, on-demand mobility services, leading to a more efficient and sustainable urban transportation system.
Challenges of Integrating Autonomous Vehicles into Existing Transportation Infrastructure
Integrating AVs into existing infrastructure presents numerous challenges. Our current road networks weren’t designed for self-driving cars, lacking the necessary infrastructure for seamless communication and navigation. Upgrading existing infrastructure to support AVs, including implementing advanced sensor networks and communication systems, would be a costly and time-consuming endeavor. Furthermore, the legal and regulatory frameworks surrounding autonomous vehicles are still under development, creating uncertainty for both manufacturers and consumers. Questions around liability in the event of accidents involving AVs also need clear and comprehensive answers. Finally, the cybersecurity of AVs is paramount; ensuring the integrity and security of their systems against hacking or malicious attacks is crucial for public safety.
Safety Features and Regulations for Autonomous Vehicles
The widespread adoption of autonomous vehicles hinges on robust safety features and comprehensive regulations. The following list Artikels key aspects:
- Redundant Systems: AVs should incorporate multiple independent systems for crucial functions like braking and steering, ensuring that a single point of failure doesn’t lead to an accident.
- Advanced Sensor Fusion: The use of multiple sensor types (LiDAR, radar, cameras) allows for a more complete and accurate understanding of the surrounding environment, enhancing safety.
- Fail-Safe Mechanisms: Systems should be designed to safely bring the vehicle to a stop or transition to manual control in the event of a malfunction.
- Cybersecurity Measures: Robust cybersecurity protocols are essential to protect against hacking and malicious attacks that could compromise vehicle safety.
- Comprehensive Testing and Validation: Rigorous testing and validation procedures are crucial to ensure the safety and reliability of AV systems before deployment.
- Clear Liability Frameworks: Establishing clear legal frameworks for liability in the event of accidents involving AVs is crucial for public acceptance and insurance purposes.
- Standardized Communication Protocols: Standardization of communication protocols between AVs and infrastructure is essential for seamless integration into existing transportation systems.
AI-Driven Parking Solutions
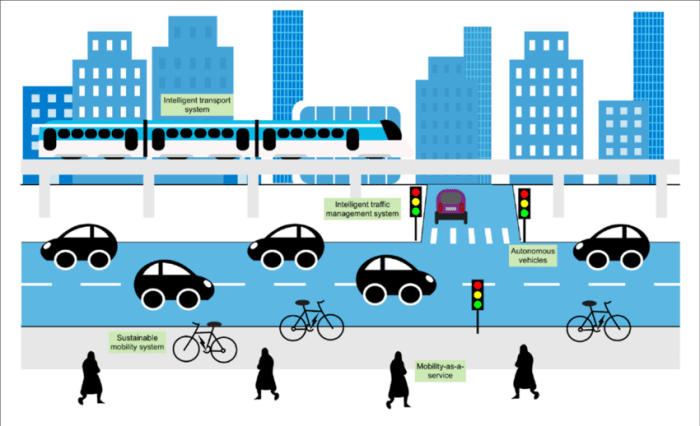
Source: researchgate.net
Urban parking woes are a common complaint – circling blocks, wasted time, and the frustration of finding nothing. AI offers a powerful solution, transforming the chaotic search for a parking spot into a streamlined and efficient process. By leveraging data and smart technology, AI-driven systems can significantly improve parking availability and reduce the time spent searching, ultimately easing congestion and improving the overall urban experience.
AI improves parking availability and reduces search times by optimizing space utilization and providing real-time information to drivers. This involves a sophisticated interplay of sensors, algorithms, and user interfaces, creating a smart parking ecosystem that benefits both drivers and city planners. The technology doesn’t just locate available spots; it anticipates demand, dynamically adjusts pricing, and even guides drivers to the most convenient and efficient parking options.
AI Technologies in Parking Guidance and Management
AI-powered parking systems rely on a combination of technologies to achieve their goals. These technologies work in concert to create a comprehensive and effective solution. For example, sensor networks embedded in parking lots provide real-time data on occupancy. This data is then processed by sophisticated algorithms that predict future demand and optimize pricing strategies. Meanwhile, user-friendly mobile apps provide drivers with up-to-the-minute information, guiding them to available spaces and potentially even reserving spots in advance.
