How Blockchain Can Improve Transparency in Supply Chains? Forget murky origins and shady dealings. Imagine a world where every step of your coffee bean’s journey, from farm to cup, is crystal clear, instantly verifiable, and tamper-proof. That’s the promise of blockchain technology, revolutionizing supply chains with unprecedented transparency and trust. This isn’t just about tracking goods; it’s about building a more ethical, efficient, and accountable global marketplace.
Blockchain’s decentralized, immutable ledger provides a secure record of every transaction and movement within a supply chain. This means enhanced traceability, preventing counterfeiting, and streamlining processes. From reducing food waste to combating human trafficking, the potential benefits are vast and far-reaching. Let’s dive into how this groundbreaking technology is transforming the way we move goods across the globe.
Introduction
Blockchain technology and supply chain transparency are two seemingly disparate concepts that are rapidly converging to revolutionize how goods move around the globe. Imagine a world where you can trace your coffee beans from the farm in Colombia to your local cafe, verifying every step of the journey with complete certainty. That’s the promise of blockchain in supply chains. This introduction will explore the fundamentals of blockchain and its potential to bring unprecedented transparency to often opaque supply chains.
Blockchain’s core principle lies in its decentralized and immutable ledger. Think of it as a shared, digital record book replicated across many computers. Each transaction or “block” is cryptographically linked to the previous one, creating an unbroken chain. This makes it incredibly difficult to alter or delete information once it’s recorded, ensuring data integrity. This is achieved through cryptographic hashing and consensus mechanisms, making the system highly secure and transparent.
Supply chain transparency, on the other hand, refers to the ability to track and trace goods throughout their journey from origin to consumer. This includes information about materials sourcing, manufacturing processes, transportation, and distribution. A transparent supply chain is crucial for building consumer trust, ensuring product quality and safety, and enhancing ethical sourcing practices.
Supply Chain Opacity Issues
Current supply chains often suffer from a lack of visibility. Consider the complexities involved in tracking a garment from its raw cotton source to the retail store. Multiple intermediaries, differing record-keeping systems, and a lack of standardized data formats create significant challenges in tracing the product’s journey. This opacity allows for issues like unethical labor practices, counterfeit goods, and inefficient logistics to thrive. For example, the fashion industry often struggles with identifying and eliminating sweatshops from their supply chains, due to a lack of visibility into their complex global networks. Similarly, the food industry faces challenges in tracing the origin of ingredients and detecting outbreaks of foodborne illnesses because of inadequate tracking and tracing systems.
Blockchain’s Solution to Supply Chain Opacity
Blockchain technology offers a powerful solution to these problems. By recording every transaction and movement of goods on a shared, immutable ledger, blockchain creates an auditable trail of the entire supply chain. This means that all participants – from farmers and manufacturers to distributors and retailers – can access and verify the same information. This shared visibility fosters greater accountability, allowing businesses to identify and address inefficiencies and ethical concerns more effectively. For example, a coffee roaster could use blockchain to verify that their beans were ethically sourced and grown using sustainable practices, providing transparency to consumers and enhancing brand reputation. Similarly, a pharmaceutical company could leverage blockchain to track the movement of drugs from manufacturing to distribution, combating counterfeiting and ensuring product authenticity. The increased traceability also enables quicker identification and response to product recalls or contamination incidents.
Tracking Goods and Materials with Blockchain
Blockchain technology offers a revolutionary approach to supply chain transparency, enabling the secure and verifiable tracking of goods and materials throughout their journey from origin to consumer. This enhanced visibility fosters trust, accountability, and efficiency across the entire supply chain ecosystem. By recording each transaction on an immutable ledger, blockchain eliminates the potential for manipulation and provides a single source of truth for all stakeholders.
