How 3D Printing is Revolutionizing the Construction Industry? Forget slow, expensive builds. We’re talking about houses, bridges, even entire neighborhoods popping up faster than you can say “concrete mixer.” This isn’t sci-fi; 3D printing is already shaking up the construction world, bringing efficiency, sustainability, and mind-blowing design possibilities. Get ready to see how this tech is changing the game.
From extrusion-based methods to binder jetting, different 3D printing technologies are being used to create everything from intricate architectural details to entire buildings. The advantages are undeniable: faster construction times, reduced waste, and a chance to build more affordable and sustainable housing. But, like any groundbreaking technology, there are hurdles to overcome. We’ll explore the challenges, the innovations, and the incredible future of 3D-printed construction.
The Rise of 3D Printing in Construction
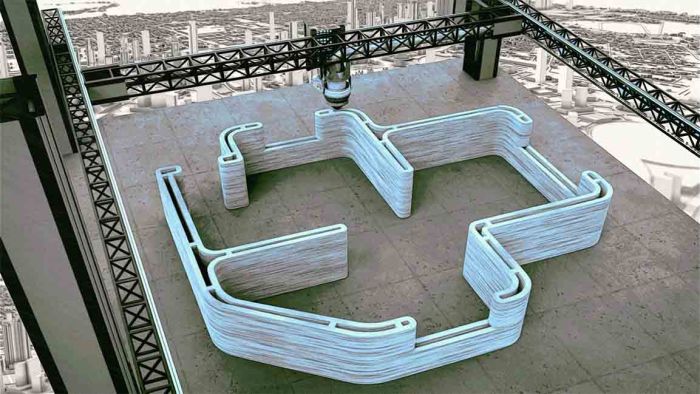
Source: fastcompanyme.com
3D printing’s impact on construction is massive, allowing for faster, cheaper, and more sustainable building. This level of innovation mirrors the potential of advancements in other sectors, like healthcare, where rapid technological leaps are transforming access to care. For instance, the possibilities opened by faster data transfer, as explored in this article on How 5G Technology Will Impact Global Healthcare Access , are equally game-changing.
Just as 3D printing is disrupting construction, 5G promises to revolutionize remote healthcare delivery and diagnostics, ultimately improving lives globally.
For decades, construction has been synonymous with painstaking manual labor and traditional methods. But a seismic shift is underway, driven by the burgeoning field of 3D printing. While the technology’s roots lie in rapid prototyping and manufacturing, its application in building structures is rapidly gaining momentum, promising a revolution in speed, efficiency, and design possibilities. This isn’t just about faster building; it’s about fundamentally changing how we approach construction.
The adoption of 3D printing in construction is propelled by several key factors. Firstly, the industry faces persistent challenges in labor shortages and rising costs. 3D printing offers a potential solution by automating significant portions of the building process, reducing reliance on manual labor and accelerating project timelines. Secondly, the demand for sustainable and environmentally friendly construction practices is increasing. 3D printing can contribute to this by minimizing material waste and allowing for the use of recycled or sustainable materials. Finally, the technology allows for greater design freedom, enabling the creation of complex and intricate architectural forms that were previously impossible or prohibitively expensive to achieve.
3D Printing Technologies in Construction
Several 3D printing technologies are being employed in construction, each with its own strengths and weaknesses. Extrusion-based 3D printing, often referred to as material extrusion, is a dominant method. It involves a nozzle that extrudes a continuous stream of material layer by layer, much like a hot glue gun building a structure. This process is particularly suitable for building with concrete, but also adaptable to other materials. Binder jetting, another common technique, utilizes a binder to selectively bond particles of a material (like sand or cement) together, layer by layer, according to a digital design. This method often results in higher-strength structures than extrusion-based methods. Other methods, such as vat polymerization (using UV light to cure resins) are also emerging, though less common currently in large-scale construction.