Dynamic Parking Pricing Based on Real-Time Demand
Implementing a dynamic pricing model for parking spaces allows for efficient resource allocation and reduces congestion. This system adjusts prices based on real-time demand and availability, incentivizing drivers to park in less congested areas during peak hours and encouraging turnover of parking spots. The price fluctuates based on factors such as time of day, day of the week, and proximity to popular destinations. This system aims to optimize parking space utilization and revenue generation for parking operators while simultaneously improving traffic flow.
| Time of Day | Weekday Price (per hour) | Weekend Price (per hour) |
|---|---|---|
| 7:00 AM – 9:00 AM | $5 | $3 |
| 9:00 AM – 5:00 PM | $3 | $2 |
| 5:00 PM – 7:00 PM | $4 | $3 |
| 7:00 PM – 7:00 AM | $2 | $2 |
This table illustrates a sample dynamic pricing structure. The actual prices would be adjusted based on real-time demand and historical data analysis. For instance, during major events or festivals, prices in high-demand areas might increase significantly, encouraging drivers to use alternative parking options or public transportation. This incentivizes a more balanced distribution of parked vehicles throughout the city, leading to reduced congestion in popular areas.
Data Collection and Analysis for AI in Urban Mobility

Source: prismic.io
AI’s impact on urban landscapes is undeniable, optimizing traffic flow with smart systems that predict congestion and reroute vehicles. This data-driven approach mirrors the revolution happening in agriculture, as detailed in this insightful article on How Smart Farming Technologies are Changing Agriculture Practices , where precision farming leverages data for optimal yields. Ultimately, both sectors highlight AI’s potential to enhance efficiency and resource management, paving the way for smarter, more sustainable futures.
The effectiveness of AI in revolutionizing urban mobility hinges critically on the quality and quantity of data used to train and refine its algorithms. Without a robust and diverse data pipeline, AI systems remain limited in their ability to accurately predict traffic patterns, optimize routes, and enhance overall efficiency. This section delves into the multifaceted world of data collection and the analytical techniques employed to unlock the potential of this information for smarter cities.
Data sources for training AI models in urban mobility are incredibly diverse, reflecting the complexity of urban environments. This rich tapestry of information allows for a more comprehensive and nuanced understanding of transportation dynamics.
Data Sources for AI in Urban Mobility
Various sources contribute to the data ecosystem fueling AI-powered urban mobility solutions. These sources, when integrated effectively, provide a holistic view of traffic flow, transportation patterns, and user behavior. This comprehensive approach is crucial for developing robust and adaptable AI models.
- GPS Data from Smartphones and Connected Vehicles: This is arguably the most significant source, providing real-time location information of countless vehicles and individuals. This data reveals traffic congestion, speed patterns, and route choices, providing a dynamic picture of urban mobility.
- Traffic Camera Footage: Images from traffic cameras offer visual data on traffic density, vehicle types, and incidents like accidents or road closures. Advanced computer vision techniques can analyze this data to identify patterns and anomalies.
- Smart Card and Ticketing Data from Public Transportation: Data from public transport systems, such as bus, train, and subway usage, reveals ridership patterns, peak hours, and popular routes. This information helps optimize schedules and improve service efficiency.
- Social Media Data: Social media posts and tweets often contain information about traffic incidents, road closures, and public sentiment regarding transportation. Sentiment analysis can gauge public perception and identify potential issues.
- Weather Data: Weather conditions significantly impact traffic flow. Integrating weather forecasts and real-time weather data allows AI systems to anticipate potential delays and adjust traffic management strategies proactively.
- Sensor Data from Smart Infrastructure: Sensors embedded in roads and infrastructure provide real-time data on various parameters such as road occupancy, speed, and even air quality. This granular data provides a precise picture of local traffic conditions.
Data Analysis Techniques for Urban Transportation
Processing the massive datasets generated by these sources requires sophisticated data analysis techniques. The choice of technique depends on the specific application and the nature of the data.
- Machine Learning Algorithms: These algorithms, such as neural networks, support vector machines, and random forests, are essential for identifying patterns and making predictions based on historical and real-time data. For instance, neural networks can be trained to predict traffic congestion based on historical traffic patterns and real-time sensor data.