Methods for Tracking Goods Using Blockchain
Several methods leverage blockchain to track goods. These methods typically involve assigning a unique identifier, such as a QR code or RFID tag, to each item. This identifier is then linked to a blockchain record containing detailed information about the product’s journey. The information is updated at each stage of the supply chain, creating a comprehensive and auditable history. Some systems use IoT sensors to automatically record data points, further streamlining the process. Other systems rely on manual data entry at various checkpoints. The choice of method often depends on factors like the type of product, the complexity of the supply chain, and the budget available.
Private vs. Public Blockchains for Supply Chain Tracking
The choice between private and public blockchains for supply chain tracking depends on the specific needs and priorities of the organization. Private blockchains offer greater control and security, as access is restricted to authorized participants. This is ideal for sensitive information or when confidentiality is paramount. However, private blockchains may lack the transparency and decentralization of public blockchains. Public blockchains, on the other hand, offer greater transparency and immutability, but they can be more complex to manage and may present security challenges. Many companies opt for permissioned blockchains, which combine elements of both private and public networks, allowing for controlled access while maintaining a degree of transparency. For example, a large retailer might use a permissioned blockchain to share information with its key suppliers while keeping sensitive internal data private.
Hypothetical Blockchain-Based Tracking System for Coffee Beans
Let’s imagine a blockchain-based tracking system for coffee beans from farm to cup. Each bag of coffee beans receives a unique QR code linked to a blockchain record at the farm. This record includes details such as the farm’s location, the date of harvest, the variety of bean, and the farmer’s name. As the beans move through the supply chain – processing, roasting, packaging, and distribution – each stage is recorded on the blockchain, updating the record with relevant information like processing dates, location, and quality control checks. The final consumer can scan the QR code on the bag to access the complete history of the beans, verifying their origin and ensuring authenticity. This enhanced transparency builds trust with consumers who are increasingly interested in the ethical and sustainable sourcing of their products. Companies like Nestle have already started exploring similar blockchain initiatives to enhance traceability and transparency within their supply chains.
Data Points Recorded at Each Stage of the Coffee Bean Supply Chain
| Stage | Location | Date | Quality Control Metrics |
|---|---|---|---|
| Farm | Specific Farm Coordinates (e.g., Latitude/Longitude) | Harvest Date | Bean Variety, Moisture Content, Weight |
| Processing Plant | Plant Location | Processing Date | Moisture Content After Processing, Defect Rate |
| Roasting Facility | Roasting Facility Location | Roasting Date | Roast Level, Weight After Roasting |
| Distribution Center | Distribution Center Location | Shipping Date | Packaging Details, Lot Number |
Enhancing Traceability and Authenticity
Blockchain technology revolutionizes supply chain transparency by offering an immutable record of a product’s journey, from origin to consumer. This enhanced traceability and verifiable authenticity combats counterfeiting and builds consumer trust, leading to significant benefits for businesses and consumers alike. This enhanced level of transparency fosters accountability and allows for quicker identification and resolution of issues throughout the supply chain.
Blockchain’s decentralized and cryptographically secured nature ensures the integrity of data. Each transaction, representing a step in the product’s lifecycle, is recorded as a block and linked to the previous block, creating an unalterable chain. This means that any attempt to tamper with the information is easily detectable. This unique characteristic empowers businesses to track products with unprecedented accuracy and verify their authenticity with high confidence.
Blockchain’s Role in Product Traceability
Blockchain dramatically improves product traceability by providing a detailed and verifiable history of a product’s journey. Every stage of the supply chain, from raw material sourcing to manufacturing, processing, distribution, and finally retail sale, is recorded on the blockchain. This granular level of detail allows businesses to pinpoint the exact location and time of any event in the product’s lifecycle. This level of traceability is crucial for responding to product recalls efficiently and effectively, minimizing potential damage to brand reputation and consumer safety. For example, if a batch of contaminated food is identified, blockchain allows for rapid identification of the affected products and their distribution path, enabling swift recall and minimizing potential health risks.
