The Rise of 5G and Its Impact on Global Connectivity is reshaping our world at breakneck speed. Forget buffering – we’re talking lightning-fast downloads, seamless video calls, and a whole new level of interconnectedness. But 5G isn’t just about faster internet; it’s a catalyst for massive change across industries, from revolutionizing healthcare with remote surgery to transforming manufacturing with hyper-efficient automation. This technological leap isn’t without its challenges, though. Deployment hurdles, privacy concerns, and the digital divide all demand careful consideration as we navigate this exciting, and sometimes daunting, new era.
This deep dive explores the technological advancements powering 5G, its global rollout, its impact on various industries, and the broader societal implications. We’ll also look at future trends and predictions, painting a picture of what a truly hyper-connected world might look like.
Technological Advancements of 5G

Source: mobulous.com
5G’s lightning-fast speeds are revolutionizing global connectivity, paving the way for a whole new level of tech integration. This is especially crucial for the development of autonomous vehicles, which rely on near-instantaneous data transfer for safe navigation; check out this article on How Autonomous Vehicles Will Change the Transportation Landscape to see how. Ultimately, 5G’s impact extends far beyond our phones, shaping the future of transportation and beyond.
5G isn’t just a faster version of 4G; it’s a fundamental leap forward in mobile network technology, promising a world of hyper-connectivity and unprecedented speed. This advancement is driven by several key technological improvements that address the limitations of previous generations, paving the way for a truly transformative digital experience.
The improvements in 5G are significant, offering a considerable boost in speed, reduced latency, and vastly increased capacity compared to its predecessors, 3G and 4G. These improvements are the result of a combination of new technologies and spectrum usage, making 5G a game-changer in various sectors.
Higher Frequency Usage (Millimeter Wave)
5G utilizes higher frequency bands, specifically millimeter wave (mmWave) spectrum, in addition to lower frequency bands. While lower frequencies offer better range, mmWave offers significantly higher bandwidth. This means that mmWave allows for much faster data transmission speeds, perfect for applications demanding high throughput like streaming 8K video or downloading massive files in seconds. However, mmWave signals don’t travel as far and are more easily blocked by obstacles, requiring a denser network of smaller cells to provide widespread coverage. Think of it like this: lower frequencies are like a strong, long-range radio signal, while mmWave is a powerful, but shorter-range laser beam. The combination allows for both broad reach and incredibly fast speeds in targeted areas.
Network Slicing
Network slicing is a key innovation in 5G architecture that allows operators to virtually partition a single network into multiple independent slices. Each slice can be customized to meet the specific needs of different applications or users. For example, one slice might be optimized for high-speed data for consumers, another for low-latency communication for autonomous vehicles, and another for reliable connectivity for industrial IoT devices. This flexibility ensures that different applications receive the precise resources they need, optimizing network performance and efficiency. Imagine a pizza: the whole pizza is the 5G network, and slicing it allows different groups to get the toppings (bandwidth, latency, etc.) they specifically want.
Comparison of 3G, 4G, and 5G Network Performance, The Rise of 5G and Its Impact on Global Connectivity
The following table illustrates the key differences in latency, speed, and bandwidth between 3G, 4G, and 5G networks. Note that these are typical values and can vary depending on the specific network implementation and conditions.
| Network Generation | Latency (ms) | Peak Download Speed (Mbps) | Bandwidth (MHz) |
|---|---|---|---|
| 3G | 100-200 | 0.384 – 2 | 5-10 |
| 4G (LTE) | 50-100 | 100-1000+ | 10-20+ |
| 5G (Sub-6 GHz) | 10-30 | 1000-10000+ | 100+ |
Global Infrastructure Deployment of 5G
The rollout of 5G networks is a global endeavor, but progress is far from uniform. A complex interplay of technological capabilities, economic realities, and regulatory frameworks shapes the speed and extent of 5G adoption across different regions. While some nations are leading the charge, others lag significantly, highlighting the uneven distribution of this transformative technology.
The geographical distribution of 5G infrastructure reveals a stark contrast between developed and developing nations. High-adoption rates are predominantly concentrated in regions with robust digital infrastructure, strong economies, and supportive government policies. Conversely, low-adoption rates are often seen in areas grappling with infrastructural limitations, economic instability, and regulatory complexities. This disparity underscores the challenges inherent in achieving truly global connectivity.
