The Future of Smart Transportation and Autonomous Public Transit is here, and it’s a game-changer. Forget crowded buses and traffic jams – imagine a future where self-driving vehicles whisk you around town efficiently and sustainably. This isn’t science fiction; advancements in AI, sensor technology, and infrastructure are paving the way for a revolution in public transport. We’ll explore the technological leaps, infrastructure needs, economic impacts, and societal shifts this transition will bring, addressing safety concerns and public perception along the way. Get ready to buckle up for a ride into the future of mobility.
This deep dive will examine the current state of autonomous vehicle technology, highlighting the incredible advancements on the horizon. We’ll delve into the infrastructure required to support this shift, including smart city initiatives and the adaptation of existing road networks. The economic and social implications will be analyzed, considering both the potential benefits and challenges, such as job displacement and the impact on accessibility. Crucially, we’ll address safety and security concerns, exploring the necessary protocols and regulations to ensure a smooth and safe transition. Finally, we’ll discuss public perception and acceptance, outlining strategies to build trust and encourage widespread adoption.
Technological Advancements in Autonomous Public Transit
The integration of autonomous vehicles into public transit systems promises a revolution in urban mobility, offering the potential for increased efficiency, safety, and accessibility. However, realizing this vision requires significant advancements in several key technological areas. Currently, the technology is still under development, but the progress made is remarkable and points towards a future where self-driving buses and trains become commonplace.
Autonomous vehicle technology for public transit is currently in various stages of development, ranging from experimental prototypes undergoing rigorous testing to limited deployments in controlled environments. Most systems rely on a combination of sensors, high-definition mapping, and sophisticated AI algorithms to navigate and operate. While fully autonomous, driverless systems are still some years away from widespread adoption in complex urban settings, substantial progress is being made, paving the way for gradual integration into public transportation networks.
Sensor Technology Advancements, The Future of Smart Transportation and Autonomous Public Transit
The next 5-10 years will likely witness significant improvements in sensor technology, crucial for the safe and reliable operation of autonomous vehicles in public transit. LiDAR (Light Detection and Ranging), radar, and cameras are the primary sensor modalities currently used. We can expect to see higher resolution and longer-range LiDAR systems capable of operating effectively in diverse weather conditions, including fog, rain, and snow. Similarly, advancements in radar technology will improve object detection and classification, even in challenging environments. Camera technology will benefit from improved image processing capabilities and the incorporation of AI-powered object recognition, enhancing the accuracy and speed of data interpretation. This combined improvement will lead to more robust and reliable perception systems for autonomous vehicles, making them safer and more dependable in real-world scenarios, such as navigating crowded city streets or dealing with unpredictable pedestrian behavior.
Artificial Intelligence and Machine Learning Advancements
AI and machine learning are the brains behind autonomous vehicles. Over the next decade, we can anticipate significant progress in several areas. Deep learning models will become more sophisticated, capable of handling complex scenarios and adapting to changing conditions with greater efficiency. This will involve advancements in reinforcement learning algorithms, enabling autonomous vehicles to learn optimal driving strategies through simulated and real-world experience. Furthermore, improved algorithms will enable better decision-making in ambiguous situations, such as navigating unexpected obstacles or responding to unforeseen events. The integration of edge computing capabilities will allow for faster processing of sensor data, enabling quicker and more accurate responses to dynamic environments. This reduction in latency is critical for safe and efficient operation, especially in high-traffic urban areas.
Comparison of Autonomous Driving Systems
Several different approaches to autonomous driving systems are being explored for public transit. Some prototypes employ a fully autonomous system where the vehicle operates completely without human intervention. Others use a driver-assistance system, providing support to a human driver but not fully automating the driving task. A third approach is a remotely supervised autonomous system where a human operator monitors and intervenes remotely if necessary. Each approach has its own advantages and disadvantages regarding safety, cost, and operational complexity. Fully autonomous systems offer the highest potential for efficiency and scalability, but they also present the greatest technical challenges. Driver-assistance systems are less ambitious but offer a more readily achievable solution in the near term. Remotely supervised systems offer a compromise, providing a safety net while allowing for a higher degree of autonomy. The optimal approach will likely depend on factors such as the specific application, the level of infrastructure support available, and the regulatory environment.