Blockchain’s Role in Verifying Product Authenticity and Preventing Counterfeiting
The immutable nature of blockchain data provides a powerful tool against counterfeiting. By assigning unique digital identifiers to products, manufacturers can create a verifiable chain of custody that is virtually impossible to forge. Consumers can use these identifiers to verify the authenticity of their purchases, ensuring they are not buying counterfeit goods. This increased transparency and accountability deters counterfeiters and protects both businesses and consumers from fraudulent products. The technology offers a high degree of security, as altering information on the blockchain would require compromising the entire network, a task that is computationally infeasible.
Examples of Industries Benefiting from Blockchain-Based Traceability and Authenticity Verification
Several industries are already leveraging blockchain to enhance transparency and combat counterfeiting. The luxury goods industry, for example, uses blockchain to verify the authenticity of high-end products, preventing the sale of counterfeit items. The pharmaceutical industry employs blockchain to track medications throughout their supply chain, ensuring their integrity and preventing the distribution of counterfeit drugs. The food industry is using blockchain to improve traceability and transparency, allowing consumers to trace the origin of their food products and verify their quality. Similarly, the automotive industry uses blockchain to track the supply of components, ensuring that the parts used in vehicles are authentic and meet quality standards.
Case Study: Reducing Counterfeiting in the Pharmaceutical Industry
The pharmaceutical industry faces a significant challenge with counterfeit drugs. These fake medications can be ineffective, contain harmful substances, or be improperly packaged, posing serious risks to public health. One company, using a blockchain-based system, implemented a solution that assigns unique digital identifiers to each drug package. This identifier is linked to a record on the blockchain, containing information about the drug’s manufacturing, distribution, and sale. Pharmacies and consumers can scan the identifier to verify the drug’s authenticity, ensuring that they are receiving a genuine product. This system has proven effective in reducing counterfeiting and increasing consumer confidence in the safety and efficacy of their medications. The system’s success is demonstrable through a significant reduction in reported counterfeit drugs in the regions where it’s implemented, quantified by a decrease in reported adverse events related to counterfeit medications.
Improving Data Security and Integrity
Traditional supply chains often rely on paper-based systems and disparate databases, creating significant vulnerabilities. Data is easily lost, misplaced, or altered, leading to inefficiencies and potentially fraudulent activities. Blockchain technology, however, offers a revolutionary approach to securing and verifying data within supply chains, ensuring greater transparency and accountability.
Blockchain’s cryptographic features significantly enhance data security and integrity. Unlike centralized databases, blockchain uses decentralized, distributed ledger technology, meaning data is not stored in a single location vulnerable to hacking or manipulation. Instead, each transaction is recorded as a “block” and linked cryptographically to the previous block, creating a permanent, tamper-evident chain.
Blockchain’s Cryptographic Security Mechanisms
Blockchain leverages cryptography to ensure data integrity and prevent unauthorized modifications. Each block contains a cryptographic hash—a unique digital fingerprint—of the previous block’s data. Any alteration to the data within a block would change its hash, immediately making the alteration detectable. This chain of hashes creates a highly secure and auditable record of all transactions. Furthermore, the use of digital signatures verifies the authenticity of each transaction, confirming the identity of participants and preventing unauthorized additions or deletions. This makes altering information incredibly difficult and instantly detectable, significantly reducing the risk of fraud and data breaches.
Data Integrity and Tamper-Proofing
Blockchain’s immutable nature is key to its ability to ensure data integrity. Once a block is added to the chain, it cannot be altered or deleted. This characteristic prevents tampering and ensures that the data remains accurate and consistent throughout the supply chain. This contrasts sharply with traditional systems where data can be easily manipulated or overwritten, potentially leading to inaccurate records and disputes. For example, a food producer could use blockchain to record the origin, processing, and transportation of its products, guaranteeing the authenticity and quality of its goods. Any attempt to alter this information would be immediately visible to all participants in the network.