Geographical Distribution of 5G Infrastructure
A hypothetical map visualizing global 5G rollout would show a vibrant patchwork of coverage. North America, parts of Europe, and East Asia would display dense, saturated coverage, represented by deep shades of blue or green. These regions boast advanced technological infrastructure and significant investments in 5G deployment. Conversely, large swathes of Africa, South America, and parts of South Asia would appear in lighter shades, indicating sparse or limited coverage. This visualization would immediately highlight the uneven distribution of 5G technology. For example, South Korea and the United States are at the forefront of 5G deployment, boasting widespread coverage and high penetration rates, while many African countries are still in the early stages of planning and implementation.
Challenges in 5G Network Deployment
Deploying 5G networks presents a unique set of challenges across different regions. Regulatory hurdles, including spectrum allocation and licensing procedures, can significantly delay or complicate deployment. Geographical limitations, such as mountainous terrain or sparsely populated areas, also pose significant infrastructural challenges, increasing the cost and complexity of network expansion. Furthermore, the high initial investment required for 5G infrastructure can be a significant barrier, particularly for developing countries with limited resources. For instance, the need for extensive fiber optic backhaul infrastructure in rural areas is a substantial obstacle, often demanding considerable public and private investment.
Investment Strategies in 5G Infrastructure Development
Different countries adopt diverse strategies for 5G infrastructure development. Some governments take a proactive role, providing substantial financial incentives and streamlining regulatory processes to encourage private sector investment. Others opt for a more hands-off approach, relying primarily on market forces to drive deployment. China, for example, has heavily invested in its 5G infrastructure, aiming for nationwide coverage. This approach is in contrast to some European nations, which have focused on fostering competition among private telecom providers to spur innovation and deployment. These differing approaches highlight the varying priorities and capabilities of nations in pursuing 5G development.
Impact on Industries and Businesses
5G’s lightning-fast speeds and low latency are revolutionizing industries, creating opportunities for unprecedented efficiency and innovation. Businesses are no longer just adapting to this technological leap; they’re actively shaping their strategies around it, leading to a wave of new business models and competitive advantages. The impact spans numerous sectors, fundamentally altering how businesses operate and compete in the global marketplace.
The transformative power of 5G is felt most acutely in sectors heavily reliant on real-time data and seamless connectivity. From remote surgery to autonomous vehicles, the enhanced capabilities of 5G are unlocking possibilities previously confined to the realm of science fiction. This section will explore how several key industries are benefiting from this technological revolution.
Healthcare’s 5G Transformation
The healthcare industry is experiencing a dramatic shift thanks to 5G. Remote surgery, enabled by 5G’s low latency, allows surgeons to operate on patients from afar with minimal delay, expanding access to specialized care in remote areas. 5G also facilitates the development of sophisticated telehealth platforms, enabling remote patient monitoring, virtual consultations, and faster diagnosis through improved image transmission. Imagine a scenario where a rural doctor can consult with a specialist in a major city, viewing real-time high-resolution images of a patient’s X-ray, resulting in immediate and accurate diagnosis and treatment. This not only improves patient outcomes but also reduces healthcare costs associated with travel and hospital stays. Furthermore, the Internet of Medical Things (IoMT) is flourishing with 5G, allowing for continuous monitoring of patients’ vital signs through wearable devices, providing early warnings of potential health issues.
Manufacturing’s Enhanced Efficiency
In the manufacturing sector, 5G is driving the adoption of Industry 4.0 principles, enabling smart factories and automated production lines. High-speed data transfer allows for real-time monitoring of equipment, predictive maintenance to minimize downtime, and the coordination of complex robotic systems with unparalleled precision. For example, a car manufacturer can use 5G to connect its assembly line robots, ensuring seamless coordination and minimizing production errors. This results in increased efficiency, reduced waste, and improved product quality. Furthermore, 5G supports the development of augmented reality (AR) applications, enabling technicians to receive real-time guidance from remote experts during repairs or maintenance, dramatically reducing downtime and improving operational efficiency.
Transportation’s Autonomous Future
The transportation industry is poised for a radical transformation with 5G. Autonomous vehicles rely heavily on real-time data exchange for safe and efficient navigation. 5G’s low latency and high bandwidth are crucial for enabling the communication between self-driving cars and their surrounding environment, including other vehicles, pedestrians, and infrastructure. This leads to safer roads, reduced congestion, and optimized traffic flow. Furthermore, 5G supports the development of intelligent transportation systems, allowing for real-time traffic management and the efficient coordination of public transportation networks. Imagine a city where autonomous buses and taxis navigate seamlessly, minimizing traffic jams and reducing commute times. This represents a significant improvement in urban mobility and reduces environmental impact through optimized routes and reduced fuel consumption.