- Deep Learning Models: These advanced machine learning algorithms are particularly well-suited for analyzing complex, high-dimensional data like images from traffic cameras. Convolutional neural networks (CNNs) can be used to detect objects (e.g., vehicles, pedestrians) and events (e.g., accidents) in traffic camera footage.
- Time Series Analysis: This technique is vital for analyzing data that changes over time, such as traffic flow and speed. Time series models can be used to forecast future traffic conditions and identify trends.
- Statistical Modeling: Traditional statistical methods, such as regression analysis and hypothesis testing, can be used to understand the relationships between different variables and to evaluate the effectiveness of different traffic management strategies. For example, regression analysis could be used to model the relationship between traffic volume and average speed.
Anonymization and Aggregation of Data for Privacy Protection
Protecting user privacy is paramount when dealing with large datasets containing personal information. Anonymization and aggregation techniques are crucial for ensuring responsible data handling.
Anonymization involves removing or modifying personally identifiable information (PII) from datasets, making it impossible to link the data back to specific individuals. Aggregation involves combining data from multiple sources to create summary statistics that do not reveal individual-level information.
For example, instead of storing the exact GPS coordinates of individual vehicles, data can be aggregated to represent the average speed and density of traffic within a specific geographic area. This approach provides valuable insights for traffic management while safeguarding individual privacy. Differential privacy techniques can further enhance privacy protection by adding carefully calibrated noise to the data, ensuring that individual contributions cannot be easily identified while preserving the overall statistical properties of the dataset.
The Ethical Considerations of AI in Urban Transportation
The integration of artificial intelligence into urban transportation systems offers immense potential for improving efficiency and mobility. However, this technological leap comes with a critical need to address the ethical implications that arise from the deployment of AI algorithms in managing our cities’ movement. Failing to consider these ethical dimensions risks exacerbating existing inequalities and creating new forms of social and individual harm.
AI algorithms, while powerful, are not inherently unbiased. Their decisions are shaped by the data they are trained on, and if this data reflects existing societal biases – for example, over-representation of certain demographics in accident reports or under-representation of others in route planning data – the AI system will perpetuate and even amplify these biases in its operations. This can lead to unfair or discriminatory outcomes for certain communities, impacting access to efficient transportation options and potentially exacerbating existing social inequalities.
Potential Biases in AI Traffic Management Algorithms
Algorithmic bias in traffic management systems can manifest in several ways. For example, an AI system trained primarily on data from wealthier neighborhoods might prioritize those areas for traffic flow optimization, leading to longer wait times and increased congestion in less affluent areas. Similarly, an algorithm trained on accident data that disproportionately reflects certain demographic groups might lead to increased surveillance or enforcement in those areas, regardless of actual risk levels. This creates a feedback loop where existing inequalities are reinforced and potentially widened by the supposedly neutral actions of an AI system. Addressing this requires careful consideration of data collection methodologies, rigorous auditing of algorithms for bias, and the development of techniques to mitigate the impact of biased data.
Privacy Concerns Related to AI-Driven Urban Transportation Monitoring
The use of AI in urban transportation often involves the collection and analysis of vast amounts of personal data. This data can include location information, travel patterns, and even biometric data from facial recognition systems used in public transportation. While this data can be used to optimize traffic flow and improve public safety, it also raises significant privacy concerns. The potential for misuse of this data, for example, through unauthorized surveillance or profiling, is a serious ethical challenge. Robust data protection measures, transparent data governance policies, and clear guidelines on data usage are crucial to mitigate these risks and ensure that individuals’ privacy rights are respected.
Strategies for Ensuring Fairness, Transparency, and Accountability in AI Urban Mobility Systems
Ensuring fairness, transparency, and accountability in AI-driven urban transportation requires a multi-faceted approach. This includes developing algorithms that are designed to be fair and equitable from the outset, using diverse and representative datasets for training, and implementing rigorous testing and auditing procedures to identify and mitigate bias. Transparency is crucial, requiring clear explanations of how AI systems make decisions and the data they rely on. Accountability mechanisms, including independent oversight bodies and robust redressal processes, are essential to ensure that those affected by AI systems have avenues for addressing grievances and seeking redress for any harms suffered. Furthermore, fostering public dialogue and engagement in the development and deployment of these systems is critical for building trust and ensuring that these technologies serve the broader public good.