Hypothetical Scenario: Autonomous Bus Integration
Imagine the city of Austin, Texas, gradually integrating autonomous buses into its existing CapMetro bus system. Initially, a limited number of autonomous buses are deployed on a dedicated, less congested route, such as a route connecting a university campus to a major transit hub. These buses operate during off-peak hours, allowing for initial testing and data collection in a relatively controlled environment. Sensors and AI algorithms are constantly refined based on real-world operational data. As confidence in the system grows, the number of autonomous buses is gradually increased, and the routes are expanded to include more challenging urban environments. CapMetro incorporates a robust monitoring system, allowing human operators to remotely supervise the autonomous buses and intervene if necessary. Over time, the autonomous bus system becomes fully integrated into the CapMetro network, offering a more efficient, reliable, and accessible public transportation option for Austin residents. This phased approach minimizes disruption while maximizing safety and data collection to inform future improvements and expansion.
Infrastructure Requirements for Smart Transportation
The transition to widespread autonomous public transit isn’t just about self-driving vehicles; it’s a complete overhaul of our urban infrastructure. We need systems that can seamlessly integrate these vehicles into existing networks, ensuring safety, efficiency, and a positive user experience. This means far more than just adding some sensors – it requires a fundamental rethink of how our cities are designed and managed.
Smart City Initiatives and Autonomous Vehicle Adoption
Smart city initiatives are crucial for facilitating the adoption of autonomous vehicles. These initiatives often involve the implementation of advanced sensor networks, data analytics platforms, and intelligent traffic management systems. For example, cities like Singapore and Amsterdam are already investing heavily in 5G networks and connected infrastructure, providing the necessary bandwidth and communication capabilities for autonomous vehicles to operate safely and efficiently. The data collected from these networks can be used to optimize traffic flow, predict potential issues, and improve the overall efficiency of the transportation system. This data-driven approach is essential for managing the complexities of autonomous vehicle operations in a dynamic urban environment. Without robust smart city infrastructure, the potential benefits of autonomous public transit will be severely limited.
Adapting Road Networks and Traffic Management Systems
Adapting existing road networks and traffic management systems for autonomous vehicles presents significant challenges. Current infrastructure is primarily designed for human-driven vehicles, with a focus on intuitive navigation and driver reaction time. Autonomous vehicles require more precise infrastructure, including highly accurate mapping, dedicated lanes, and improved communication systems. For instance, clear road markings and standardized signage are essential for autonomous vehicles to accurately perceive their surroundings. Furthermore, traffic signals and road designs need to be adapted to accommodate the unique operational characteristics of autonomous vehicles, such as their ability to communicate with each other and with traffic management systems. The transition requires careful planning and significant investment to ensure the safe and efficient integration of autonomous vehicles into existing traffic flows. Retrofitting existing infrastructure will be a considerable undertaking, demanding a phased approach and careful consideration of cost-effectiveness.
Infrastructure Needs Comparison: Autonomous Buses, Trams, and Trains
The infrastructure needs for different types of autonomous public transit vary significantly. While autonomous buses require relatively minor modifications to existing road networks, autonomous trams and trains necessitate more substantial infrastructure upgrades.