Data Flow and Security Measures in a Blockchain-Based Supply Chain
Imagine a flowchart depicting the movement of goods and data through a blockchain-based supply chain. The process begins with the origin of a product (e.g., a farm). Each step in the supply chain—harvesting, processing, packaging, transportation, and retail—is recorded as a transaction on the blockchain. Each transaction includes relevant data, such as location, date, time, and product details. These transactions are then cryptographically hashed and added to a new block. This block is verified by multiple nodes in the network, ensuring its authenticity and integrity. Once verified, the block is added to the blockchain, creating a permanent and auditable record. The cryptographic hashes linking each block ensure that any tampering would be immediately detectable. Access control mechanisms, such as private keys, further secure the network and prevent unauthorized access or modifications. This creates a highly secure and transparent system, where all participants have access to verifiable data about the product’s journey.
Streamlining Supply Chain Processes
Blockchain technology offers a powerful solution to the age-old problem of inefficient supply chain management. By creating a shared, immutable ledger, it dramatically simplifies processes, reduces delays, and ultimately lowers costs. This transparency and efficiency ripple through every stage, from procurement to final delivery and payment.
Blockchain’s impact on supply chain streamlining is multifaceted, impacting procurement, logistics, and payment systems in significant ways. Its decentralized nature eliminates the need for intermediaries in many cases, fostering direct communication and collaboration between stakeholders. This leads to faster transaction times and improved overall efficiency.
Procurement Processes
Blockchain can revolutionize procurement by automating and simplifying the process of sourcing, ordering, and tracking goods. Smart contracts, self-executing agreements written into the blockchain, can automatically trigger payments upon delivery verification, eliminating lengthy invoice processing and disputes. For example, a manufacturer could program a smart contract to automatically release payment to a supplier once a shipment is confirmed as received and inspected, based on data recorded on the blockchain. This eliminates the need for manual verification and reconciliation, reducing processing time and costs.
Logistics and Tracking
Real-time tracking of goods and materials throughout the supply chain is another key benefit. Blockchain provides a single source of truth, eliminating discrepancies and ensuring all parties have access to the same information. This improved visibility allows for proactive management of potential delays or disruptions. Imagine a scenario where a shipment is delayed due to unforeseen circumstances. With blockchain, all stakeholders are immediately notified, allowing for rapid adjustments to mitigate the impact. This proactive approach minimizes disruptions and keeps the supply chain running smoothly. Walmart, for instance, has successfully leveraged blockchain to track its food supply chain, significantly improving efficiency and traceability.
Payment Systems, How Blockchain Can Improve Transparency in Supply Chains
Traditional payment methods in supply chains often involve multiple intermediaries, leading to delays and increased costs. Blockchain-based payment systems, however, offer a faster, more secure, and more transparent alternative. Smart contracts can automate payments upon the fulfillment of certain conditions, such as delivery confirmation or quality inspection. This reduces the risk of fraud and eliminates the need for manual reconciliation. Furthermore, cryptocurrencies can facilitate cross-border payments with lower transaction fees and faster processing times compared to traditional banking systems. This is particularly beneficial for global supply chains.
Cost Savings
The cost savings associated with blockchain implementation in supply chain management are substantial. By reducing delays, minimizing errors, and automating processes, companies can significantly lower their operational costs. The elimination of intermediaries, such as banks and clearing houses, further reduces transaction fees. Studies have shown that blockchain can reduce supply chain costs by up to 15%, depending on the specific implementation and industry. These savings are realized through reduced labor costs, faster processing times, and minimized disputes. The improved efficiency and transparency also contribute to reduced waste and inventory management costs. For example, a company could save millions of dollars annually by streamlining its payment processes and reducing inventory holding costs through improved visibility and tracking.