Potential Business Applications of 5G by Industry
The potential applications of 5G are vast and diverse. The following list provides a glimpse into the opportunities across various sectors:
The possibilities extend far beyond these examples. As 5G technology matures and becomes more widely adopted, we can expect even more innovative applications to emerge, transforming industries and reshaping the business landscape.
- Healthcare: Remote surgery, telehealth, remote patient monitoring, medical imaging, drug discovery and development.
- Manufacturing: Smart factories, predictive maintenance, automated production lines, augmented reality for technicians, supply chain optimization.
- Transportation: Autonomous vehicles, intelligent transportation systems, real-time traffic management, connected cars, drone delivery.
- Retail: Enhanced customer experience through AR/VR applications, smart shelves and inventory management, personalized marketing.
- Energy: Smart grids, remote monitoring of energy infrastructure, improved energy efficiency.
- Agriculture: Precision farming, remote monitoring of crops and livestock, automated irrigation systems.
Societal Impact and Implications: The Rise Of 5G And Its Impact On Global Connectivity
The rise of 5G isn’t just about faster downloads; it’s a seismic shift impacting every facet of our lives. From how we work and connect to the very nature of our digital rights, 5G’s societal implications are profound and far-reaching, demanding careful consideration and proactive strategies to mitigate potential risks while maximizing its benefits. This section explores the complex interplay between 5G technology and society, examining its potential to both bridge and widen the digital divide, and its impact on our privacy, security, and daily routines.
The expansion of 5G presents both unprecedented opportunities and significant challenges for global society. Its influence on digital equity, privacy, and societal structures is undeniable, requiring a nuanced understanding of its multifaceted impact to navigate its potential consequences effectively.
Digital Equity and Access to Information
5G’s potential to democratize access to information is immense. High-speed, low-latency connectivity can bridge the digital divide, connecting remote communities and underserved populations to essential services like education, healthcare, and e-government. Imagine a rural school in a developing country leveraging 5G for real-time video conferencing with expert teachers, or a remote healthcare facility using telemedicine to provide critical consultations. However, the reality is more complex. The cost of infrastructure deployment and the digital literacy gap could exacerbate existing inequalities if not addressed proactively. Unequal access to 5G technology and digital literacy training could further marginalize already disadvantaged communities, creating a “5G divide” that mirrors, and potentially worsens, the existing digital divide. Governments and telecommunications companies need to implement inclusive policies and invest in digital literacy programs to ensure that the benefits of 5G are shared equitably.
Privacy and Security Concerns
The exponential increase in data generated and transmitted through 5G networks raises serious privacy and security concerns. With more devices connected and more data flowing, the potential for data breaches and misuse increases dramatically. The increased reliance on connected devices and services also expands the attack surface for cybercriminals. Consider the potential vulnerabilities of smart homes, autonomous vehicles, and industrial IoT devices. A single breach could compromise sensitive personal information, disrupt critical infrastructure, or even endanger lives. Robust cybersecurity measures, data privacy regulations, and public awareness campaigns are crucial to mitigate these risks and build trust in the 5G ecosystem. The development of secure and privacy-preserving technologies, like blockchain and federated learning, will also be critical.
Societal Changes from Widespread 5G Adoption
The widespread adoption of 5G is expected to trigger significant societal changes, transforming how we work, interact, and live. Remote work will become even more prevalent, with 5G enabling seamless collaboration and communication across geographical boundaries. The rise of the metaverse and augmented reality experiences will reshape social interactions, creating new opportunities for connection and entertainment, but also potentially leading to increased social isolation if not managed carefully. Furthermore, advancements in automation and AI, facilitated by 5G’s capabilities, will likely impact employment patterns, requiring workforce retraining and adaptation to new job roles. The emergence of smart cities, leveraging 5G for optimized traffic management, energy efficiency, and public safety, will also reshape urban environments. However, these changes also present challenges, such as the need for robust social safety nets to support workers displaced by automation and the potential for increased surveillance and erosion of personal freedoms if appropriate safeguards are not in place.
Potential Benefits and Drawbacks of 5G for Society
The societal impact of 5G is a double-edged sword. It offers tremendous potential benefits, but also presents significant challenges that must be addressed proactively.
Let’s weigh the pros and cons:
- Benefits: Improved healthcare through telemedicine, enhanced education through online learning, economic growth through innovation and new industries, increased accessibility for remote communities, improved public safety through connected infrastructure, more efficient transportation systems, and new forms of entertainment and social interaction.
- Drawbacks: Increased risk of data breaches and privacy violations, potential for job displacement due to automation, exacerbation of the digital divide, increased energy consumption, potential for increased surveillance, and ethical concerns related to AI and autonomous systems.
