Smart Homes: The Intersection of Internet of Things (IoT) and Smart Homes – it’s more than just a catchy title; it’s the future of living. Imagine a house that anticipates your needs, adjusts the lighting to your mood, and even preheats your coffee before you wake up. That’s the promise of smart home technology, powered by the interconnected web of devices known as the Internet of Things. This isn’t science fiction; it’s a rapidly evolving reality blending convenience, efficiency, and a dash of futuristic cool.
This deep dive explores the core components of smart home systems, from the communication protocols that keep everything talking (think Zigbee, Z-Wave, and Wi-Fi) to the security considerations that are crucial for peace of mind. We’ll unravel the intricacies of cloud computing and data analytics in smart homes, and look at real-world applications – from automated lighting to enhanced security systems – that are transforming how we live. Get ready to peek into a future where your home is more than just shelter; it’s your intelligent, responsive partner.
Defining Smart Homes and the Internet of Things
Smart homes and the Internet of Things (IoT) are increasingly intertwined, transforming how we live and interact with our environments. Understanding their individual definitions and the synergistic relationship between them is crucial to grasping the potential and implications of this technological convergence.
Smart homes leverage technology to automate and enhance various aspects of domestic life, offering convenience, comfort, and improved security. This goes beyond simple automation; it’s about creating a responsive and interconnected living space that adapts to the needs and preferences of its occupants.
Smart Home Characteristics and Functionalities
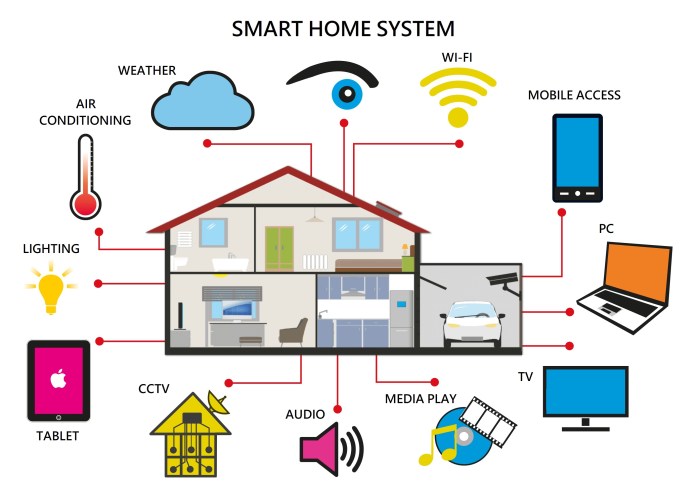
A smart home system typically includes interconnected devices and appliances that can be controlled remotely or automatically. Key functionalities include automated lighting, climate control (heating, cooling), security systems (alarms, surveillance), entertainment systems (streaming services, smart TVs), and appliance management (refrigerators, washing machines). The level of integration and sophistication varies greatly depending on the system’s complexity and the number of connected devices. For instance, a basic smart home might involve only smart light bulbs controlled via a smartphone app, while a more advanced system could integrate all home systems for seamless automation and personalized experiences, such as automatically adjusting the lighting and temperature based on the time of day and occupancy.
Internet of Things (IoT) Core Components and Role in Smart Homes
The Internet of Things (IoT) is a network of physical objects—”things”—embedded with sensors, software, and other technologies for the purpose of connecting and exchanging data with other devices and systems over the internet. Core components include sensors (collecting data on temperature, light, motion, etc.), actuators (controlling devices based on sensor data), embedded systems (processing data and executing actions), network connectivity (Wi-Fi, Bluetooth, etc.), and cloud platforms (for data storage, processing, and analysis). The IoT provides the crucial infrastructure for smart home technology, enabling communication and data exchange between various devices and systems. Without the IoT’s ability to connect and share data, a smart home would simply be a collection of independent smart devices. Imagine a smart thermostat that cannot communicate with the smart blinds; the home lacks the integrated functionality that defines a truly smart environment.
Comparison of Smart Home Systems
Different smart home systems vary significantly in their functionalities, integration capabilities, and levels of complexity. Some systems are proprietary, meaning they only work with devices from a specific manufacturer, while others are open-source or utilize open standards, allowing for greater interoperability between devices from different brands. For example, a system built around Amazon Alexa might only integrate seamlessly with other Alexa-compatible devices, while a system using a more open standard like Matter allows for broader device compatibility. The choice between a proprietary or open system depends on individual needs and preferences, balancing the convenience of a streamlined ecosystem with the flexibility of a more open platform. Furthermore, some systems prioritize ease of use and simplicity, while others offer more advanced features and customization options. The level of technical expertise required to set up and manage a smart home system also varies depending on the complexity of the system and the level of user support provided.