Addressing Challenges and Limitations
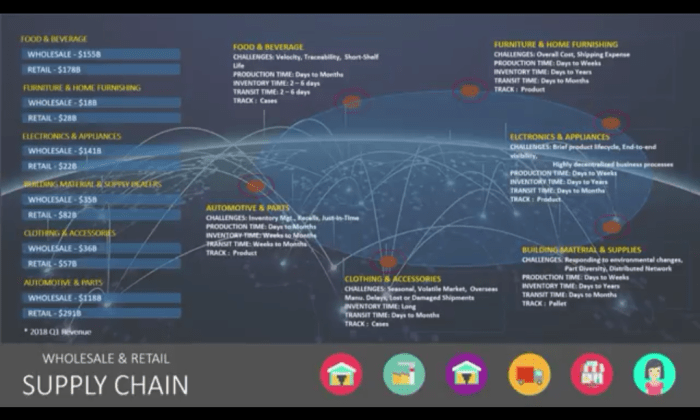
Source: smashoid.com
Blockchain’s ability to track goods from origin to consumer boosts supply chain transparency, ensuring ethical sourcing and reducing fraud. This increased visibility is further amplified by advancements in logistics, such as the changes brought about by autonomous vehicles, as discussed in this insightful article: How Autonomous Vehicles Will Change the Transportation Landscape. Ultimately, the seamless integration of these technologies promises even greater accountability and efficiency within global supply chains.
Implementing blockchain technology in supply chains, while offering transformative potential, isn’t without its hurdles. Several key challenges need careful consideration to ensure successful and widespread adoption. Overcoming these obstacles requires a collaborative effort from across the industry, fostering standardization and a shared understanding of the technology’s capabilities and limitations.
Scalability, interoperability, and regulatory uncertainty are significant barriers to entry. The complexity of integrating blockchain into existing, often legacy, supply chain systems presents another layer of difficulty. Understanding these limitations is crucial for developing effective strategies for mitigating risks and maximizing the benefits of this innovative technology.
Scalability and Performance Issues
Blockchain’s inherent limitations in processing large volumes of data quickly can pose a significant challenge for large-scale supply chains. Processing every transaction on a public blockchain can be slow and expensive, especially when dealing with the vast amounts of data generated by global supply chains. For example, a large retailer managing millions of products across numerous suppliers might find the transaction speeds of some blockchain networks insufficient for real-time tracking and updates. This necessitates exploring solutions such as private or permissioned blockchains, which offer better control and scalability but may sacrifice some of the decentralization benefits of public blockchains. Furthermore, innovative approaches like sharding and layer-2 scaling solutions are actively being developed to address these performance bottlenecks.
Interoperability and Data Standardization
Different blockchain platforms often lack the ability to seamlessly communicate and share data with each other. This interoperability challenge prevents businesses using different blockchain solutions from effectively collaborating. Imagine a scenario where a manufacturer uses one blockchain platform for tracking raw materials, while a distributor uses another for managing finished goods. Without interoperability, these two systems cannot easily exchange information, hindering the overall transparency and efficiency of the supply chain. The lack of standardized data formats also complicates the process, as each company might use different data structures and protocols. This necessitates the development of common standards and protocols to enable seamless data exchange across different blockchain networks and systems.
Regulatory Hurdles and Legal Frameworks
The nascent nature of blockchain technology means that regulatory frameworks are still evolving. The lack of clear legal guidelines and regulations surrounding data ownership, privacy, and liability in blockchain-based supply chains creates uncertainty for businesses. For instance, questions regarding data security, compliance with existing data protection laws (like GDPR), and the legal enforceability of smart contracts on a blockchain remain largely unanswered in many jurisdictions. This necessitates collaborative efforts between industry stakeholders and regulatory bodies to develop clear and consistent legal frameworks that foster innovation while ensuring compliance and protecting consumer rights.
Impact on Different Stakeholders
The successful implementation of blockchain technology in supply chains will impact various stakeholders differently. Suppliers may benefit from improved transparency and traceability, leading to enhanced trust and potentially higher efficiency. Manufacturers could gain better control over their supply chains and reduce risks associated with counterfeit products or unethical sourcing practices. Retailers can enhance consumer trust and brand reputation by providing greater transparency into the origin and journey of their products. Consumers, in turn, may benefit from increased confidence in the authenticity and sustainability of the products they purchase. However, smaller businesses might face challenges in adopting blockchain due to its complexity and associated costs. Therefore, strategies are needed to ensure equitable access and benefits for all stakeholders.