Comparison of 3D Printing Materials in Construction
The choice of material significantly impacts the performance, cost, and sustainability of a 3D-printed structure. Different materials offer unique advantages and disadvantages.
| Material | Advantages | Disadvantages | Applications |
|---|---|---|---|
| Concrete | High strength, readily available, cost-effective | Can be heavy, requires careful curing, susceptible to cracking | Walls, foundations, prefabricated elements |
| Recycled plastic | Sustainable, lightweight, relatively inexpensive | Lower strength compared to concrete, potential for UV degradation | Modular structures, temporary buildings, interior partitions |
| Soil/Earth | Sustainable, readily available, good thermal insulation | Lower strength, susceptible to weather damage, requires specific soil composition | Walls in specific climates, low-cost housing |
| Polymer composites | High strength-to-weight ratio, customizable properties, durable | Can be expensive, may require specialized equipment | High-performance structures, specialized components |
Applications of 3D Printing in Construction
3D printing is no longer a futuristic fantasy; it’s rapidly transforming the construction landscape, offering innovative solutions for design, speed, cost, and sustainability. This technology allows for the creation of intricate structures previously impossible with traditional methods, opening up exciting possibilities across various sectors of the industry.
Complex Architectural Designs, How 3D Printing is Revolutionizing the Construction Industry
3D printing’s ability to handle complex geometries is a game-changer for architects. Imagine creating free-flowing, organic shapes, intricate facades, and personalized designs previously limited by the constraints of traditional construction techniques. The precision of 3D printing allows for the seamless integration of different materials and the creation of highly detailed architectural elements, leading to unique and visually stunning buildings. This technology empowers architects to push creative boundaries, resulting in structures that are both functional and aesthetically captivating. For example, the intricate latticework designs that are now possible with 3D printing could lead to buildings with improved ventilation and natural light.
Infrastructure Component Construction
Beyond buildings, 3D printing is making inroads into infrastructure projects. The construction of bridges, roads, and other large-scale components can benefit significantly from this technology. Large-scale 3D printing can create prefabricated components like bridge supports or road segments off-site, reducing on-site construction time and minimizing disruption. The ability to print with specialized materials also allows for the creation of stronger, more durable infrastructure elements. For instance, imagine a bridge support printed using a high-strength concrete composite, capable of withstanding extreme weather conditions and lasting for decades longer than traditionally built counterparts.
Affordable and Sustainable Housing
One of the most impactful applications of 3D printing in construction lies in its potential to revolutionize affordable and sustainable housing. By automating many aspects of the building process, 3D printing can significantly reduce labor costs and construction time. This efficiency translates directly to lower housing costs, making it more accessible to a wider population. Furthermore, 3D printing allows for the use of sustainable and recycled materials, reducing the environmental impact of construction. This opens the door for the creation of eco-friendly homes with reduced carbon footprints, contributing to a more sustainable built environment. Imagine communities built with homes printed using locally sourced, recycled materials, drastically minimizing transportation costs and emissions.
Examples of Successful 3D-Printed Construction Projects
Several successful 3D-printed construction projects worldwide showcase the technology’s potential.
One example is a 3D-printed office building in Dubai. Imagine a sleek, modern structure with a complex, curved facade, created layer by layer with a massive 3D printer. The building’s design incorporates intricate patterns and textures, showcasing the technology’s ability to create unique architectural features. The speed of construction was significantly faster than traditional methods, demonstrating the efficiency of 3D printing for large-scale projects. The exterior is a light grey, almost white, with subtle variations in tone reflecting the varying density of the printed material. Large, expansive windows dominate the façade, allowing for abundant natural light to enter the interior.
Another example is a 3D-printed house in Mexico. This project focuses on affordable housing, demonstrating the technology’s ability to create sustainable and cost-effective homes. The house is a modest, single-story structure with a simple yet functional design. The exterior is a warm terracotta color, reflecting the local environment and building materials. The design incorporates passive solar features to optimize energy efficiency, reducing the need for extensive heating and cooling systems. The walls are textured, with a slightly rough surface that adds visual interest and provides insulation. A small, shaded patio area is integrated into the design, providing an outdoor space for relaxation.
Advantages of 3D Printing in Construction
3D printing is rapidly transforming the construction landscape, offering a plethora of advantages over traditional methods. From dramatically reducing project timelines and costs to enhancing sustainability and design freedom, the benefits are significant and far-reaching, promising a future of faster, cheaper, and more sustainable buildings.