Key Technologies in Smart Home IoT Integration
Smart homes aren’t just about fancy gadgets; they’re a complex interplay of technologies working seamlessly together. This integration relies heavily on specific communication protocols, cloud infrastructure, and essential hardware components. Let’s delve into the technical backbone of this increasingly popular home automation system.
Communication Protocols in Smart Home IoT Networks
Various communication protocols enable the interconnectedness of devices within a smart home. Each protocol boasts unique strengths and weaknesses, influencing its suitability for specific applications. Choosing the right protocol often depends on factors like range, power consumption, security needs, and data rate requirements. The following table compares some of the most prevalent protocols.
| Protocol | Range | Power Consumption | Security | Data Rate |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Zigbee | Up to 100 meters indoors | Low | AES-128 encryption | 250 kbps |
| Z-Wave | Up to 30 meters indoors | Low | AES-128 encryption | 100 kbps |
| Wi-Fi | Varies greatly depending on router and environmental factors; generally hundreds of meters outdoors | Moderate to High | WPA2/WPA3 encryption | Varies greatly depending on standard, generally several Mbps |
| Bluetooth | Up to 10 meters | Low | AES-128 encryption (Bluetooth 5 and later) | 1 Mbps (Bluetooth 5) |
The Role of Cloud Computing and Data Analytics
Cloud computing forms the brains of many smart home systems. It provides the storage and processing power needed to handle the massive amounts of data generated by interconnected devices. Think of your smart thermostat learning your preferences and adjusting accordingly – that learning process relies on data stored and analyzed in the cloud. Data analytics further enhances functionality by identifying patterns, predicting needs, and personalizing the smart home experience. For example, analyzing energy consumption data from various appliances can help optimize energy usage and potentially reduce bills. Similarly, data from smart security systems can identify potential threats and alert homeowners proactively.
Essential Hardware Components in Smart Home IoT Systems
The physical manifestation of a smart home is its hardware. This consists primarily of three key components: sensors, actuators, and gateways.
Sensors are the eyes and ears of the system, constantly monitoring various aspects of the home environment. Examples include motion sensors (detecting movement), temperature sensors (measuring temperature), and light sensors (detecting ambient light levels). Actuators, on the other hand, are the muscles, carrying out actions based on sensor data or user commands. These could be smart light bulbs, motorized blinds, or smart locks. Finally, the gateway acts as the translator, connecting the various devices within the home network to the internet and the cloud. It allows communication between sensors, actuators, and the cloud-based services that manage the smart home system. Without a gateway, many smart home devices would be limited in their functionality, unable to communicate with external systems or receive remote control commands.
Security and Privacy Concerns in Smart Home IoT: The Intersection Of Internet Of Things (IoT) And Smart Homes

Source: intersog.com
Okay, let’s talk about the elephant in the smart home: security and privacy. It’s awesome to have a fridge that orders groceries and lights that dim themselves, but what happens when those conveniences become targets for hackers or when your data gets misused? The interconnected nature of smart home devices creates both exciting opportunities and serious risks. Let’s dive into the potential pitfalls and how to navigate them.
Potential Security Vulnerabilities in Smart Home IoT Devices and Networks
The interconnectedness that makes smart homes so convenient also creates numerous potential entry points for malicious actors. A single compromised device can act as a gateway to your entire network, potentially allowing access to sensitive information and control over other devices. Understanding these vulnerabilities is the first step towards securing your smart home.
- Weak or Default Passwords: Many smart home devices ship with default passwords that are easily guessable. This provides a straightforward path for unauthorized access.
- Insecure Network Protocols: Some devices use outdated or insecure communication protocols, making them vulnerable to eavesdropping and data manipulation.
- Lack of Encryption: Data transmitted between devices and the cloud may not be encrypted, leaving sensitive information exposed.
- Software Vulnerabilities: Outdated firmware or software with known vulnerabilities can be exploited by attackers to gain control of devices.
- Unpatched Devices: Many smart home device manufacturers are slow to release security patches, leaving users exposed to known vulnerabilities for extended periods.
- Lack of Device Authentication: Without proper authentication mechanisms, it’s easy for unauthorized devices to join the network.
- Phishing Attacks: Users may be tricked into revealing their login credentials through phishing emails or malicious websites.
Methods for Mitigating Security Risks, The Intersection of Internet of Things (IoT) and Smart Homes
Fortunately, there are several steps you can take to significantly reduce your risk. A multi-layered approach is best, combining hardware and software solutions.
Strong passwords and multi-factor authentication are fundamental. Regular software updates are crucial to patching vulnerabilities. Consider using a separate network for your smart home devices, isolating them from your main network and sensitive data. Finally, encryption, both in transit and at rest, is essential for protecting your data.