| Feature | Autonomous Bus | Autonomous Tram | Autonomous Train |
|---|---|---|---|
| Road/Track Infrastructure | Minor modifications to existing roads; potential need for dedicated bus lanes | Requires dedicated tram lines, often with upgraded power and signaling systems | Requires dedicated rail lines, including signaling, electrification, and potentially track upgrades |
| Communication Systems | Vehicle-to-infrastructure (V2I) communication for traffic signal interaction; potential need for 5G or similar high-bandwidth networks | V2I communication crucial for safe operation within the tram network; potentially integrated with broader city-wide communication systems | Sophisticated communication systems for train control and safety; often relying on dedicated signaling and communication networks |
| Power Supply | Internal combustion engine, electric battery, or hybrid systems | Typically electric, requiring overhead lines or on-board power storage | Typically electric, relying on overhead lines or third rail systems |
| Safety Systems | Redundant sensor systems, emergency braking, and fail-safe mechanisms | Similar to buses, but with additional safety systems to manage interactions with other trams and pedestrians | Highly sophisticated safety systems, including automatic train protection (ATP) and train control management (TCM) systems |
Economic and Social Impacts of Autonomous Public Transit

Source: medium.com
Self-driving buses and AI-powered traffic systems promise a smoother, greener commute, but this futuristic vision hinges on vast data collection. The very convenience offered by smart transportation raises crucial questions about privacy, as detailed in this insightful article on The Impact of Technology on Personal Data Protection. Successfully navigating this data landscape is key to unlocking the true potential of autonomous public transit and ensuring a future that’s both efficient and respects individual rights.
The shift towards autonomous public transit promises a radical reshaping of our cities and economies. While the technological hurdles are significant, the potential economic and social consequences are even more profound, presenting both incredible opportunities and significant challenges that we need to address proactively. This section explores the multifaceted impacts of this transformative technology.
Reduced Labor Costs and Increased Efficiency
Autonomous vehicles, by their nature, eliminate the need for human drivers. This translates directly into substantial cost savings for public transit systems. The expense of salaries, benefits, and training for drivers represents a significant portion of operating budgets. Automated systems, while requiring initial investment in technology and maintenance, can offer long-term cost reductions, potentially freeing up resources for infrastructure improvements or service expansion. Furthermore, optimized routing and scheduling algorithms inherent in autonomous systems promise increased efficiency, leading to reduced fuel consumption and improved overall operational effectiveness. For example, a city like San Francisco, with its complex traffic patterns, could see significant improvements in transit times and reduced congestion with the implementation of a well-integrated autonomous bus network. This translates to both economic benefits and improved quality of life for citizens.
Job Displacement in the Transportation Sector
The automation of public transit inevitably raises concerns about job displacement. Millions of people globally are employed as public transit drivers, and the transition to autonomous systems will undoubtedly lead to job losses in this sector. While some argue that new jobs will emerge in the areas of vehicle maintenance, software development, and system management, the nature and number of these new roles may not fully offset the job losses in driving. This necessitates proactive strategies for retraining and upskilling displaced workers, ensuring a just transition for those affected. Initiatives focusing on providing educational opportunities and supporting the creation of new, related employment sectors are crucial to mitigate the negative social and economic consequences of automation.
Improved Accessibility for Individuals with Disabilities
Autonomous public transit holds the potential to significantly enhance accessibility for individuals with disabilities. Self-driving vehicles can be designed with features specifically catering to the needs of people with mobility limitations, visual impairments, or cognitive challenges. For instance, features like automated ramps, clear audio announcements, and intuitive interfaces can greatly improve the ease and safety of public transit usage for this population. Furthermore, the ability to schedule and book rides through accessible apps removes the reliance on physical assistance for some users, promoting greater independence and inclusion. This contrasts sharply with traditional public transit systems, which often struggle to meet the specific needs of disabled individuals.
Societal Changes Resulting from Widespread Adoption
The widespread adoption of autonomous public transit will lead to a series of significant societal changes. Reduced traffic congestion, for example, can lead to less stress, improved air quality, and increased productivity as commute times decrease. Changes in urban planning are also likely, as the reliance on personal vehicles could diminish, freeing up valuable urban space for pedestrian areas, parks, or other community amenities. However, concerns regarding data privacy, cybersecurity vulnerabilities, and the potential for algorithmic bias need careful consideration. Ensuring equitable access to autonomous transit systems across different socioeconomic groups is also crucial to avoid exacerbating existing inequalities. The transition will require careful planning and public engagement to ensure a positive and inclusive outcome for all members of society.
Safety and Security Considerations

Source: paultan.org
The transition to autonomous public transit promises a revolution in urban mobility, but this exciting future hinges critically on addressing safety and security concerns. While the technology holds immense potential, the inherent complexities of operating driverless vehicles in dynamic urban environments necessitate robust safety protocols and rigorous security measures. Failure to adequately address these issues could severely hamper public acceptance and the successful implementation of autonomous transit systems.