Mitigation Strategies
Addressing the challenges of blockchain implementation requires a multi-faceted approach. This includes investing in research and development to improve scalability and interoperability, actively participating in the development of industry standards and best practices, and engaging with regulatory bodies to create clear and supportive legal frameworks. Collaboration among businesses, technology providers, and regulatory authorities is paramount. Education and training programs are also essential to equip businesses with the knowledge and skills needed to effectively implement and manage blockchain solutions in their supply chains. Furthermore, pilot projects and phased implementation strategies can help organizations assess the feasibility and benefits of blockchain before committing to large-scale deployment. This gradual approach can mitigate risks and ensure a smoother transition to a blockchain-enabled supply chain.
Future Trends and Applications
Blockchain’s impact on supply chain transparency is just beginning. As the technology matures and adoption increases, we can expect even more innovative applications and a profound reshaping of how goods move around the world. This section explores the exciting future of blockchain in supply chain management, highlighting key trends and showcasing potential societal and environmental benefits.
The evolution of blockchain technology itself, coupled with increasing industry acceptance, is paving the way for a more efficient, secure, and transparent global supply chain. We’re moving beyond simple tracking to sophisticated systems that leverage AI, IoT, and other technologies to create truly transformative solutions.
Integration with Other Technologies
The true power of blockchain in supply chain management will be unlocked through its seamless integration with other cutting-edge technologies. Imagine a system where IoT sensors constantly monitor product conditions throughout the journey, automatically recording data onto a shared, immutable blockchain ledger. This data could be analyzed using AI to predict potential disruptions, optimize logistics, and even improve product design based on real-world usage patterns. For example, a smart refrigerator could automatically record its temperature and alert the supply chain if a shipment of perishable goods is at risk. This integrated approach will provide unprecedented levels of real-time visibility and control.
Enhanced Traceability and Product Lifecycle Management
Blockchain offers the potential to create a comprehensive digital twin of a product’s journey, from raw material sourcing to end-of-life disposal. This allows for granular traceability, enabling businesses to quickly identify the origin of materials, track production processes, and monitor a product’s entire lifecycle. This level of transparency fosters accountability and allows for proactive intervention in case of product recalls or quality issues. A concrete example is the ability to trace the exact farm and harvest date of coffee beans used in a particular cup of coffee, offering consumers unparalleled transparency and confidence in the product’s origin and quality.
Supply Chain Financing and Insurance
Blockchain’s ability to create secure, transparent records is revolutionizing supply chain financing. By using smart contracts, payments can be automatically triggered upon verification of milestones, reducing delays and improving cash flow for all parties involved. Similarly, blockchain-based insurance solutions can provide real-time risk assessment and automated claims processing, reducing administrative burdens and increasing efficiency. Imagine a scenario where insurance payouts for damaged goods are automatically processed upon verification of damage through blockchain-recorded sensor data, significantly speeding up the claims process.
Societal and Environmental Impacts
Widespread adoption of blockchain in supply chains promises significant societal and environmental benefits. Increased transparency will help combat counterfeiting and fraud, ensuring consumers receive authentic products. Improved traceability allows for better monitoring of ethical labor practices and environmental sustainability throughout the supply chain. Furthermore, optimized logistics and reduced waste contribute to a more environmentally friendly supply chain, minimizing carbon footprint and resource consumption. For instance, a company using blockchain to track its timber sourcing can ensure that its products are sourced from sustainably managed forests, promoting responsible forestry practices and reducing deforestation. This transparency builds consumer trust and supports sustainable business practices.
Final Wrap-Up: How Blockchain Can Improve Transparency In Supply Chains
Source: slidesharecdn.com
The integration of blockchain into supply chains marks a significant leap towards greater transparency and accountability. While challenges remain, the potential benefits – increased efficiency, reduced fraud, and enhanced consumer trust – are undeniable. As the technology matures and adoption grows, we can expect to see even more innovative applications, reshaping global trade and fostering a more ethical and sustainable future. The future of supply chains is transparent, and it’s powered by blockchain.