Future Trends in AI and Urban Mobility
The integration of artificial intelligence into urban transportation systems is still in its nascent stages, yet the potential for transformative change is undeniable. We’re on the cusp of a revolution, where AI will not just improve efficiency but fundamentally reshape how we move around our cities. This section explores the exciting advancements on the horizon and paints a picture of what the future of urban mobility might look like.
The next decade will witness a rapid acceleration in AI’s capabilities, leading to more sophisticated and integrated urban transportation systems. This isn’t simply about tweaking existing systems; it’s about creating entirely new paradigms of movement and accessibility.
Predictive Traffic Management and Personalized Routing
Imagine a city where traffic jams are a thing of the past, or at least, significantly minimized. This isn’t science fiction. Advanced AI algorithms, leveraging real-time data from various sources (connected vehicles, sensors, weather forecasts), can predict traffic patterns with remarkable accuracy, hours or even days in advance. This predictive capability allows for proactive traffic management, dynamically adjusting traffic light timings, suggesting alternative routes to drivers, and even influencing public transport schedules to optimize flow. The result is a smoother, faster, and less stressful commute for everyone. For instance, imagine a system that reroutes delivery trucks based on real-time traffic analysis, minimizing congestion during peak hours and ensuring timely deliveries.
Hyper-Personalized Public Transportation
Public transportation is poised for a significant upgrade. AI can personalize the public transit experience, going beyond simple route optimization. Imagine an app that suggests the optimal mode of transport (bus, train, bike share, ride-sharing) based on real-time conditions, individual preferences, and even your current location and destination. The system could even predict potential delays and suggest alternative routes or modes of transport to minimize disruption. This level of personalization increases ridership and makes public transport a more attractive option for a wider range of commuters. Think of a system that automatically adjusts bus routes based on passenger demand fluctuations throughout the day, ensuring sufficient capacity on busy routes and avoiding overcrowding.
Autonomous Vehicle Integration and Shared Mobility
The rise of autonomous vehicles (AVs) will inevitably reshape urban landscapes. AI will be crucial in managing the complex interactions between AVs, human-driven vehicles, pedestrians, and cyclists. This requires sophisticated algorithms capable of handling real-time decision-making in dynamic environments. Furthermore, AI can optimize the utilization of AVs through shared mobility platforms, reducing the number of vehicles on the road and minimizing environmental impact. For example, imagine a fleet of autonomous robo-taxis operating seamlessly within a designated area, dynamically adjusting their routes and pick-up points based on real-time demand.
A Glimpse into a Future Smart City
Picture Neo-Kyoto, a futuristic city seamlessly blending traditional Japanese architecture with cutting-edge technology. Transportation is fluid and efficient. Autonomous vehicles glide silently along dedicated lanes, while personalized public transport systems whisk commuters to their destinations with pinpoint accuracy. AI-powered traffic management systems ensure smooth flow, eliminating congestion and reducing commute times. Overhead drones monitor traffic patterns in real-time, providing data to the central AI system, which constantly optimizes the entire transportation network. Pedestrians navigate effortlessly, guided by interactive maps projected onto the pavement, and smart parking systems guide drivers to available spaces, eliminating the frustration of circling endlessly for a spot. The air is cleaner, the streets are quieter, and the city moves with a harmonious rhythm, orchestrated by the intelligent infrastructure humming beneath its surface. This isn’t just a technological advancement; it’s a societal shift towards a more efficient, sustainable, and enjoyable urban experience.
Final Review

Source: hyscaler.com
The integration of AI into urban transportation systems isn’t just about faster commutes; it’s about creating smarter, more efficient, and ultimately, more sustainable cities. While challenges remain—from ethical considerations to the need for robust infrastructure—the potential benefits are undeniable. As AI technologies continue to evolve, we can anticipate a future where urban mobility is not just improved, but fundamentally transformed, leading to a more connected, accessible, and enjoyable urban experience for everyone. The journey has begun, and the destination is a future where getting around is less of a headache and more of a breeze.