Autonomous vehicles, unlike human drivers, lack the adaptability and intuitive decision-making skills honed through years of experience. This necessitates a multifaceted approach to safety, encompassing both technological safeguards and comprehensive regulatory frameworks. The potential for accidents, both from technical malfunctions and external factors, necessitates proactive mitigation strategies to build public trust and ensure the safe and reliable operation of these systems.
Potential Safety Risks in Autonomous Public Transit
Autonomous vehicles, despite their advanced technology, are not immune to malfunctions. Software glitches, sensor failures, and unexpected environmental conditions (like heavy snow or fog) can all compromise the vehicle’s ability to navigate safely. Furthermore, the interaction between autonomous vehicles and other road users (pedestrians, cyclists, and human-driven vehicles) presents unique challenges. Unpredictable human behavior can lead to accidents, requiring the autonomous system to react swiftly and accurately in complex situations. For example, a sudden lane change by a human driver could necessitate an immediate and precise response from the autonomous vehicle to avoid a collision. The potential for accidents involving pedestrians, especially children or the elderly, also necessitates careful consideration of safety protocols and system design.
Safety Protocols and Regulations for Autonomous Public Transit
Mitigating the risks associated with autonomous public transit requires a multi-layered approach. Robust testing and validation procedures are crucial to ensure the reliability and safety of the autonomous driving system. This includes extensive simulations and real-world testing under diverse conditions. Furthermore, stringent regulatory frameworks are essential to establish clear safety standards and operational guidelines. These regulations should cover aspects such as vehicle design, software validation, operational procedures, and emergency response protocols. Regular inspections and maintenance of autonomous vehicles are also critical to prevent malfunctions and ensure continued safe operation. Finally, a comprehensive data recording and analysis system allows for the identification of potential safety issues and the continuous improvement of the system’s safety performance. The establishment of clear liability frameworks in case of accidents is also crucial for public confidence and legal clarity.
Cybersecurity in Autonomous Vehicles
The reliance on sophisticated software and interconnected systems in autonomous vehicles makes them vulnerable to cyberattacks. Hackers could potentially gain control of the vehicle’s systems, leading to serious safety risks. Protecting against such attacks requires robust cybersecurity measures, including secure software development practices, encryption of data communication, and intrusion detection systems. Regular security audits and penetration testing are essential to identify and address vulnerabilities. Furthermore, collaboration between manufacturers, cybersecurity experts, and regulatory bodies is crucial to establish industry-wide security standards and best practices. The potential for large-scale disruption or even malicious attacks highlights the critical need for proactive cybersecurity measures. For example, a successful cyberattack could potentially lead to a large-scale disruption of the autonomous transit system, causing significant inconvenience and potential safety hazards.
Measures to Ensure Passenger Safety and Security
Ensuring passenger safety and security within autonomous public transit vehicles requires a comprehensive approach.
- Redundant safety systems: Multiple backup systems should be in place to ensure safe operation even in case of component failure.
- Emergency communication systems: Passengers should have easy access to emergency communication systems to contact operators or emergency services.
- Interior safety features: Features such as seatbelts, airbags, and reinforced passenger compartments should be incorporated to minimize injury in the event of an accident.
- Real-time monitoring: Remote monitoring of vehicle status and passenger safety should be implemented to enable timely intervention in case of emergencies.
- Passenger information systems: Clear and informative displays should provide passengers with real-time updates on the vehicle’s status and journey progress.
- Accessible design: The vehicles should be designed to be accessible to passengers with disabilities, ensuring their safety and comfort.
- Driverless vehicle emergency stops: Clearly visible and easily accessible emergency stop buttons should be provided within the passenger compartment.
Public Perception and Acceptance
Public perception and acceptance are paramount to the successful implementation of autonomous public transit. Without widespread buy-in from the public, even the most technologically advanced system will struggle to gain traction. This section explores the factors influencing public opinion and strategies for building trust and addressing concerns.