Future Trends and Predictions

Source: editorialge.com
The future of 5G is less about a single technology and more about a rapidly evolving ecosystem. We’re looking at a period of explosive growth, punctuated by significant technological leaps and inevitable challenges. Predicting the exact trajectory is tricky, but based on current trends and technological advancements, we can paint a reasonably clear picture of the next decade.
The next five to ten years will see 5G become deeply woven into the fabric of our digital lives, impacting everything from how we work and play to how cities are managed and healthcare is delivered. This expansion will be driven not only by increased network coverage but also by continuous technological improvements and the synergistic effects with other emerging technologies.
5G Adoption Rates Over the Next 5-10 Years
Experts predict a dramatic increase in 5G subscriptions globally. While precise figures vary depending on the source and region, most forecasts point to a significant surge. For example, a report by Ericsson predicts that 5G subscriptions will reach over 5 billion by 2028, representing a considerable portion of the global mobile subscriber base. This growth will be particularly pronounced in regions with strong government support for infrastructure development and a high demand for high-bandwidth applications, such as in Asia and North America. However, adoption rates will vary significantly across different countries, influenced by factors like economic development, regulatory frameworks, and the availability of affordable 5G devices.
Evolution of 5G Technology: Advancements and Upgrades
5G is not a static technology; it’s constantly evolving. We can expect several key advancements in the coming years. The focus will be on increasing speed and capacity through techniques like network slicing and improved spectrum utilization. Furthermore, the integration of artificial intelligence (AI) for network optimization and self-healing capabilities will become increasingly important. Beyond 5G, the development and deployment of 6G are already underway. 6G promises even higher speeds, lower latency, and the ability to support a vastly increased number of connected devices. While widespread 6G deployment is still several years away, research and development efforts are intense, with a focus on technologies like terahertz frequencies and advanced antenna systems. This will likely lead to a gradual transition from 5G to 6G, with both technologies coexisting for a period.
Challenges and Opportunities in 5G Development and Implementation
Despite its potential, 5G faces several challenges. The high cost of infrastructure deployment remains a significant hurdle, particularly in developing countries. Regulatory hurdles and spectrum allocation issues can also impede progress. Addressing security concerns related to data privacy and network vulnerabilities is crucial for widespread adoption. On the opportunity side, 5G presents a massive economic driver, creating jobs in infrastructure development, device manufacturing, and the development of new applications. The potential for innovation across various sectors is immense, offering solutions to existing problems and creating entirely new possibilities. For instance, the implementation of smart city initiatives relies heavily on the capabilities of 5G.
Impact of 5G on Other Emerging Technologies
5G will act as a powerful catalyst for other emerging technologies. Its high bandwidth and low latency are essential for the success of the Internet of Things (IoT), enabling the seamless connection and communication of billions of devices. The ability to process massive amounts of data in real-time will be crucial for the advancement of artificial intelligence (AI), particularly in areas like machine learning and deep learning. The combination of 5G and AI will drive innovations in autonomous vehicles, smart healthcare, and industrial automation. For example, remote surgery using robotics will become increasingly feasible with the speed and reliability of 5G networks, allowing for better healthcare access in remote areas. Furthermore, the development of augmented and virtual reality (AR/VR) applications will be significantly enhanced by the capabilities of 5G, creating immersive and interactive experiences for users.
Last Point
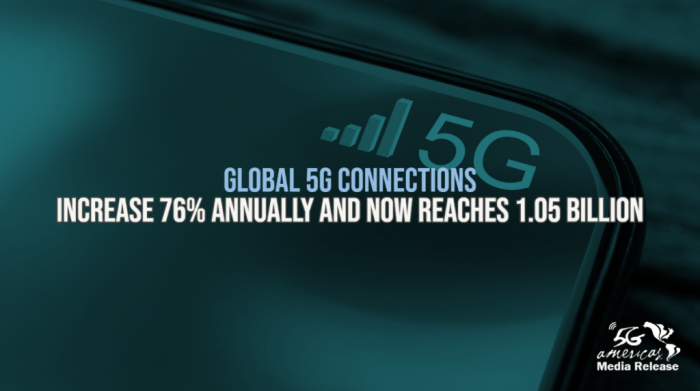
Source: 5gamericas.org
From self-driving cars to telemedicine, the impact of 5G is undeniable and far-reaching. While challenges remain in ensuring equitable access and addressing potential risks, the potential benefits of this revolutionary technology are too significant to ignore. The future of global connectivity is undeniably 5G-powered, promising a world where information flows freely, innovation thrives, and possibilities are limitless. But the journey to fully realize this potential requires careful planning, strategic investment, and a commitment to responsible innovation.