Reduced Construction Time and Labor Costs
3D printing significantly accelerates construction. Instead of relying on manual labor for bricklaying or pouring concrete, a 3D printer can lay down layers of material with remarkable speed. This automation drastically cuts down on labor costs, as fewer workers are needed on-site. For example, a project that might take months using traditional methods could be completed in weeks using 3D printing. This speed translates directly into cost savings for developers, as labor is often the most significant expense in construction. Furthermore, the reduced on-site time minimizes potential delays caused by weather or other unforeseen circumstances. Companies like ICON are already building homes in a fraction of the time compared to conventional methods, demonstrating the real-world impact of this technology.
Construction Waste Reduction and Sustainability
One of the most compelling aspects of 3D printing in construction is its potential for minimizing waste. Traditional construction methods generate substantial amounts of waste materials, often ending up in landfills. 3D printing, however, uses only the necessary amount of material, significantly reducing waste generation. The precise deposition of material also minimizes material overages and rework, further contributing to a more sustainable building process. Furthermore, the use of sustainable building materials, such as recycled plastics or bio-based composites, can be seamlessly integrated into the 3D printing process, creating environmentally friendly structures. This aligns perfectly with the growing global focus on sustainable construction practices and reduces the environmental impact of the building industry.
Enhanced Design Flexibility and Customization Options
3D printing unlocks unprecedented design flexibility. Complex geometries and intricate details, impossible to achieve with traditional methods, become readily attainable. This opens up a world of possibilities for architects and designers, allowing them to create unique and customized structures tailored to specific needs and preferences. Imagine homes with organically shaped walls, intricate facades, or integrated furniture – all made possible by the design freedom offered by 3D printing. This level of customization was previously limited by the constraints of traditional building techniques and significantly expands the potential for architectural innovation.
Precision and Accuracy of 3D-Printed Structures
3D-printed structures boast superior precision and accuracy compared to traditionally built ones. The layer-by-layer deposition process ensures consistency and minimizes errors. This leads to stronger, more durable, and more precisely dimensioned buildings. This enhanced accuracy reduces the likelihood of structural imperfections, leading to improved building performance and longevity. The level of control afforded by 3D printing also allows for the incorporation of advanced features, such as integrated insulation or complex reinforcement systems, enhancing the overall quality and performance of the structure. This contrasts sharply with traditional methods, where human error and the limitations of manual labor can lead to inconsistencies and inaccuracies.
Challenges and Limitations of 3D Printing in Construction
3D printing in construction, while brimming with potential, isn’t without its hurdles. The technology, though rapidly advancing, still faces significant limitations in terms of scale, material choices, regulatory frameworks, and workforce preparedness. Overcoming these challenges is crucial for the widespread adoption of this innovative building method.
Scale and Material Diversity Limitations
Currently, the size and complexity of structures that can be 3D printed are limited. Most projects focus on smaller-scale buildings or components, like walls or prefabricated modules. Large-scale projects present logistical challenges, including the need for massive printing machines and the efficient delivery of substantial amounts of printing material. Furthermore, the range of printable materials is relatively narrow compared to traditional construction methods. While concrete is a common choice, the ability to print with diverse materials, like steel, wood, or specialized composites, is still under development. This limits the architectural and design possibilities. For example, while a house might be successfully 3D printed using a concrete mix, replicating the intricate details of a historical building using the same technology presents a significant material challenge.
Regulatory Hurdles and Safety Concerns
The construction industry is heavily regulated, and 3D-printed structures must meet existing building codes and safety standards. The novelty of the technology means that these regulations often lag behind its development, creating a regulatory bottleneck. There are also concerns about the long-term durability and structural integrity of 3D-printed buildings, particularly in the face of extreme weather conditions or seismic activity. Rigorous testing and certification processes are needed to address these safety concerns and build confidence in the technology. For instance, a lack of clear guidelines regarding the fire resistance of 3D-printed materials could delay the approval of projects using this technology.