Public opinion surveys consistently reveal a mixed bag when it comes to autonomous vehicles. While many appreciate the potential benefits like increased efficiency and safety, significant anxieties remain surrounding reliability, safety in unforeseen circumstances, and job displacement for human drivers. Overcoming these concerns is crucial for widespread adoption.
Strategies to Build Public Trust and Address Safety Concerns
Building public trust requires a multi-pronged approach. Transparency is key; the public needs to understand how these systems work, the safety protocols in place, and the rigorous testing procedures undertaken before deployment. This includes open communication about potential limitations and how these are being addressed. Furthermore, demonstrating a commitment to safety through independent audits and public release of safety data will significantly boost confidence. Addressing the concerns about job displacement requires proactive measures like retraining programs for affected workers and highlighting the creation of new job opportunities within the autonomous vehicle industry. Pilot programs in controlled environments, allowing the public to experience the technology firsthand, can help alleviate fears and foster familiarity. Finally, engaging with community leaders and addressing specific concerns raised by local populations is vital for fostering trust at a grassroots level.
A Hypothetical Public Outreach Campaign
A successful public outreach campaign would leverage various channels to reach diverse demographics. This could involve:
- Interactive Exhibits and Demonstrations: Setting up interactive displays at public events, shopping malls, and community centers to allow people to experience simulations and interact with autonomous vehicle technology in a safe and controlled setting.
- Targeted Social Media Campaigns: Utilizing social media platforms to disseminate informative content, address public concerns, and engage in conversations with potential users. This includes short, engaging videos showcasing the benefits of the technology.
- Public Forums and Town Hall Meetings: Hosting public forums and town hall meetings to engage directly with the community, answer questions, and address concerns transparently.
- Partnerships with Community Organizations: Collaborating with community organizations and leaders to build trust and ensure that the benefits of autonomous public transit are accessible to all segments of the population.
- Educational Programs in Schools and Universities: Introducing the concept of autonomous vehicles and their societal impact into educational curricula to foster a positive perception among younger generations.
Infographic: Benefits of Autonomous Public Transit
Imagine an infographic with a clean, modern design. The title, “The Future is Riding with Us: Autonomous Public Transit,” is prominently displayed. The infographic would use a combination of icons, charts, and concise text to illustrate key benefits. One section, using a stylized bus icon, would highlight “Increased Efficiency,” with a bar graph comparing the passenger capacity and speed of autonomous buses versus traditional buses. Another section, featuring a leaf icon, would show “Reduced Emissions,” using a pie chart to illustrate the reduction in greenhouse gas emissions compared to traditional vehicles. A third section, with an accessibility symbol, would depict “Improved Accessibility,” showing icons representing elderly individuals, people with disabilities, and families with strollers, emphasizing ease of use and access for all. Finally, a small map showing a network of efficient autonomous bus routes would illustrate the improved connectivity and coverage. The overall color scheme would be bright and optimistic, using calming blues and greens to represent sustainability and technological advancement. The infographic would conclude with a call to action, encouraging readers to learn more about the initiative. The visual representation would clearly and concisely communicate the significant advantages of autonomous public transit.
Integration with Other Transportation Modes: The Future Of Smart Transportation And Autonomous Public Transit
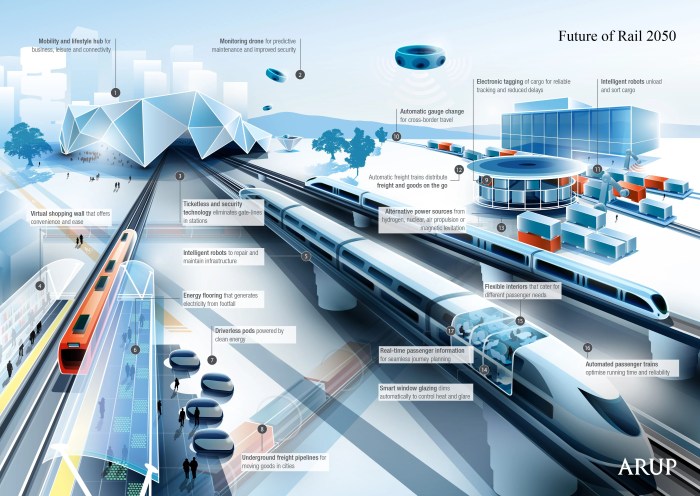
Source: interestingengineering.com
The future of smart transportation isn’t just about autonomous buses; it’s about a seamless, integrated network where different modes work together harmoniously. Imagine a world where your journey, from your doorstep to your destination, is effortlessly orchestrated, blending the convenience of autonomous vehicles with the flexibility of other options. This requires careful planning and sophisticated coordination between various transportation systems.