Smart homes, the epitome of IoT convenience, are raising serious privacy questions. The sheer volume of data collected by interconnected devices necessitates robust security measures, and this is where the impact of regulations like GDPR comes into play. Check out this insightful piece on How Data Privacy Laws are Impacting Technology Development to understand the challenges.
Ultimately, balancing smart home functionality with user privacy is key to the future of IoT.
Privacy Concerns Related to Data Collection and Usage in Smart Home IoT Systems
The convenience of smart home devices comes at a cost: the collection of vast amounts of personal data. This data, ranging from your daily routines to your energy consumption habits, can be valuable to marketers and even more concerning, to malicious actors. Transparency and control over your data are paramount.
Many smart home devices collect data without explicit user consent, and the data usage policies of many companies are opaque and complex. This lack of transparency raises significant privacy concerns.
Example Privacy Policy
This is an example, and specific requirements may vary by jurisdiction:
Data Collection: We collect data necessary for the functionality of our devices, including usage patterns and device performance. We may also collect anonymized aggregate data for improving our services. We do not collect sensitive personal information without your explicit consent.
Data Usage: We use collected data to improve our products and services, personalize your experience, and provide support. We do not sell your personal data to third parties.
Data Security: We implement robust security measures to protect your data from unauthorized access, use, or disclosure. These measures include encryption, access controls, and regular security audits.
Data Retention: We retain your data only for as long as necessary to fulfill the purposes for which it was collected. You have the right to request access to, correction of, or deletion of your data.
User Consent: We obtain your explicit consent before collecting and using sensitive personal data. You have the right to withdraw your consent at any time.
Applications and Use Cases of Smart Home IoT
Smart homes aren’t just a futuristic fantasy anymore; they’re a rapidly growing reality, weaving together convenience, security, and energy efficiency in exciting new ways. The Internet of Things (IoT) is the invisible thread connecting all the pieces, allowing your appliances, gadgets, and systems to communicate and work together seamlessly. Let’s dive into the practical applications that are transforming how we live.
The integration of IoT devices in smart homes offers a multitude of benefits beyond simple automation. It’s about creating a living space that anticipates your needs, responds to your preferences, and ultimately improves your quality of life. This interconnectedness not only enhances convenience but also contributes to significant cost savings and heightened security.
Smart Lighting
Smart lighting systems offer more than just the ability to switch lights on and off remotely. These systems allow for customizable lighting scenes, adjusting brightness and color temperature to suit the mood or time of day. For instance, you can program your lights to mimic a sunrise, gradually increasing brightness to gently wake you up, or create a relaxing ambiance in the evening with warm, dim lighting. Energy savings are a significant benefit; smart bulbs can be scheduled to turn off when not needed, reducing energy consumption.
Smart Climate Control
Smart thermostats learn your preferences and adjust the temperature accordingly, optimizing energy usage and ensuring your home is always comfortable. Many smart thermostats offer geofencing capabilities, automatically adjusting the temperature based on your location. If you’re away from home, the thermostat will automatically lower the temperature, saving energy; and when you’re approaching, it’ll start warming or cooling the house to your preferred setting. This proactive approach significantly reduces energy waste and lowers utility bills.
Smart Security Systems
Smart security systems offer a significant upgrade over traditional systems, integrating features like remote monitoring, video surveillance, and smart locks. These systems provide real-time alerts via smartphone notifications, allowing you to monitor your home even when you’re away. Smart locks enable keyless entry using codes or smartphone apps, offering convenience and enhanced security by eliminating the risk of lost or stolen keys. Video doorbells and security cameras with motion detection further enhance security, providing visual confirmation of visitors and deterring potential intruders.
Smart Entertainment Systems
Smart entertainment systems centralize and streamline your home’s audio and video experiences. You can control multiple devices, such as TVs, speakers, and streaming services, using a single app or voice commands. This allows for seamless transitions between different entertainment options and provides a unified, user-friendly experience. Smart speakers with voice assistants can also act as central hubs for controlling other smart home devices, making it even more convenient to manage your home environment.
Benefits of Smart Home IoT Integration
The advantages of integrating IoT devices into your smart home are numerous and impactful. Energy efficiency is a major benefit, with smart devices optimizing energy consumption across various systems. Convenience is dramatically enhanced, automating tasks and providing remote control over various aspects of your home. Enhanced safety and security are also key advantages, with smart systems providing real-time monitoring and alerts, contributing to peace of mind.