Skilled Labor and Workforce Training Challenges
The operation and maintenance of 3D printing equipment require specialized skills and training. A shortage of skilled professionals capable of designing, operating, and maintaining these complex machines is a significant barrier to wider adoption. Furthermore, existing construction workers may need retraining to adapt to this new technology. This necessitates substantial investment in educational programs and training initiatives to equip the workforce with the necessary skills. The lack of qualified technicians to troubleshoot equipment malfunctions could lead to significant project delays and cost overruns.
Summary of Challenges
The widespread adoption of 3D printing in construction faces several interconnected challenges:
- Limited Scale and Material Diversity: Current technology struggles with large-scale projects and offers limited material options, restricting design flexibility.
- Regulatory Hurdles and Safety Concerns: A lack of clear regulations and concerns about long-term durability and structural integrity hinder project approvals and public confidence.
- Skilled Labor Shortages: The need for specialized training and a lack of skilled professionals create bottlenecks in project execution and maintenance.
Future Trends and Innovations in 3D Printing for Construction
The construction industry, already undergoing a digital transformation, is poised for a quantum leap thanks to advancements in 3D printing technology. The future isn’t just about faster builds; it’s about smarter, more sustainable, and resilient structures, achieved through the integration of cutting-edge technologies and innovative materials. We’re on the cusp of a new era where buildings are designed, printed, and even self-repair, all thanks to the evolving landscape of additive manufacturing.
AI and Robotics Integration in 3D Printing
The synergy between 3D printing and AI/robotics promises to revolutionize construction efficiency and precision. AI algorithms can optimize print paths, predict material usage, and even detect and correct errors in real-time. Robotic arms, guided by AI, can handle complex printing tasks, working autonomously or collaboratively with human operators. Imagine a construction site where robots tirelessly work around the clock, precisely laying down layers of material, ensuring perfect accuracy and minimizing human error. This level of automation not only accelerates construction but also reduces labor costs and improves safety. Companies like ICON are already showcasing the potential of this integration with their autonomous construction robots that print entire homes in a fraction of the time compared to traditional methods.
Development of New Materials and Printing Techniques
The development of new materials is crucial for expanding the applications and capabilities of 3D printing in construction. Researchers are exploring high-performance concretes, self-healing polymers, and bio-based materials that offer enhanced durability, strength, and sustainability. Furthermore, advancements in printing techniques, such as multi-material printing and hybrid approaches combining 3D printing with traditional construction methods, will further enhance the versatility of the technology. For instance, the development of materials that can withstand extreme weather conditions, such as those used in ICON’s Vulcan material, opens up possibilities for constructing buildings in previously inaccessible or challenging environments.
3D Printing for Smart and Self-Healing Buildings
The future of 3D-printed buildings extends beyond mere structural integrity. The integration of sensors, actuators, and smart materials enables the creation of self-healing structures that can adapt to changing environmental conditions and even repair minor damage autonomously. Imagine buildings that automatically adjust their temperature, monitor their own structural health, and even repair cracks or minor damage without human intervention. This capability reduces maintenance costs, enhances building lifespan, and promotes sustainability. This involves embedding sensors within the printed material itself, allowing the structure to “feel” stress points and trigger self-repair mechanisms.
Hypothetical Future Scenario: 3D-Printed Urban Development
Imagine a future cityscape where entire neighborhoods are constructed using 3D printing technology. Modular housing units, customized to individual needs, are printed on-site, reducing transportation costs and environmental impact. Public infrastructure, such as bridges and pedestrian walkways, are created with intricate designs and enhanced durability, all thanks to the precision and speed of 3D printing. This scenario envisions a more sustainable, efficient, and aesthetically pleasing urban environment, where buildings are not just structures but integrated parts of a smart, responsive ecosystem. This isn’t science fiction; companies are already exploring this potential, with projects demonstrating the feasibility of building entire communities using this technology. This shift would reduce construction time significantly, minimize waste, and allow for greater architectural creativity, leading to a transformation in how we design and build our cities.
Closing Notes: How 3D Printing Is Revolutionizing The Construction Industry
The construction industry is on the cusp of a major transformation. 3D printing isn’t just a trend; it’s a powerful tool reshaping how we design, build, and live. While challenges remain, the potential for faster, cheaper, more sustainable, and incredibly creative construction is undeniable. The future of building is being printed, one layer at a time, and it’s going to be amazing.