Autonomous public transit’s success hinges on its ability to seamlessly integrate with existing transportation networks. This integration isn’t just about physical connectivity, but also about data sharing and coordinated scheduling to optimize the overall travel experience. Failing to achieve this integration would limit the potential benefits of autonomous vehicles, leaving them as isolated islands in a larger, fragmented transportation landscape.
Autonomous Vehicles and Ride-Sharing Services
Ride-sharing services, like Uber and Lyft, have revolutionized personal transportation. Integrating autonomous public transit with these services presents exciting possibilities. Autonomous buses could act as feeders, transporting passengers to and from central hubs where they can connect to ride-sharing vehicles for the final leg of their journey. This hybrid approach could address the “last-mile problem,” a common challenge in public transportation where reaching final destinations from transit stops can be difficult. For example, a passenger could take an autonomous bus to a major transportation hub, then seamlessly transfer to a ride-sharing vehicle to reach their specific address, all managed through a single, integrated app. This system would provide both the efficiency of public transit and the personalized convenience of ride-hailing services.
Autonomous Vehicles and Bike-Sharing Programs
The integration of autonomous public transit with bike-sharing programs offers a compelling combination of speed and flexibility for shorter distances. Autonomous buses could serve as efficient connectors between residential areas and bike-sharing stations, enabling passengers to combine the speed of bus travel with the convenience and health benefits of cycling for shorter commutes. For instance, a commuter might take an autonomous bus to a centrally located bike-sharing station, then cycle the final kilometer to their office. This multimodal approach could alleviate traffic congestion in city centers and promote a healthier lifestyle. The system could be further enhanced by real-time information sharing, indicating the availability of bikes at nearby stations and integrating the cost of the bus and bike ride into a single fare.
Real-Time Information Sharing and Coordination
A successful multimodal transportation system relies on real-time data sharing and coordination. Imagine a centralized platform that tracks the location and availability of autonomous buses, ride-sharing vehicles, and bikes in real-time. This platform would use sophisticated algorithms to optimize routes, predict delays, and provide passengers with the most efficient and convenient travel options. The system could dynamically adjust routes and schedules based on real-time demand and traffic conditions, ensuring that passengers always have access to the best available transportation mode. This would require a robust communication infrastructure capable of handling large volumes of data and providing seamless integration between different transportation providers.
Examples of Successful Multimodal Transportation Systems
Several cities have already implemented successful multimodal transportation systems. Singapore, for instance, boasts an extensive and well-integrated public transportation network that includes buses, trains, and taxis. The integration of autonomous vehicles could further enhance this system by improving efficiency, reducing congestion, and expanding access to underserved areas. Similarly, cities like Amsterdam have invested heavily in cycling infrastructure, creating a network of bike paths and lanes that complement their public transportation system. The addition of autonomous feeder buses could further enhance this model, providing convenient access to the city’s extensive bike-sharing network. These existing systems provide a strong foundation upon which to build future multimodal transportation networks that incorporate autonomous vehicles.
Final Review
The future of transportation is autonomous, smart, and undeniably exciting. While challenges remain – from infrastructure upgrades to public acceptance – the potential benefits are too significant to ignore. Autonomous public transit promises increased efficiency, reduced emissions, improved accessibility, and a more sustainable urban landscape. By addressing safety concerns and fostering public trust, we can unlock a future where getting around is easier, greener, and more equitable for everyone. The journey to this future will require collaboration, innovation, and a willingness to embrace change, but the destination is worth the ride.