Hypothetical Smart Home Scenario
Imagine a scenario where you’re away from home for the day. Your smart thermostat automatically lowers the temperature to conserve energy. As you approach your house, your smart lock receives a signal from your smartphone, unlocking the door before you even reach it. Upon entering, your smart lights automatically turn on, creating a welcoming ambiance. Your smart security system confirms your presence, disabling any alarms. Meanwhile, your smart speaker begins playing your favorite playlist. This seamless integration exemplifies the power and convenience of a well-connected smart home.
Future Trends and Challenges in Smart Home IoT
Source: visioforce.com
The smart home revolution is far from over; in fact, it’s just getting started. We’re on the cusp of a new era where our homes become even more intuitive, responsive, and integrated into our daily lives. But this exciting future also presents significant hurdles to overcome. Let’s explore the trends shaping this evolution and the challenges that need addressing for widespread adoption.
The next decade will witness a dramatic shift in how we interact with our smart homes, driven by advancements in several key areas. This isn’t just about adding more gadgets; it’s about creating a seamless, intelligent ecosystem that anticipates our needs and adapts to our lifestyles.
Emerging Trends in Smart Home IoT Technology
AI is rapidly transforming the smart home landscape. Imagine a system that learns your preferences – from your ideal coffee temperature to the perfect lighting for reading – and adjusts automatically. This predictive capability, powered by machine learning, moves beyond simple automation to true personalization. Edge computing, processing data locally instead of relying solely on the cloud, enhances security and responsiveness, making the system faster and more resilient to internet outages. Finally, improved interoperability is crucial. The current fragmented ecosystem, where devices from different manufacturers often don’t talk to each other, needs to evolve. Standardization efforts are underway to ensure a more unified and user-friendly experience. Consider a scenario where your smart thermostat seamlessly communicates with your smart blinds to optimize energy consumption based on weather conditions and your schedule – this level of integration is the ultimate goal.
Challenges to Widespread Adoption of Smart Home IoT
Despite the promise, widespread adoption faces significant obstacles. Cost remains a major barrier for many consumers. The initial investment in smart devices and the ongoing expenses of maintenance and upgrades can be substantial. Complexity is another hurdle. Setting up and managing a network of interconnected devices can be daunting for technically unsophisticated users. This leads to a need for user-friendly interfaces and intuitive setup processes. Finally, standardization issues are crucial. The lack of interoperability between devices from different manufacturers creates frustration and limits the potential benefits of a truly integrated smart home. For example, a user might purchase a smart lock from one company and a smart security system from another, only to find they don’t integrate properly, compromising the overall security and convenience.
Visual Representation of Smart Home Evolution
Imagine a timeline spanning the next decade. At the beginning (2024), we see a collection of disparate smart devices – a smart speaker here, a smart lightbulb there – operating largely in isolation. By 2027, we see increased integration, with devices beginning to communicate and work together more effectively. By 2030, AI plays a central role, personalizing the home environment based on individual user preferences and anticipating needs. By 2034, the smart home is seamlessly integrated with other aspects of life, such as transportation and healthcare, creating a truly connected and personalized living experience. This evolution isn’t linear; it’s an iterative process with incremental improvements and breakthroughs along the way. Imagine a house that not only adjusts lighting and temperature but also proactively manages energy consumption, anticipates maintenance needs, and even alerts emergency services in case of an accident – that’s the vision for the future.
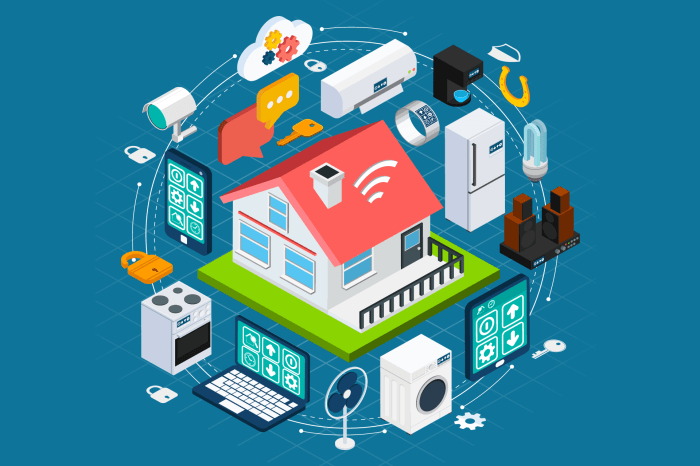
Final Wrap-Up
Source: martech.org
The convergence of the Internet of Things and smart homes is revolutionizing how we interact with our living spaces. While challenges remain – particularly around security, privacy, and standardization – the potential benefits are undeniable. From energy efficiency gains to enhanced safety and unprecedented convenience, smart homes are paving the way for a more connected, intuitive, and ultimately, more comfortable future. The journey towards truly intelligent homes is ongoing, but the direction is clear: smarter, safer, and more personalized living experiences await.
